Principles of Biology II - Bio 1108K Exam 2
1/139
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
What is the taxon name of this organism?
Anthophyta phylum (angiosperms/flowering plants: flower and fruit)

What is the taxon name of this organism?
Bryophyta phylum (Mosses)

What is the taxon name of this organism?
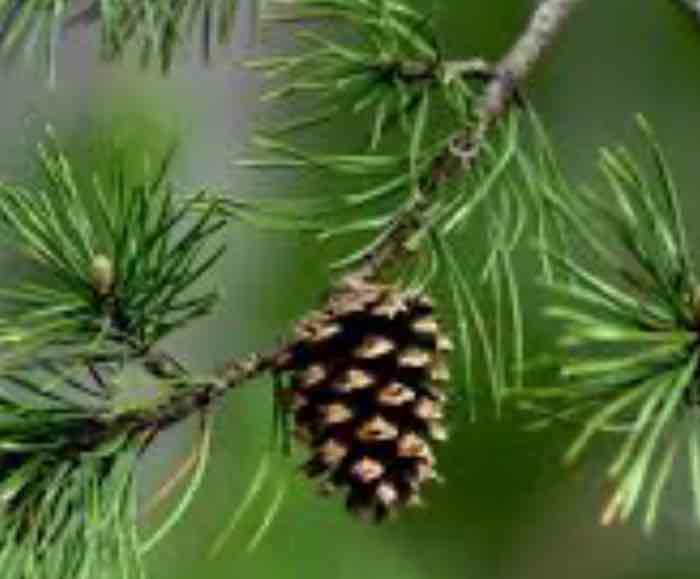
Coniferophyta phylum

What is the taxon name of this organism?
Cycadophyta phylum (Cycads)

What is the taxon name of this organism?
Ginkgophyta phylum (Ginkgo)
What is the taxon name of this organism?
Hepatophyta phylum (Liverworts)

What is the taxon name of this organism?
Ascomycota phylum (sac fungi)

What is the taxon name of this organism?
Basidiomycota phylum


What is the taxon name of this organism?
Mucoromycota phylum
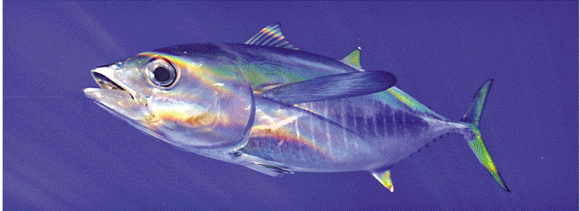
What is the taxon name of this organism?
Actinopterygii (Ray-finned fishes)


What is the taxon name of this organism?
Amphibia

What is the taxon name of this organism?
Annelida (earthworm or leech)

What is the taxon name of this organism?
Arachnida


What is the taxon name of this organism?
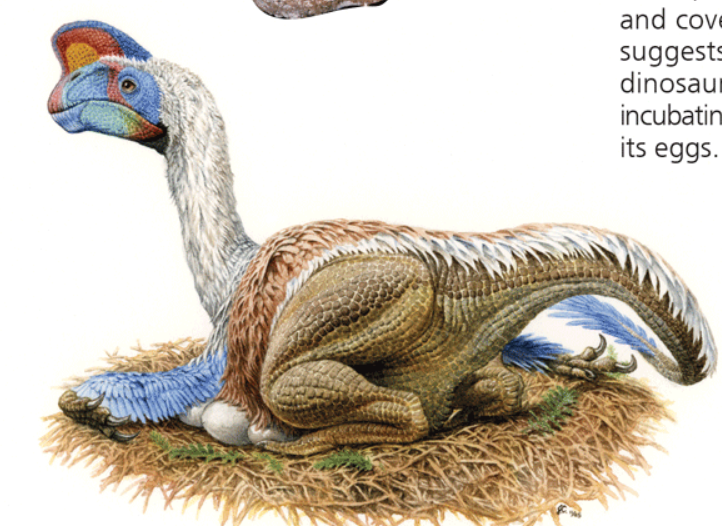
Aves (birds)


What is the taxon name of this organism?
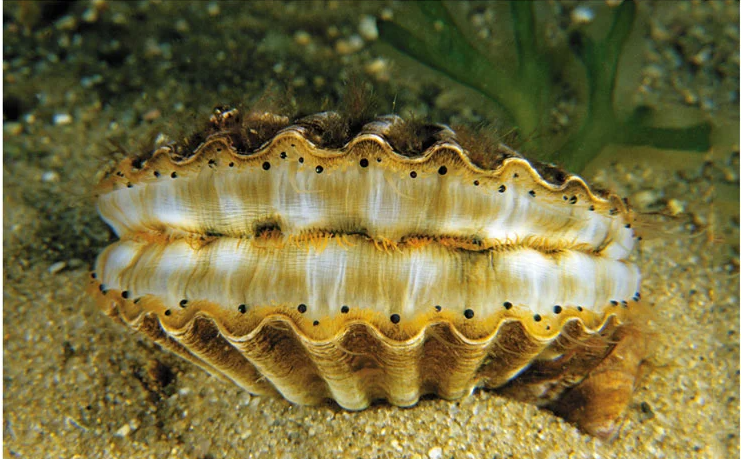
Bivalvia (clams, oysters, etc.)
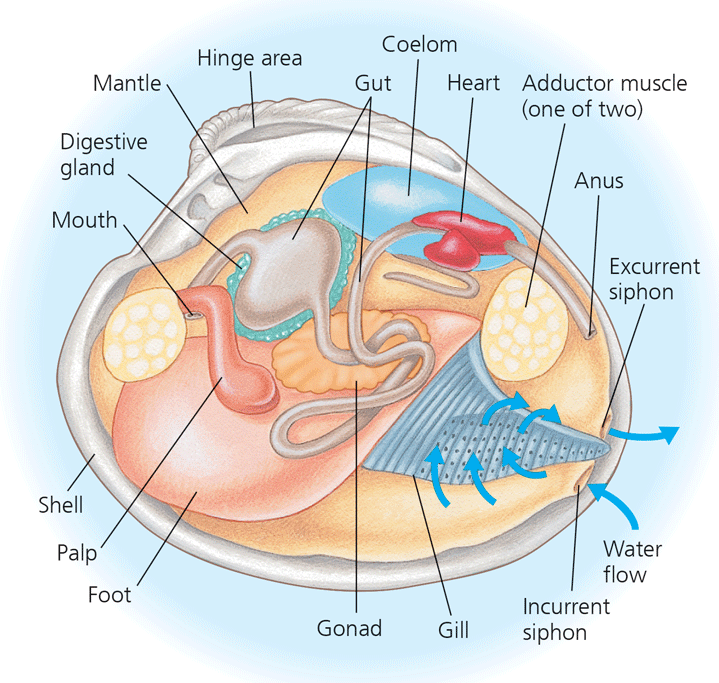

What is the taxon name of this organism?
Cephalochordata (lancelets)

What is the taxon name of this organism?
Cephalopoda
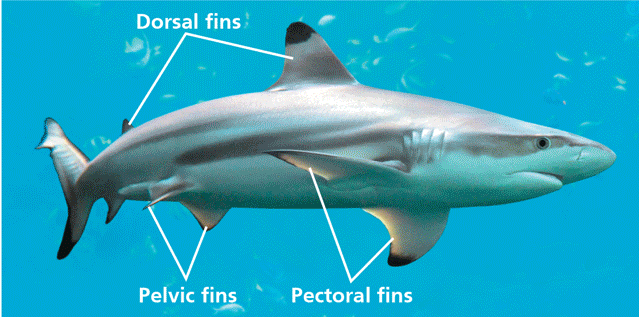
What is the taxon name of this organism?
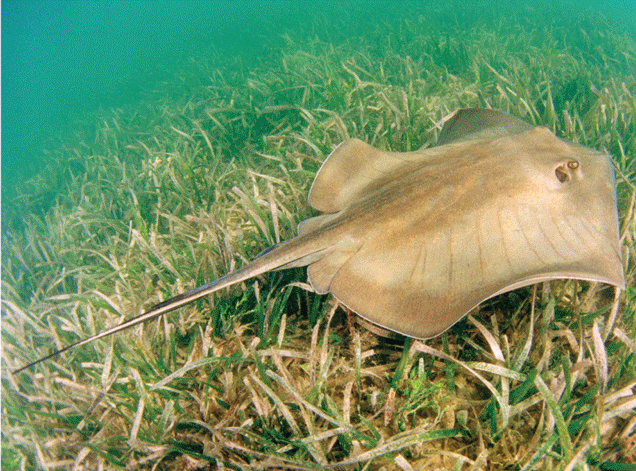
Chondrichthyes

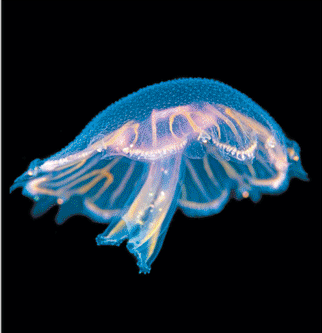
What is the taxon name of this organism?
Cnidaria


What is the taxon name of this organism?
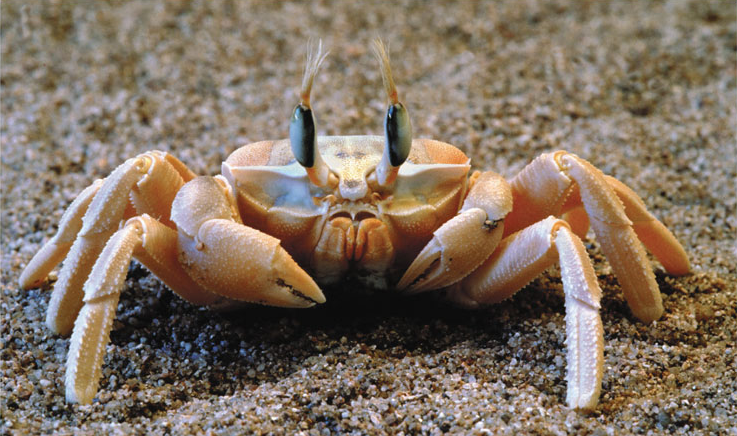
Crustacea

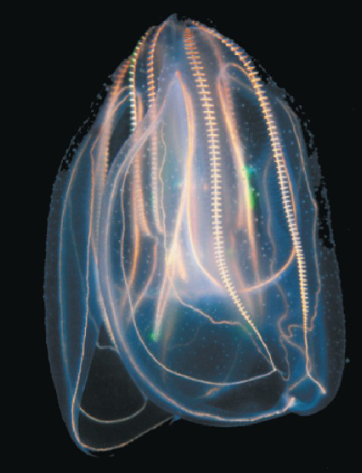
What is the taxon name of this organism?
Ctenophora

What is the taxon name of this organism?
Echinodermata

What is the taxon name of this organism?
Gastropoda
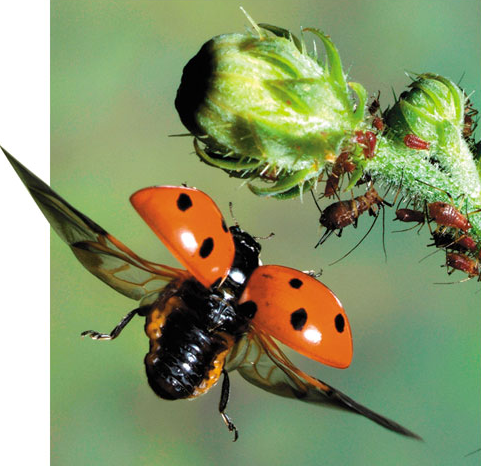

What is the taxon name of this organism?
Insecta (grasshopper, ladybug, butterfly, etc.)
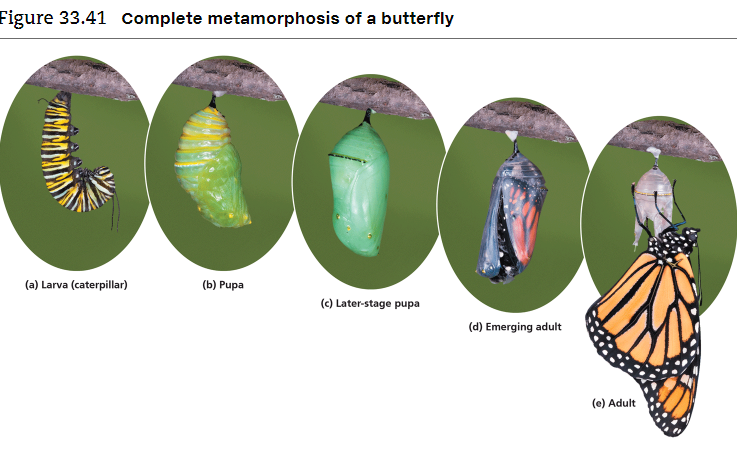

What is the taxon name of this organism?
Mammalia (possum, platypus, primate, bats, etc.)
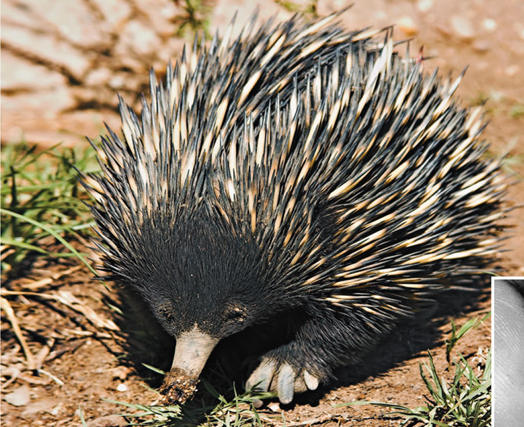
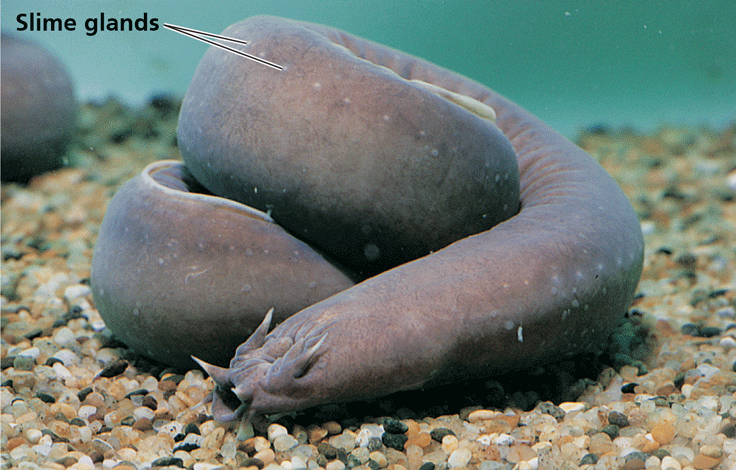


What is the taxon name of this organism?
Myxini (hagfishes)
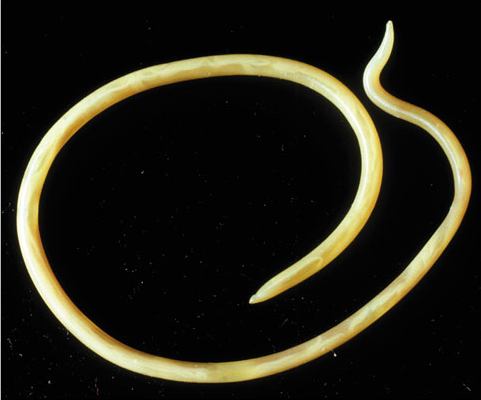
What is the taxon name of this organism?
Nematoda (roundworms)
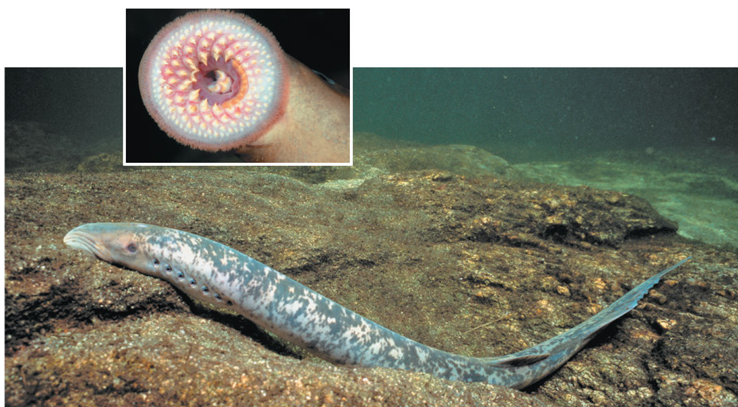
What is the taxon name of this organism?
Petromyzontida (lampreys)
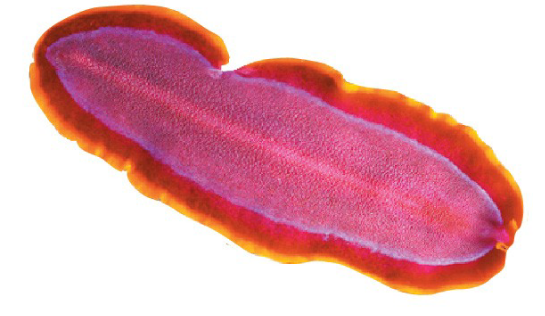
What is the taxon name of this organism?
Platyhelminthes (flatworm)

What is the taxon name of this organism?
Porifera (sponges)

What is the taxon name of this organism?
Reptilia (non-avian)


What is the taxon name of this organism?
Aves or in broader terms: avian reptiles
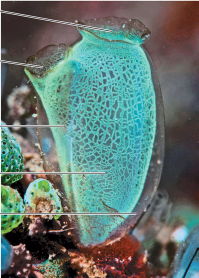
What is the taxon name of this organism?
Urochordata (Tunicate)
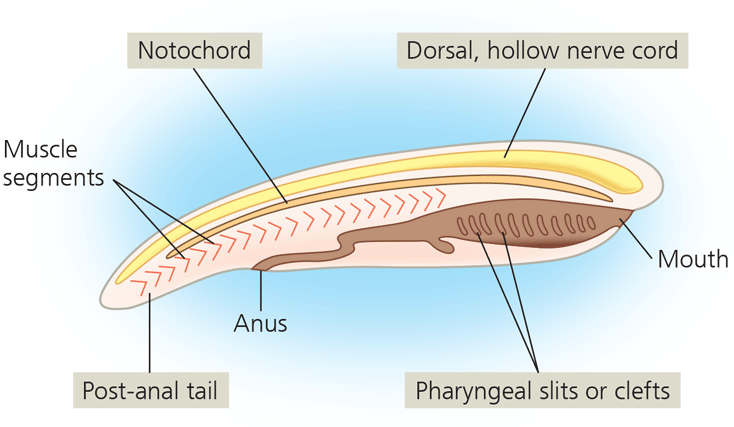
Name the four Chordate characteristics
Notochord; dorsal, hollow nerve cord; post-anal tail; pharyngeal slits or clefts

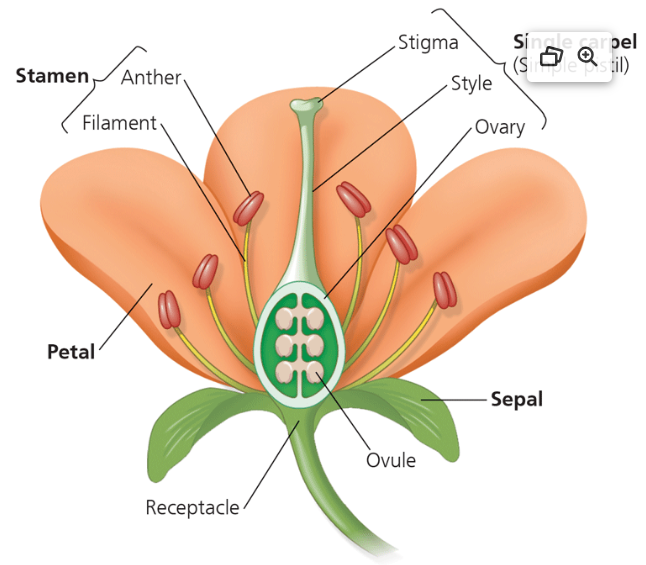
Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Anthophyta phylum
Angiosperms have two key adaptations: flowers and fruit. A flower is a specialized shoot with up to four types of modified leaves called flower organs: sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels.
For fruits, as seeds develop, the ovary wall thickens and the ovary matures into a fruit. Fruits protect seeds and aid in their dispersal.

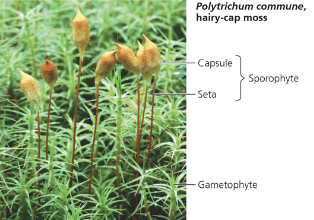
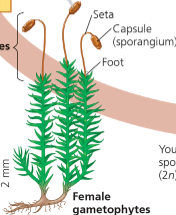
Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Bryophyta phylum
Species such as the feather moss Pleurozium harbor nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria that increase the availability of nitrogen in the ecosystem.

Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Coniferophyta
Most are evergreens, meaning they do not shed their leaves in the winter. They have both male and female cones, which form needle-like structures.


Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Cycadophyta
Can be recognized like a palm tree. They bear large cones rather than fruits. Their leaves are quite large compared to the stem and grow out in a rosette around the stem

Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Ginkgophyta
Have leaves that are fan-shaped and double-lobbed, with two branched-out veins. Their leaves grow in clusters, resembling the maidenhair fern. The leaves also have stomata only on the lower surface


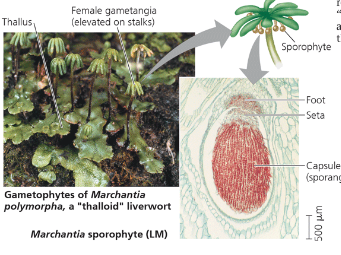
Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Hepatophyta
Liverworts, are named for their liver-shaped gametophytes. They are small plants because they lack vein-like tubes to conduct moisture and nutrients. They have leaflike structures that lack vascular tissue.


Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Ascomycota
Named after the ascus, a sac-shaped structure that contains ascospores and also small asexual spores called conidia.


Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Basidiomycota
The club-like shape of the basidium (a cell in which karyogamy occurs, followed immediately by meiosis) gives rise to the common name club fungus.
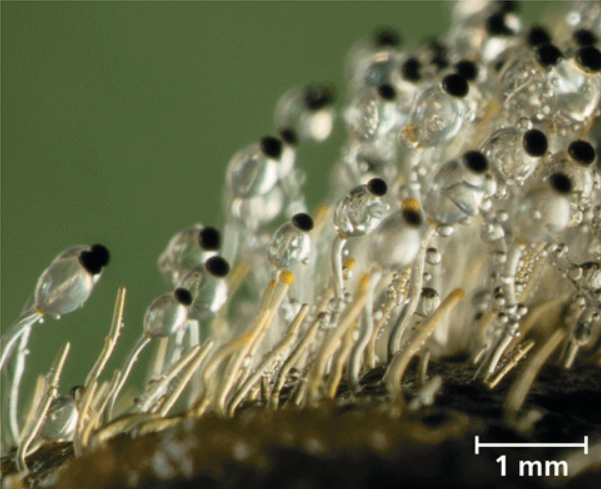


Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Mucoromycota
This fungi lack cross-walls (septa) in their hyphae, which can be observed under a microscope. They often form fluffy, cotton-like colonies on agar plates in laboratory settings.
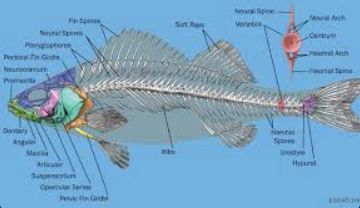
Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Actinopterygii
Named for the bony rays that support their fins

Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Amphibia
One reason they require relatively wet habitats is that they rely heavily on their moist skin for gas exchange; if their skin dries out, they cannot get enough oxygen. They have moist, smooth skin with glands that keep it lubricated.

Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Annelida
The taxon name means “little rings,” referring to the body’s resemblance to a series of fused rings. They have long, cylindrical bodies that are divided into segments by visible rings.

Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Arachnida
Class of invertebrate with eight legs and two body segments. They have a small, rounded body and long, thin legs. They also have six pairs of appendages.
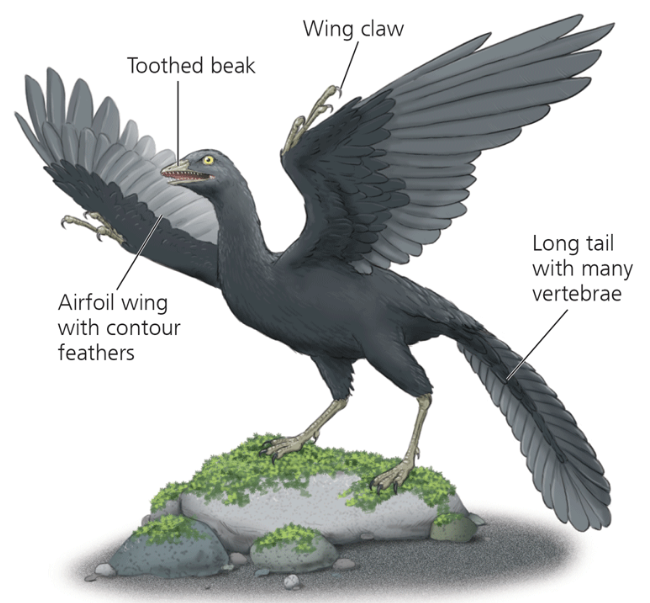
Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Aves
Lack a urinary bladder, and the females of most species have only one ovary. Living ones are also toothless. These adaptations facilitate flight by including weight-saving modifications that make flying more efficient.

Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Bivalvia
They have a shell divided into two halves. The halves are hinged, and powerful adductor muscles draw them tightly together to protect the animal’s soft body.

Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Cephalochordata
This phylum is called lancelets, which get their name from their bladelike shape. As larvae, lancelets develop the four chordate characteristics.

Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Cephalopoda
The only molluscs with a closed circulatory system, in which the blood remains separate from fluid in the body cavity.
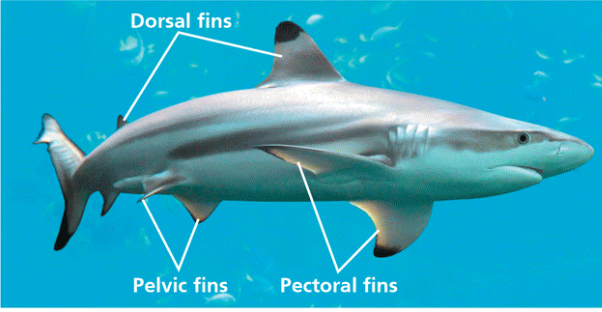
Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Chondrichthyes
The taxon name means “cartilage fish.” They have a skeleton predominantly composed of cartilage, though often impregnated with calcium. They have a ventral mouth and a flexible skeleton made of cartilage instead of bone.

Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Cnidaria
The basic body plan of this animal is a sac with a central digestive compartment, the gastrovascular cavity. A single opening in this cavity functions as both a mouth and an anus.

Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Crustacea
They are the only arthropods with two pairs of antennae. Three or more pairs of appendages are modified as mouthparts, including the hard mandibles. Walking legs are present on the thorax. They also have appendages on their post-genital region, or “tail.”
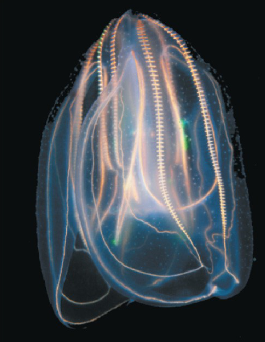
Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Ctenophora
Have eight “combs” of cilia that propel them through the water

Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Echinodermata
Have a coelom, a thin epidermis that covers an endoskeleton of hard calcareous plates, and most species are prickly from skeletal bumps and spines.
They also have a water vascular system, which is a network of hydraulic canals branching into extensions called “tube feet.”

Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Gastropoda
They have a shell that is secreted by glands at the edge of the mantle. They also obtain tentacles and a large foot with a flat sole for crawling.
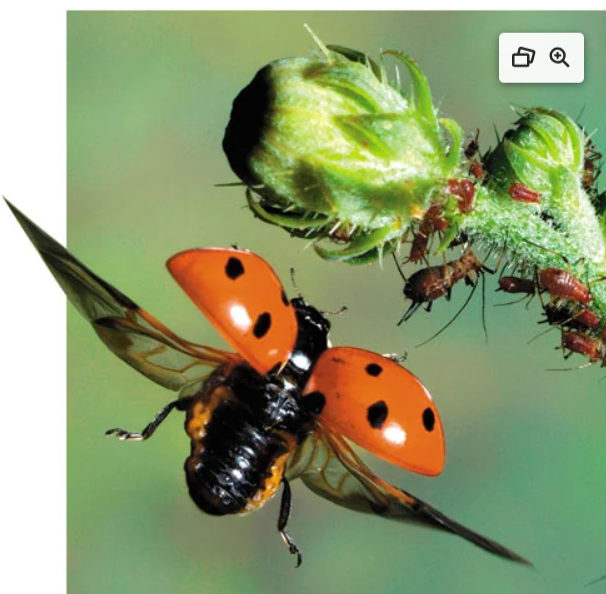

Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Insecta
The body has three regions: the head, thorax, and post-genital region. The segments that form the head are fused. They have six legs, except for some immature forms like caterpillars. They also have one pair of antennae on their heads.
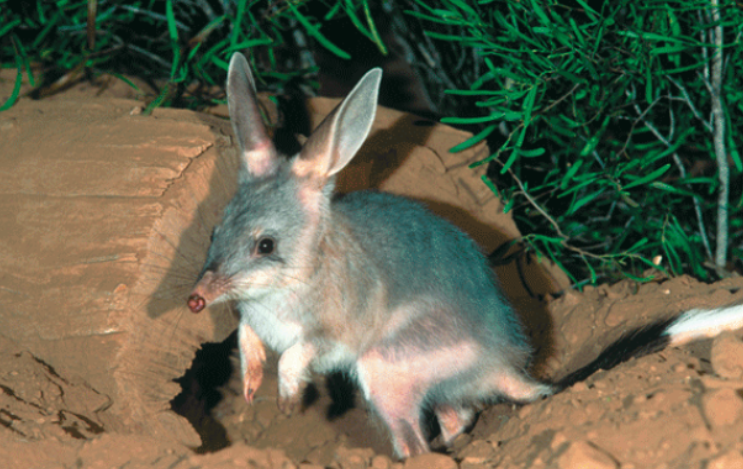

Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Mammalia
They are named for their distinctive mammary glands, which produce milk for offspring.

Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Myxini
Known as hagfishes. Jawless vertebrates that have highly reduced vertebrae and a skull that is made of cartilage. They have a small brain, eyes, ears, and a nasal opening that connects with the pharynx. Their mouths contain tooth-like formations made of the protein keratin.
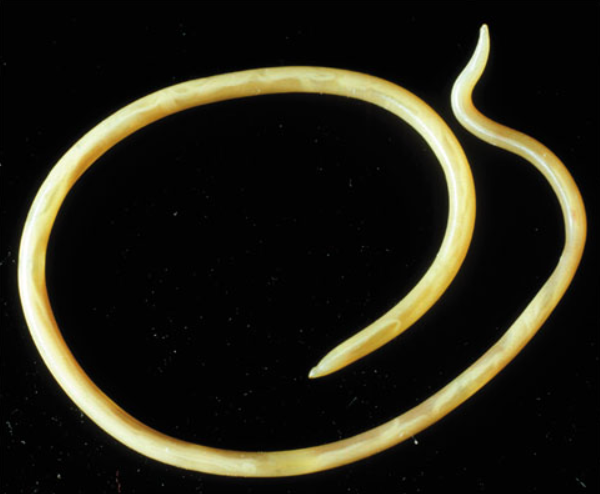
Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Nematoda
The body is covered by a tough cuticle (a type of exoskeleton); as the [round] worm grows, it periodically sheds its old cuticle and secretes a new, larger one. They also have an alimentary canal, though they lack a circulatory system.

Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Petromyzontida
The skeleton of lampreys is made of cartilage. Unlike the cartilage in most vertebrae, lamprey cartilage contains no collagen. Lampreys have a flexible sheath around their rod-like notochord.

Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Platyhelminthes
The taxon name means “flat worm.” They have thin bodies that are flattened on both the ventral and dorsal sides.
They lack a body cavity. Their flat shape increases their surface area, placing all their cells close to water in the surrounding environment or in their gut.

Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Porifera
They lack tissues, groups of similar cells that act as a functional unit, as in muscle tissue and nervous tissue. The body of a sponge consists of two layers of cells separated by a gelatinous region called the mesohyl.

Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Reptilia
Have tough, scaly skin (scales that contain keratin) that protects them from predators and reduces water loss. They also shed the outer layer of their skin as they grow.

Name one or more traits you can observe to distinguish the identity of Urochordata
Also named as tunicates. They are built like a barrel with two openings, or siphons, projecting from each other (excurrent siphon and incurrent siphon).

Name the mode of nutrition of Anthophyta
Autotroph

Describe an ecosystem service attributed to Anthophyta
Angiosperms, serve as major sources of food and consumer goods, such as building materials, textile fibers, spices and herbs, and medicine.

Name the mode of nutrition of Bryophyta
Autotroph
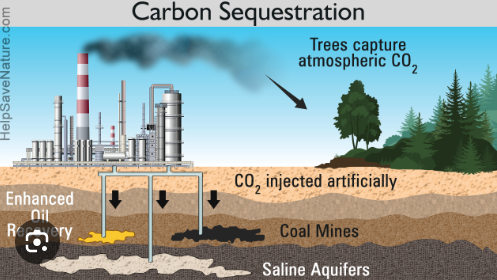
Describe an ecosystem service attributed to Bryophyta
Captures and/or stores carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. It’s goal is to reduce global warming.
They colonize sterile soils absorb nutrients and water and releases them slowly back into the ecosystem, contributing to the formation of soil for new plants to grow on.
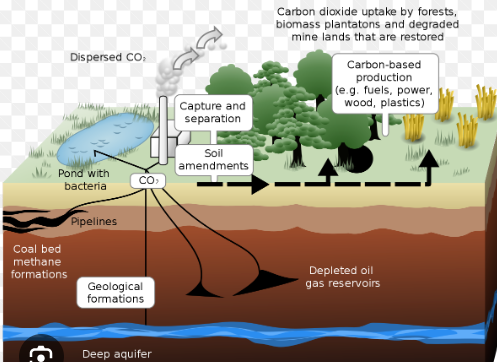

Name the mode of nutrition of Coniferophyta
Autotrophs

Describe an ecosystem service attributed to Coniferophyta
Store carbon to slow climate change (like bryophytes). They also provide forest products, including lumber and firewood. Their main role is providing a wildlife habitat. They create opportunities for recreation, including hunting, bird-watching, hiking, and horseback riding.

Name the mode of nutrition of Cycadophyta
Autotroph

Describe an ecosystem service attributed to Cycadophyta
Used for food and medicine. Starch is also obtained from this phylum

Name the mode of nutrition of Ginkgophyta
Autotroph

Describe an ecosystem service attributed to Ginkgophyta
Known to resist air pollution and pests, so it is used as a street tree and also because of its beautiful foliage (leaves turning yellow in the fall).

Name the mode of nutrition of Hepatophyta
Autotroph
Describe an ecosystem service attributed to Hepatophyta
Form microhabitats for insects and entire microorganisms.
Their greatest impact is indirect, including the reduction of erosion along streambanks, the collection and retention of water in tropical forests, and the formation of soil crusts in deserts and polar regions.

Name the mode of nutrition of Ascomycota
Heterotroph

Describe an ecosystem service attributed to Ascomycota
Are important decomposers, breaking down organic materials, such as dead leaves and animals, and helping the detritivores (animals that feed on decomposing material) to obtain their nutrients.

Name the mode of nutrition of Basidiomycota
Heterotroph

Describe an ecosystem service attributed to Basidiomycota
Are decomposers. They decompose and recycle. They absorb nutrients by feeding on decaying matter, and play a significant role in the carbon and nutrient cycles.

Name the mode of nutrition of Mucoromycota
Heterotroph

Describe an ecosystem service attributed to Mucoromycota
Are primary decomposers of organic matter in soil. These fungi are found as filamentous molds, decomposers in soil or on plants, or as root symbionts.
They appear to aid in plant growth, plant stress resilience, and soil health.

Name the mode of nutrition of Actinopterygii
Heterotroph

Describe an ecosystem service attributed to Actinopterygii
Ray-finned fishes serve as a major source of protein for humans. They also control prey populations and play a fundamental role in food chains.

Name the mode of nutrition of Amphibia
Heterotroph

Describe an ecosystem service attributed to Amphibia
They eat insect pests, which is beneficial to agriculture and they help control mosquitoes, which benefits human health.
They play a dual role as both prey and predators and act as a food source for higher-order chordates like snakes, birds, and mammals.

Name the mode of nutrition of Annelida
Heterotroph

Describe an ecosystem service attributed to Annelida
Serve as decomposers. They break down organic material, which contributes to nutrient cycling and ecosystem health. They also serve as a food source for other invertebrates and fish.

Name the mode of nutrition of Arachnida
Heterotroph

Describe an ecosystem service attributed to Arachnida
Like spiders, they help control insect populations. They eat harmful insects like flies and cockroaches, which can destroy crops. They can also enrich soil with nutrients. They are food sources for other chordates like birds, lizards, etc.
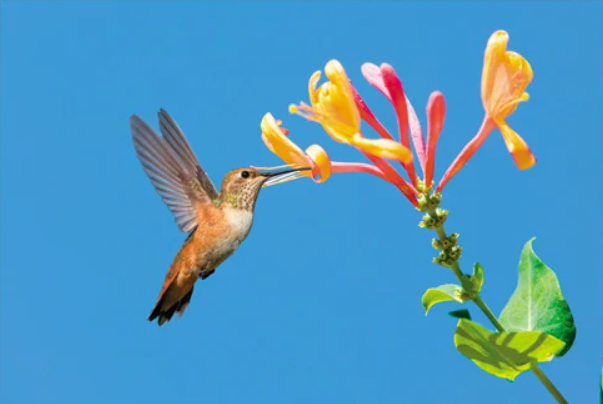

Name the mode of nutrition of Aves
Heterotroph
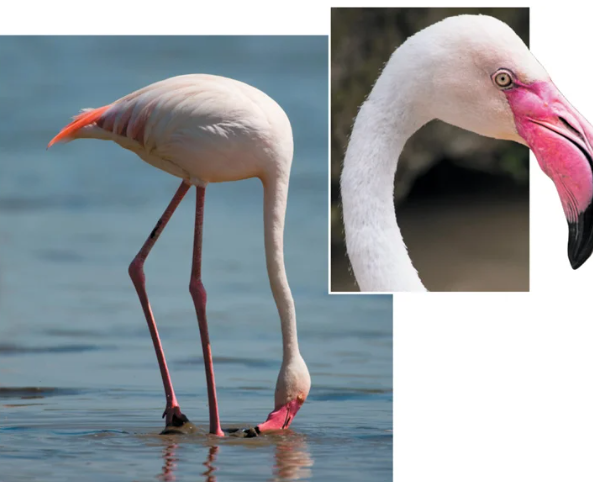

Describe an ecosystem service attributed to Aves
They play many roles, including predators, pollinators, scavengers, seed dispersers, seed predators, and pest control.

Name the mode of nutrition of Bivalvia
Heterotroph

Describe an ecosystem service attributed to Bivalvia
Filter water and serve as habitat and prey for variety of sea life

Name the mode of nutrition of Cephalochordata
Heterotroph

Describe an ecosystem service attributed to Cephalochordata
Lancelets are known to be filter feeders, meaning they feed on plankton and other small organic particles by filtering them out of the water. By doing so, they help regulate the population sizes of planktonic organisms.

Name the mode of nutrition of Cephalopoda
Heterotroph

Describe an ecosystem service attributed to Cephalopoda
They are great sources of food for humans and even marine life. They are a key component of food webs, providing a major prey source for fish, including tuna and salmon, cetaceans like dolphins, sea lions, and whales, and a variety of sea birds.