Working model+ LTM
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Working model
updated model, explains how memory is an active model
Capacity is measured in “operation span”, not ‘chunks.”
Processing span and Digit span
embodied within sensory-motor systems
Modality independent
Ex. you can remember sound independently from images

Processing span
how many items a person can successful “do”
ZAPS memory and Multiplication task
digit span
How many items a person can remember
(ex. list)
3 modality-specific stores (working memory)
Visual spatial sketchpad (vision)
Episodic buffer (time)
phonological loop (sound)
Central executive (working memory model)
centrals the processes tha control the flow of info, dorects what info has acess to what
Phonological loop
audio process of working memory, storage capacity ~2 seconds
Claim support for modality-specific stores
Audio interference (Aba Aba Aba) affects phonological loop memory, but not visual spatial memory
Matienence rehearsal
encodement factor for LTM, keeps things active in WM, doesn’t actually keep things in LTM
(repeating a phone number in your head)
Elaborate rehearsal
encoding factor for LTM, establishes long and durable representation, connecting it with initial knowledge
Ex. Associating a new name with someone you know
level of processing
how much you work with material corresponds to how well it’s encoded within the LTM
Mnemonics
component of elaborate rehearsal
Ex. ROY G BIV
Why do factors help encode in LTM?
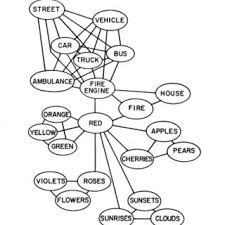
network of representations
Info is represented as a network, and connections can spread and activate other nodes
Ex. Car to fire truck to red to strawberry
explains how we understand “hints”
Networks help us understand why factors work, and they create and strengthen node connections
Encoding specificity
theory explain existence of context-dependent learning
states that when you learn, a pattern of activation is created that reflects everything about your current stet (when you learned info)
sensory/state becomes part of activation and a “recreation” or when you learned the info
Ex. Scuba diving example, remembering when you’re drunk
Context-specific
remembering better based on the world around you
ex. chewing mint gum in a library while doing math homework
State-speicifc learning
learning better based on you physical state
ex. doing math homework while plastered
remembering
the activation of previously established connections