Single Case Research Methodology: Chapter 1
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Goal of science
To advance knowledge
The process by which we advance knowledge
Research--the systematic investigation and manipulation of variables to identify associates and understand processes that occur in typical contexts
Applied Research
Systematic investigation related to the pursuit of knowledge in practical realms or to solve real world problems. Example: Seeking to identify interventions that result in improved physical activity for children with Down Syndrome.
Single Case Design
Evaluation method used to rigorously test the success of an intervention or treatment on a particular case, and to provide evidence on effectiveness from a small sample size
Independent Variables
Variables manipulated by researchers (interventions)
Dependent Variables
The variables we expect to change given the manipulation (target behaviors)
Baseline Phase
Present pattern before intervention
Intervention Phase
Occurs after a stable baseline is established. DV is measured to determine the effect the IV has on the DV
Internal Validity
Study contains adequate mechanisms for ensuring the outcomes are related to your intervention procedure rather than extraneous factors
Experimental Control
To show that the experimental procedures (intervention) and only the experience procedures are responsible for behavior change
Functional Relationship
The relationship between changes in an independent variable (intervention) and changes in a dependent variable (behavior); a cause-and-effect relationship.
Evidence Based Practice
Intervention procedures that have been scientifically verified as being effective for changing a specific behavior of interest, under given conditions, and for particular participants
What constitutes a "practice?"
A curriculum, behavioral intervention, systems change, or education approach designed to be used by families, educators,, or students with the express expectation that implementation will result in measurable, educational, social, behavioral, or physical benefit.
Reliability
Consistency of measurement; Achieved by defining the target behavior (or event) clearly and concisely so that two independent observers consistently agree on scoring what they observe.
"at the heart of the scientific method"
Replication
Threats to Internal Validity
Variables other than the planned independent variable that could result in changes in the dependent variable.
Nomothetic Research Approaches
Generally based in the natural sciences and are characterized by attempting to explain associations that can be generalized to a group given certain circumstances.
Idiographic Research Approaches
attempt to specify associations that vary based on certain characteristics or contingencies present for the participant or case of interest.
Characteristics of Group Design
Large number of individuals divided into one of two or more study conditions; Includes a control condition and treatment condition
Deductive Analysis
Hypotheses are formulated prior to conducting a study to test a theory
Inductive Analysis
Using a qualitative study approach to collect data and describe themes or trends in the data without offering a theory
Validity
Accuracy of measurement
Quality Indicators for Single Case Research
1. Description of participants and setting
2. Dependent variable
3. Independent variable
4. Baseline
5. Experimental Control/Internal Validity
6. External Validity
Baseline Logic
Participants serve as their own control
Practice-Based Evidence
Using data generated during treatment to inform the process and outcome of treatment.
Similarities Between Practitioners and Applied Researchers
1) Be able to identify and analyze problems
2) Generate creative solutions
3) Implement an intervention in a systematic manner
4) Document the effect of the intervention
5) Act on the date in an ethical and responsible way
History
Refers to events that occur during an experiment, but are not related to the planned procedural changes, that may influence the outcome
Maturation
Refers to the changes in behavior due to the passage of time
Testing
A threat in any study that requires participants to respond to the same test repeatedly , especially during the baseline or probe condition; it is the likelihood that the repeated assessment task will result in a participant behavior change;
Instrumentation
Concerns with the measurement system; They are of particular concern in SCD studies because of repeated measurement by human observers who may make errors
Procedural Infidelity
The lack of adherence to condition protocols by study implementers. If the procedures of an experimental condition (baseline, probe, intervention, maintenance, generalization) are not consistently implemented across behavior episodes, time, interventionists, etc.
Attrition
Refers to the loss of participants during the course of a study, which can limit the generality of the findings, particularly if participants with certain characteristics are likely to drop out.
Selection Bias
Choosing research participants in a way that differentially impacts the inclusion or retention of participants in a study, when compared to the population of interest
Attrition Bias
The likelihood that participant loss (attrition) impacts the outcome of a study
Sampling Bias
Occurs in SCD when researchers use additional, non-explicated, reasons for including or excluding potential participants
Multiple Treatment Interference
When a study participants' behavior is influenced by more than one planned "treatments" or interventions during the course of the study.
Sequential Confounding
The order in which experimental conditions are introduced to participants may influence their behavior
Instability
The amount of variability in data
Cyclical Variability
A specific type of data instability that refers to a repeated and predictable pattern in the data series over time.
Regression to the Mean
Likelihood that following an outlying data point, data are likely to revert back to levels closer to the average value
Adaptation
A period of time at the start of an investigation in which participants' recorded behavior may differ from their natural behavior due to the novel conditions under which data are collected
Hawthorne Effect
Participants' observed behavior not being representative of their natural behavior as a result of their knowledge that they are participants in an experiment
Main Types of Single Subject Designs
1. Reversal Design
2. Multiple Baseline Design
3. Multielement Design
4. Changing Criterion Design
AB Design
One baseline (A) followed by one treatment (B)
Reversal Design
ABA - baseline, treatment, baseline;
ABAB- baseline, treatment, baseline, treatment
Advantages: Simple, yet powerful example of experimental control
Disadvantages: Consider ethics--is it appropriate to discontinue treatment? Irreversibility--behavior may not return to baseline (confounding variable is always the first assumption for irreversibility
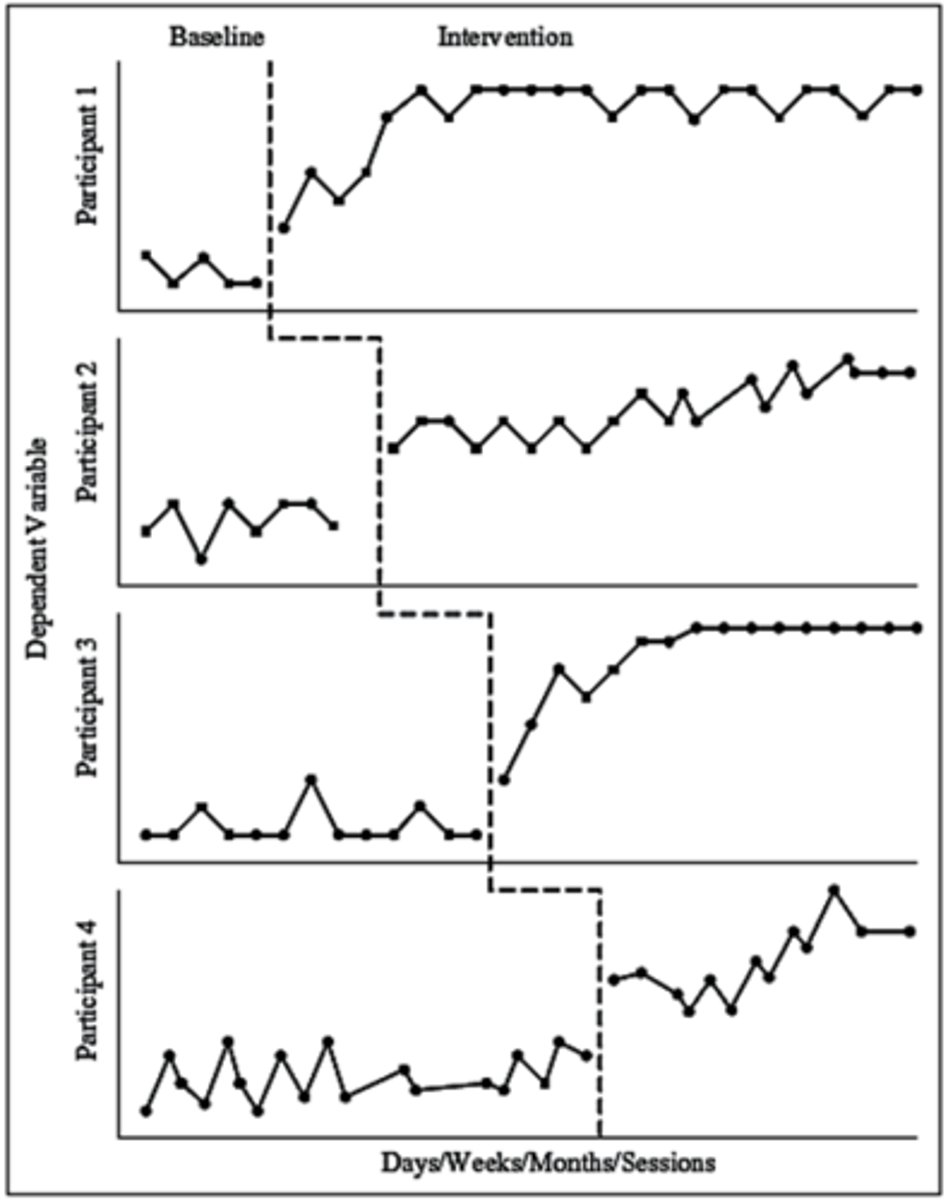
Mutliple Baseline Design
Sequential introduction of IV across baselines; Baseline increases across subjects, settings, or behaviors
Which is a reversal design?
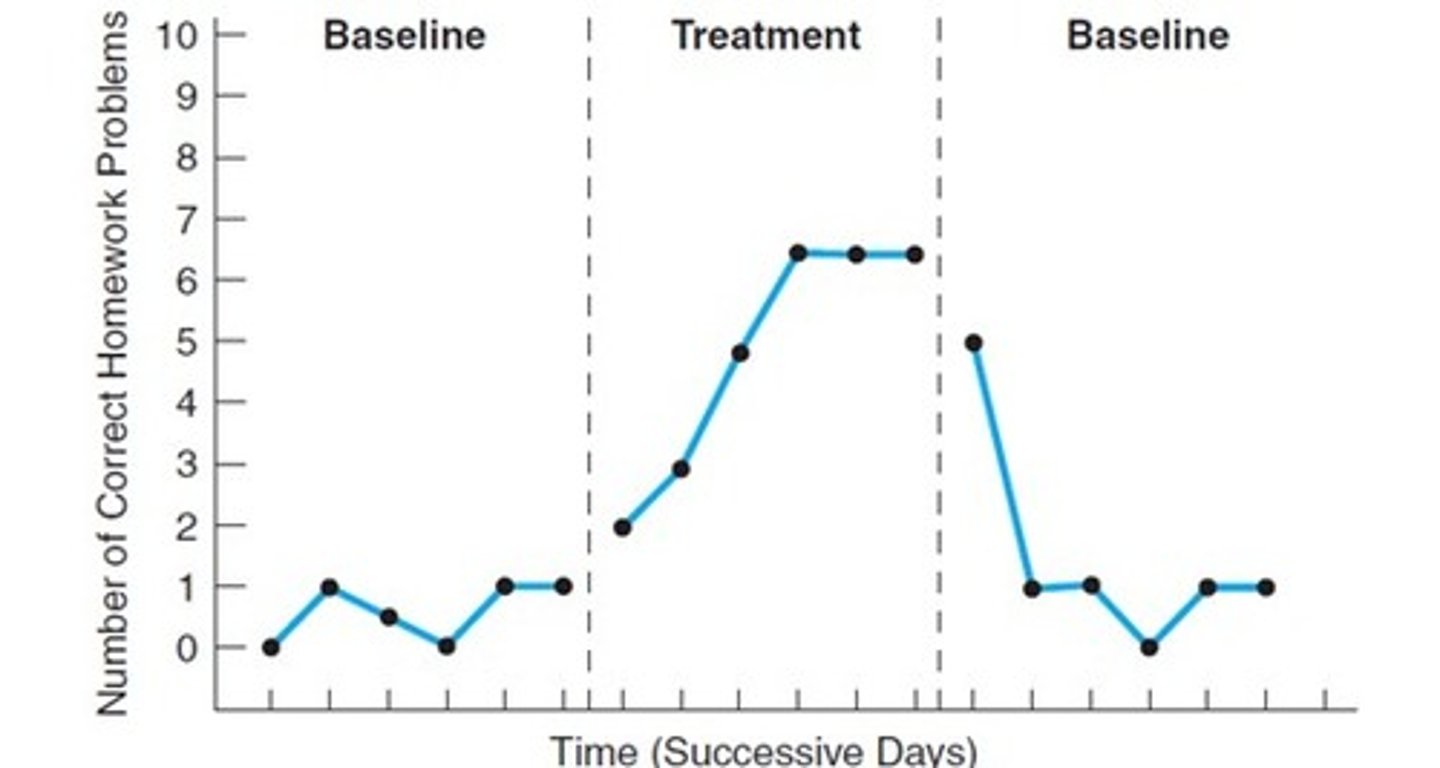
Which is a Changing Criterion Design?
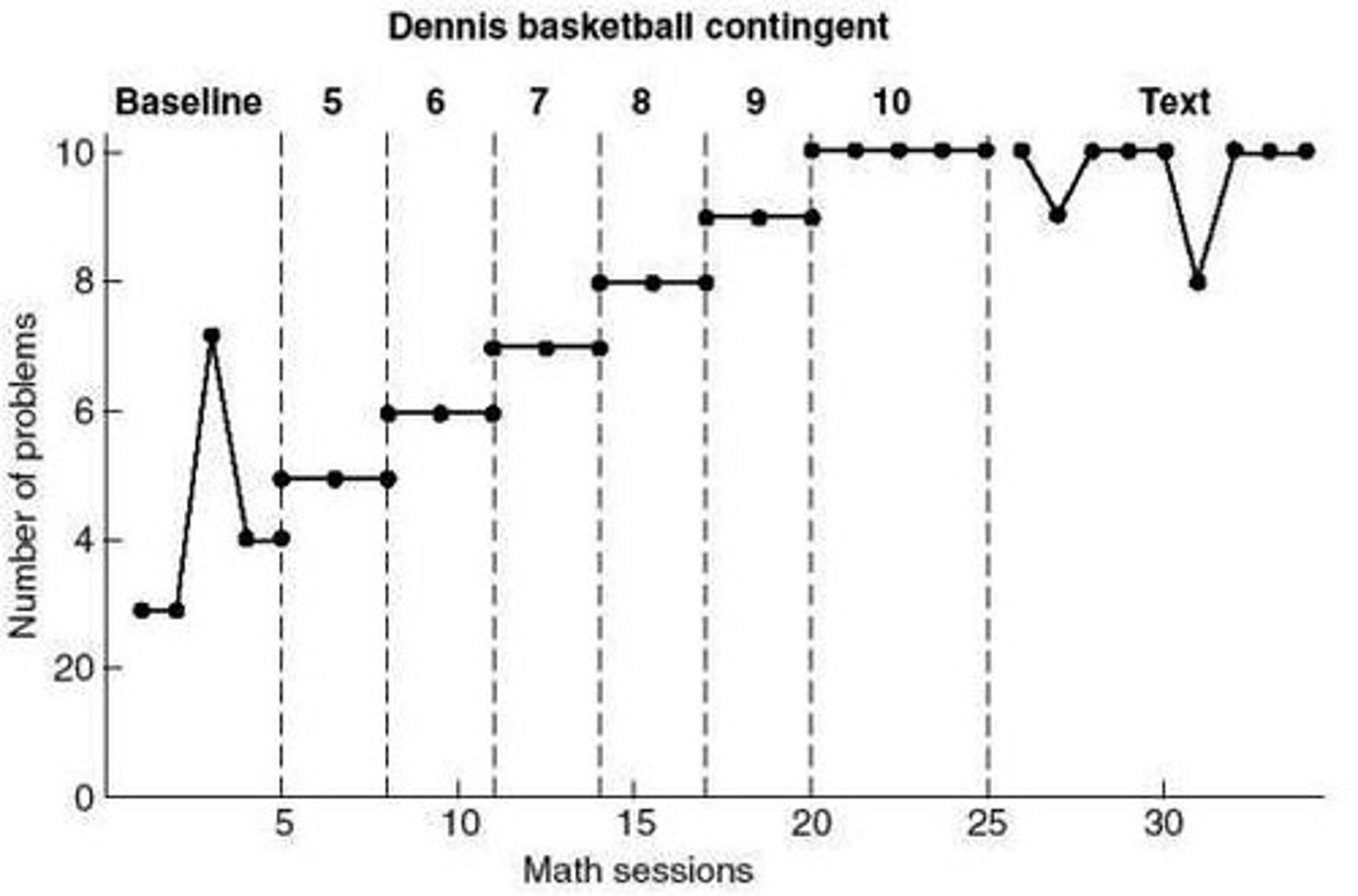
Which is a Multielement Design?
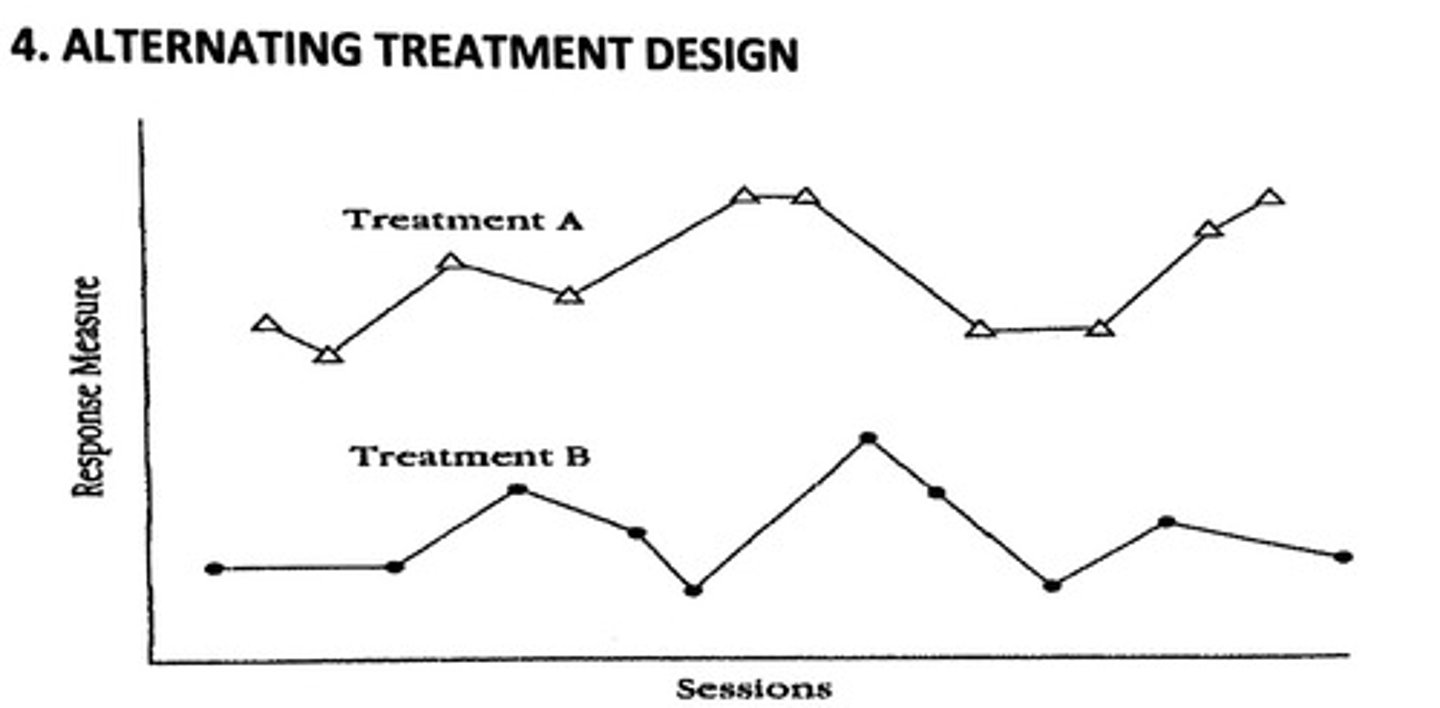
Which is a Multiple Baseline Design?