Primary structure - L7
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
The primary structure is the..
linear sequence of amino acids
Formation of peptide bond
happens through a condensation reaction - H2O removed
happens between COOH group of one amino acid and Nh2 group of another amino acid
forms peptide bond
peptide group is CONH
process requires energy
amino acids in proteins are called..
amino acid residues
what are teh amino aicds on each terminal called
the amino group on one terminal is called N terminal
the carboxyl group on other terminal is called C terminal (can form another peptide bond)
Chains are usually drawn
left (N terminus) → right (C terminus)
what are Eupeptide bonds
peptide bonds formed from a carboxyl group of one amino acid and an amino group of another
Isopeptide bonds
peptide bonds formed from Carboxyl group from a side chain of an amino acids and an amine group from another amino acid side chain
why do Proteins absorb light at 190-220 nm?
due to peptide bond
Peptide bond is… (properties)
planar and rigid
little flexibility/ little rotation around the bond
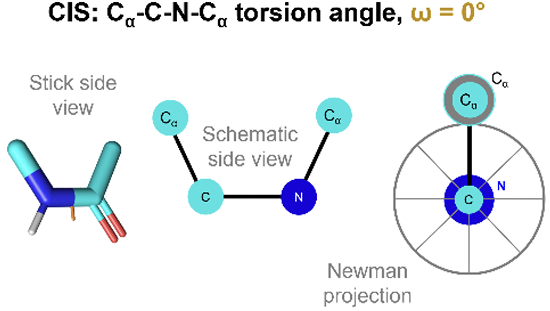
what is the cis conformation of peptide bond and what is the torsion angle
more likely found in proline residues
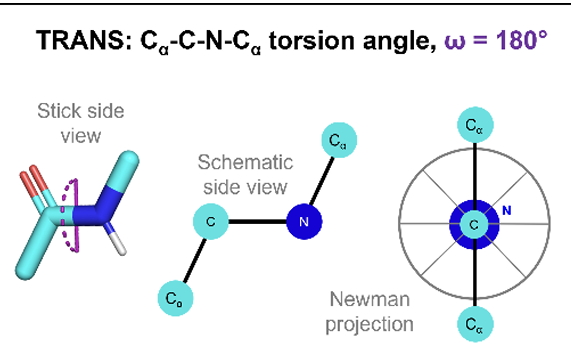
what is the trans conformation of peptide bond and what is the torsion angle
more common
Proposed proposed the α-helix and β-sheet structure of proetisn assuming ..
Peptide bond is planar
All amino acid residues are equivalent in terms of backbone conformation
each amide proton is hydrogen bonded to an oxygen atom of another residue with an N–O distance of 2.72 Å
the 3 main torsion angles in peptides..
Omega → 180, as peptide bond is rigid and planar
Pie → between alpha carbon and nitrogen, can be naything as C-N bond is a single bond
Psi → between alpha carbon and carboxyl group, can be anything as C-C bond is a single bond

as we have so many possible pie and psi bonds soes this mean we can have mu;tiple combinsations
no because only a limited number are possible due to steric hindrance (collisions or clashes between atoms)
what does a Richmand plot show?
are accessible values for pie and Psi torsion angles which are displayed
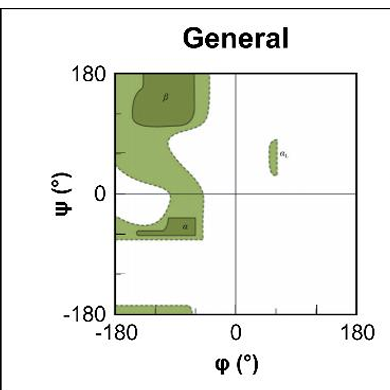
what does the white area show?
shows area where atoms come closer than the sum of there van der walls radii
this is sterically disallowed
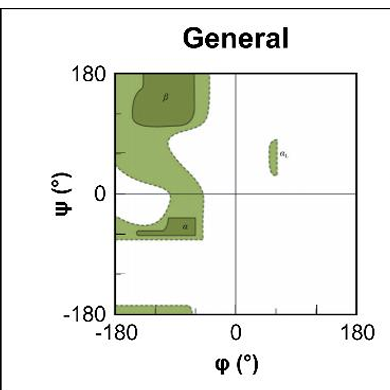
what are the dark green regions?
regions where there are no steric clashes
sterically allowed
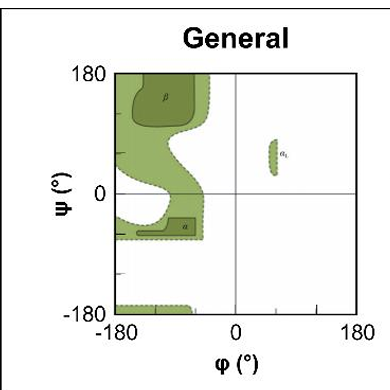
what do light green areas show ?
are regions where slightly smaller VDW radii are used, atoms are allowed to come a little close together
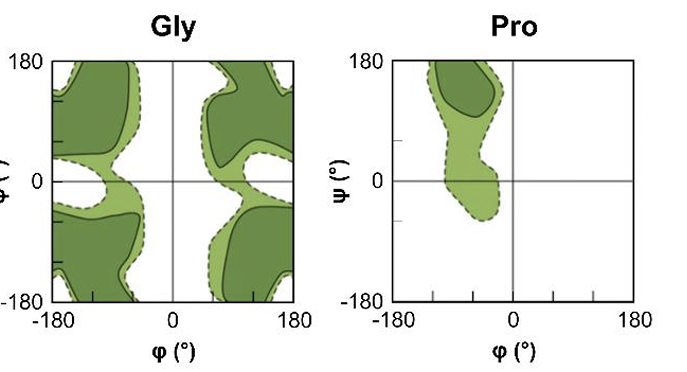
what are teh 2 amino acids that look different in their richmand plot?
Glycine → as has no side chain and so can adopt angles in all 4 quadrants
Proline → has a 5 membered ring in side chain making it more restricted in the amount of angles that can form
2 amino acids that are covalently bonded are called..
dipeptide
when a few amino acids joined together called..
oligoepetide
when have many amino acids joined together called..
polypeptide
name peptides form..
left → right
Examples of Oligonucleodtides
Aspartame → artifitial, non-carbohydrate sweetner, its a methy ester from dipeptide of aspartic acid + phenyalanine, used in soft drinks
Oxitosin → secreted by pituitary gland, induces labor, it is a cyclic nanopetpid protein
Glutathione → tripeptide where glutamic residues Y carbon contribute to peptide chain, good reducing agent and protects cells
Endophins → natural painkiller secreted by pituitary glands, interacts with receptors in brain to inhibit pain signals. e.g. B - endophin contains 31 amino acid residues
what is molecular weight given in
Dalton D
1 D = 1g/mol
how to moleuclar weight of peptid
addition of isotopic masses of all amino aids in peptide +isotopic mass of 1 water molecule
What is averadge moleular weight of a protein and 1 amino acid
protein →110 D
amino acid → 128 D
how do we c compare DNA sequences, across species and within one species?
through multiple sequence alignments (MSAs)
when amino acids are identical in 2 seuqnced
they are absolutely conserved shown by *
when the amino acids are similar
they are conserved/ invariant shown by :
when there is no similarity
not conserved
what does this tell us
so studying MSAs tells us areas that are conserved are very important to the function of that protein
helps us locate motifs (usually only small amino aicds long)
what are examples of motifs:
active sites
binding sites
post - translation modification sites
repeats (AAs that are repeated could be important for structure)
how many codons are there:
61
64 including 3 stop signals
Motifs are visualized with..
consensus sequences
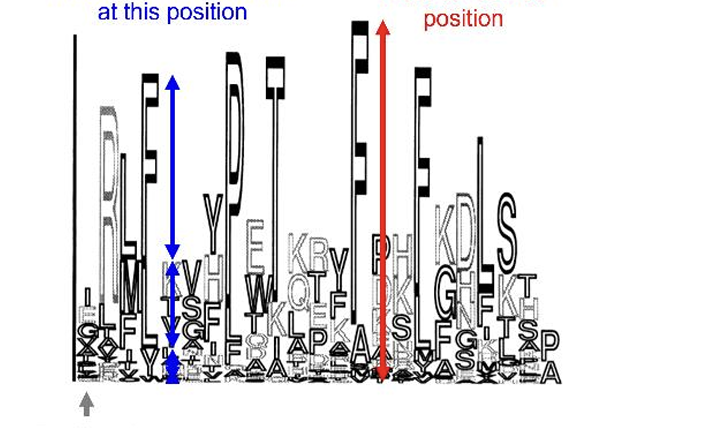
what does this show
the height indicates how conserved that position is
the height of each symbols shows how common that amino acid is
Proteins that have diverged from a common ancestral gene are known as
Homoglos
what are orthologs
homologous proteins that are the same as our ancestors do the same things, found in many species that share a common ancestor
what are paralogs
Homologous proteins with same genome, arise due to gene duplication, there function has now changed