Structure of DNA, DNA Replication, Protein Production
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Nucleic acids are
DNA and RNA
DNA and RNA are made from
nucleotides
Nucleotide structure of DNA and RNA is
A phosphate, 5 carbon sugar, and nitrogenous base.
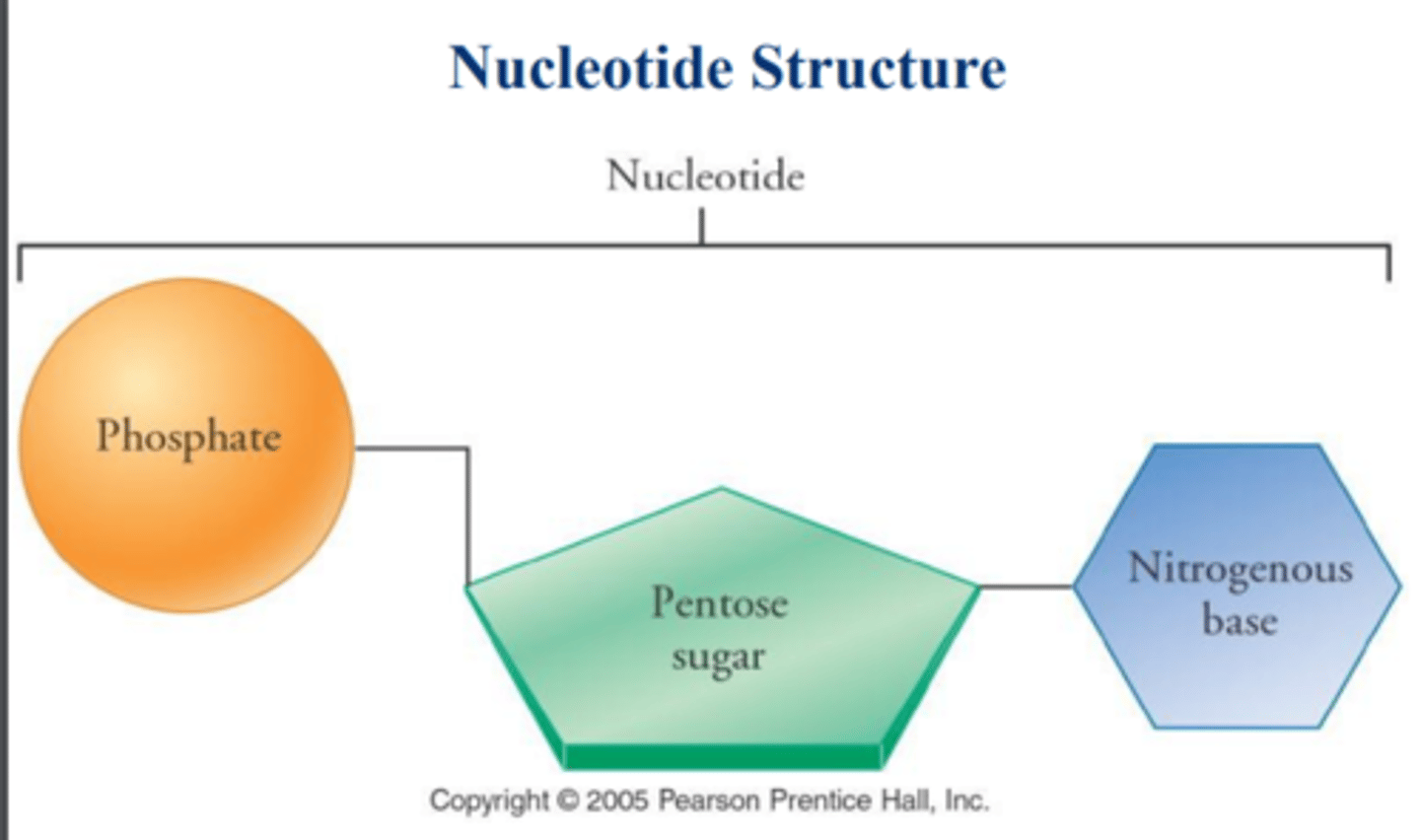
What is the sugar in DNA?
deoxyribose
What is the sugar of RNA?
ribose
In DNA how are nucleotides bonded together?
The sugar and phosphate covalently bond to each other
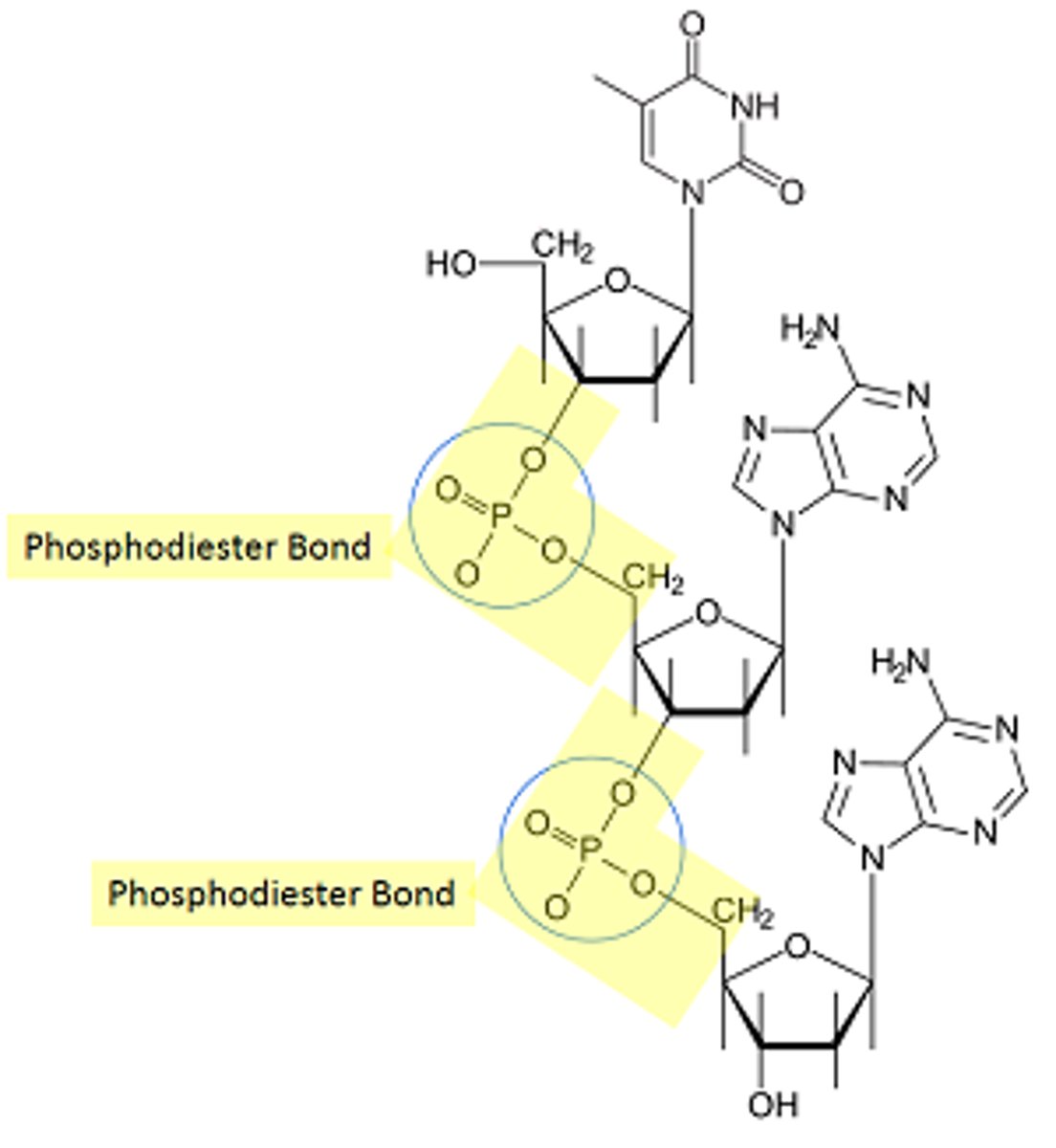
What are the bases in DNA
A, T, C, G
What are the bases in RNA
A, U, C, G
What are the complementary bases in DNA
A=T and C=G
What are the complementary bases in RNA
A=U and C=G
Nucleotide Structure pic
When does DNA replication occur?
before cell division
In DNA replication the original strand is called _______ and the new strand is called_______
Original - parental
New - daughter
First Step of DNA replication? - (1)
First, the enzyme helicase comes in and unwinds the DNA and breaks the hydrogen bond between the bases
Second Step DNA replication? - (2)
Second, the enzyme DNA polymerase comes in and attaches to the open strands and builds the new complementary strand from the parental strand
DNA replication is called
semi-conservative replication
How many phosphates do new coming nucleotides have
three phosphates
How many phosphates are used to bond to sugar
One
What supplies the energy to build new DNA strand?
The breaking bond of the last two phosphates
What supplies the energy to be used to build the new strand?
Nucleoside triphosphates ATP, GTP, TTP and CTP.
DNA replication timing
When DNA replication occurs in the cell cycle
Helicase
Enzyme responsible for unwinding DNA during replication
DNA polymerase
Enzyme responsible for synthesizing new DNA strands during replication
Point mutation in DNA
One incorrect base pairing
Mutation outcomes can be
beneficial, harmful, or neutral
Mutation - Random error (1)
Is a simple mistake that is fixed by DNA polymerase, overall a neutral mistake.
Mutation - Mutagens (2)
Mutagens are harmful, they are chemicals that damage the DNA and cause mutation in recognition, either a base is skipped or misread
What happens to the cell before cell replication (mutagens)
Either enzymes repair the damage (DNA polymerase) or the cell undergoes apoptosis
What happens to the cell after cell replication (mutagens)
If the cell replicates, mutation becomes permanent.
Mutations - Evolution(3)
Is beneficial, drives towards better survival and reproduction
Structural differences between DNA and RNA
Shape
Sugar
Bases
Function Location
DNA - double helix RNA - linear
DNA - deoxyribose RNA - Ribose
DNA - ATCG RNA - AUCG
DNA - In nucleus RNA - in cytoplasm
Structural similarities in DNA and RNA
They are both __________acids
Composed of linked __________
Have a _________________ backbone
Have 4 types of __________
Sugar and phosphate are __________bond
Nucleic Acids
Nucleotides
Sugar/phosphate back bones
Bases
Covalent
DNA and RNA complementary base pairing
A T C G = U A G C
Role in protein production: Nucleus
Where DNA is located, the template to produce mRNA
Role in protein production: Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
Where the protein is created
Role in protein production: Golgi Complex/Body
Where proteins are packaged and shipped to their destination
What is the structure of proteins
sequence of amino acids that form a polypeptide chain
What are the monomer units of proteins?
amino acids
What is transcription and translation?
Transcription is DNA to RNA, translation is RNA to protein
Where does RNA polymerase bind to the DNA
promoter region
What is the function of RNA polymerase?
brings complementary RNA nucleotides together and binds them together into a chain that makes mRNA from DNA during transcription.
What are the steps of transcription
RNA polymerase binds to DNA and creates mRNA, when the transcript it complete the mRNA leaves the nucleus
What are the steps of translation?
1) mRNA leaves _ _ _ _ _ _ _and enters _ _ _ _ _ _
2)mRNA binds with _ _ _ _ _ _ _
3)tRNA with _ _ _aa attached binds to the _ _ _ _codon _ _ _and enters at the _ site of the ribosome
4) next tRNA with aa binds to mRNA _ _ _ _ _ at the _ site
5) Bond between _ _ _ _ and MET aa is _ _ _ _ _ _
6) A _ _ _ _ _ _ _ bond is formed between _ _ _ and the following _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
1)The mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters the cytosol.
2. mRNA binds to the ribosome
3. The tRNA with the methionine (MET) amino acid attached, binds to the mRNA codon AUG, at the "P site"
4. tRNA with the next amino acid attached binds to the mRNA codon at the "A site"
5. The bond between the tRNA and MET amino acid is broken
6. A peptide bond is formed between the MET and second amino acids.
7)The transfer RNAs and the mRNA all move over one space on the ribosome = _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
8) free tRNA now moves to the _ site of the ribosome
9) the following tRNA has _ _ _ aa and is in the _ site leaving the _ site open
10)tRNA with _ _ _ _ _ aa is brought to _ site and free tRNA is released from _ site
11) This cycle continues until _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ , releasing the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ chain and the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ breaks apart releasing the _ _ _ _
7. The transfer RNAs and the mRNA all move over one space on the ribosome = translocation.
8. Now the "free tRNA", which used to hold the MET amino acid,is now in the "E site"
9. The tRNA with two amino acids is in the "P site" and the "Asite" is open
10. The next tRNA with the 3rd amino acid is brought into the "Asite"11. The "free tRNA" is released from the "E site"
11. Translation continues until a stop codon is reached, no tRNAbinds to the stop codon, instead the polypeptide chain isreleased and the ribosome breaks apart, releasing the mRNA
codons and amino acids
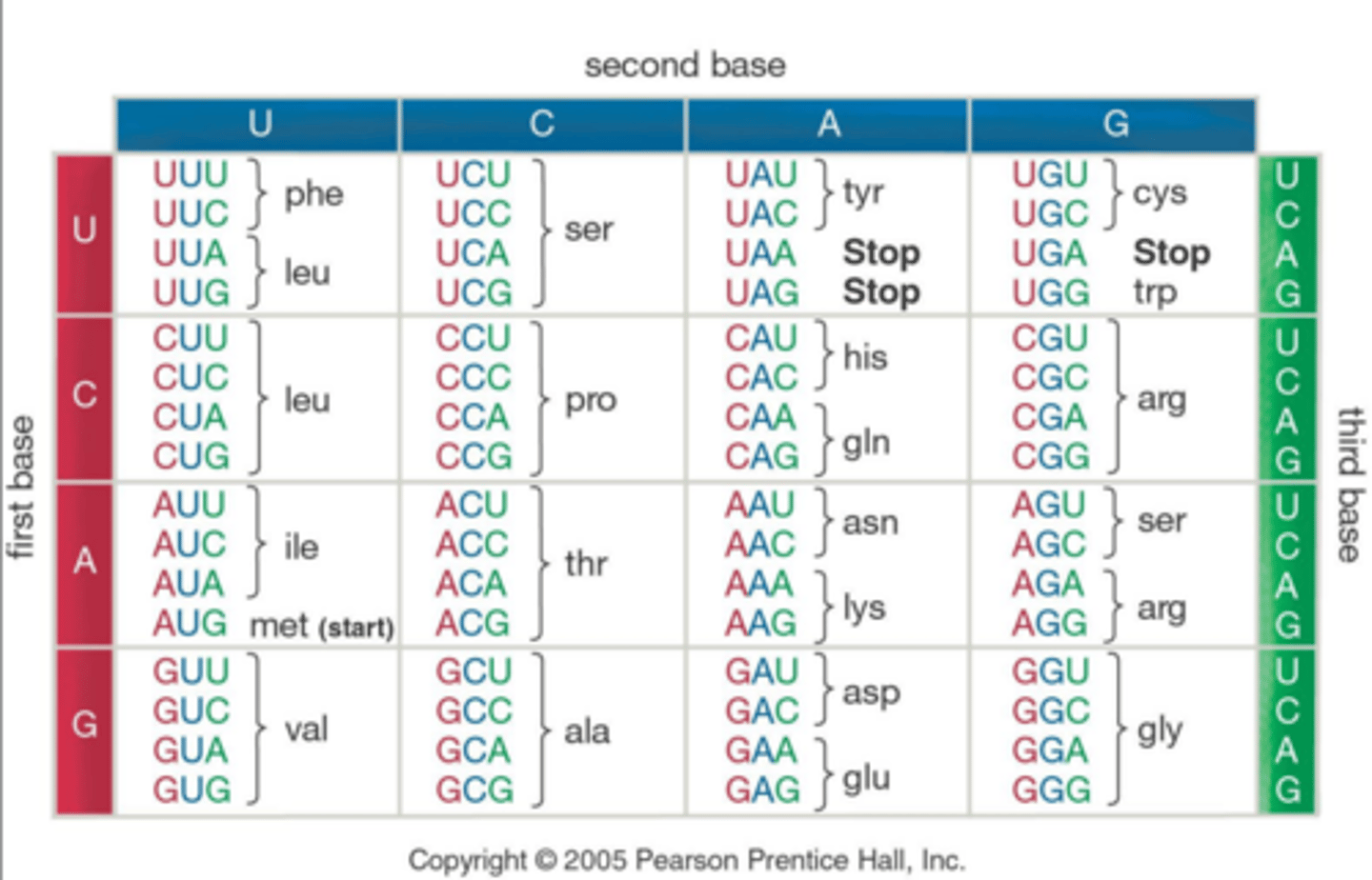
Types of RNA
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
RNA molecule that carries copies of instructions for the assembly of amino acids into proteins from DNA to the rest of the cell
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
An RNA molecule that functions as an interpreter between nucleic acid and protein language by picking up specific amino acids and recognizing the appropriate codons in the mRNA
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
enzymatic portion of the ribosome
DNA polymerase
An enzyme that catalyzes the formation of the DNA molecule.
catalyze means
to speed up
RNA polymerase
enzyme that links together the growing chain of RNA nucleotides during transcription using a DNA strand as a template
Helicase
Enzyme responsible for unwinding DNA during replication
semiconservative replication
Method of DNA replication in which parental strands separate, act as templates, and produce molecules of DNA with one parental DNA strand and one new DNA strand
complimentary base pairing
hydrogen bonding between particular bases
point mutation
gene mutation in which a single base pair in DNA has been changed
Mutagens
physical and chemical agents that interact with DNA to cause mutations
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
promotor region
portion of a gene that signals for RNA polymerase to start transcription
polypeptide chain,
chain of amino acids
peptide bond
Bonds that connect amino acids.
Translocation
The process in which a segment of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome.
transcription,
synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template
Translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
Codon
group of three nucleotide bases that = 1 amino acid
Anticodon
three base sequence on tRNA that is complementarity to the codon of mRNA
Intron
sequence of DNA that is not involved in coding for a protein
exon
expressed sequence of DNA; codes for a protein