Transport and Diffusion of Gases in the Respiratory System
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
What factors can affect lung capacity?
Sex, body type, and lifestyle.
How does smoking affect lung capacity?
Smoking significantly decreases lung capacity.
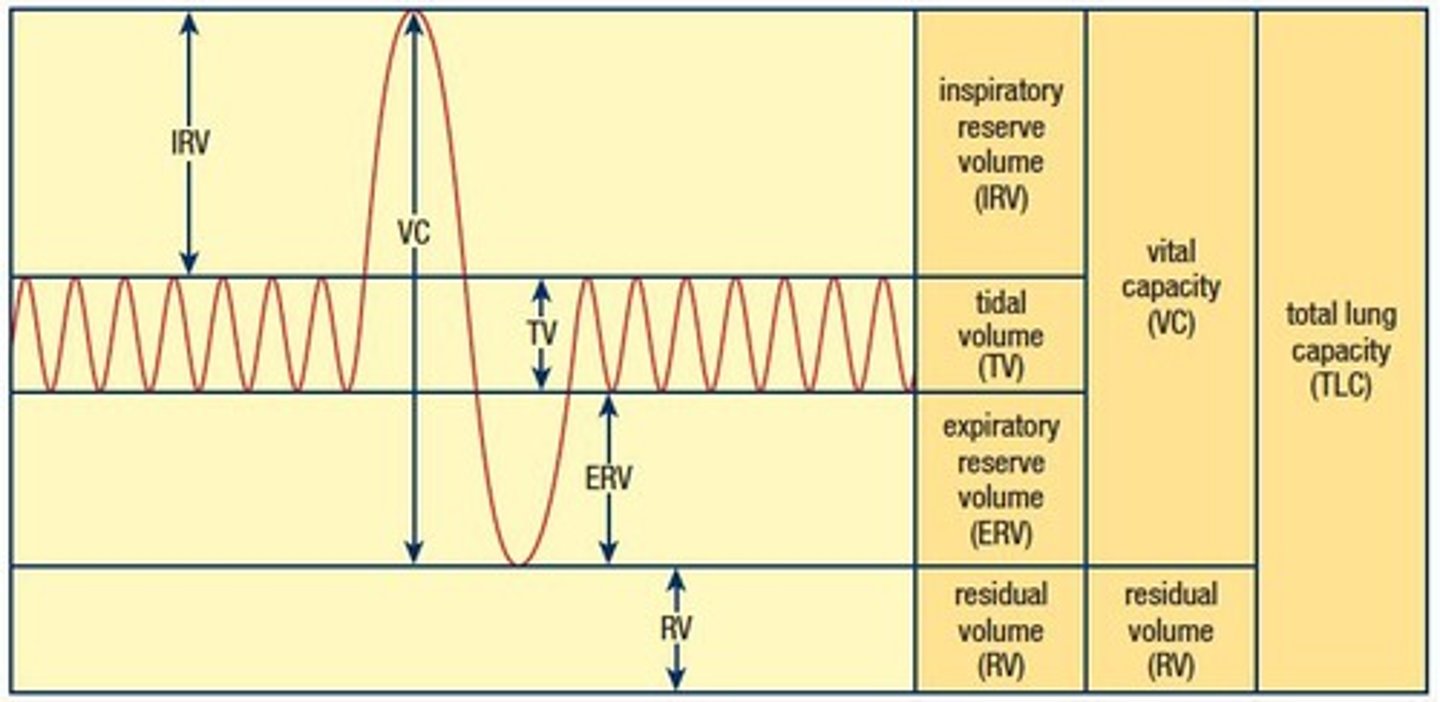
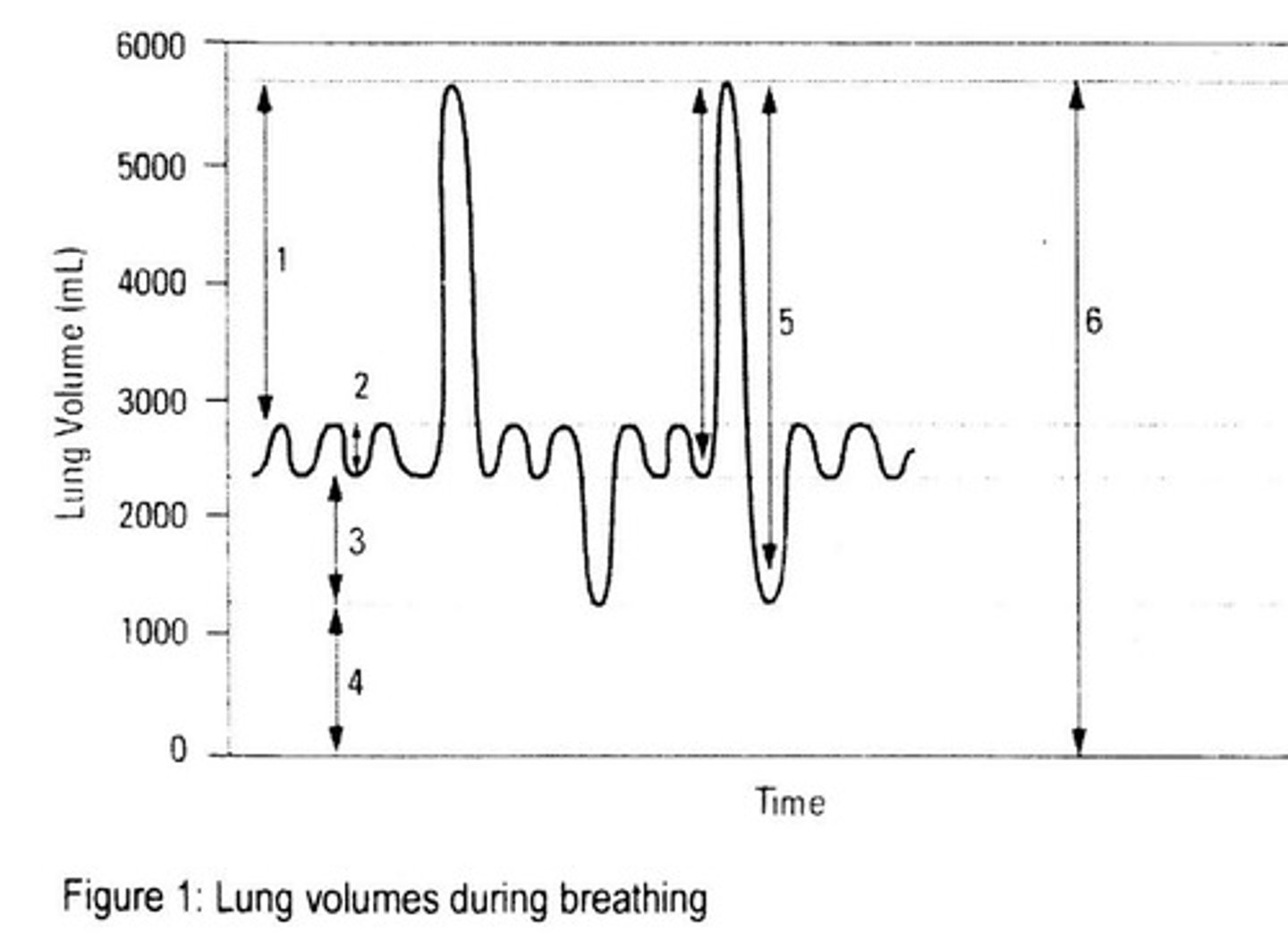
What is tidal volume?
The amount of air that passes in and out of the lungs during normal, involuntary breathing, approximately 0.5 L in the average adult.
Does normal breathing involve a complete exchange of air in the lungs?
No, normal breathing does not involve a complete exchange of the air in the lungs.
What is inspiratory reserve volume?
The amount of additional air that can be forcibly inhaled after a normal inhalation, approximately 2.5 L.
What is expiratory reserve volume?
The amount of air that can be forcefully exhaled after tidal volume, approximately 1 L.
What is residual volume?
The amount of air that always remains in the lungs even after maximal exhalation, preventing lung collapse, approximately 150 mL.
What is vital capacity?
The maximum amount of air that can be inhaled or exhaled, approximately 4.4 L to 4.8 L in males and 3.4 L to 3.8 L in females.
What is total lung capacity?
The maximum volume of air that can be held in the lungs at any given time, approximately 6 L.
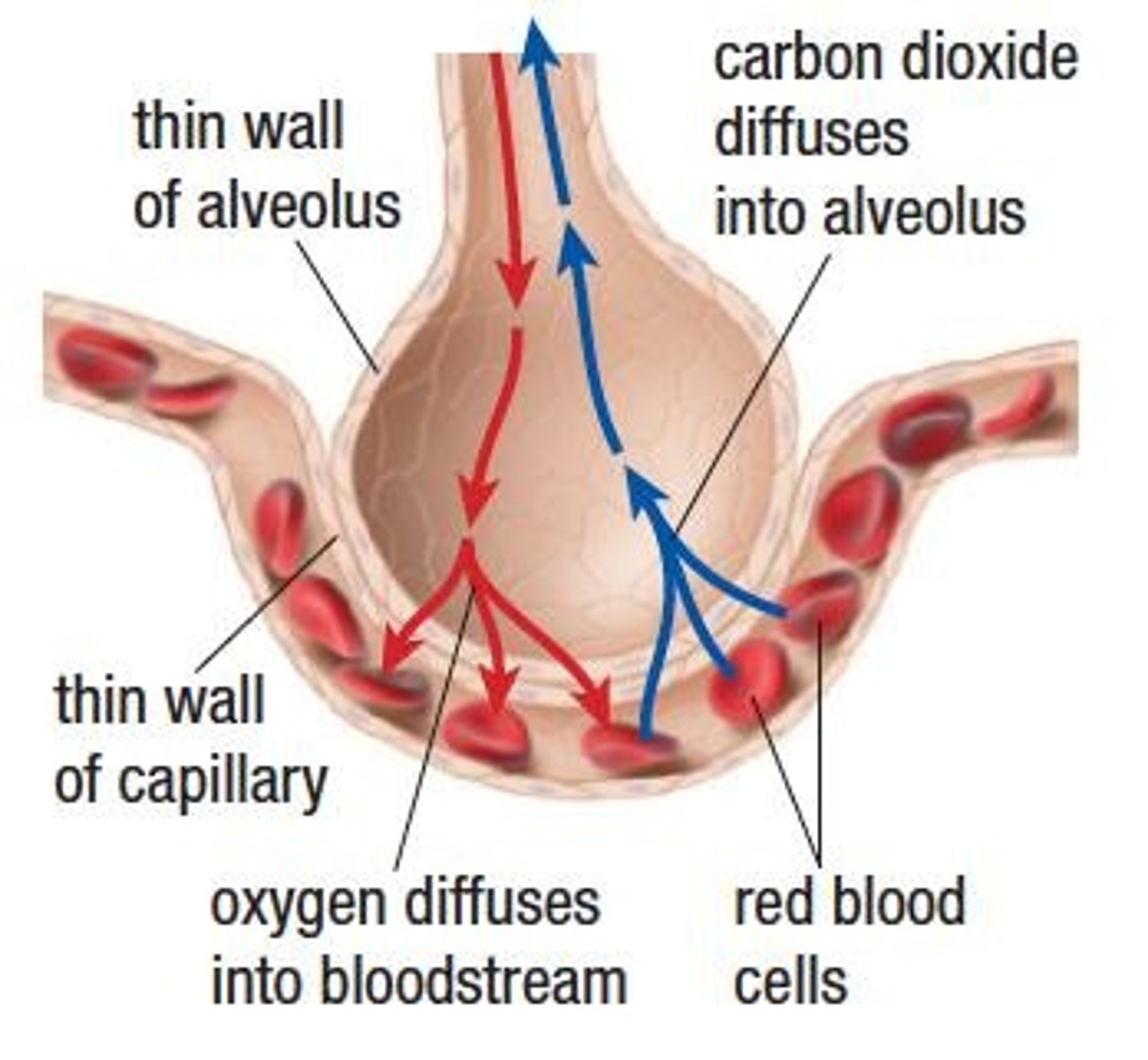
How does gas exchange occur?
By diffusion across a moist cell membrane.
What is diffusion in the context of gas exchange?
The movement of a gas from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
What are the three factors that affect the rate of diffusion?
Surface area of the cell membrane, concentration difference, and diffusion distance.
How does surface area affect the rate of diffusion?
The larger the surface area, the greater the rate of diffusion.
How does concentration difference influence diffusion?
The greater the difference in concentration, the more rapid the rate of diffusion.
What is the significance of diffusion distance in gas exchange?
The shorter the distance traveled, the greater the rate of diffusion.
At what two locations does gas exchange occur?
1. The lungs (External Respiration) 2. (Second location not provided in notes).
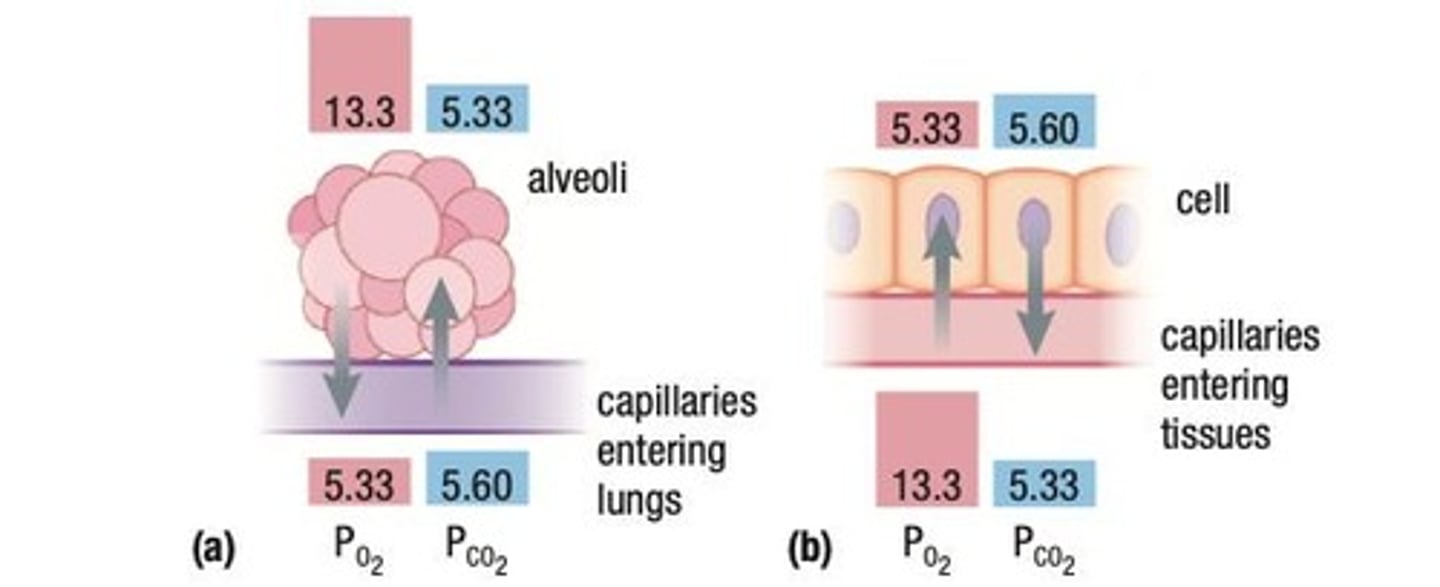
What is external respiration?
The exchange of O2 and CO2 between the alveoli and the pulmonary capillaries.
What happens to blood returning from systemic circulation to the heart?
It is rich in CO2 produced from cellular respiration and is pumped to the lungs.
Why does CO2 diffuse from pulmonary capillaries into the alveoli?
Because the concentration of CO2 in the pulmonary capillaries is higher than in the alveoli.
What role does ventilation play in respiration?
Ventilation brings O2 into the lungs, where its concentration is higher in the alveoli than in the pulmonary capillaries.
What is the principle of gas diffusion in respiration?
Each gas diffuses from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
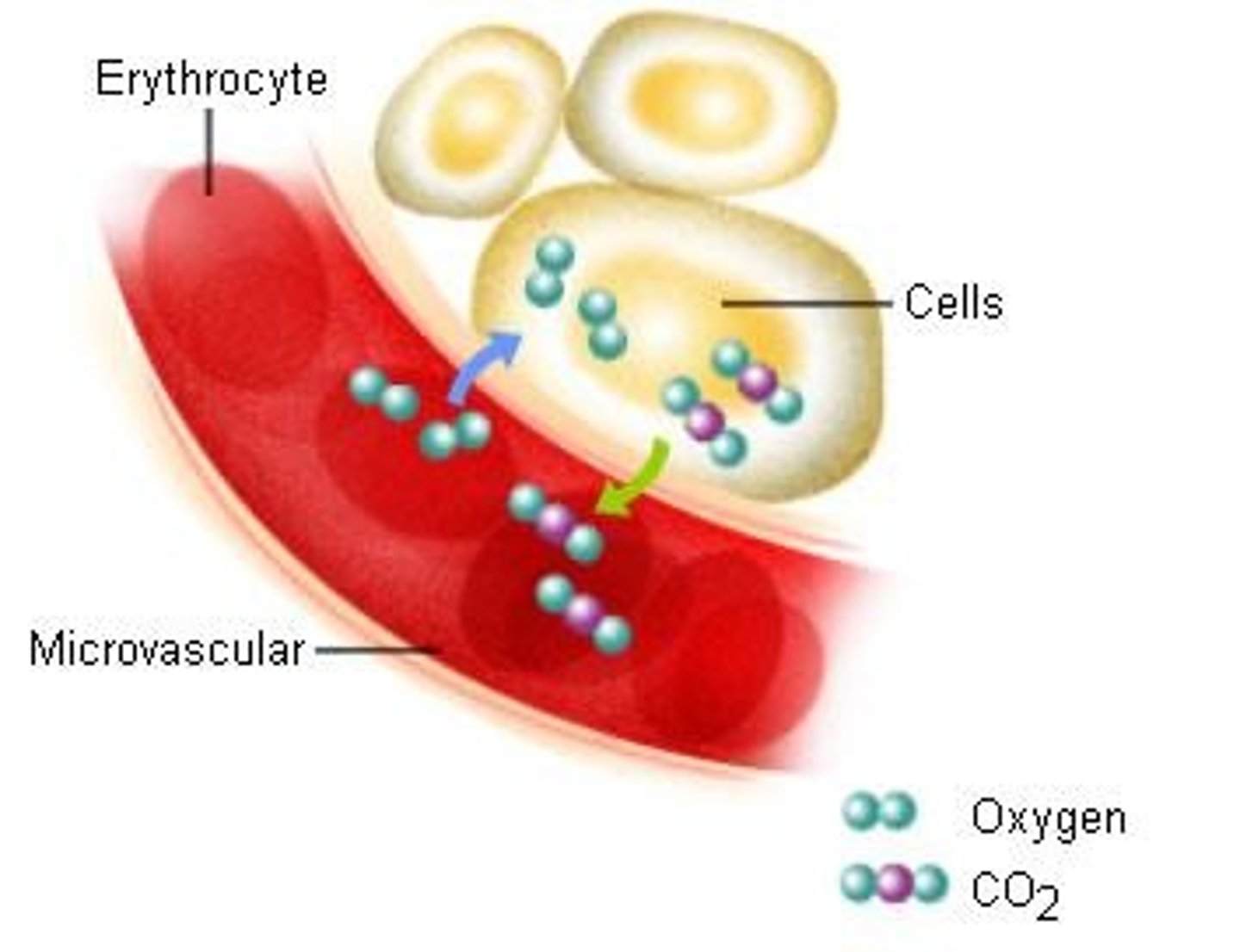
What is internal respiration?
The exchange of O2 and CO2 between the systemic capillaries and body tissue.
What is the concentration of O2 in blood that leaves the heart?
It has a high concentration of O2 and a low concentration of CO2.
Why does O2 diffuse from systemic capillaries into body tissue?
Because the concentration of O2 is higher in the systemic capillaries than in the body tissue.
What happens to CO2 produced by body cells during cellular respiration?
It diffuses from the body tissue into the systemic capillaries.
What is the significance of partial pressures in gas exchange?
Gases diffuse across a cell membrane from an area of higher pressure to an area of lower pressure.
What is the SI unit for pressure used in gas exchange?
Pascal (Pa), typically measured in kilopascals (kPa).
What is the partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) in the alveoli compared to pulmonary capillaries?
In the alveoli, PO2 is 13.3 kPa, while in the pulmonary capillaries it is 5.33 kPa.
What is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO2) in the pulmonary capillaries compared to the alveoli?
PCO2 is 5.6 kPa in the pulmonary capillaries and 5.33 kPa in the alveoli.
What is the partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) in systemic capillaries compared to body cells?
In systemic capillaries, PO2 is 13.3 kPa, while in body cells it is 5.33 kPa.
What is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO2) in systemic capillaries compared to body cells?
PCO2 is 5.6 kPa in systemic capillaries and 5.33 kPa in body cells.
How is oxygen transported in the circulatory system?
Oxygen is transported attached to hemoglobin in red blood cells (98.5%) and dissolved in blood plasma (1.5%).
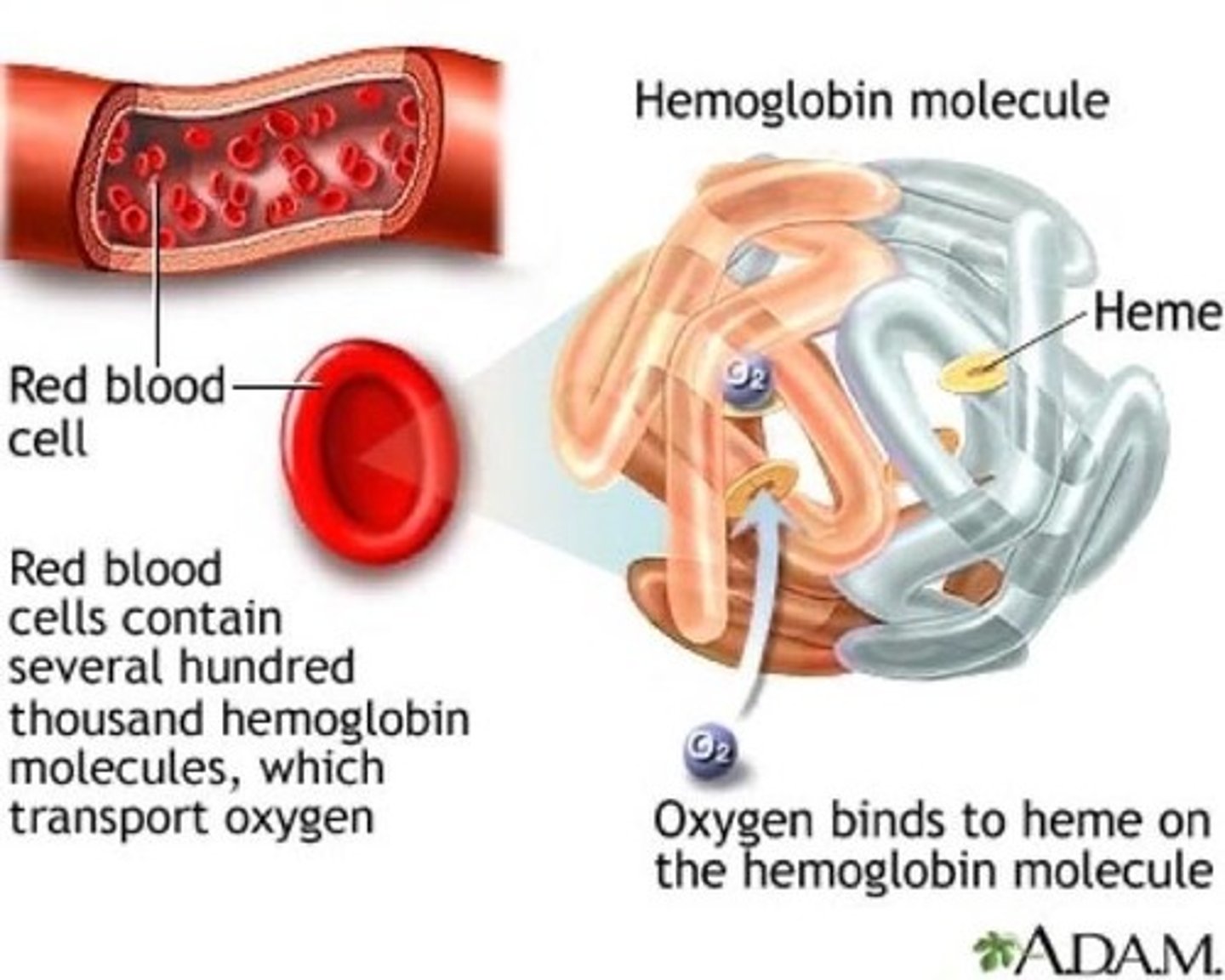
What is hemoglobin?
An iron-containing protein in red blood cells that binds with oxygen to form oxyhemoglobin.
What color does oxyhemoglobin give to oxygenated blood?
Bright red.
What color is deoxygenated blood?
Dark red.
How much does hemoglobin increase the blood's capacity to carry oxygen?
By nearly 70 times.
How is carbon dioxide transported in the blood?
About 10% is dissolved in blood plasma.

What percentage of carbon dioxide binds to hemoglobin to form carbaminohemoglobin?
About 20%.
How does carbon dioxide bind to hemoglobin?
CO2 binds to amino groups (NH2) on the polypeptide chains of hemoglobin, not to iron like oxygen.
What is the primary form in which carbon dioxide is transported in the blood?
As bicarbonate ions (HCO3-), which account for about 70% of CO2 transport.
What reaction occurs when carbon dioxide reacts with water in plasma?
It forms carbonic acid (H2CO3), which quickly separates into bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) and hydrogen ions (H+).
What issue arises from the formation of bicarbonate ions and hydrogen ions in the blood?
The creation of hydrogen ions can lead to changes in blood pH, creating a potential problem for acid-base balance.
What is the effect of H+ ions on plasma acidity?
H+ ions can increase the acidity of the plasma, which can be life-threatening.
How do H+ ions affect hemoglobin?
As hemoglobin releases oxygen to body tissues, H+ ions attach to hemoglobin and are transported to the lungs, preventing dangerous accumulation in the blood.
What happens to H+ ions at the lungs?
At the lungs, H+ ions are released from hemoglobin and recombine with bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) to reform carbon dioxide and water.
What is the atmospheric pressure at sea level?
The atmospheric pressure at sea level is 101.3 kPa.
How does altitude affect air density and pressure?
At higher altitudes, air density decreases, causing total air pressure to decrease while the composition of gases remains the same.
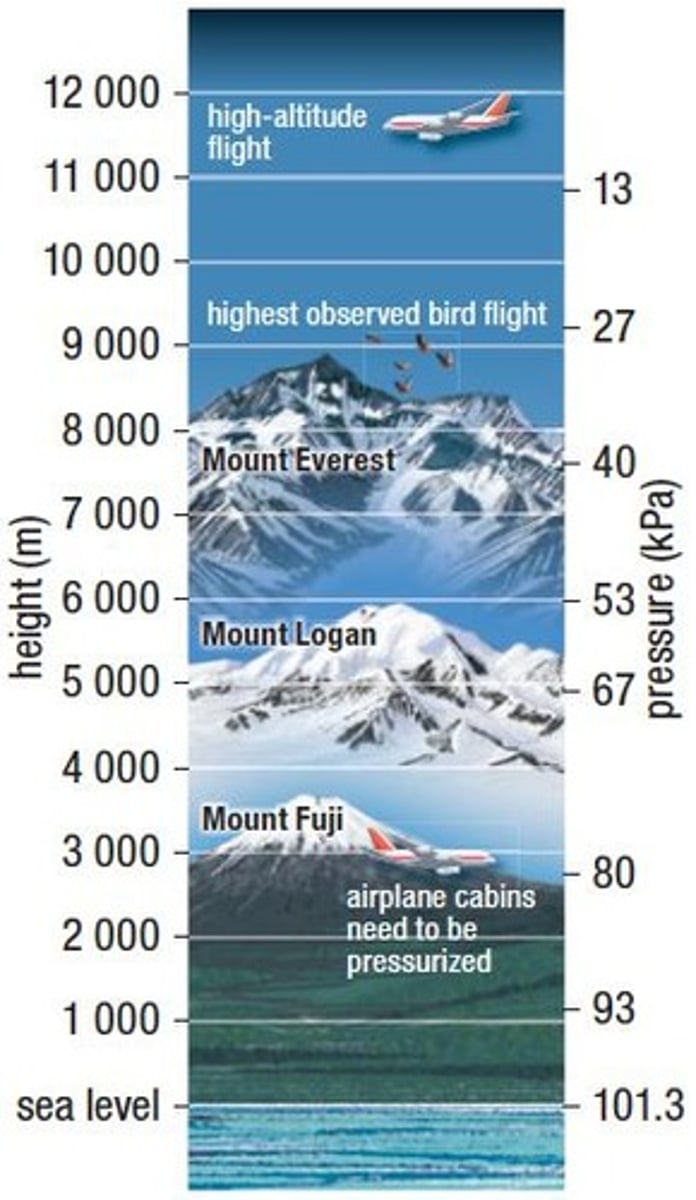
What is the partial pressure of oxygen at sea level?
The partial pressure of oxygen at sea level is around 21.17 kPa.
What is the partial pressure of oxygen at 2000 m altitude?
At 2000 m, the partial pressure of oxygen is about 17 kPa.
What is the partial pressure of oxygen at 7000 m altitude?
At 7000 m, the partial pressure of oxygen is only about 8.6 kPa.
What happens to the partial pressure of oxygen above 7000 m?
Above 7000 m, the partial pressure of oxygen is too low to survive.
How does altitude affect the diffusion of oxygen?
At high altitudes, the pressure gradient of oxygen (PO2) between the air and blood is reduced, decreasing the rate of diffusion of oxygen into the pulmonary capillaries.
What are the symptoms of altitude sickness?
Altitude sickness symptoms include shortness of breath, headache, dizziness, tiredness, and nausea.
What role does erythropoietin (EPO) play at high altitudes?
The kidneys increase the secretion of EPO, which stimulates the production of red blood cells (RBCs) to enhance oxygen delivery to body cells.
How can RBC count change with altitude exposure?
Remaining at high altitude for a few weeks can increase RBCs from 5,000,000/mL to 7,000,000/mL.
Why do athletes train at high altitudes?
Athletes train at high altitudes to increase their RBC count, improving their aerobic capacity (VO2 max) and endurance.
What is the lifespan of red blood cells?
Red blood cells have a lifespan of 90-120 days.
What is blood doping?
Blood doping is the practice of boosting the number of RBCs in the bloodstream to enhance athletic performance.
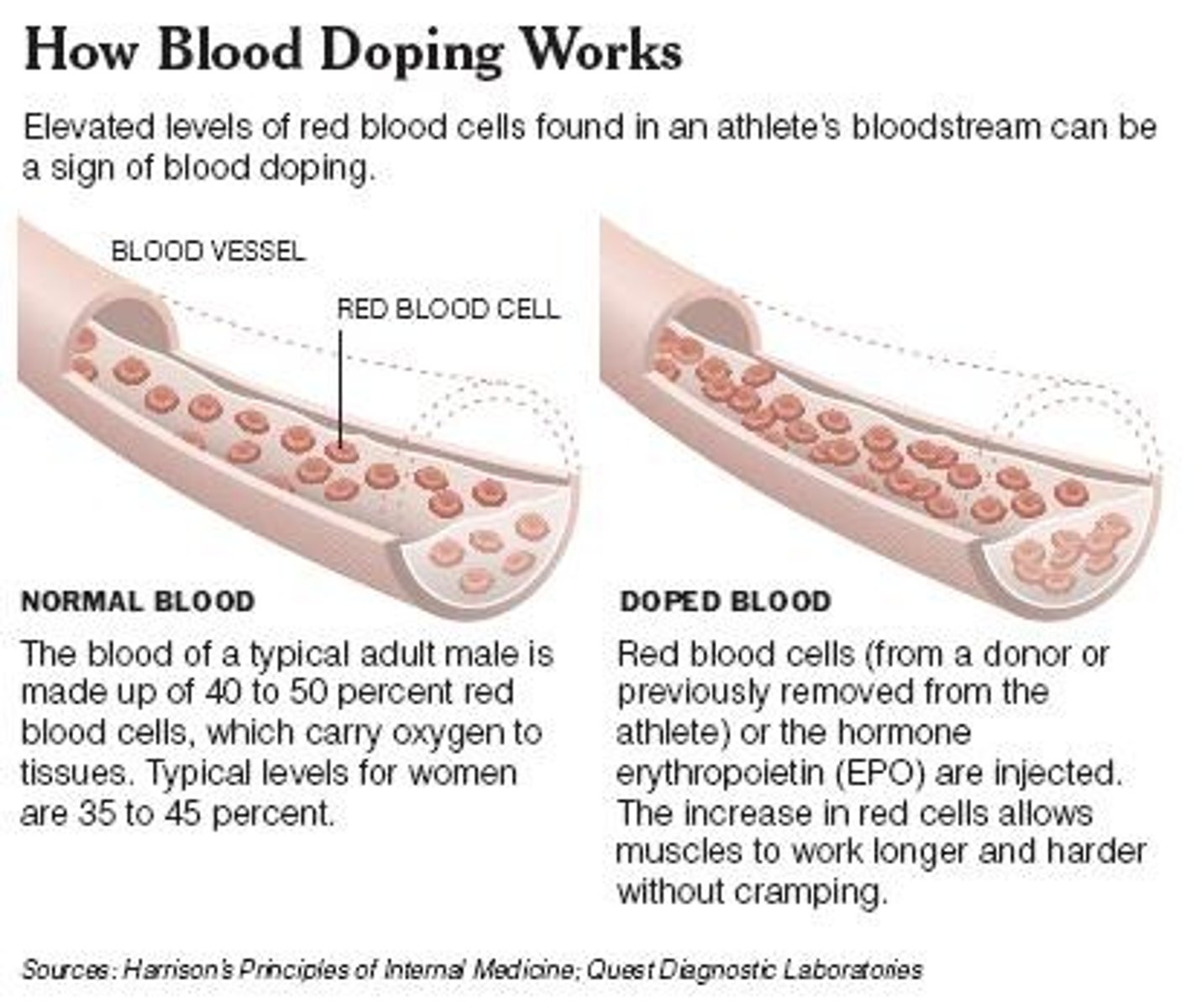
Is synthetic EPO allowed in competitions?
The synthetic version of EPO is a banned substance in competitions such as the Olympic Games.
How can natural and synthetic EPO be distinguished?
A urine test is available that can distinguish between natural and synthetic EPO.
What controls regular breathing (Tidal Breath)?
Regular breathing is an involuntary action controlled by signals from the respiratory center in the brain stem.
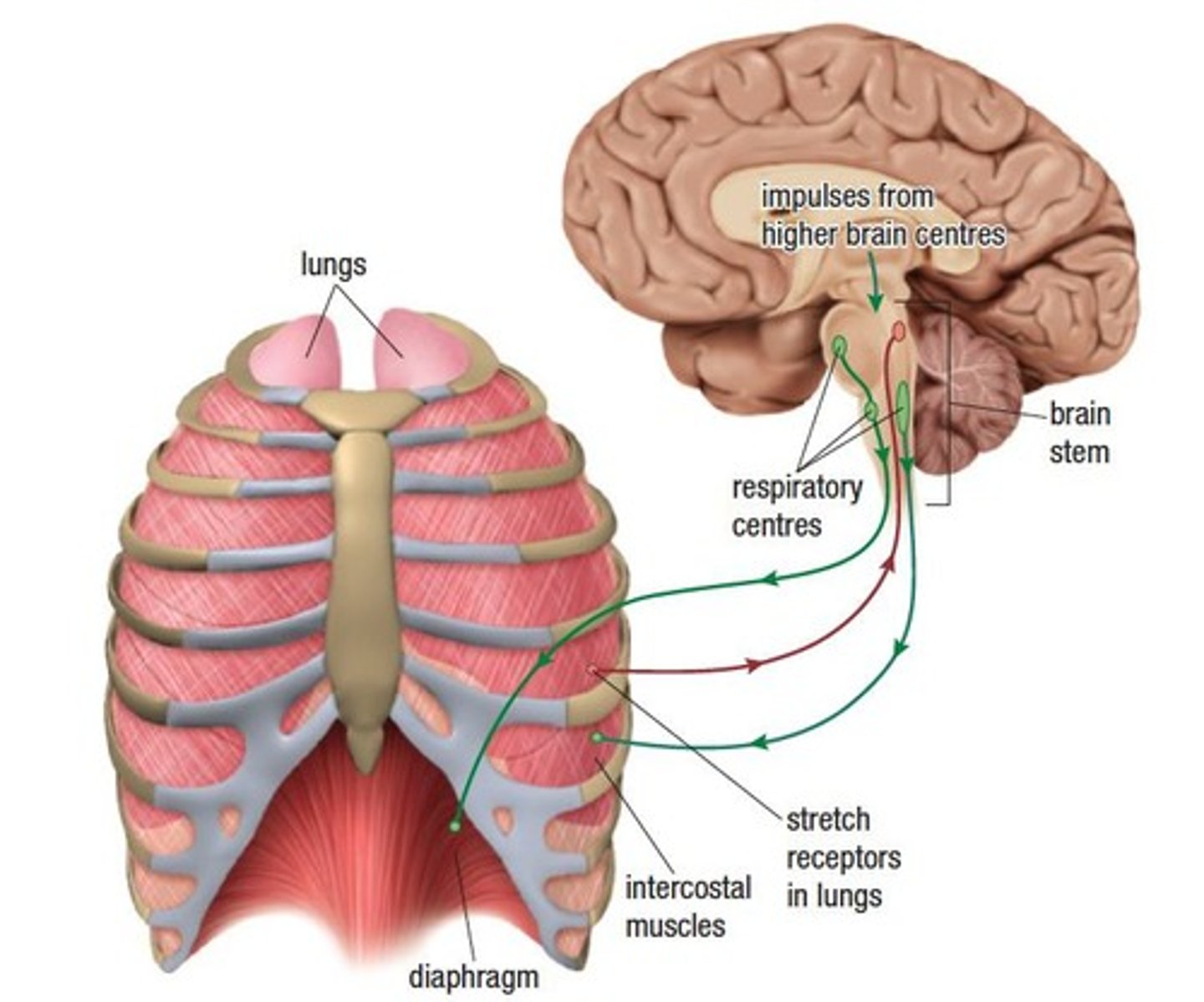
What happens during inhalation?
The brain signals the diaphragm and intercostal muscles to contract, causing inhalation.
What role do stretch receptors play in breathing?
Stretch receptors in the lungs send signals back to the brain indicating lung expansion, which helps regulate exhalation.
Can we consciously override breathing signals?
Yes, we can consciously override breathing signals for a short period, such as when holding our breath, talking, or singing.
What is a normal breathing rate for adults?
A normal breathing rate is 12-20 breaths per minute, depending on body size.
How does breathing rate differ between genders and ages?
Women tend to breathe more rapidly than men (16-20 breaths/minute), and children breathe twice as fast as adults.
What continuously monitors the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood?
Chemical receptors in the brain, arteries leading to the brain, and arteries leaving the heart.
What is the primary factor that controls the rate of breathing?
The concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood.
How does an increase in aerobic cellular respiration affect carbon dioxide levels?
It increases carbon dioxide levels, which combines with water to form carbonic acid and lowers blood pH.
What triggers the respiratory center in the brainstem?
Receptors detect a decrease in blood pH.
What happens to the breathing rate in response to increased carbon dioxide levels?
The brain sends signals to increase the breathing rate to exhale more carbon dioxide.
How does exercise affect breathing and heart rates?
Breathing and heart rates increase to reduce carbon dioxide levels in the blood.
What is VO2 in the context of oxygen usage?
The rate at which oxygen is used in the body, measured in mL/kg/min.
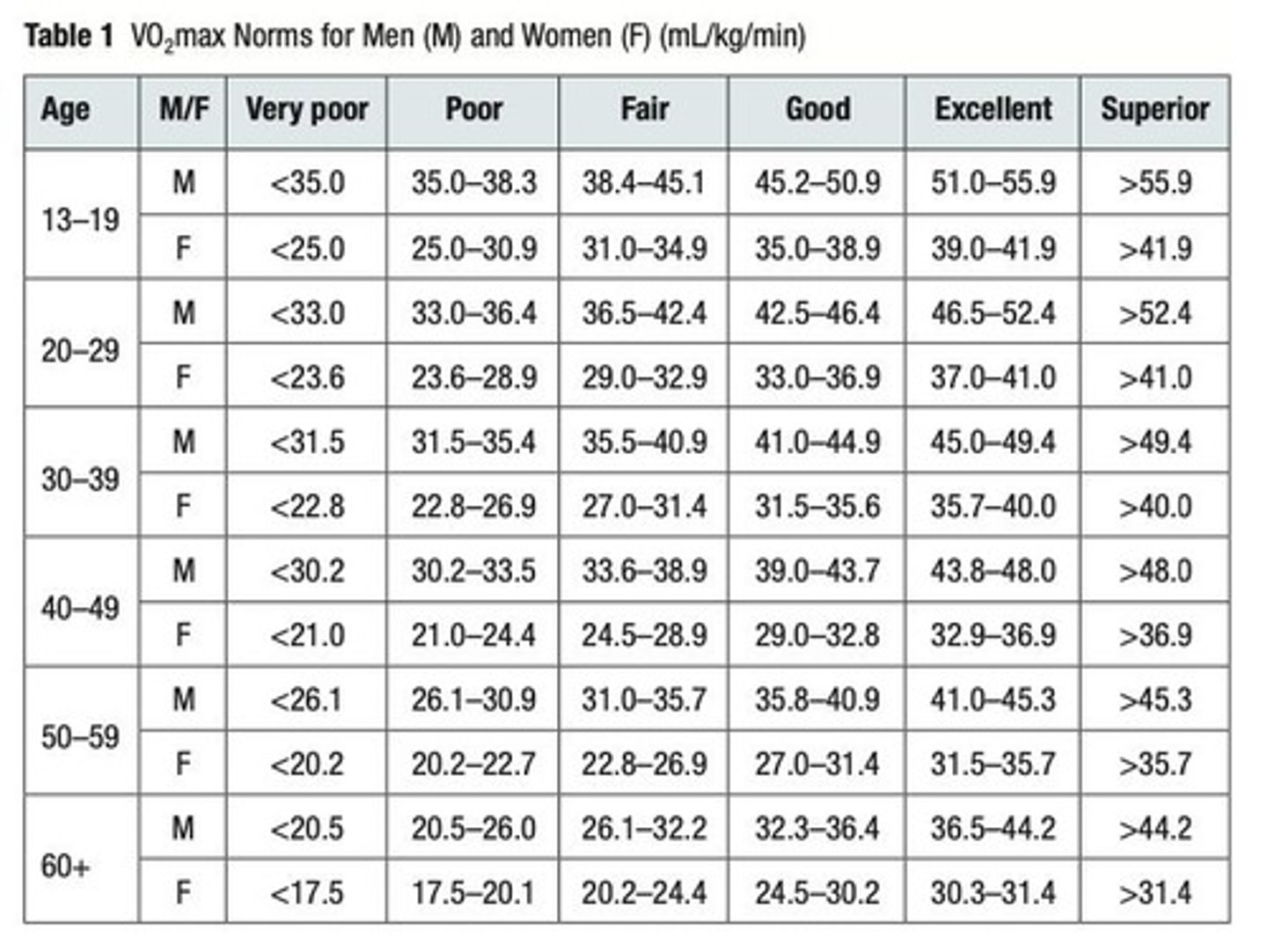
What does VO2 max represent?
The maximum amount of oxygen an individual can use during sustained, intense physical activity, also measured in mL/kg/min.
What factors influence VO2 and VO2 max?
Age, weight, and sex.
How can VO2 and VO2 max be measured?
Using a spirometer, which measures the volume of air moving into and out of the lungs.
What is the significance of the weak bond between oxygen and hemoglobin?
It allows for easier release of oxygen to body tissues.
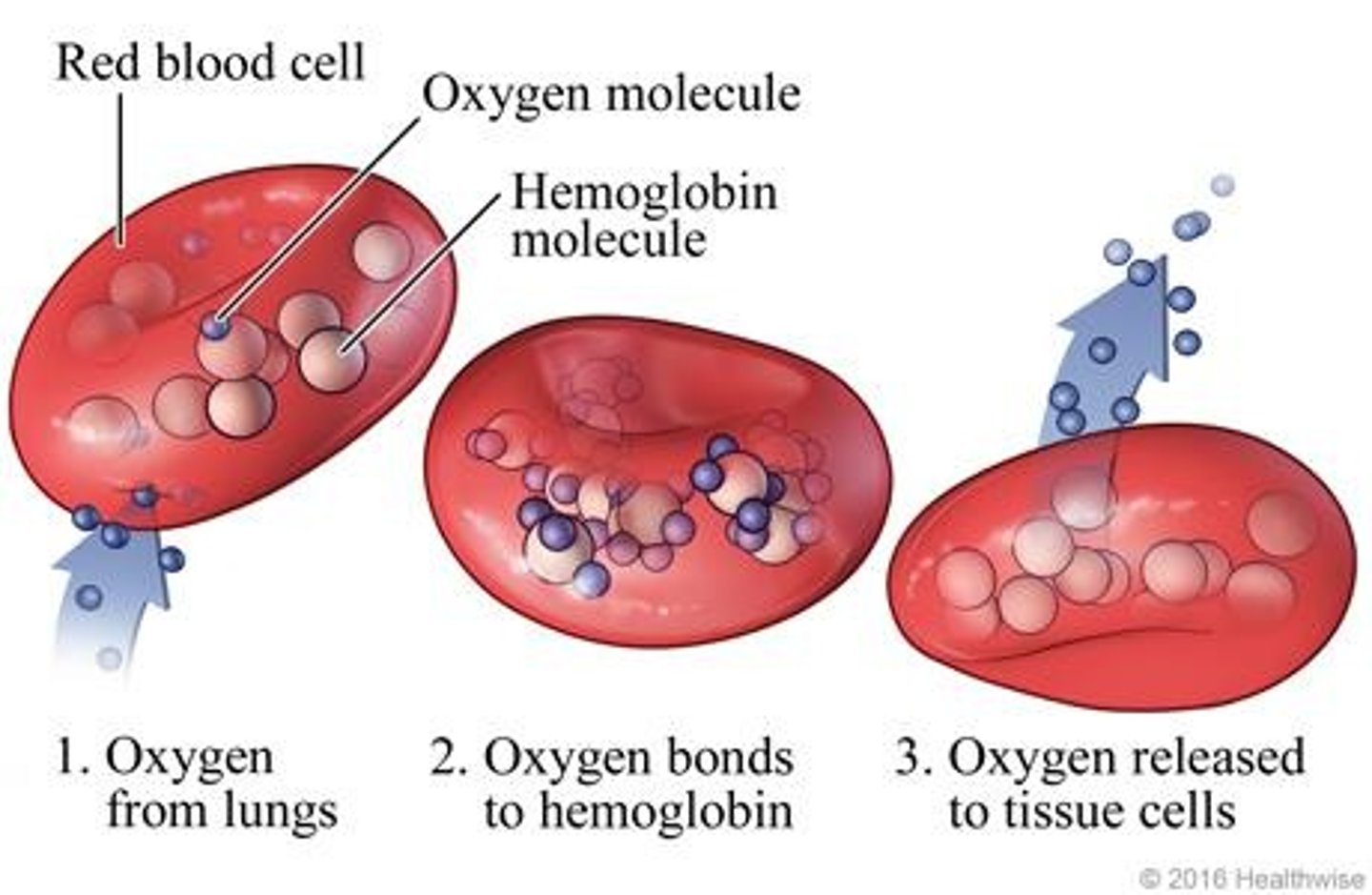
What role do red blood cells and hemoglobin play in gas exchange?
They transport oxygen from the lungs to the body and carbon dioxide from the body to the lungs.
What are the three ways carbon dioxide is transported in the blood?
1. Dissolved in plasma, 2. Bound to hemoglobin, 3. As bicarbonate ions (HCO3-).
What part of the hemoglobin molecule does oxygen bind to?
The iron atoms in the heme groups.
What part of the hemoglobin molecule does carbon dioxide bind to?
The amino acids in the globin chains.
Why is the breathing rate of a baby higher than that of an adult?
Babies have a higher metabolic rate and smaller lung capacity, requiring more frequent breaths.
Why does physical activity increase the breathing rate?
To meet the increased demand for oxygen and to eliminate carbon dioxide produced during exercise.
Explain the process of gas exchange in the lungs. What gases are exchanged?
Oxygen moves from the alveoli into the blood, while carbon dioxide moves from the blood into the alveoli.
How thick are the walls of the alveoli and capillaries?
Both are one cell thick, facilitating efficient gas exchange.
What is the process through which oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged in the lungs?
Diffusion, driven by differences in partial pressures.
What happens to blood coming from the heart to the lungs in terms of oxygen and carbon dioxide levels?
It has a low level of oxygen and a high level of carbon dioxide.
What is tidal volume (TV)?
The amount of air inhaled or exhaled during normal breathing.
What is inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)?
The additional amount of air that can be inhaled after a normal inhalation.
What is expiratory reserve volume (ERV)?
The additional amount of air that can be exhaled after a normal exhalation.
What is residual volume (RV)?
The amount of air remaining in the lungs after a forced exhalation.
What is vital capacity (VC)?
The maximum amount of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inhalation.