SCIENCE - Chapter 2: Climate
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
study of atmosphere and atmosphere phenoma including weather and climate
Meteorology
expert or student of meteorology or a weather forecaster
uses scientific principles to observe, explain and forecast our weather
Meteorologist
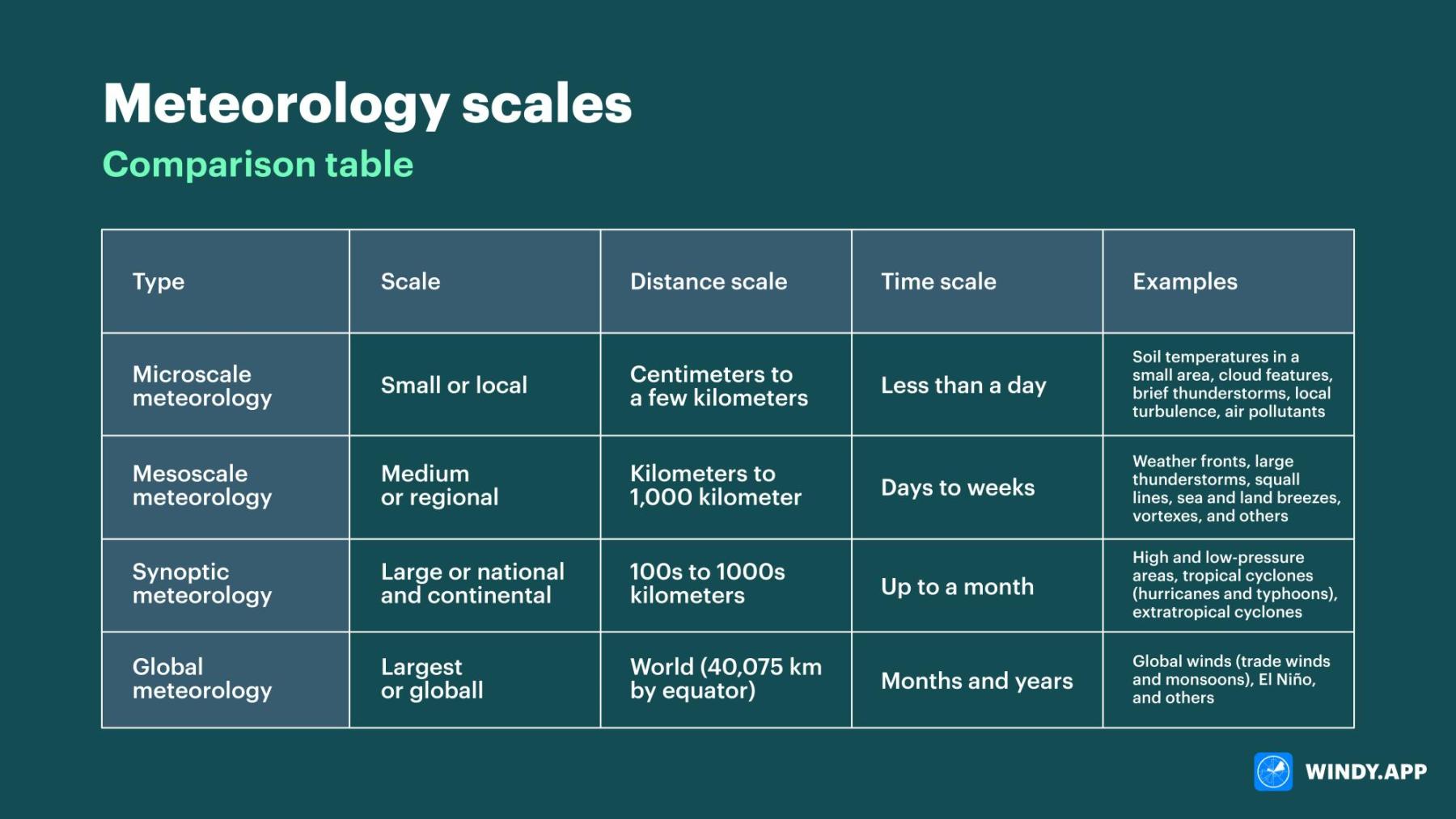
4 Metorological Scales
Microscale
Mesoscale
Synoptic Scale
Global Scale
short-lived atmosphere phenomena >1km
short life spans (less than a day)
study the processes that occur between sol, vegetation, surface water
small or local
Example:
Features of Clouds
Tornado
Microscale Meteorology
studies phenomena like thunderstorms, windstorms, land and sea breeze
range size from a few km to roughly 1000 km
medium or regional
Example:
Large thunderstorms
weather fronts
Mesoscale Meteorology
Large or national and continental
large scale or cyclonic scale
high and low pressure systems on local weather forecasts
100s to 1000s km
up to a month
Ex:
High and low pressure areas
Tropical Cyclones (Hurricanes and Typhoons)
Extratropical Cyclones
Synoptic Meteorology
Largest or global
weather patterns related to the transport of heat wind and moisture from the tropics to the poles
40,075 km by equator
months and years
Ex:
Global Winds
Trade winds and monsoons
El Nino and El Nina
Westerlies
Global Scale Meteorology
4 Meteorological Scales
____________ and __________ describes the condition of the atmosphere
Weather and Climate
short term condition of the atmosphere
mostly happens in the troposphere
Weather
average weather of an area over a long period of time
long term average condition of atmosphere of a location
Climate
Factors Affecting the Weather
Temperature
Humidity
Precipitation
Wind Speed
Scientific Study of Climate
Climatology
Factors Affecting Climate
Latitude
Altitude
Distance form the ocean
Topography
Ocean Currents
imaginary lines
east-west location/direction across earth
Latitude
5 lines of latitude
Arctic Circle (66.5 N)
Tropic of Cancer (23.5 N)
Equator (0 degrees)
Tropic of Capricorn (23.5 S)
Antarctic Circle (66.5 S)
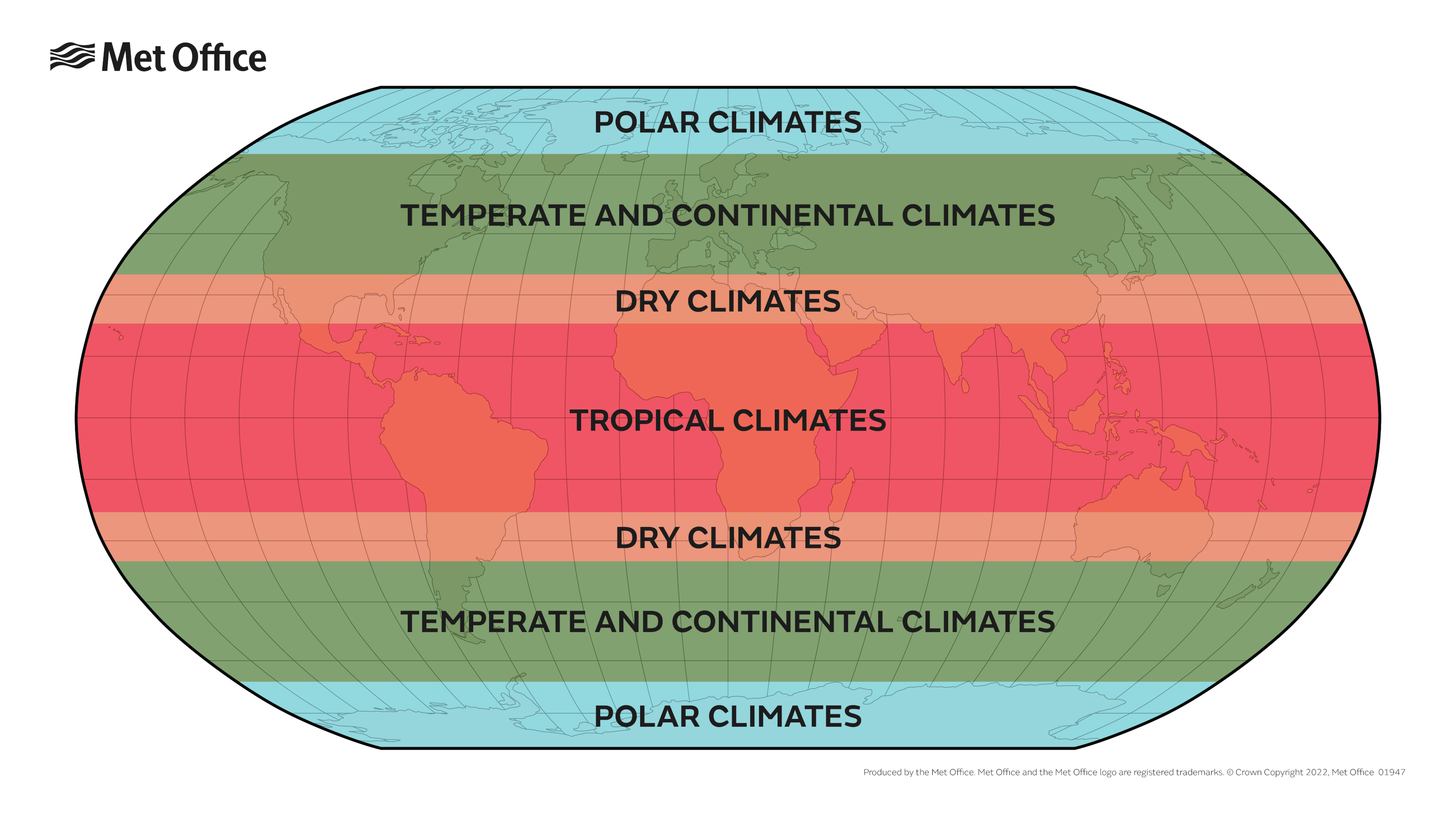
Different parts of the earth receive different amounts of solar radiation because earth is tilted on its axis
Climate Zones
height of an area above sea level
as altitude increases, temp increases
temp decreases 6.5 Celsius for every 1 km increase in altitude
Altitude
Elevation: 1500 KM
Annual Average temp: 16 Celsius
Baguio
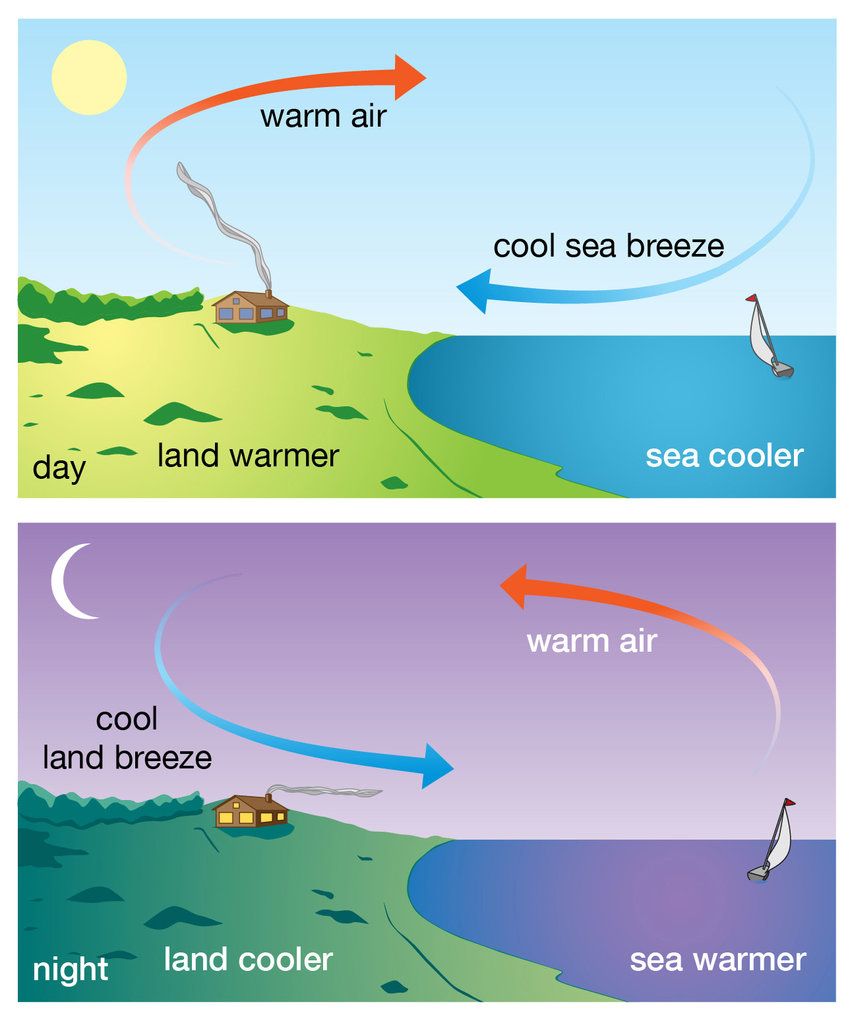
when the sun’s heat reaches earth, it heats up both bodies of land and water
areas nearby bodies of water have more moderate climate ranges and higher average precipitation
Distance from the Ocean
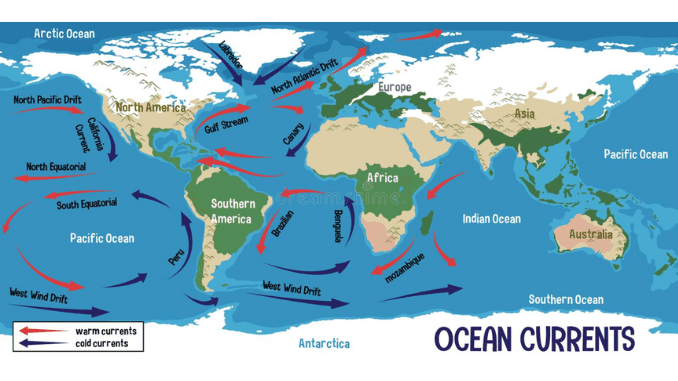
the rotation of the earth is west to east
Northern Hemisphere - clockwise
Southern Hemisphere - Counter Clockwise
Rotation is affected by the rotation of the earth in its axis
ocean currents that flow away from the equator carry warm water
air above warm water has high temp also
Ocean Currents
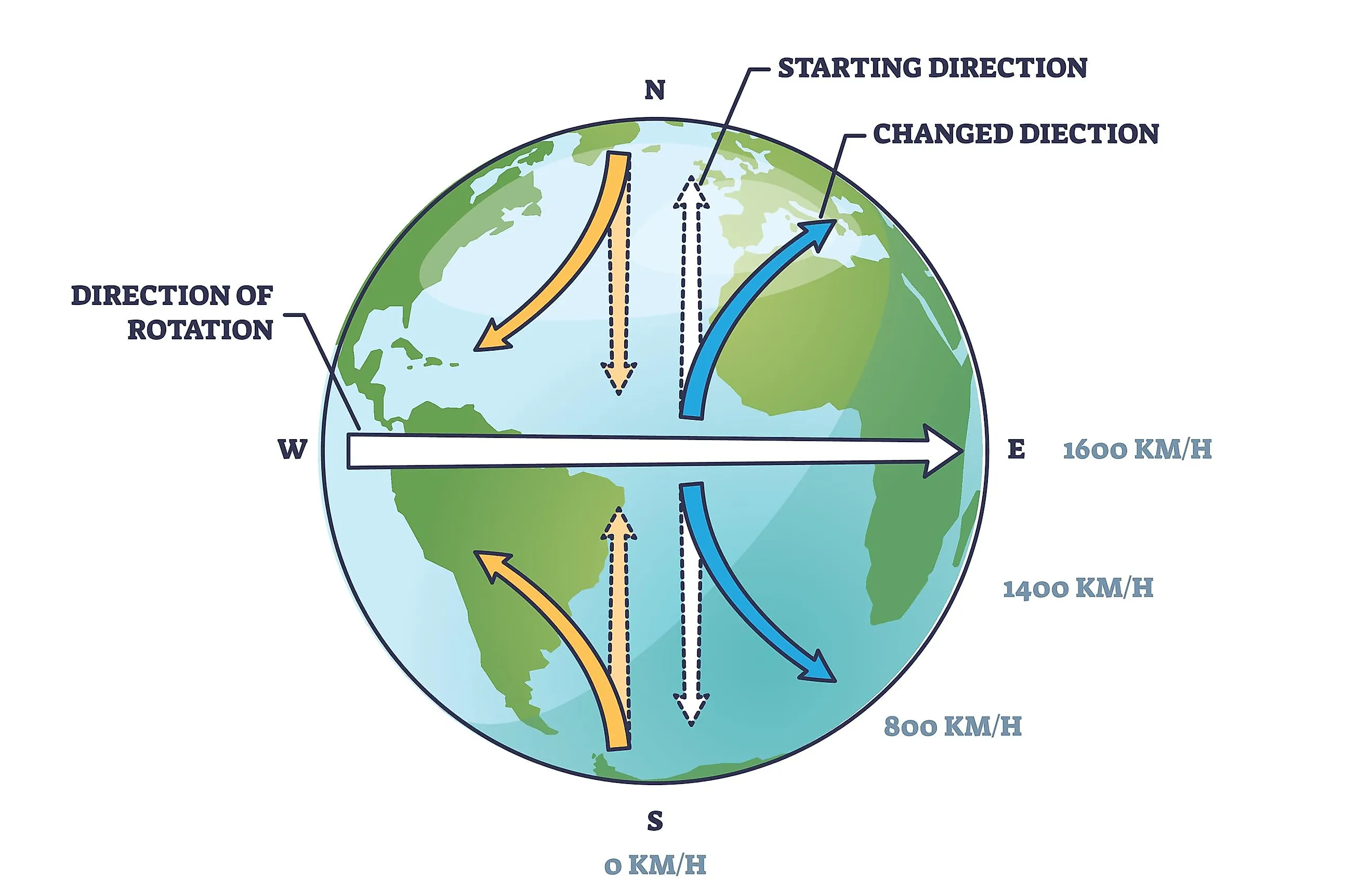
apparent deflection of objects moving in a straight path relativ to the earths surface
Named by French mathematician Gaspard Gustave de Coriolis
Coriolis Effect (Part of Ocean Currents)
contains greenhouse gases that are found in the atmosphere such as CO2 (Carbon Dioxide), CH4 (Methane), H2O (Water Vapour)
solar energy is reflected back to space and some are trapped
warming of the earth because of trapped greenhouse gases
Greenhouse Effect
keep our planet warm and is essential for life
absorbs energy by trapping it in the atmosphere
too much may cause global warming
higher greenhouse gases, more radiation is absorbed which causes a rise in the temp of the earth
Greenhouse Gases
Earths temp will be -18 Celsius if theres no greenhouse effect
No Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse Gas Emissions in the PH
55% Energy
29% Agriculture
9% Waste
7% Industrial Processes
Major Causes of Greenhouse Effect
Burning
Deforestation
Landfill
Farming
Transportation
scientists capture atmospheric carbon dioxide and store it underground
Carbon Sequestration
Top 10 Countries that emit the most CO2
China
USA
India
Russia
Japan
Iran
Germany
Saudi Arabia
South Korea
Indonesia
196 Parties/countries attended
Dec 12 2015
Goal is to hold the increasing of the global ave. temp to well below 2 Celsius above pre-industrial levels and pursue efforts the limit the temp increase to 15 Celsius above pre-industrial lvls
Paris Agreement 2015
rise of the temp on earth
increase of magnitude of the greenhouse effect
leads to a rapid change in climate (climate change)
Global warming
change in the ave. temp and cycles of weather over a long period of time
since 1880 (industrialization), scientists have kept thermometer based records of the global surface temp
the planet is becoming warmer the climate is changing
Climate Change
mitigation, adaptation, future risks
policy makers
IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change)
What causes climate change
fossil fuels (burning) - generating energy
deforestation
reduction of biodiversity (unstable ecosystem)
Climate change is damaging environments across our planets:
extreme weather
sea level rise
melting of ice caps and sea ice
warming ocean temp
Factors affected
food farming
communities
animals
plants
ocean life
habitat
Ways to prevent climate change
grow own food
meat free days at school and home
reduce amt of electricity used at schools and home
tree planting activity
supreme decision making body of the convention
review national communications and emmision inventories submitted by parties
the countries who have contributed the least to the climate crisis are the ones who are affected the most
COP (Conference of the Parties)
patterns in the pacific ocean
El Nino and La Nina
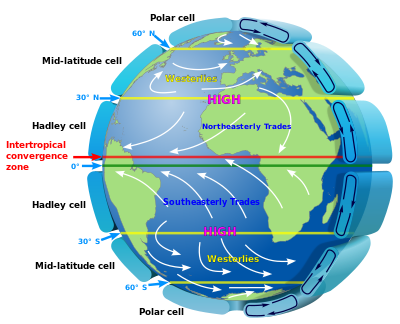
moves from east to west along the equator
Trade Winds (Easterly Winds)
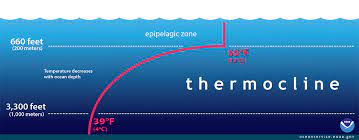
transition layer between warmer mixed water at ocean surface and cooler deep water below
upwelling of colder water is blocked by the large quantities of warm surface water in WPO
Cold water is rich in nutrients
Thermocline
climate phenomena on earth due to its ability to change the global atmospheric circulation, which in turn, influences temp and precipitation across the globe
ENSO (El Nino Southern Oscillation)
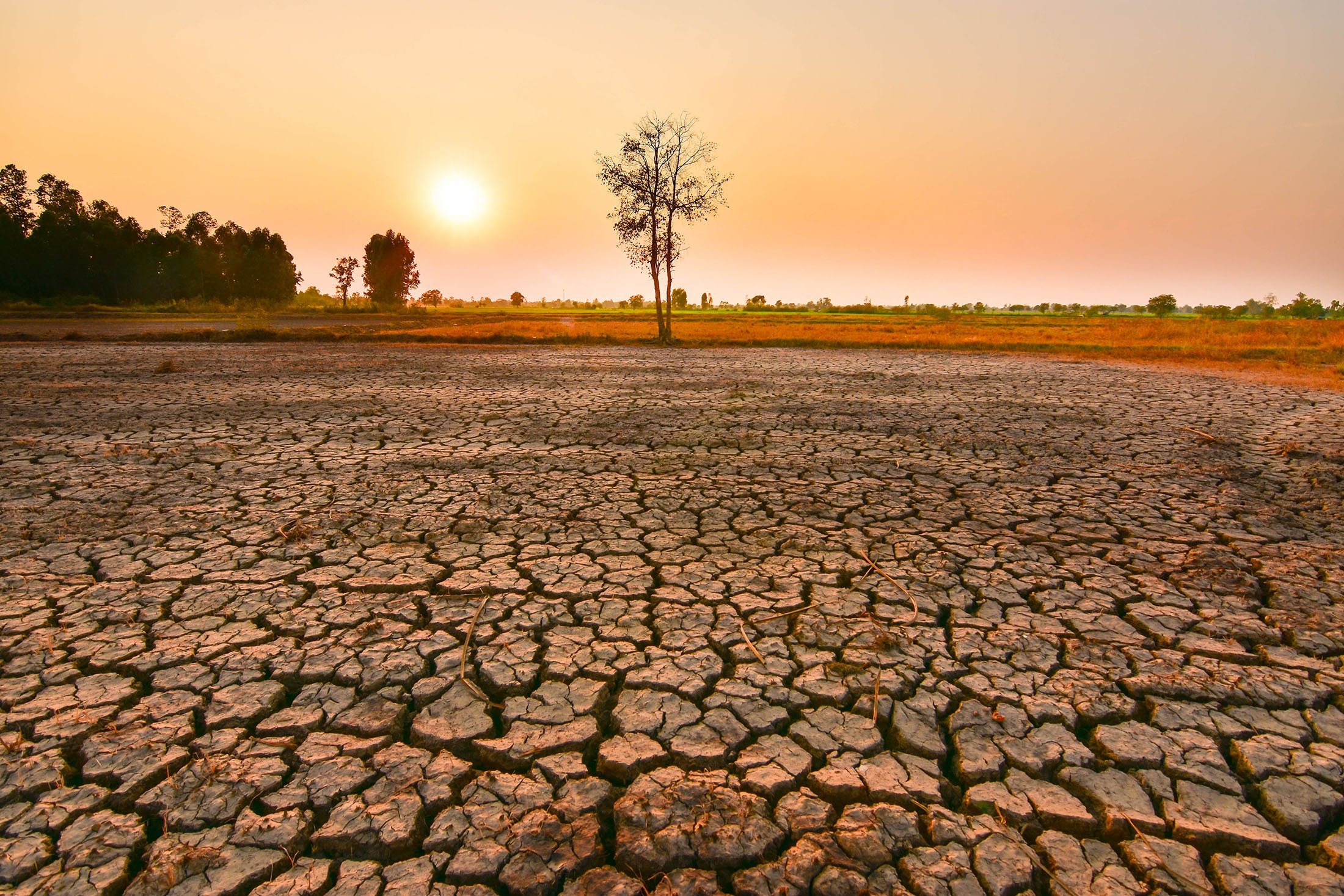

occurs during the xmas season (dec to feb)
trade winds that move from East to West are weakened
climate pattern that describes the unusual warming of surface waters in the Eastern Pacific Ocean
El Nino
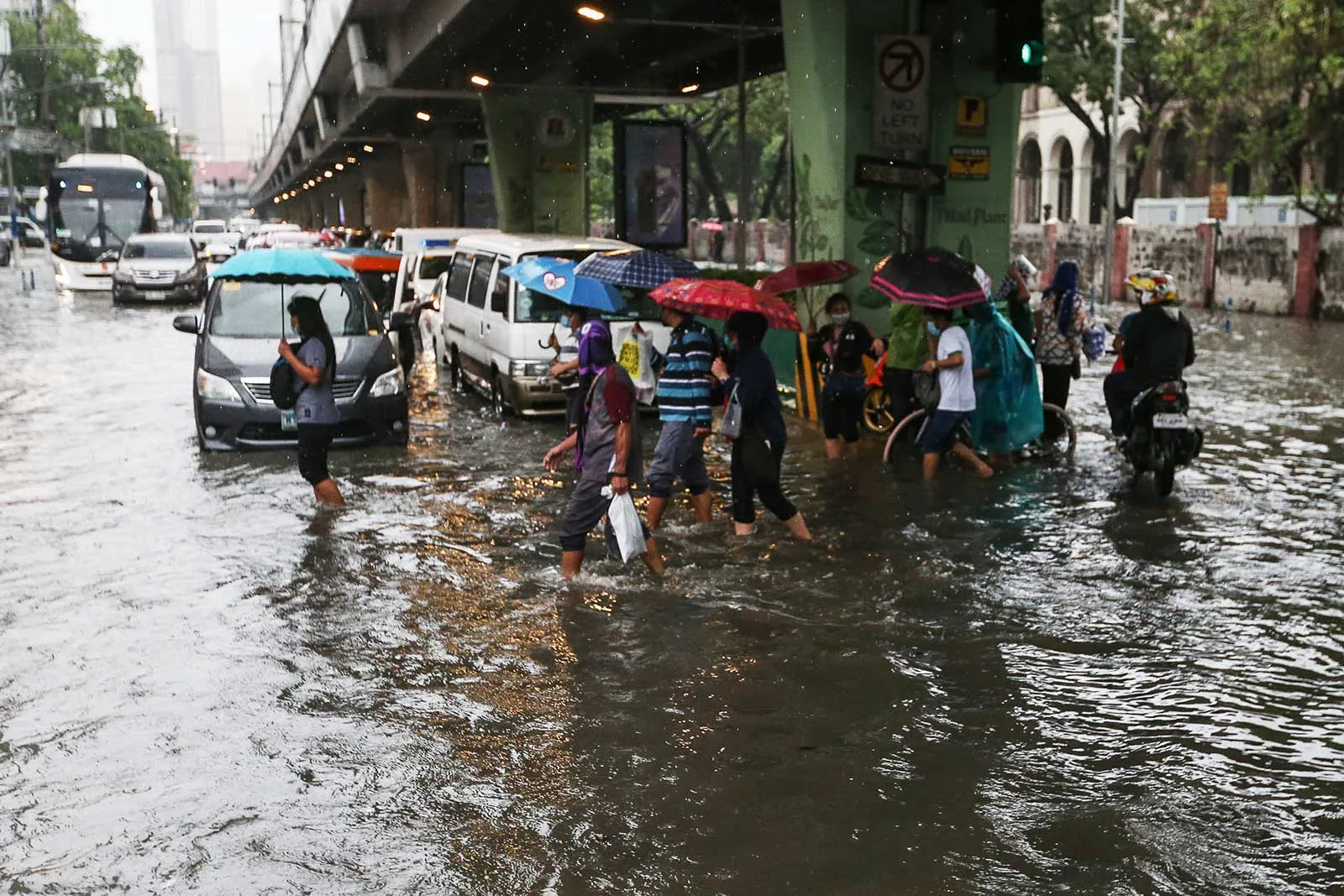

unusual heavy rainfall and low temp
trade winds that move from E to W are strengthened
triggered by the cooling of the eastern part of the pacific ocean
La Nina
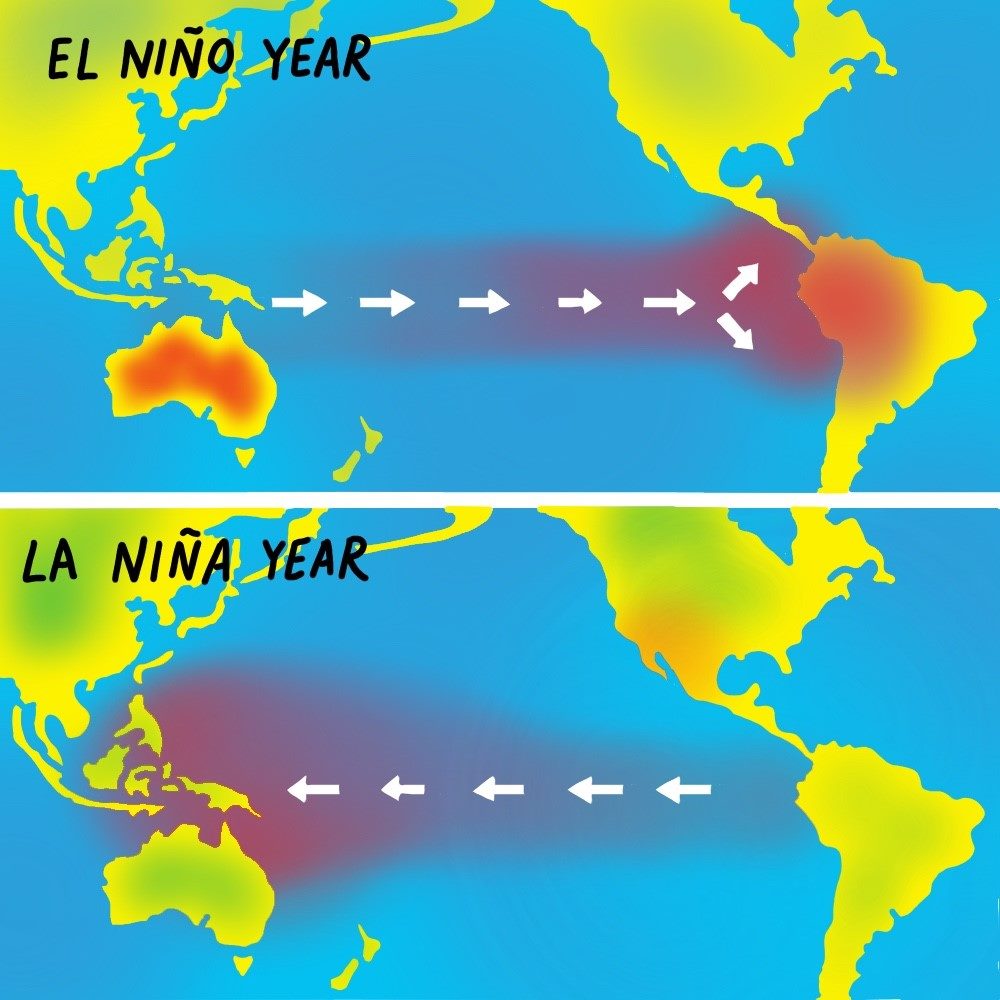
Difference of La Nina and El Nino
La Nina
heavy rainfall
water contaminated
dengue, leptospirosis
and malaria
El Nino
little rainfall
heat cramps, heat exhaustion, heat stroke