Mechanics
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
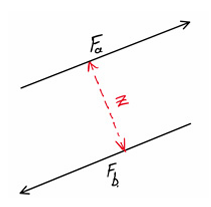
Equation for moment of a couple
Mcouple = Fa × Z = Fb × Z
Static equilibrium
We can say that an object is in a state of static equilibrium if it satisfies the following three conditions,
∑Fx = 0
∑Fy = 0
∑M = 0
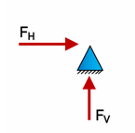
Pin support
It prevents translation in both x and y directions but does not resist bending moments.
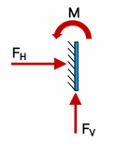
Build-in / cantilever / encastre supports
These supports are fixed in place, preventing both translation and rotation, and can resist bending moments as well as vertical and horizontal forces.
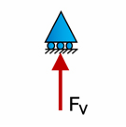
Roller Support
-Linear motion is restricted in one axis only
-Like pin supports, roller supports do not provide any resistance to rotation
The Joint Resolution Method for Truss Analysis
The joint resolution method involves evaluating force equilibrium at each joint or node and using the equations of statics to solve for the unknown member forces.
The Method of Sections for Truss Analysis
Instead of isolating a single joint, the method of sections involves us making an imaginary cut through the entire structure. In doing so, we reveal the internal member forces in the members our plane cuts through. We can then evaluate equilibrium of the sub-structure created by the cut.
Statical Determinacy
If the the number of unknowns is equal to the number of members, denoted by M we might say that once 2J = M , our truss is statically determinate.
Torsional Deformation
The twisting of an object due to applied torque, often measured as the angle of rotation per unit length.
Shear strain
γmax = rφ/L where γmax is the maximum shear strain, r is the distance from the center of rotation, φ is the angle of rotation, and L is the length of the object.
We can state the shear stress, at a radius r as
τ = τmaxρ/r
The torsion formula
τmax = Tr / Ip where τmax is the maximum shear stress, T is the applied torque, r is the radius at which the stress is being calculated, and Ip is the polar moment of inertia.
Resultant force and centre of pressure
R=ρgAy, where R is the resultant force, ρ is the fluid density, g is the acceleration due to gravity, A is the area of the object submerged, and y is the depth of the centroid of the submerged area.
Equation for depth to the centre of pressure
D = sin2(φ) I0/Ay where D is the depth to the center of pressure, φ is the angle of inclination, I0 is the second moment of area about the centroid, A is the area, and y is the depth of the centroid.
Archimedes Principle
States that a body immersed in a fluid experiences a buoyant force equal to the weight of the fluid it displaces.
Equation for polar moment of inertia
πd4/32 for a circular section