Plant science(Vocab) - Unit 1 grade 10
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
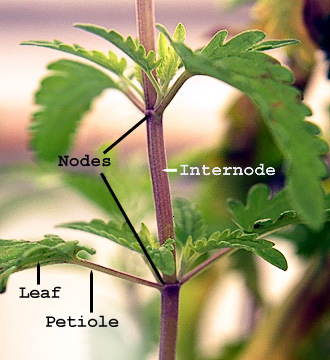
Node
where new growth occurs - weather thats a leaf, bud - they contain mersimatic tissue
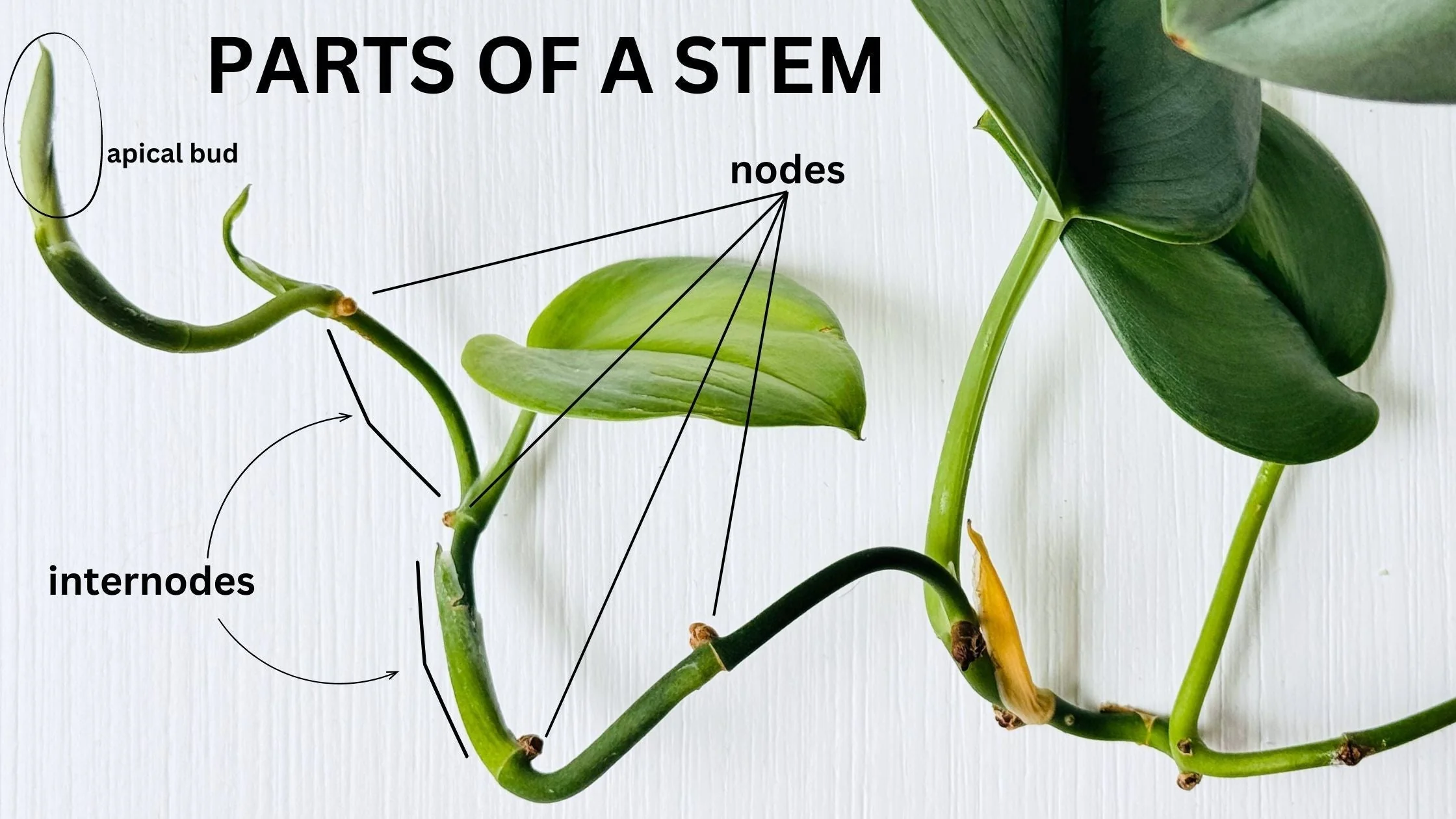
Internode
space between nodes
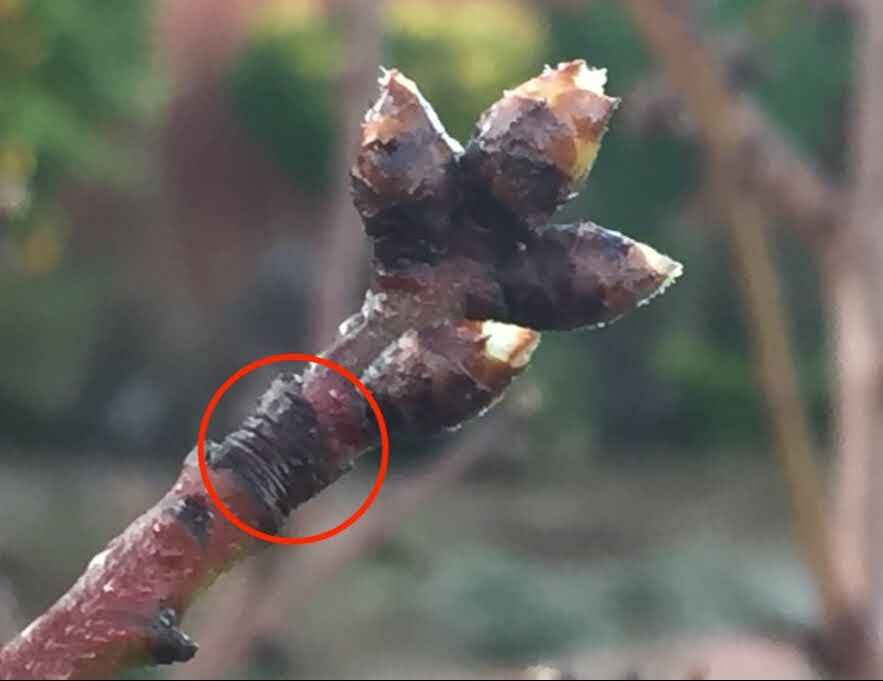
Bud scale scar
shows where the terminal bud was last year, anything above it is new growth

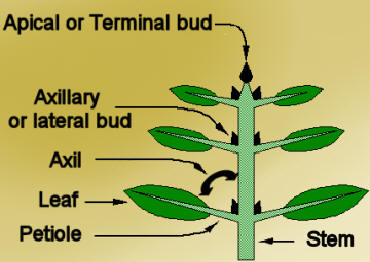
Axillary Bud/lateral bud
bud thats on the side of a leaf or branch

Terminal/Apical Bud
at the very tip of the plant( a flower can also techinically be terminal or apical)
Pedicel
the stem that is directly attached to the flower, it supports the flower!
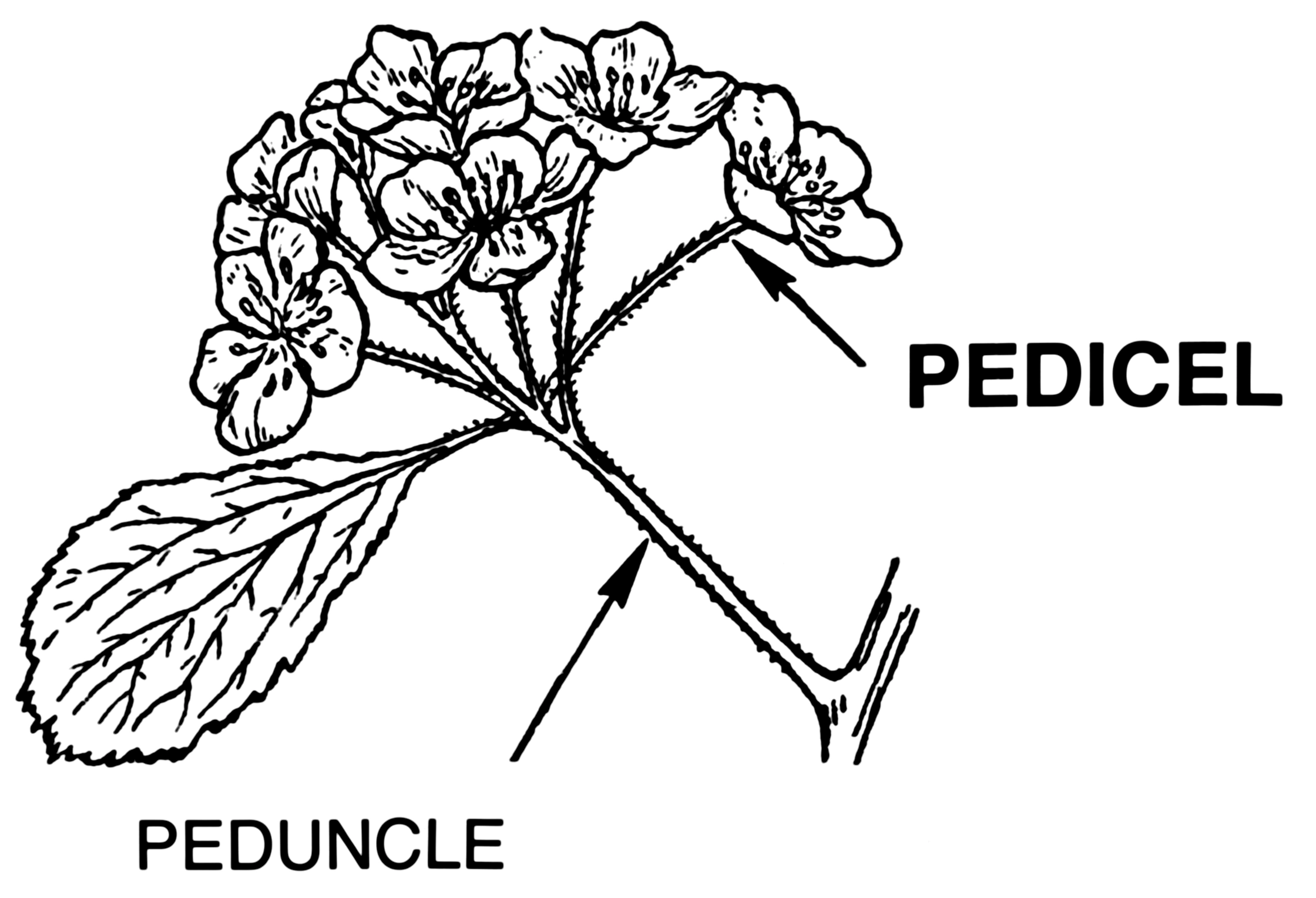
Peduncle
stem that connects all the flowers(flower head) to the main stem
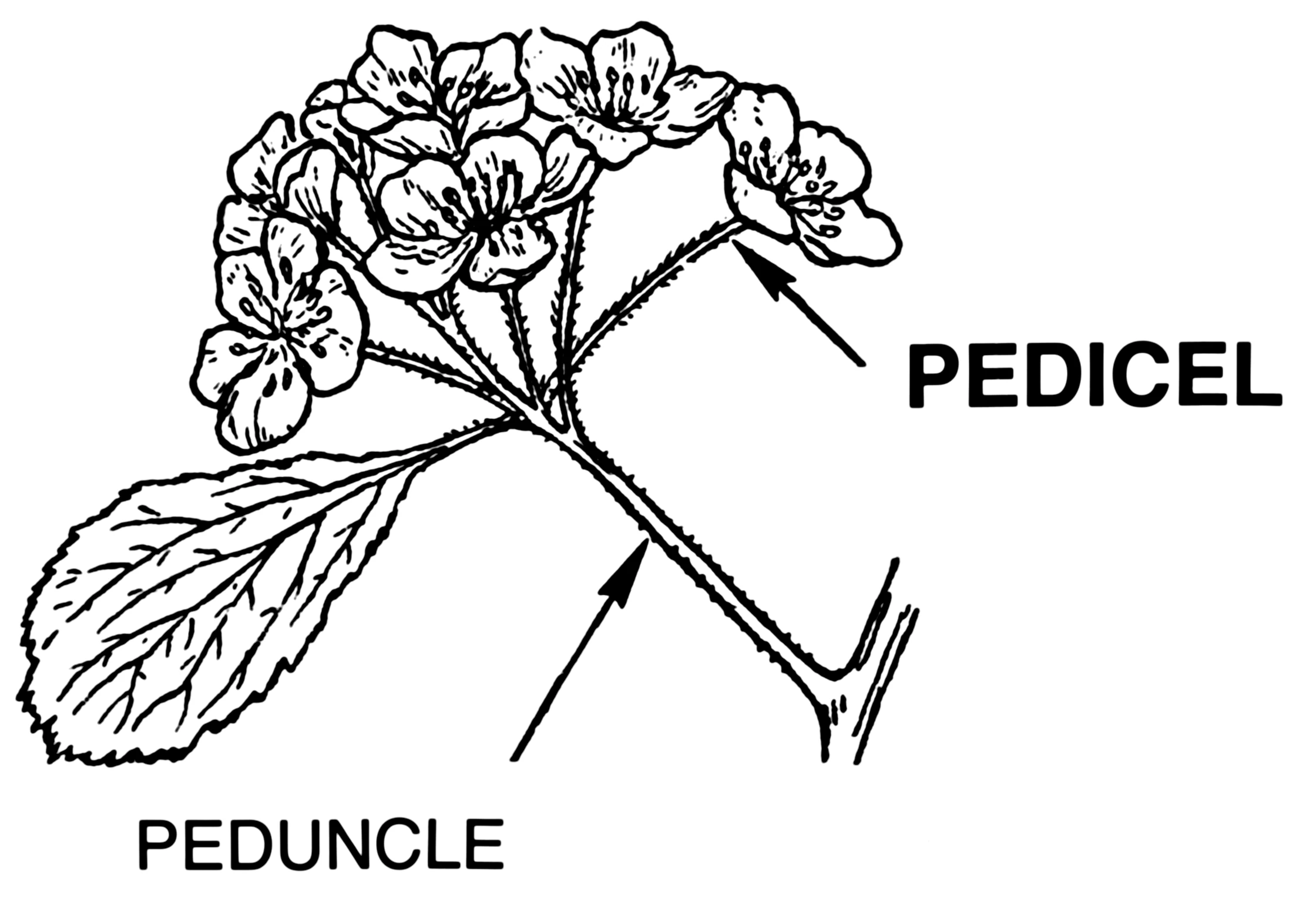
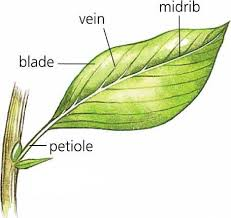
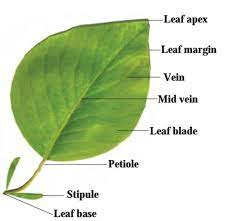
Petiole
stem/stalk that connects the leaf blade to the stem
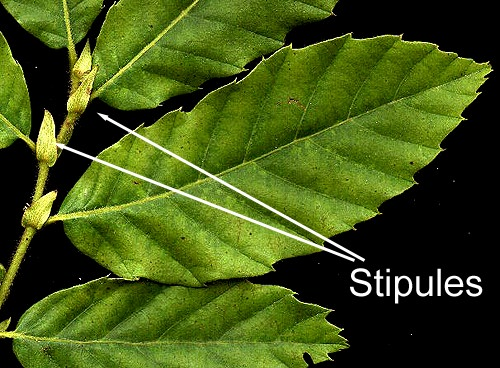
stipule
next to the petiole, looks like a flap, or where another node could be
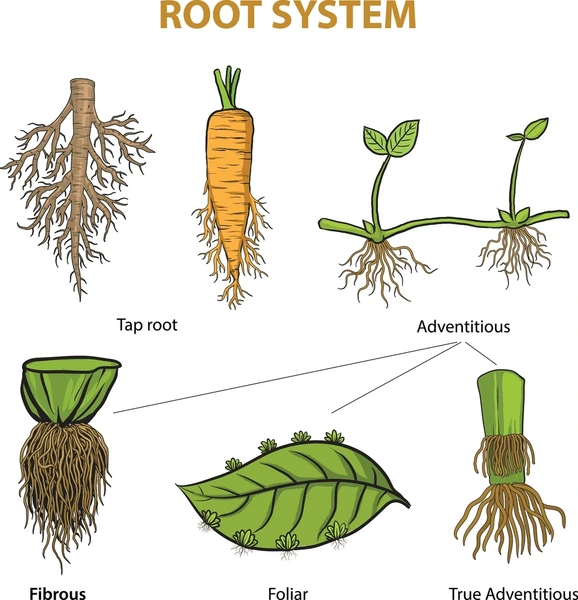
Taproot
central root
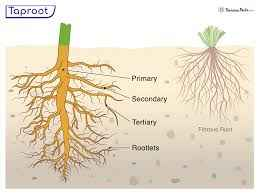
Lateral Root
roots that are attached to the primary root on the side
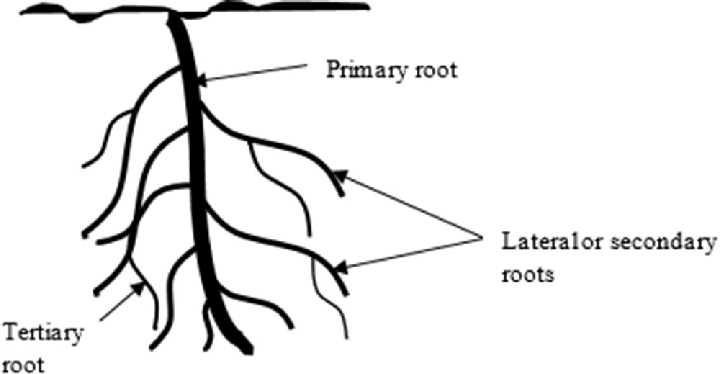
Root Hair
on lateral and primary/tap root - absorb water and nutrients

Root Apex
the very bottom point of the root(tap root)
Root Cap
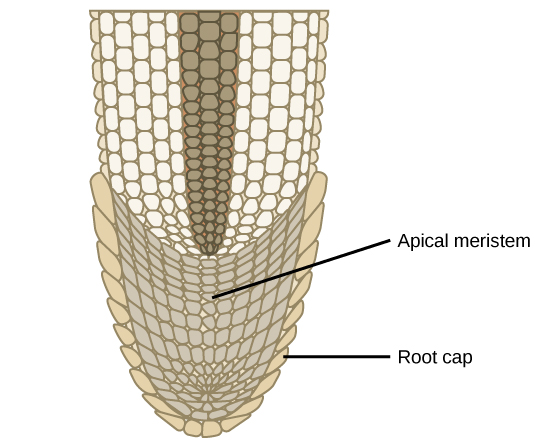
Apical Meristem
found in the tip of the plant shoot and root responsible for cell division and primary growth
Lateral Meristem
found in the cambuim layer between xylem and phloem - responsible for secondary growth
Meristematic tissue
group of cell dividing cells that are responsible for the plant growth, and they continosly create new cells, that differentiate into roots, stems, leaves, ect..
Adventitious roots
roots that form from non root tissue
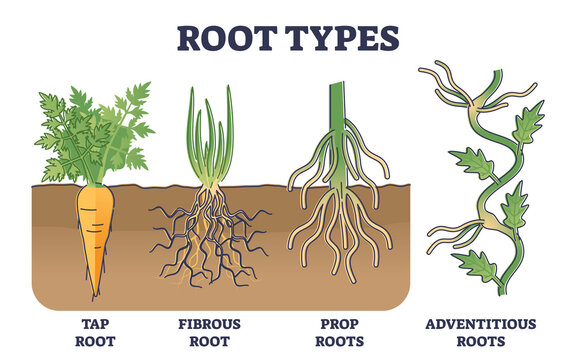
Foliar Roots
roots that grow on the upper side of the petiole
Prop roots
a type of adventitous root that grow from a plants stem or branch downard into soil - provide stability
Leaf base
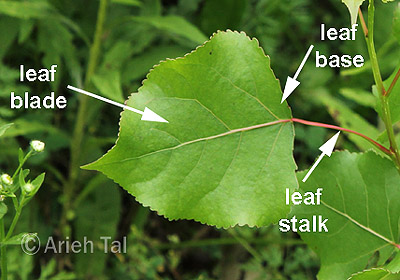
Margin
the outer edge of a leaf

Midrib
central vein

Leaf Apex
top point/shape of leaf
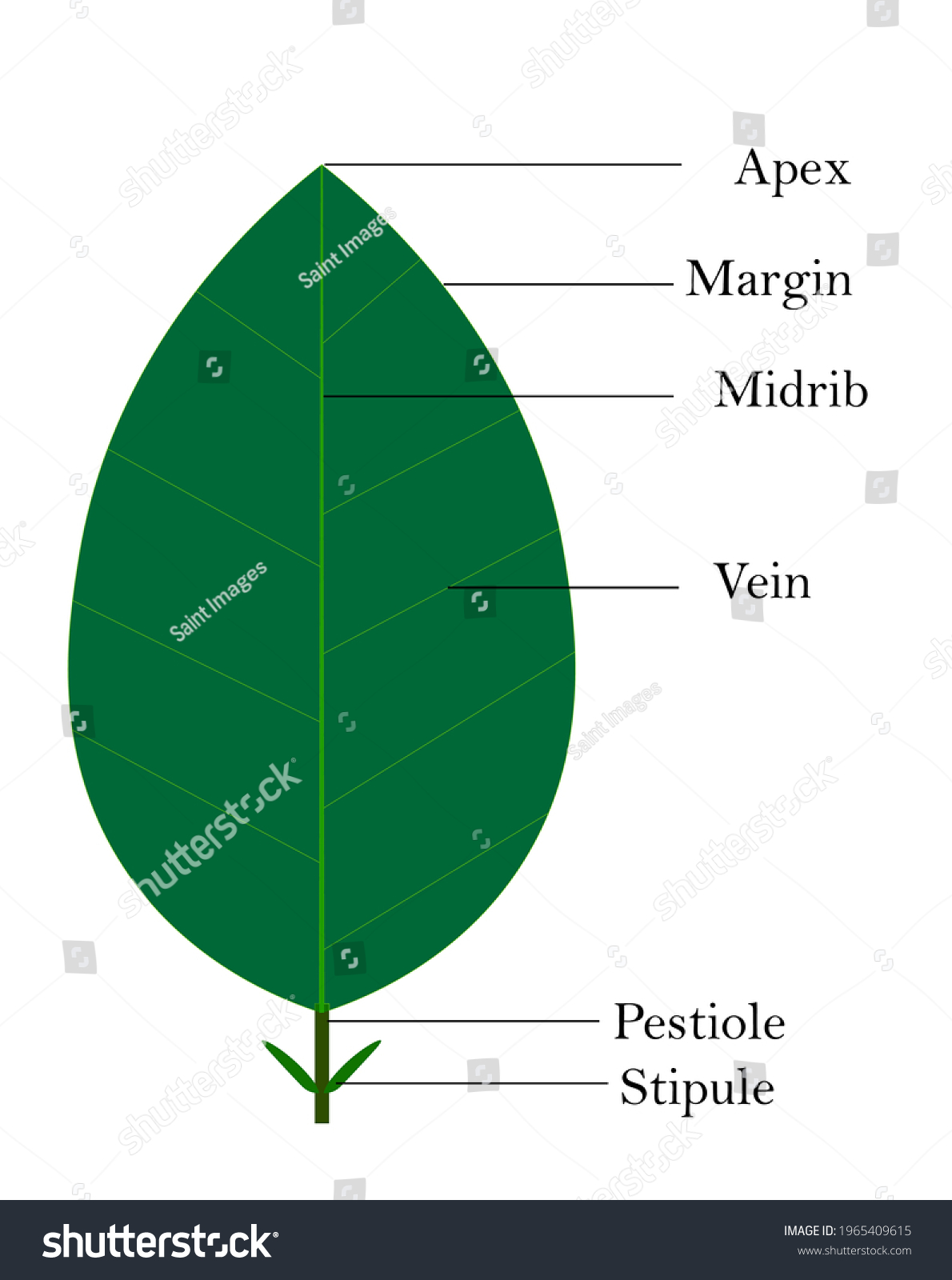
Leaf Blade
where photosyenthisis occurs!
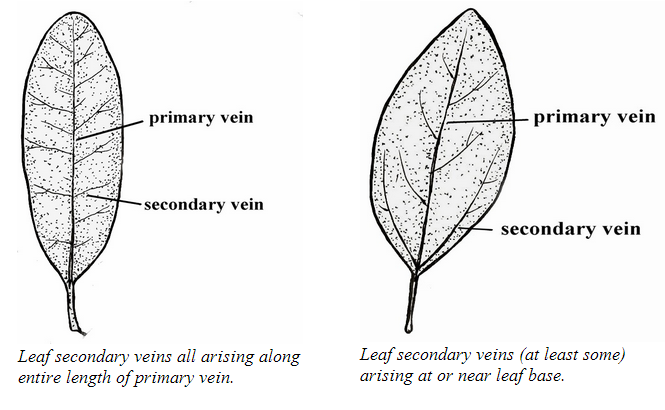
Secondary Vein
smaller veins that come out of mid rib
Compound leaf
several leafets/parts in a single stem
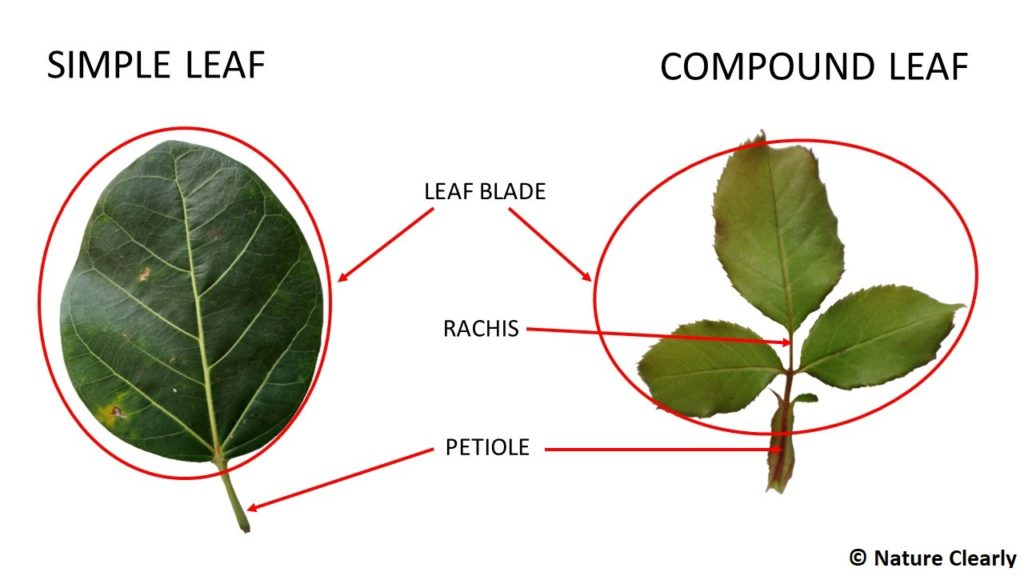
Simple Leaf
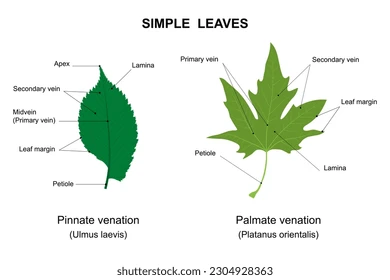
Palmate

Dichotomous Key
a tool used for identifying an unknown item or organism by presenting a series of paired, contrasting choices
UUpper epidermis
barrier to protect from water loss same goes for lower
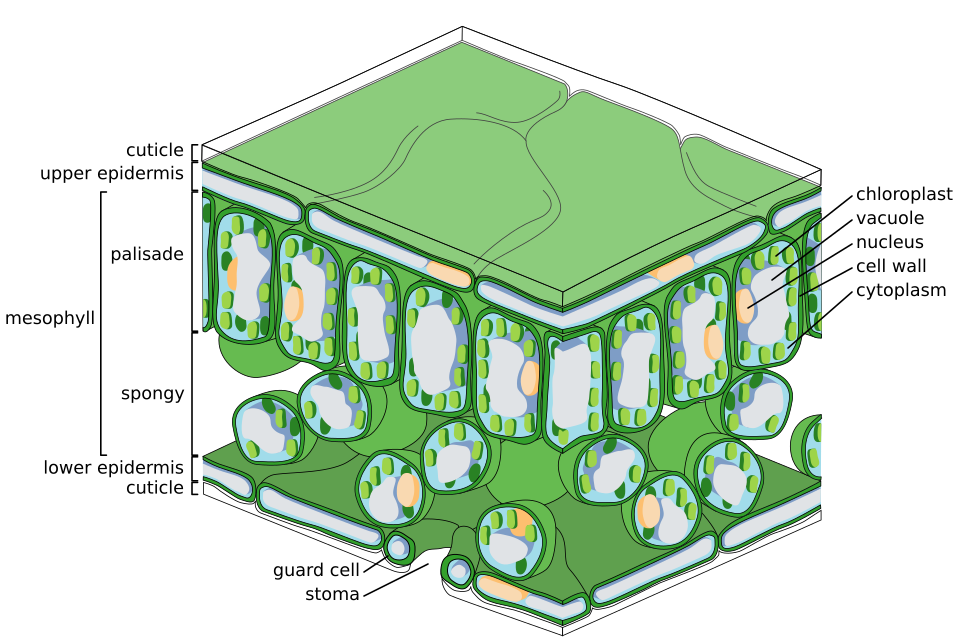
Lower Epidermis
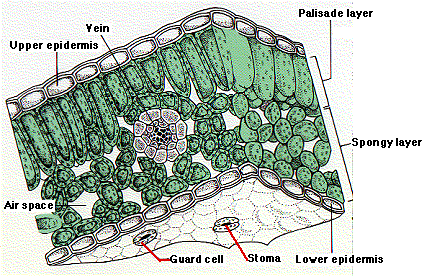
PPalisade Mesophyll
oval shaped - absorb sunlight have chloroplasts in them, photoysnthesis occurs in them
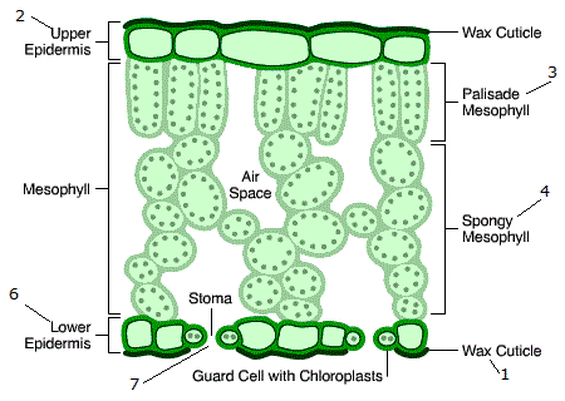
Spongy Mesophyll
circlular - does gas exchange, has air space, turns co2 into oxygen
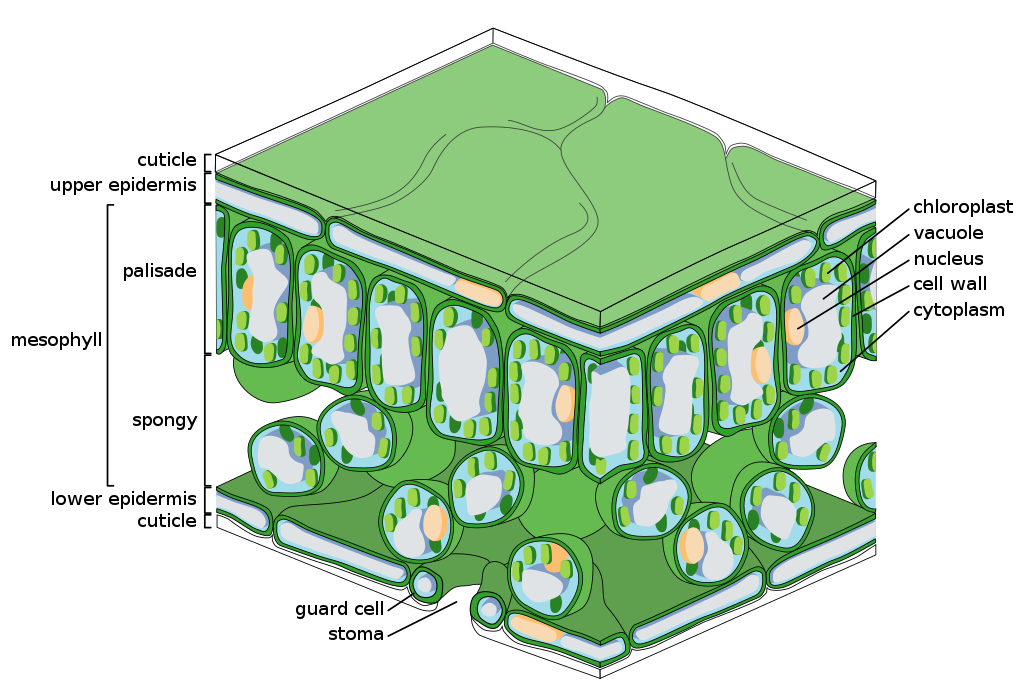
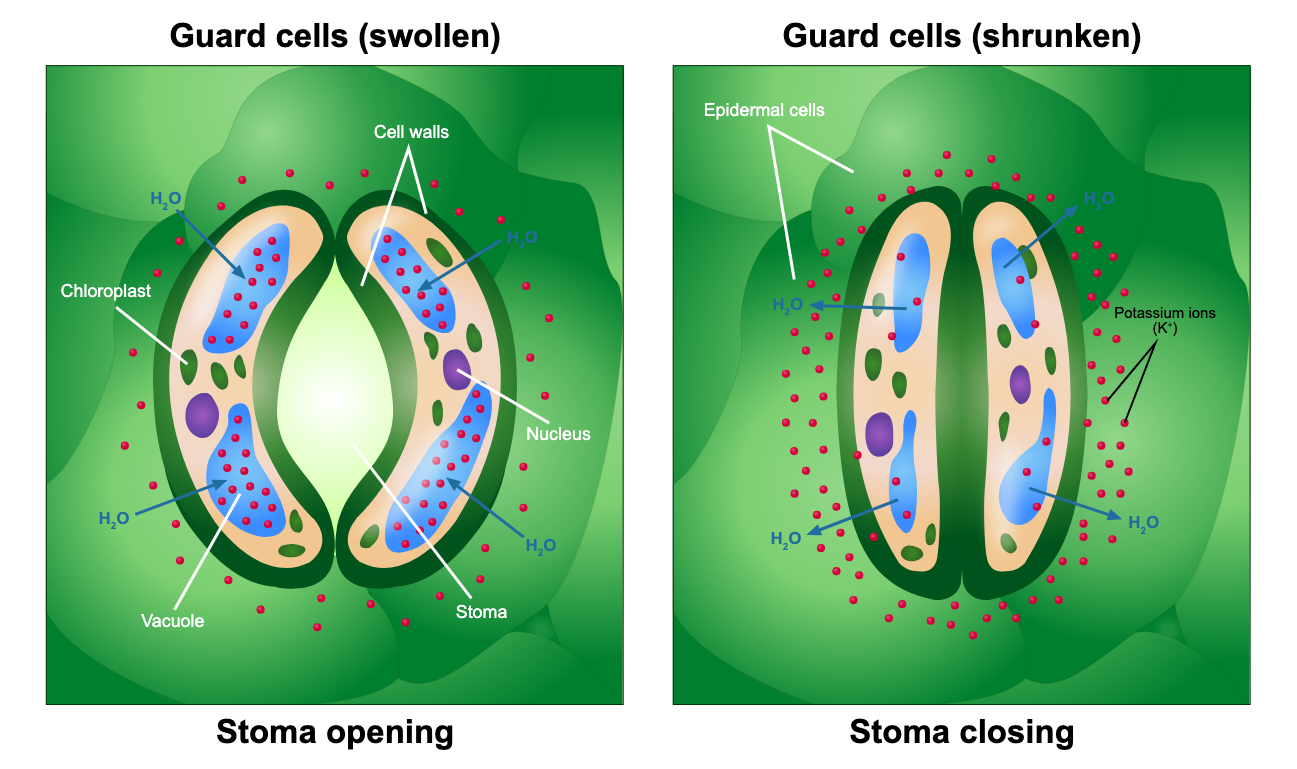
Stoma
whole in between guard cells, opens and closes to let water in or out as well as some gases
Stomata
plural of stoma - does gas exchange
Guard Cell
open and close stoma
Cuticle
top layer of plant internal prevents water from getting out/in protects leaf
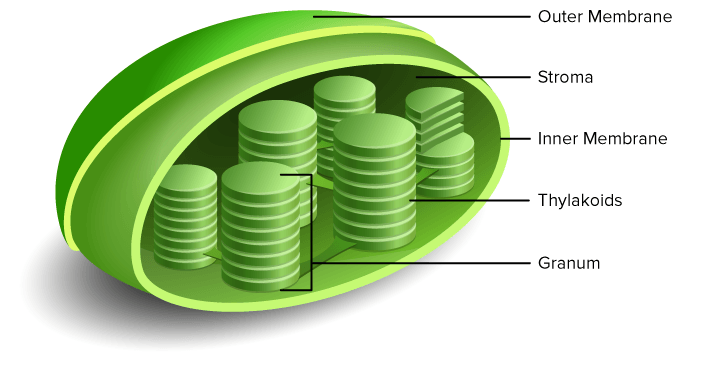
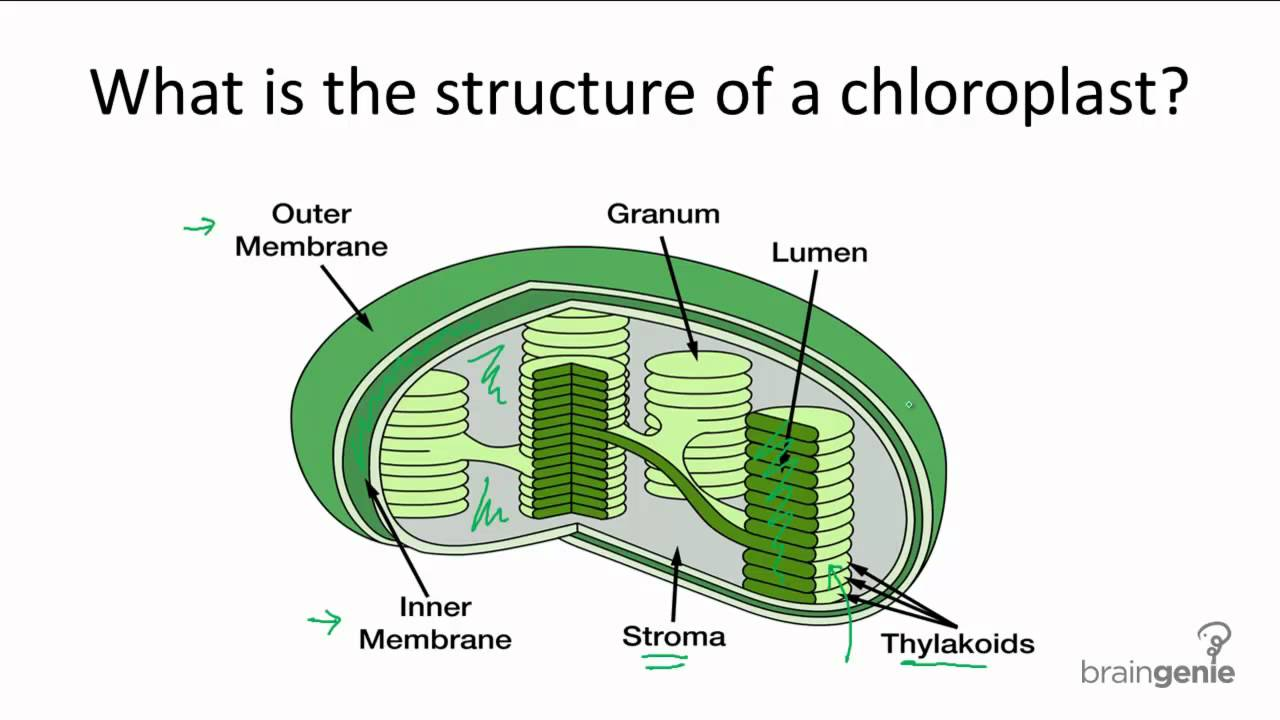
Outer Membrane
outer barrier of cholorplasts - allows gas to pass through
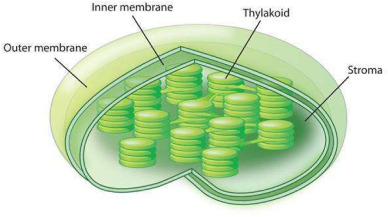
Inner Membrane
acts as a barrier for molecules in and out of stoma
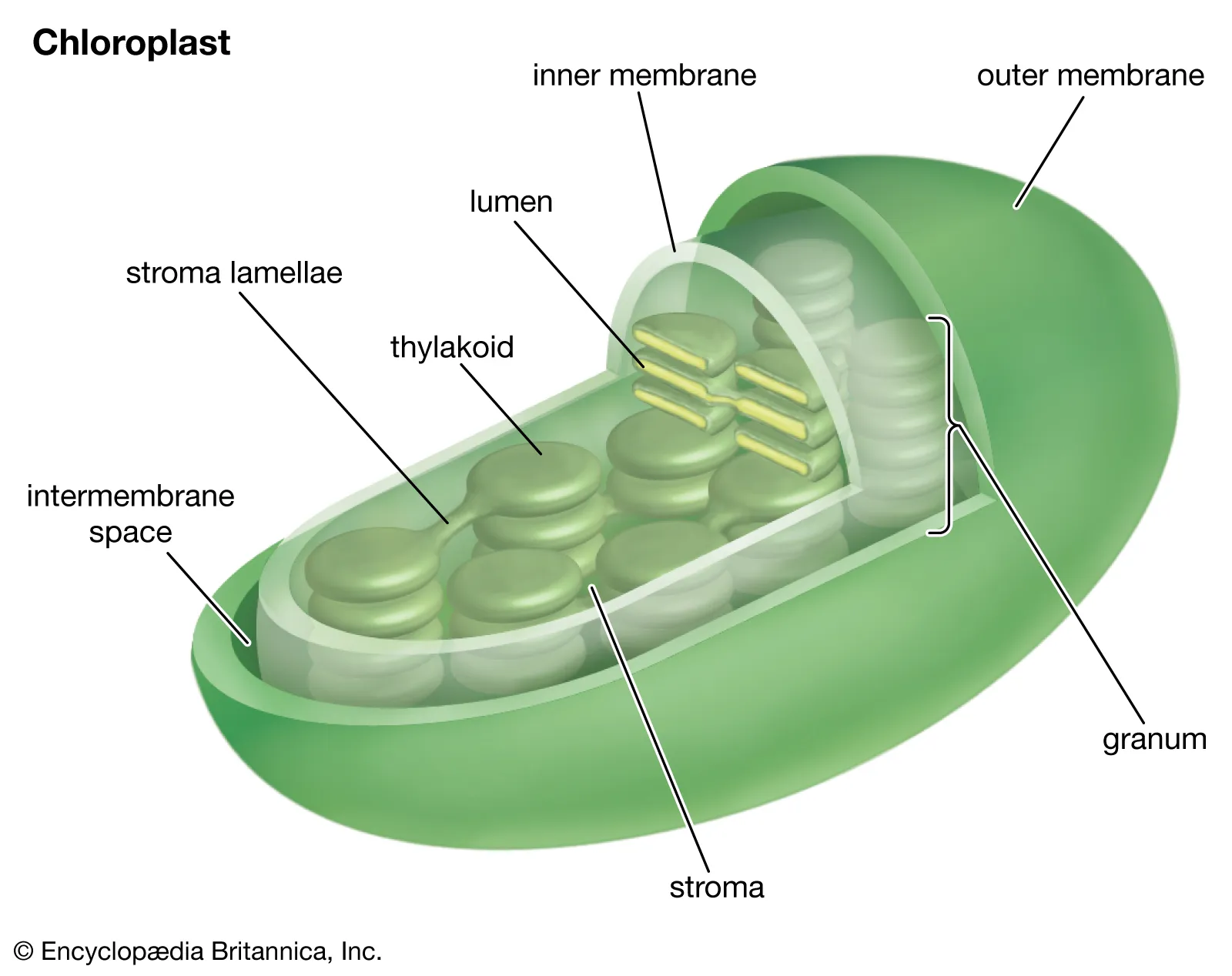
Stroma
in chloroplast fluid surrounding thylakoids - where enzymes and energy are produced during light reactions/calvin cycle
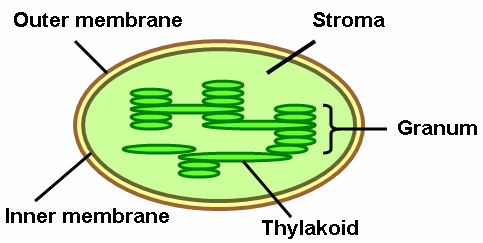
Thylakoid
convert light energy into atp
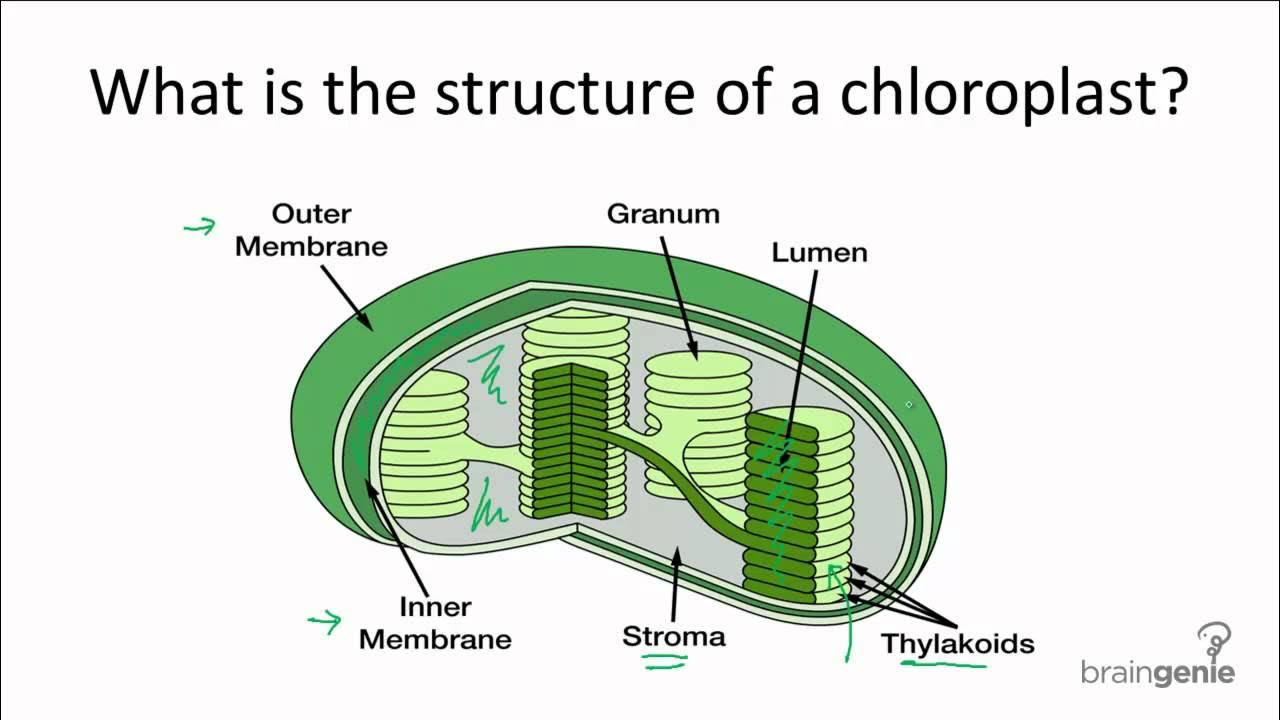
Granum(grana)
stack of thylakoids
Lumen
inside thylakoid light reactions
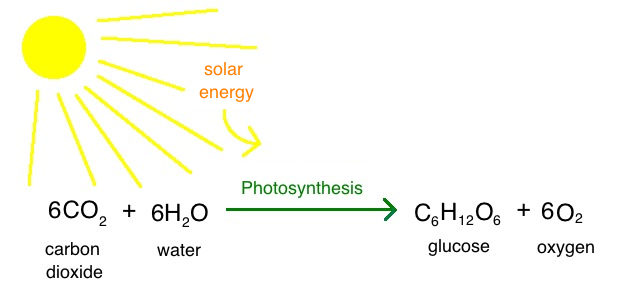
H20
water
C6H12o6
product of photosynthesis its glucose
Photorespiration
happens when there is no co2 in photosynthesis, the stoma can take in oxygen instead of co2, which causes the oxygen to create something new, which the plant cannot use, so the plant has to break it down using more energy
plant respiration
the continuous cellular process where plants break down sugars, using oxygen to produce ATP (usable energy), carbon dioxide, and water
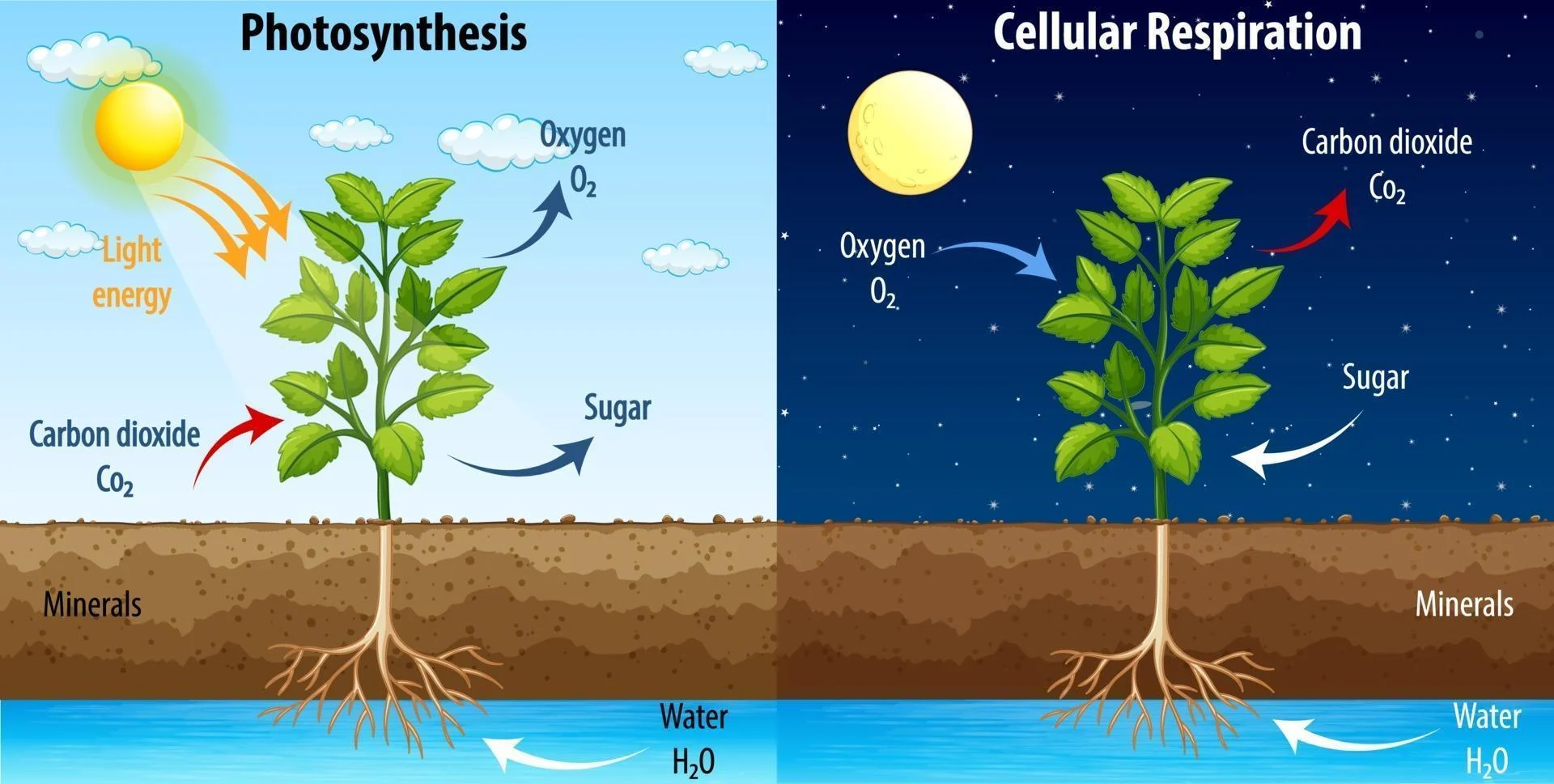
Photosynthesis
NADPH
caused by light reactions - high energy molecule
ATP
ENERGY - generated by the light reaction cycle, then is used in the calvin cycle to synthesis glucose
Krebs Cycle
reactions within the mitochondria that break down sugars into energy
Light Reaction
first stage of photosynthesis - light is captured by chloropyhll, which is converted into ATP and NADPH, releasing oxygen
Calvin cycle
uses the NADPH and ATP from the light reaction to convert co2 into sugar
GFibrous Roots
Xylem
found in stem - found in guard cell , transports water
Phloem
also found in guard cell - transports sugars
BuBundle Sheath
holds the xylem and phloem
CChloroplast
where photosynthesis occurs - found in mesophyll, guard cell, bundle sheatg…
Chhlorophyll
green pigment - found in chloroplast - absorbs light
Gas Exchange
co2 is taken in and oxygen is released through the stoma/stomata
Oxygen
by product
Water Vapor
boiling from liquid water/transpiration
Water Cycle
evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipation, run off,
Transpiration
absorb water through roots and then release water vapor from stomata/stoma
Carbon Dioxide
plant takes this in
Negative Pressure
Lenticel
pores/ gas exchange on the outside of plants, mostly fruits, black or white

Corn Sweat
Spile
Reverse Osmosis