Micro exam 1
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
What is microbiology?
The scientific study of microorganisms
What are considered microorganisms?(6 major groups)
Fungi
Algae
Virus
Bacteria
Protozoa
Careers in microbiology
Medical
Industrial
Immunology
Environmental
Public health and epidemiology
Agricultural
Medical Career In microbiology
Diagnose & treat infections
Environmental career in microbiology
Studies how microbes interact with the environment
Agricultural career in microbiology
Microbes and food productions
Public Health and Epidemiology career in microbiology
track disease spread
Industrial career in microbiology
used to make products with microbes
Immunology career in microbiology
studies how the immune system responds
Immune defense vs microbes
What was Koch known for
Koch Postulates (Germ Theory)
determined that a bacillus was responsible for anthrax in farm animals
Discovered sporulation
Developed methods of staining
Determined causative agents for many bacteria/ infections
Discovered how to grow tuberculosis in culture
Koch Postulates
Disease always in sick, not in well individuals. (the microorganisms must be found in abundance in all organisms suffering from the disease, but should not be found in health organism)
isolate microorganisms (the microorganisms must be isolated from a diseased organism and grown in pure culture)
Infection with pure microbes result in disease (the cultured organisms should cause disease when introduced into a health organism)
Re-isolate microorganisms from infected individuals (the microorganisms must be re isolated from the inoculated, diseased experimental host and identified as being identical to the original specific causative agent)
Fracastoro
early version of germ theory
He said that disease could spread from
Direct contact
Indirect contact
Through air
He did not conduct any experiments
Pauteur (Pasteurized)
He was mainly known for the swan neck experiment
Disproved spontaneous generation with swan neck flask experiment
Developed a vaccine for anthrax and rabies
Discovered microbial fermentation with spillage in beer and wine
Swan Neck Flask experiment
Put broth in swan neck flask so no outside air can enter
Boil the broth to kill any microorganisms
When you break the flask, bacteria enters the sterile broth and organism growth occurs
Lister
Ward fever
Use carbolic disinfectant during surgery
Aseptic technique
He tracked death rate of surgeries before and after using carbolic acid on open wounds, surgical tools, and bandages
Hooke
Named cell
Observed cork cell under microscope
Leeuwenhoek
First person to accurately describe living microbes
Used a simple microscope
Bacteria
Prokaryotic
usually unicellular
Cell wall contains peptidoglycan
Reproduced by binary fission
Can be beneficial(gut bacteria) or pathogenic
Can by many different shapes (cocci, bacilli, & spirilla)
Some form endospores (super resistant)
Can exchange DNA
EX- E. coli & Streptococcus
Fungi
Eukaryotic
Cell walls made of chitin
Include yeasts (unicellular) and molds/mushrooms (multicellular)
Absorb nutrients from the environment by absorption
Reproduce by spores
Important decomposers; some cause disease (athlete’s foot, ringworm)
Grow as hyphae forming a mycelium
Not photosynthetic
Ex- Yeast:Candida. Molds:Penicillin
Viruses
Not living cells
Made of DNA or RNA never both
protein coat (capsid); some have envelopes
Obligate intracellular parasites (must infect a host cell to reproduce)
Much smaller than bacteria
Cause diseases like influenza, HIV, COVID-19
Extremely small
No metabolism of their own
Replicate only inside host cells
Algae
Eukaryotic
Cell wall (often cellulose)
Photosynthetic (contain chlorophyll)
Mostly aquatic
Can be unicellular or multicellular
Produce a large amount of Earth’s oxygen
Not plants (lack true roots, stems, leaves)
Ex- diatoms & green algae
Protozoa
Eukaryotic
Unicellular
Usually motile (flagella, cilia, or pseudopodia)
Heterotrophic (consume organic material)
Many are free-living; some are pathogenic (malaria, amoebic dysentery)
No cell wall
Many are parasitic
Complex life cycle
Live in water or host
archaea
Prokaryotic, but genetically different from bacteria
Cell walls lack peptidoglycan
Often live in extreme environments (hot springs, salty lakes)
Rarely pathogenic
Important in evolution and ecology
Unique membrane lipids
unicellular
a sexual
Helminths
Eukaryotic, multicellular
Not microscopic as adults, but eggs/larvae are
Include roundworms, tapeworms, flukes
Parasitic lifestyle
Kingdom & Domain
From broadest → most specific:
Domain → Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species
Dear King Philip Came Over For Good Spaghetti
When did Prokaryote and Eukaryote appear
Prokaryotes 3.5 billion years ago
Eukaryotes 2.1-1.8 billion years ago
(Earth 4.6 billion years ago & Humans 1.2 billion years ago)
What organisms are considered prokaryotes
Bacteria
Archaea
Does Bacteria have a nucleus ?
No
Does Bacteria have a mitochondria ?
No
Does Bacteria have a Golgi apparatus?
No
Does Bacteria have chloroplast ?
No
Does Bacteria have a endoplasmic reticulum ?
No
Does Bacteria have Linear chromosomes?
No
Does Bacteria have a capsule ?
Only some
Does Bacteria have a flagella ?
Only some
Does Bacteria have Pili/ Fimbriae
Only some
Does Bacteria have plasmids?
Only some
Does Bacteria have endospores?
Only some
Does Bacteria have photosynthesis ?
Only some
Does Bacteria have oxygen use virus ?
only some
Does Bacteria have pathogenicity
Only some
Does Bacteria have a small size?
Yes
Does Bacteria have a cell wall present?
only some (peptidoglycan)
Does Bacteria have a cell membrane ?
Yes
Does Bacteria have ribosomes ?
Yes 70s
Is bacteria unicellular?
Yes
How does bacteria reproduce?
Asexually by binary fission
Does Bacteria have genetic material?
Yes singular or circular DNA molecule
Does Bacteria have cytoplasm ?
Yes
Does Bacteria have a prokaryotic or eukaryotic structure?
Prokaryotic- no membrane bound organelles or nucleus
Is Glycocalyx (Capsule & slime) prokaryotic or eukaryotic feature? and what is it’s function ?
Prokaryotic-Outer coating – not all bacteria
Protects against desiccation (drying out)
Prevents phagocytosis by host immune cells
Helps bacteria adhere to surfaces (biofilms)
Increases virulence in pathogenic bacteria
Can fit tight or loosely and diffuse
Lies outside the cell wall
Made of Made of
polysaccharides or proteins
Is Flagella prokaryotic or eukaryotic feature and what is it function
Prokaryotic-Motility & attachment structures
Flagella
Features
Long, whip-like structures
Made of flagellin
Anchored in the cell envelope
Functions
Movement (chemotaxis)
Helps bacteria move toward nutrients or away from toxins
Is Fimbriae (Pili) a prokaryotic or eukaryotic feature and what is it function?
Prokaryotic-Motility & attachment structures
Features
Short, thin, hair-like projections
More numerous than flagella
extends from cell surface
helps in adhesion to other cells and surfaces
Functions
Attachment to surfaces or host cells
Sex pili allow DNA transfer during conjugation
Is a cilia a prokaryotic feature?
No-True cilia are NOT found in bacteria (they are eukaryotic).
Is cell membrane a prokaryotic or eukaryotic feature and what is it’s function?
Prokaryotic-Plasma Membrane
Features
Phospholipid bilayer
No sterols (except Mycoplasma)
May contain enzymes for respiration
Functions
Selectively controls entry and exit of substances
Site of metabolic processes (e.g. ATP production)
Maintains internal environment
Is a cell wall a prokaryotic or eukaryotic feature and what is it’s function?
Prokaryotic-Present in most bacteria
Features
Rigid outer layer
Made of peptidoglycan
Gram-positive: thick layer
Gram-negative: thin layer + outer membrane
Functions
Maintains cell shape
Prevents osmotic lysis
Provides protection
What feature does this and is it prokaryotic or eukaryotic ?
Only in some bacteria)
Features
Dormant, thick-walled structures
Contain DNA and minimal cytoplasm
Highly resistant to heat, chemicals, radiation, dehydration
Functions
Survival in harsh conditions
Germinate when conditions improve
Endospores & Prokaryotic
What feature does this and is it prokaryotic or eukaryotic ?
Features
Single, circular DNA molecule
Not enclosed by a nuclear membrane
Located in nucleoid region
Functions
Contains essential genes
Controls metabolism, growth, and reproduction
Bacterial Chromosome / Nucleoid & Prokaryotic
What feature does this and is it prokaryotic or eukaryotic ?
Optional genetic elements
Features
Small, circular DNA molecules
Replicate independently of chromosome
Functions
Carry non-essential but advantageous genes
Often encode antibiotic resistance or virulence
Can be transferred between bacteria
Plasmids & Prokaryotic
What feature does this and is it prokaryotic or eukaryotic ?
Features
70S (50S + 30S subunits)
Free in cytoplasm
Functions
Protein synthesis
Tiny particles that is made of protein and RNA
Ribosomes & Prokaryotic
What feature does this and is it prokaryotic or eukaryotic ?
(Storage structures)
Features
Granules in cytoplasm
May store glycogen, lipids, phosphate, sulfur
Functions
Nutrient and energy storage
Help survival during nutrient scarcity
Inclusions/Granule & Prokaryotic
coccus


What is this ?
coccus
bacillus

what is this?
bacillus

what is this ?
coccobacillus
coccobacillus


What is this?
spirillum
spirillum

What is this?
vibrio
vibrio

What is this?
spirochete
spirochete

Pair of two coccus ?
cocci
Group of 4 or more cells in a square
Tetrad
Cluster of cocci ?
staphylococcus
pair of two cocci ?
diplococcus
chain of cocci?
streptococcus
chain of rods?
streptobacillus

diplococcus
Tetrad
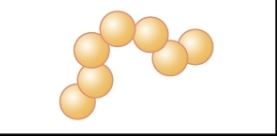
streptococcus
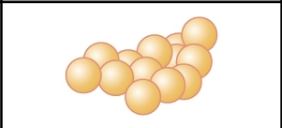
staphylococcus
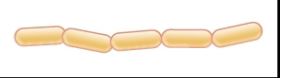
streptobacillus
Thick peptidoglycan layer
Teichoic & lipoteichoic acid
Stains purple
Gram + or -
Gram +
Single, thin sheath of peptidoglycan
• Outer membrane
– LPS (outermost)
– Lipoprotein (innermost)
Stains pink/red
Gram + or - ?
Gram -
Chemotaxis
Stimulus | Chemicals | |
Directional? | Yes | |
Positive response | Toward nutrients | |
Negative response | Away from toxins | |
Common in | Many bacteria |
Phototaxis
Stimulus | Light | |
Directional? | Yes | |
Positive response | Toward light | |
Negative response | Away from intense light | |
Common in | Photosynthetic bacteria |
Mycoplasma cell membrane
High concentration of sterols > rigidity
Archae cell membrane
Hydrocarbons instead of fatty acids
Plasma Membrane
Very thin (5-10 nm)
• Contain primarily phospholipids and proteins
• Provides a site for functions such as energy reactions, nutrient
processing, and synthesis
• Regulates transport (selectively permeable membrane)
• Secretion
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic similarities
Cell (plasma) membrane
Cytoplasm
DNA as genetic material
Ribosomes (protein synthesis)
Carry out metabolism
Can reproduce and grow
Differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic
Prokaryotes-small, no nucleus, DNA is circular, single cellular, no histones except archaea, and no membrane bound organelles
Eukaryotes-large, nucleus, Linear DNA, multi cellular, histones, and membrane bound organelles
Evidence of Endosymbiotic theory
circular DNA, 70S ribosomes, double membrane, binary fission
What does the Endosymbiotic theory explain?
Origin of eukaryotic cells
Why mitochondria and chloroplasts resemble bacteria
Why eukaryotic cells are more complex and energy-efficient
What is the Endosymbiotic theory
that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated as free-living prokaryotes that were engulfed by a larger ancestral eukaryotic cell, forming a mutualistic (symbiotic) relationship
eukaryotic organelles?
Nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, Rough and Smooth ER, Golgi apparatus, Lysosomes, Chloroplast , vacuole, and centrioles
centrioles
only in animal cells
Organize spindle fibers during cell division
Cylindrical microtubule structures
eukaryotic
Vacuole
eukaryotic
Large central vacuole in plant cells
Smaller or absent in animal cells
Storage
Maintains turgor pressure
pH and ion balance
Chloroplasts
plants & algae only
Double membrane
Thylakoids and grana
Chlorophyll
Own DNA and ribosomes
Photosynthesis