Inflation
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Consumer Price Level (CPI)
a measure of the cost of living during a particular period
measures:
the cost of a standard basket of goods and services in a given year
relative to the cost of the same basket of goods and services in the base year
base year changes periodically
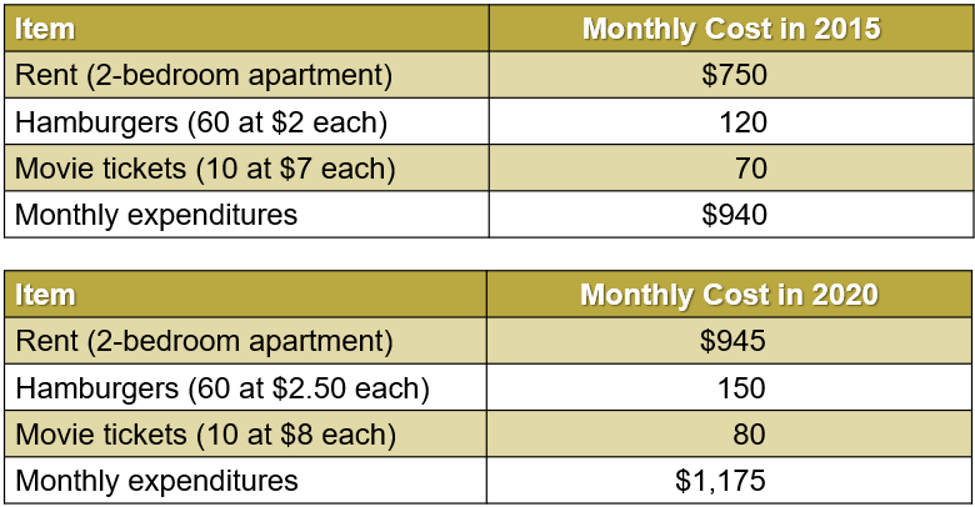
Calculating CPI
CPI = 1375/1060 = 1.30
Price Index
measures the average price of a given quantity of goods and services relative to the price of the same goods and services in a base year
Inflation
measures how fast the average price level is changing over time
Rate of Inflation
the annual percentage rate of change in the price level (as measured, for example, by the CPI)
Deflation
a situation in which most goods or services are falling over time, so that inflation is negative
Expressing a Nominal Quantity in Real Terms
divide it by its price index
Real Wages
the wage paid to the worker measured in terms of purchasing power
for any given period is calculated by dividing the nominal wage by the CPI for that period
Indexing
increases a nominal quantity each period by the percentage increase in a specified price index
prevents the purchasing power of the nominal quantity from being eroded by inflation
automatically adjusts certain values, such as Social Security payments, by the amount of inflation
if prices increase 3% in a given year, the Social Security recipients receive 3% more
no action by Congress required
sometimes included in labour contracts
Minimum Wage
congress sets it in nominal terms
Publicised debate results in periodic increases
Indexing would be simpler and less controversial
Politicians appear to benefit from the debate
Increasing minimum wage can contribute to inflation
Companies pass on their increased labour costs to consumers in the form of higher prices
Tight Labour Market
a situation where there is a low level of unemployment and a high level of job vacancies, which means that there are many job opportunities and relatively few workers to fill them in
employers have to compete for workers, which can push up wages and salaries
What can a Tight Labour Market Lead to?
increase in labour costs can be passed onto consumers in the form of higher prices for goods and services leading to inflation
increased consumer spending as workers have more disposable income
this increased demand can put upwards pressure on prices, leading to inflation
What is a Tight Labour Market a Sign of?
a strong economy, but if left unchecked can also lead to higher inflation and potential wage-inflationary spirals
Why is it a Concern that CPI may Overstate Inflation?
can lead to unnecessarily increased government spending, higher debt repayments on inflation-indexed government bonds, higher public wages due to indexation, higher benefits
Why might CPI Overstate the Cost of Living?
it’s based on a fixed basket of goods and services, which doesn’t reflect substitution or changes in consumption
What Limitation does CPI have in Terms of Product Quality?
doesn’t fully account for changes in quality over time
CPI Quality Adjustment Bias
its measurement of price changes but not quality changes
adjusting for quality is difficult
large number of goods
subjective differences
incorporating new goods is difficult
no base price for this year’s new goods
CPI Substitution Bias
Uses a fixed basket of goods and services
When the price of a good increases, consumers buy less and substitute other goods
Failing to account for substitution overstates inflation and CPI
What does the GDP Price Deflator Measure?
changes in prices for all goods and services produced in an economy
Why is GDP Price Deflator Different from the CPI?
it’s more comprehensive because it isn’t based on a fixed basket of goods
How does the GDP Price Deflator Correct for Inflation in GDP?
by using a base year and comparing current prices to that base year
How can Inflation Distort Perceptions of Economic Growth?
it can make an economy appear to grow in dollar terms even if real output hasn’t increased
GDP Price Deflator Formula
(Nominal GDP/Real GDP) x 100
captures how much of the nominal GDP increase is due to price changes (inflation/deflation) vs how much is due to actual increases in the quantity of goods and services produced
Price Level
a measure of the overall level of prices at a particular point inn time as measured by a price index such as the CPI
Relative Price
The price of a specific good/service in comparison to the prices of other goods and services
Can change markedly without corresponding changes in inflation
Inflation distorts relative prices
Consumer decisions are distorted, and markets are less able to allocate resources to their best use
What does an Increasing Relative Price do?
encourages consumers to save money on expensive products and search for their substitutes, while companies try to bring more products to the market to gain profit
The Costs of Inflation
Changes in relative price don’t necessarily imply a significant amount of inflation
Inflation can be high without affecting relative prices
To counteract relative price changes, government policy would have to affect the market for specific goods
To counteract inflation, the government must use monetary and fiscal policy
Distortion Caused by Taxes
Taxes that aren’t indexed distort the tax incentives for people to work, save and invest
Lower savings and investment means lower economic growth - a real cost of inflation
The income tax treats the nominal interest earned on savings as income, even though part of the nominal interest rate merely compensates for inflation
The after-tax real interest rate falls, making saving less attractive
Bracket Creep
inflation can push individuals into higher tax brackets even if their real income hasn’t increased
What Happens when Inflation Increases the Cost of Cash?
Manage cash balances to limit losses
More frequent, smaller withdrawals cost consumers and businesses time, travel - a real cost of inflation
Banks process more transactions, increasing costs - another real cost of inflation
Costs of Managing Cash
called ‘shoe-leather’ costs, referring to the cost of frequent trips to the bank
Unexpected Redistribution of Wealth
caused by unexpected inflation which confuses incentives
What happens if Workers Salaries aren’t Indexed and Inflation is Higher than Anticipated?
salaries lose purchasing power
employers gain at the expense of workers
How does Unexpectedly High Inflation benefit Borrowers at the Expense of Lenders?
they repay with dollars worth less than anticipated
Menu Costs
Costs of adjusting prices
During inflation times, it’s necessary to update price lists and other posted prices
This is a resource-consuming process that takes away from other productive activities
Prices are sticky and adjust with a delay; don't always move in line with changing economic conditions and outside market forces
What does Higher Interest Rates mean for Households and Firms
they spend more on interest debt payments, leaving them with less money to spend on anything else
When given a Nominal Interest Rate, the Higher the Inflation Rate…
the lower the real inflation rate
Real Interest Rate
the annual percentage increase in the purchasing power of financial assets
Nominal Interest Rate
the annual percentage increase in the dollar value of an asset
most commonly stated rates
Inflation-Protected Bonds
pay a real rate of interest plus the inflation rate
The Fisher Effect
the tendency for nominal interest rates to be high when inflation is high and low when inflation is low
The Fisher Equation
Real interest rate = nominal interest rate - inflation
R = i - 𝜋
What Happens when the Government Increases Spending?
it increases demand for goods and services, which can lead to higher prices (demand-pull inflation)
What is Demand-Pull Inflation?
inflation caused when demand exceeds the supply of goods and services, leading to price increases
How can the Government Finance its Spending?
through borrowing or ‘printing money’, which increases the money supply and borrowing costs
What is Monetary Inflation?
inflation resulting from an increase in the money supply, causing the value of money to decline
How do Transfer Payments like Welfare Benefits impact Inflation?
they increase demand without increasing supply, potentially leading to higher inflation
How can Government Spending Help Reduce Inflationary Pressures?
by investing in infrastructure and productive activities that increase the supply of goods and services
How does Inflation impact Government Budget?
can limit borrowing ability and increase the budget deficit
How does Inflation affect Government Revenue?
can reduce it and other income sources, leading to potential spending cuts or more borrowing
What Fiscal Pressure arises from Increased Welfare Payments Indexed to Inflation?
increases spending obligations, placing upward pressure on the budget unless taxes are raised
What is Stagflation?
a phenomenon in which an economy experiences both high inflation and stagnant economic growth at the same time
What Typically causes Stagflation?
supply-side shocks to the economy, such as increase in the price of oil or other important inputs, which push up prices while also reducing economic growth and increasing unemployment
Why is Stagflation difficult to address with Monetary Policy?
traditional tools like cutting interest rates are less effective because prices are already rising
How can Fiscal Policy worsen Stagflation?
increasing government spending can raise inflation further, worsening the problem
What is the challenge in reversing High Consumer Prices during Stagflation?
government must reduce demand carefully to lower inflation without triggering a recession or worsening Stagflation