Metabolism: Cell level systems: Biology: GCSE (9:1)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Metabolism
The sum of all the reactions in a cell or the body
Metabolism includes
The synthesis of new molecules, the breakdown of existing molecules and the process of respiration
Energy transferred by cellular respiration
Is used by organisms for the continual enzyme-controlled processes of metabolism
Enzymes and metabolism
Enzymes regulate most cellular reactions and are essential for the synthesis and breakdown of molecules
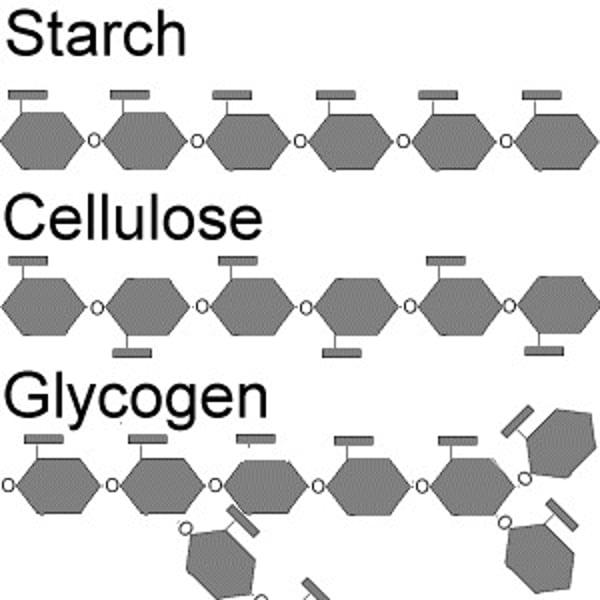
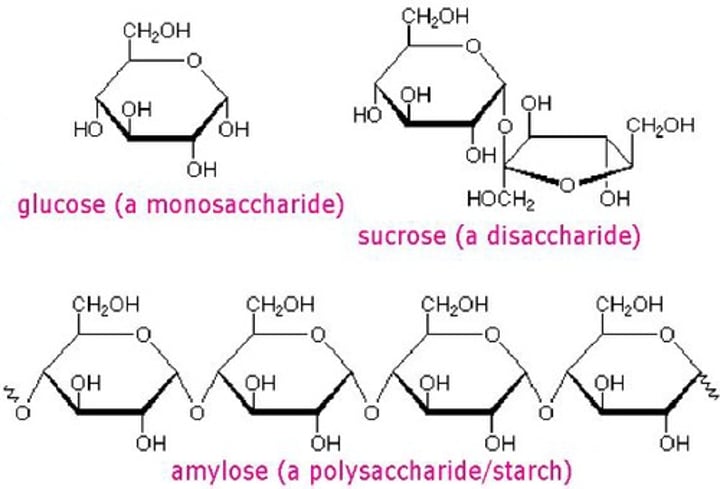
Conversion of glucose to complex carbohydrates
Glucose can be converted into starch, glycogen and cellulose
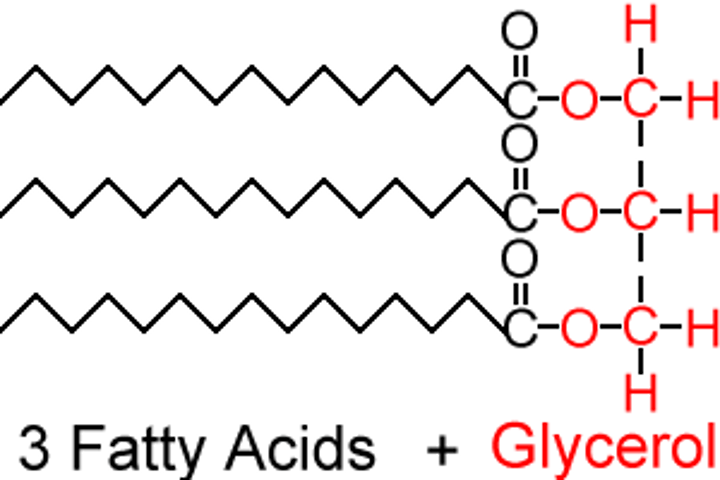
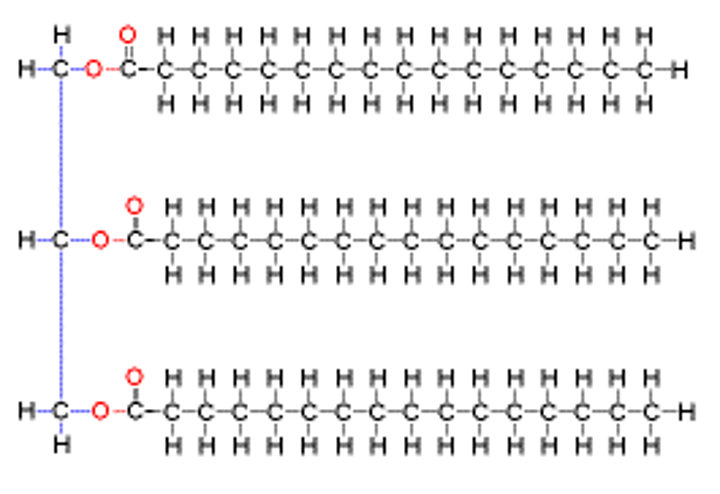
Formation of lipid molecules
One molecule of glycerol joins with three fatty acids
Amino acid production
Glucose and nitrate ions form amino acids which are used to make proteins
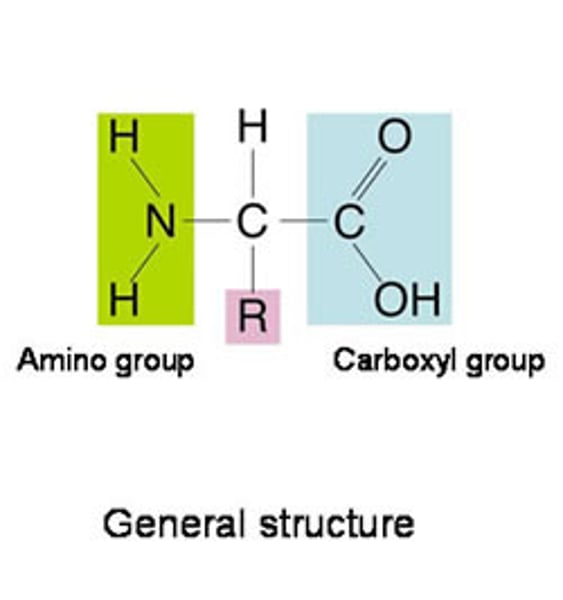
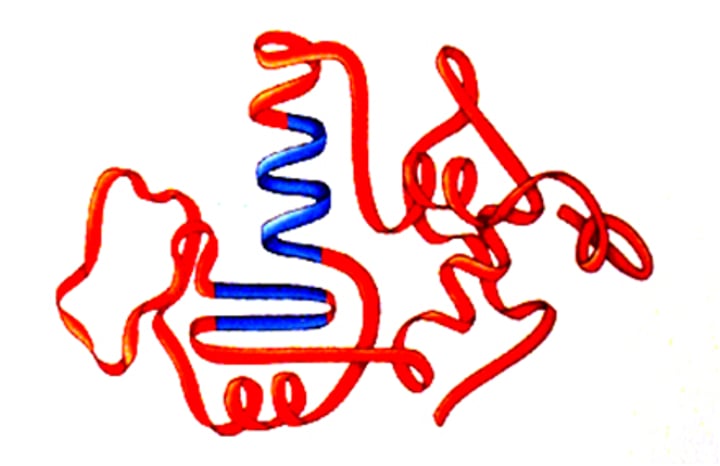
Protein synthesis
Amino acids join together in specific arrangements to form proteins
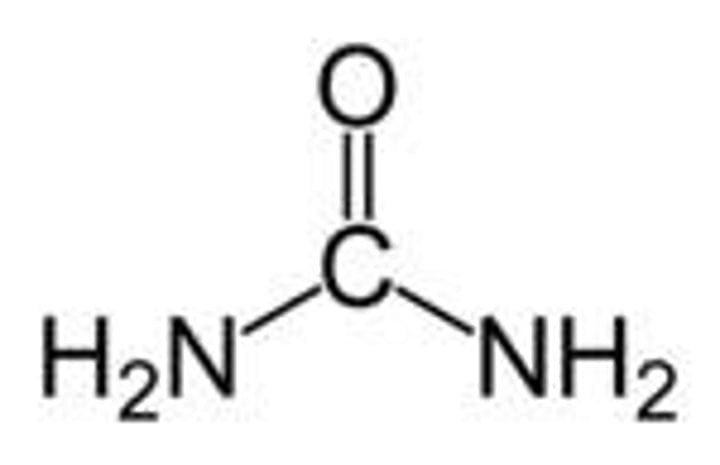
Urea excretion
Excess proteins are broken down to form urea for excretion
Digestion
Requires energy from respiration to break down large insoluble molecules into smaller soluble molecules
Carbohydrates
Provide energy for chemical reactions and can break down into sugars
Proteins
The building blocks of cells and tissues that can break down into amino acids
Lipids
An energy store of fats and oils that can break down into glycerol and fatty acids
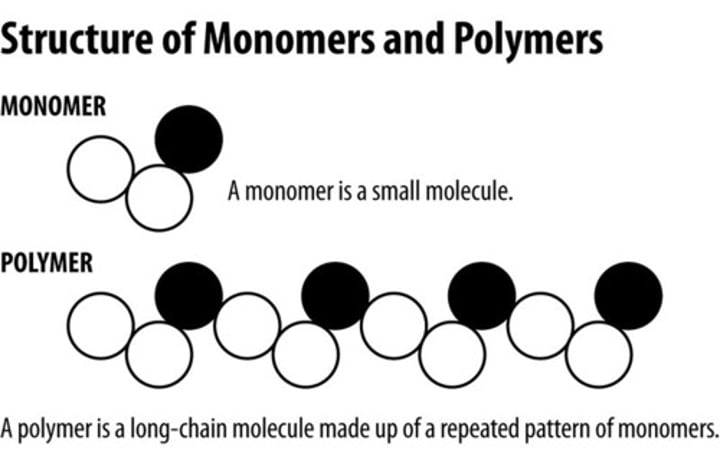
Monomer
A simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers, such as glucose which can be used to make up a complex carbohydrate called glycogen
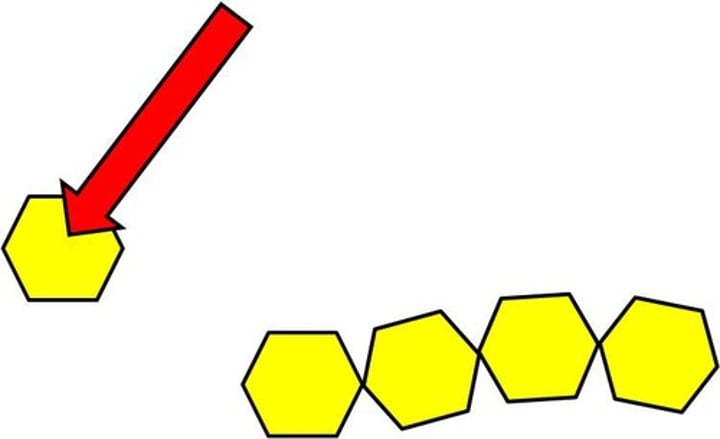
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together, such as glycogen which is made up of many glucose molecules