MSK II: Force/Load intollerance Foot & Ankle presentations
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
PT diagnosis
tendinopathy = load
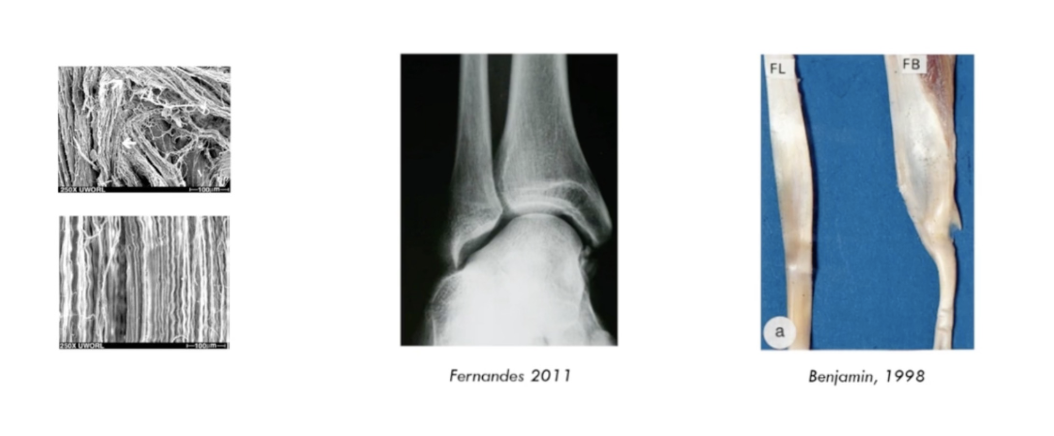
photo 1:
injured tendon with collagen fibers all over the pale, theres no organization
extracellular matrix leads to unorganized of collagen while laying down
realign collagen fibers
lay down and respond to load
photo 2:
this person had eversion
their body adapted to force over time and have this acetabularized talocrual joint
photo 3: size difference with load and without
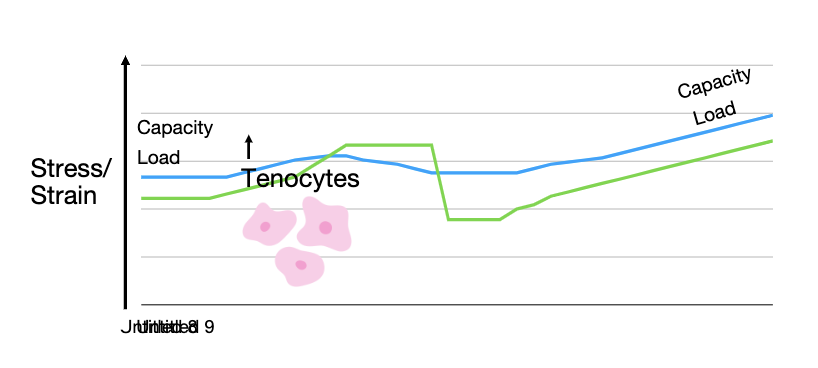
its all About the load
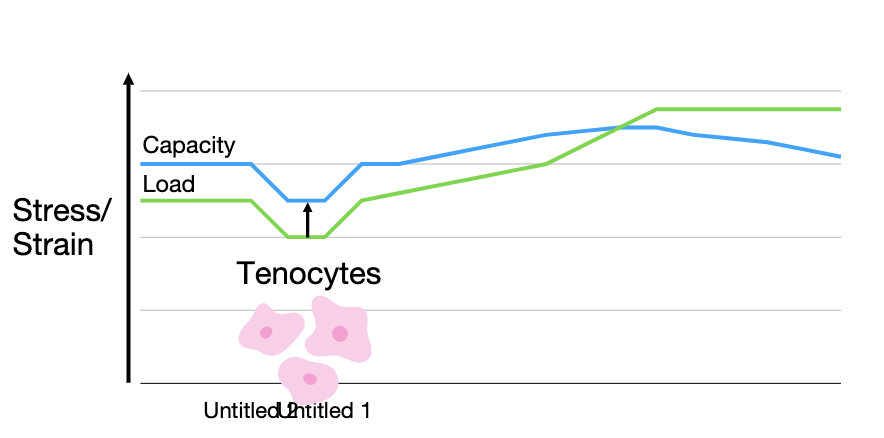
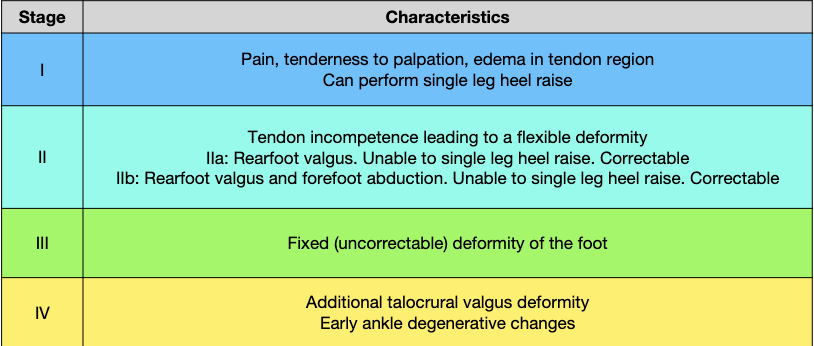
“Your tissue capacity will only ever be as great as the load you’ve placed on it previously”
Load vs capacity
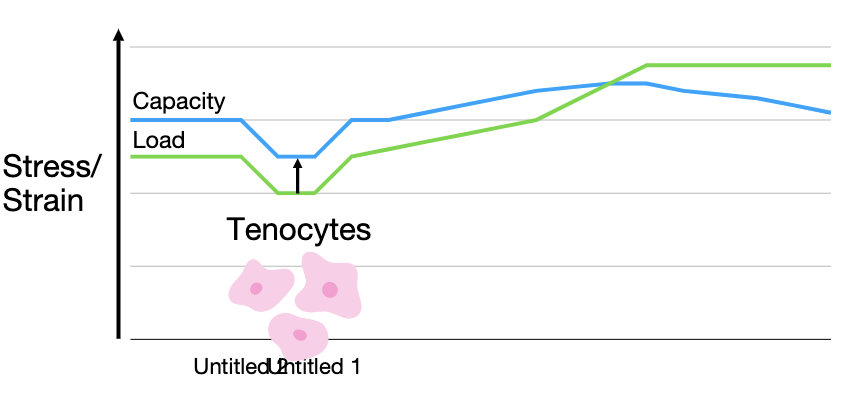
what does blue line on chart represent?
the tendons capacity and the normal ability our tendons have for day to day activities
warehouse job to sedentary job capacity decrease
capacity has ability to change with stress/strain with exercise
what happens when load goes above capacity?
injury
a large load can cause tendinopathy or tear
so if we do something we’ve never done before but run a marathon when we haven’t run in 3 years then our capacity wouldn’t be able to handle it and our load exceeds the capacity of the tendon
where do you start?
SINSS, specifcally Nature
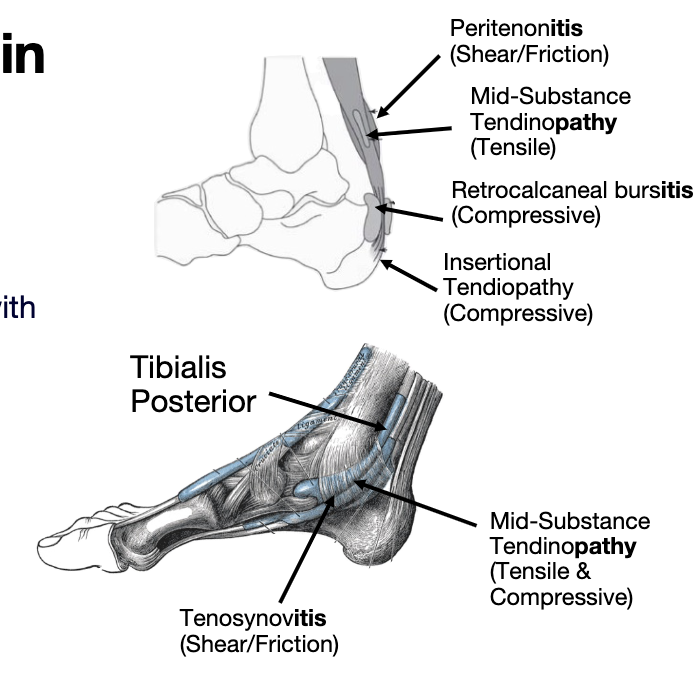
1. Tensile Load- Store & Release Energy
2. Compressive Load- Interface with other structures
3. Tensile & Compressive Loads
4. Shear & Friction Load
4 types of stress
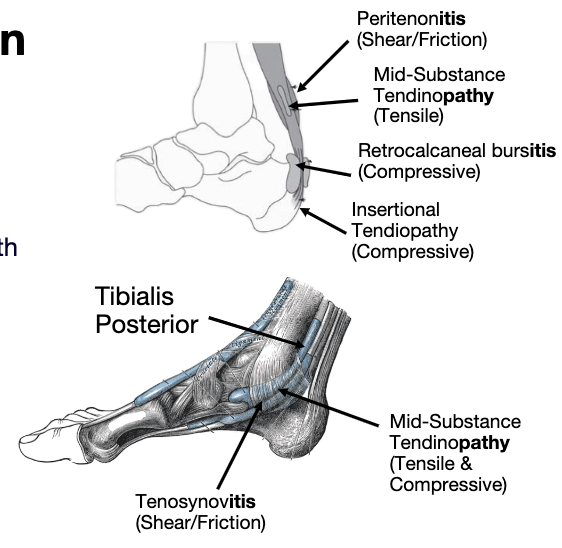
midportion of achilles
where tendon stores and release energy
CPG
where we exceed the capacity of the tendon is where we have injury
Tensile or mid-substance pain will increase as the load increases
(double leg heel raise < single leg heel raise < double leg hop <
Single leg hop)
Tensile Load- Store & Release Energy
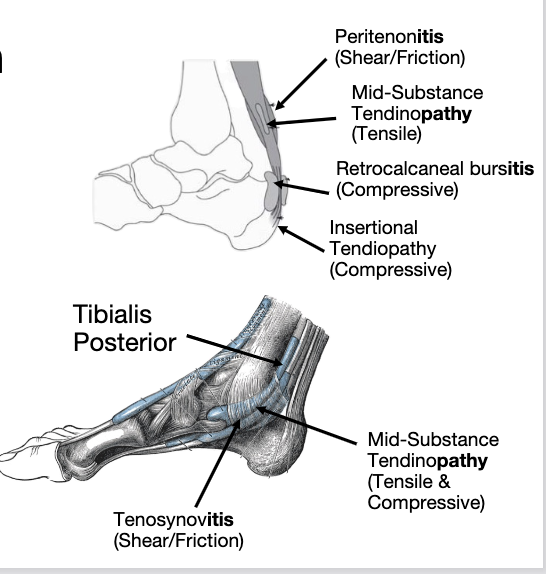
tendon comes together with other structures pressing on each other
more insertional achilles tendinopathy pressing against the calcaneus
tibilias posterior is a tendon typically exposed to compressive load as it goes thru the tarsal tunnel
rare in isolation
Increased pain with stretch/excursion of the tendon
Compressive Load- Interface with other structures
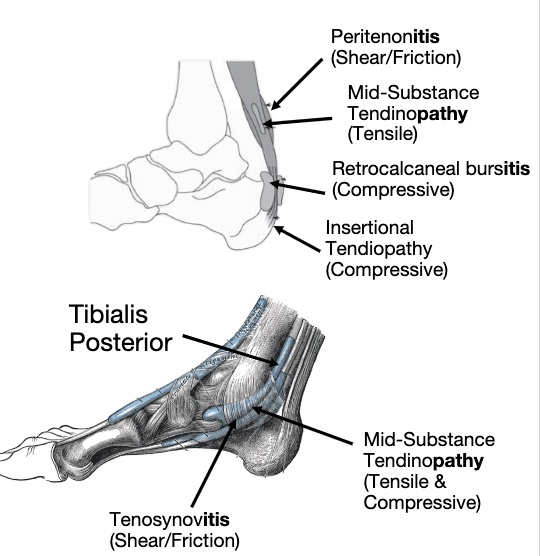
Tensile & Compressive Loads
Increased pain with repetitive low load
movementsheath that covers the tendon itself it gets friction between the structures underneath it and causes pain and discomfort after that
Shear & Friction Load
when will tensile increase?
tensile will increase when load increases
when is tensile worse?
double leg heel raise < single leg heel raise < double leg hop < Single leg hop
what will increase compressive stress?
increase with stretch/excursion of the tendon
what to avoid with compressive stress
unilateral movements in weight bearing (single leg, heel raise, and plyometrics)
end range dorsiflexion
what helps with compressive stretch
stretching helps (static)
isometrics and isotonics in pain free range is okay but stay away from end range dorsiflexion
heel raises help unload tendon
what to stay away with compressive & tensile stress together?
isotonics or isometrics are okay but stay away from end range dorsiflexion
still give a heel lift
squats with wedge under heels
pain with both
what increases pain in shearing/friction?
swimming, riding bike, walking all increase pain
stray away from repetitive low load movements
where is the pain?
Palpation- Sensitive, Not Specific
Achilles pain is localized- 2 fingers in mid tendon for mid- substance (tensile), 1 finger at insertion for insertional (compressive)
Peritenon pain is more diffuse
is palpating more sensitive or specific?
sensitive - means that the test is good at detecting the disease when it is present
is there night pain with tendon related pain?
Usually no night pain with mid-substance
Can have pain and stiffness in the am.
Subsides within 30 minutes
does mid-substance pain get worse with or without activity?
Mid-substance pain subsides with activity.
Peritenon pain increases with activity

clinical practice guidelines
MAKE SURE TO READ
Tendon Specific Considerations- Achilles Tendon
tibialis posterior signs and symptoms
Pain medial foot that worsens with activity
May have redness, swelling, and localized tenderness over tib post tendon
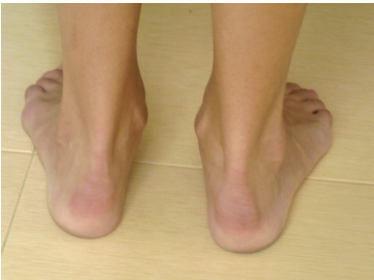
Rearfoot valgus, flattened midfoot, and forefoot abduction
what are cardinal signs of inflammation
May have redness, swelling, and localized tenderness over tib post tendon
what is signs or components of pronation
Rearfoot valgus, flattened midfoot, and forefoot abduction
if tibialis posterior is compressive what should be given to the patient ot help
give patient taping and towel
tibialis posterior stages- johnson classification
Pain, tenderness to palpation, edema in tendon region Can perform single leg heel raise
stage 1 johnson classifciation
Tendon incompetence leading to a flexible deformity
IIa: Rearfoot valgus. Unable to single leg heel raise. Correctable
IIb: Rearfoot valgus and forefoot abduction. Unable to single leg heel raise. Correctable
navicular drop or heel drop
stage 2 johnson classifciation
Fixed (uncorrectable) deformity of the foot
unaddressed for a long time
use more manual therapy
talocrual or midfoot mobility
stage 3 johnson classifciation
additional talocrural valgus deformity Early ankle degenerative changes
permanent everted
stage 4 johnson classifciation
Pain medial plantar region
Unilateral
Insidious onset
Sharp/local pain with palpation
Sharp/local pain upon WBing after period of NWB
Pain gradually improves with activity, then worsens
Pain with ext 1st MTP
right on insertion of calcaneus and go on the arch with walking
windlass test - astrik sign
great toe extension, dorsiflexion mobs.
plantar fasica signs and symptoms

MAKE SURE TO READ
plnatar fascia clinical practice guidelines
EdURep
Educate
Unload
Reload
Prevent
Management of Tendon Related Presentations
where to start reloading ?
isometircs- pain free range
isotonics NWB, then WB
how to prevent reinjury?
educate to not increase capacity
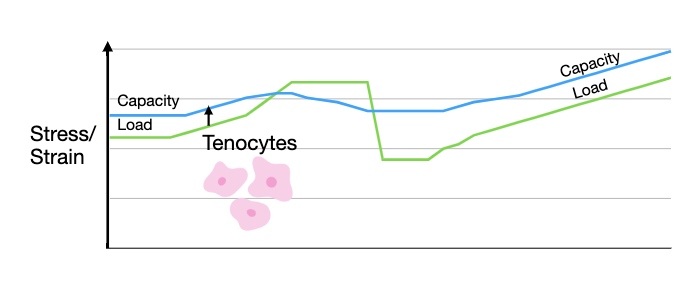
educate

dont tell them they have tears or tenonitis use tendinopathy
words matter
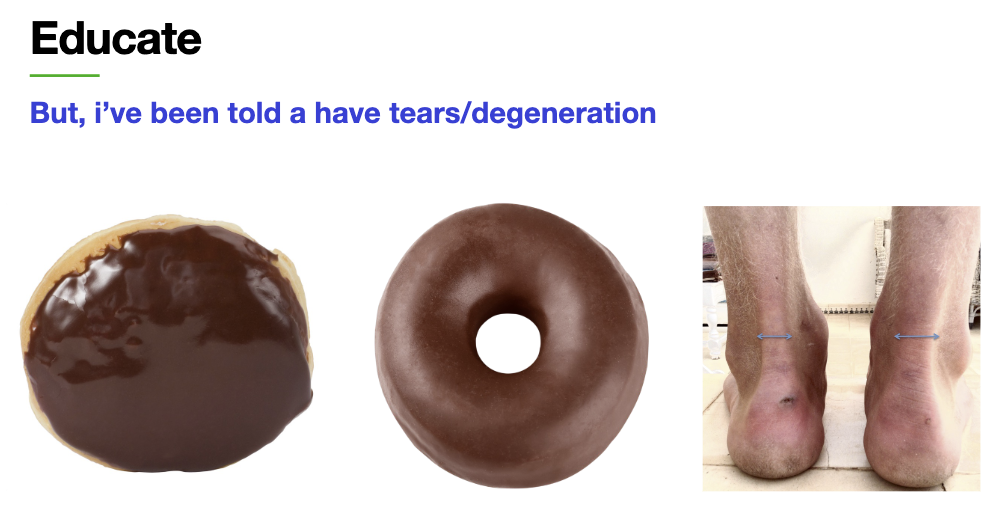
imaging doesnt tell the whole story
educate patients that there will be good and bad days PT is not a linear increase
remove the provactive load
Unload

limit fast loading
Tensile/mid-substance Tendinopathy

Limit stretch on the tendon
Compressive
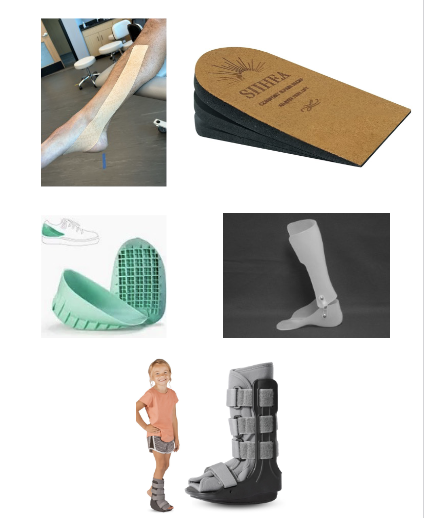
tape
heel lift
heel cup
orthosis
mobilize
address movement coordination deficits
increase cadence
other considerations to unload
Support muscle, Support arch
tape
Compressive (Tib Post, Achilles insertion
heel lift
plantar fasica
heel cup
Prefab or custom for plantar heel pain, Custom/hinged AFO/CAM boot for tib post- NOT MID SUBSTANCE OR INSERTIONAL ACHILLES
orthosis
joint and soft tissue restrictions
mobilize
what could be addressed with unload?
Address movement coordination deficits
what can we increase to unload?
Increase cadence- Running or walking
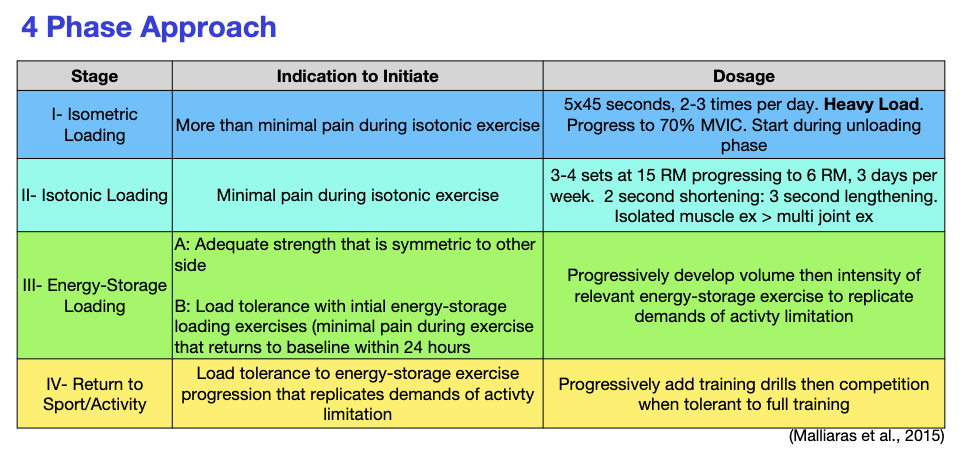
reload: 4 phase approach
how hard can someone perofrm isometric contraction
MVIC
what should pain level be normally when exercising?
5/10, increased pain isnt bad as long as its 5 or below
More than minimal pain during isotonic exercise
stage 1: isometric loading
indication to initiate
5x45 seconds, 2-3 times per day. Heavy Load. Progress to 70% MVIC. Start during unloading phase
stage 1: isometric loading
doseage
Minimal pain during isotonic exercise
stage II - Isotonic Loading
indication to initate
3-4 sets at 15 RM progressing to 6 RM, 3 days per week. 2 second shortening: 3 second lengthening. Isolated muscle ex > multi joint ex
stage II- isotonic loading
dosage
A: Adequate strength that is symmetric to other side
B: Load tolerance with intial energy-storage loading exercises (minimal pain during exercise that returns to baseline within 24 hours
stage III- energy storage loading
indication to initiate
Progressively develop volume then intensity of relevant energy-storage exercise to replicate demands of activty limitation
volume and intensity
walking
hopping but not jumping
stage III- energy storage loading
dosage
Load tolerance to energy-storage exercise progression that replicates demands of activty limitation
stage IV- return to sport/activity
indication to initiate
Progressively add training drills then competition when tolerant to full training
providing load
stage IV- return to sport/activity
dosage
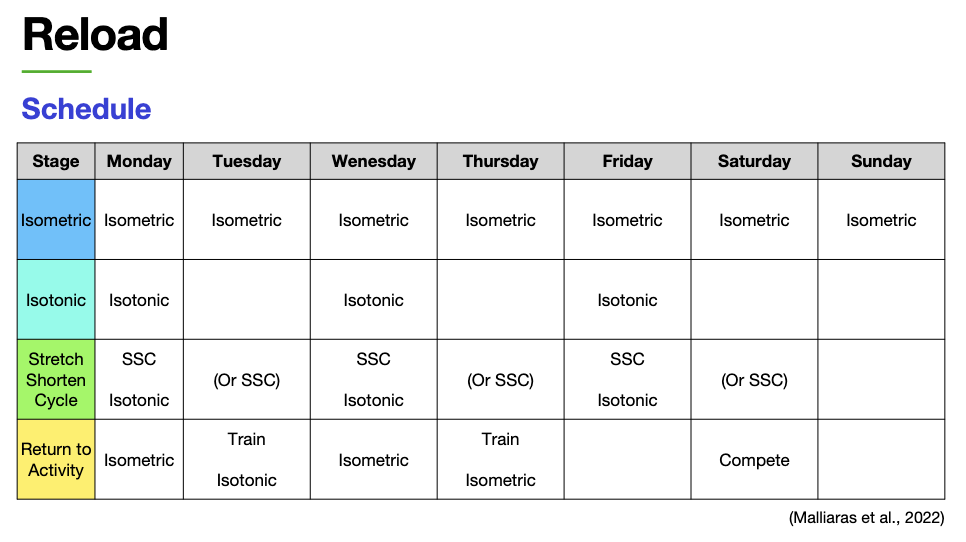
reload: schedule
how many days a week to do isometric exercises?
everyday
how many days a week to do isotonic exercises?
3 days a week, make sure to get rest days
how many days a week to do SSc exercises?
3 - 6 days is good
what shoukd you train to return to activity?
isometric
train isotonic
There is much less evidence specifically related to insertional Achilles tendinopathy Limit stretch and activities requiring full ankle DF
compressive tendinopathy: load progression
Isolated soleus and gastroc during isotonic stage
Loading Specific Tendon Considerations: achilles
May need to start with open chain and progress to closed chain isotonic exercises
Add Resistance band around distal tibia during heel raises
Loading Specific Tendon Considerations: Tibialis posterior & fibularii

Initial loading is through stretching then
progress to heel raise with towel roll under
toes
Loading Specific Tendon Considerations: plantar fascia
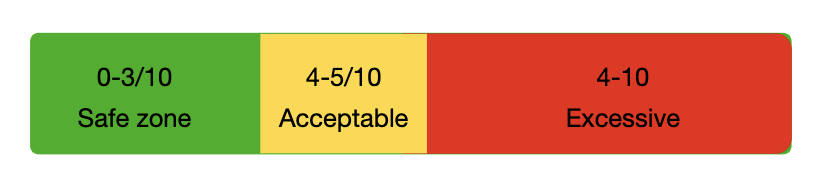
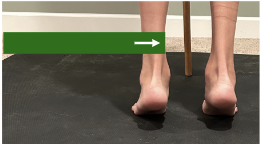
whats appropriate load?
NPRS scores vary among patients. identify levels accordingly
more important: return to baseline within 24 hours
if goes away in 24 hours okay but if not then not acceptable
continue working on capacity to limit the chance
prevent
Adiposity- High BMI
Cholesterol (Tilley et al., 2015)
Smoking
Diabetes (Ranger et al., 2016)
Rheumatoid arthritis, gout, dyslipidemias, spondyloarthropathies
Medications: Hormone replacement, contraceptives, Fluoroquinolones,
Statins (Tilley et al., 2015
Other Pain and Disability Drivers
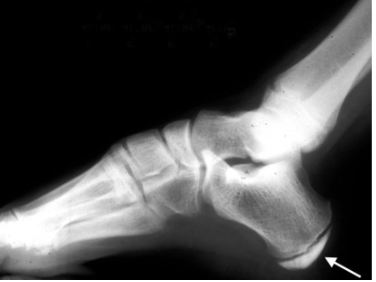
A Note about Sever’s Disease
Young athletes (11-13)
Associated with growth spurts
Be careful with your language
Activity modification
Stretch the gastroc/soleus
inflammation of calcaenus growth plate
manage by decreasing pull of gastroc
increase muscle length there with soft tissues techniques
Calcaneal apophysitis
Local tenderness, swelling, exertion pain
X-ray
If x-ray (-) and no improvement > MRI
Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport (RED-S)
High Risk sites may require period of immobilization and decreased WBing
Navicular, 5th metatarsal, hallux sesamoids, medial malleolus, anterior distal tibia
Treat mobility and movement coordination impairments, EdUReP.
Bone stress injuries take much longer to resolve vs. acute fracture
A Note about Bone Stress Injuries