EMT HCC UNIT 3 EXAM!
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Three types of radio
Portable (handheld), mobile (in vehicle), and base station (fixed spot)
When to use cell phone vs radio to call
Use your radio first for all formal communication (Communicating with dispatch, medical direction, hospital, EMTS, and multiple agencies.
Use your cell phone only when the radio:
• Doesn't work
• Is out of range
• Would violate patient confidentiality
FCC (Federal Communications Commission)
The FCC has jurisdiction over all radio operations in the United States, including EMS. It regulates radio traffic, assigns frequencies, issues licenses, and ensures that communication is clear, safe, and legal.
- FCC makes sure EMTs, dispatchers, and hospitals use radios correctly, don't interfere with each other, and follow legal standards.
Repeat back medication orders
- After receiving the order, repeat the order word by word. Repeat it even if denied, do the procedure, or give medication.
- If order appears to be inappropriate, question the physician.
Medical Radio Report
units identification and level of providers, estimated time of arrival, patient's age and sex, chief complaint, brief, pertinent history of the present illness, major past illnesses, mental status, baseline vital signs, pertinent findings of the physical exam, emergency medical care given, response to emergency medical care, contact medical direction if required
Therapeutic Communication
Verbal and nonverbal communication techniques that encourage patients to express their feelings and to achieve a positive relationship.
Use eye contact
Be aware of your position and language
Use language only they can understand
Be honest
Use the patient’s proper name
Listen
Children:
Always come to the child’s eye level
Tell truth to children
Objective vs. Subjective
Objective is observable, measurable, and verifiable
Subjective is from an individual point of view
How to correct a PCR error
Electronic PCR:
Correct data and add an addendum that explains changes you made and why
Paper PCR:
Draw single horizontal line through error, initial, and then write correct info beside it; no erasing
Discovered at a later date:
single line through error, mark with initials and the date, and add correct info to the end of report or in sperate note
Oral Glucose
a form of glucose (a kind of sugar) that can be taken by mouth as a treatment for a conscious patient (who can swallow) with an altered mental status and a history of diabetes.
- Tube of gel
- Apply to a tongue depressor and place between the patient’s cheek and gum or under the tongue
- Patient swallows glucose so it can be easily absorbed into the digestive tract and bloodstream, which carries it to the brain
Hypoxia
Low oxygen saturation of the body, not enough oxygen in the blood
Signs = altered mental status, cyanosis, increased work of breathing
Medications EMT's can administer
Aspirin, oral glucose, oxygen, prescribed bronchodilator inhalers, nitroglycerin, activated charcoal, naloxone, and epinephrine (auto-injectors)
Epinephrine
Patient that is highly allergic to something causes life-threatening changes in the airway and circulation (anaphylaxis)
Reverses: Medication that will help constrict blood vessels and relax airway passages
- Epinephrine Auto-injector is a syringe with a spring-loaded needle that will release and inject epinephrine into the muscle
5 Rights
right patient, right drug, right dose, right route, right time
Routes of Administration
Oral, Sublingual (placed under tongue and dissolves), Inhalation, Intranasal (sprayed in nostrils), Intravenous (Injected into a vein), Intramuscular (Injected into a muscle), Subcutaneous (Injected under skin), Intraosseous (Injected into bone marrow cavity), and Endotracheal (Sprayed directly into a tube inserted into the trachea.)
Reassess pt. after meds
After admistration, you must reassess
Look for any changes - Improvements, deteriorations, or unintended effects
Clearly document medications given -5 Rs and any effects should be documented
What's normal/abnormal signs for children
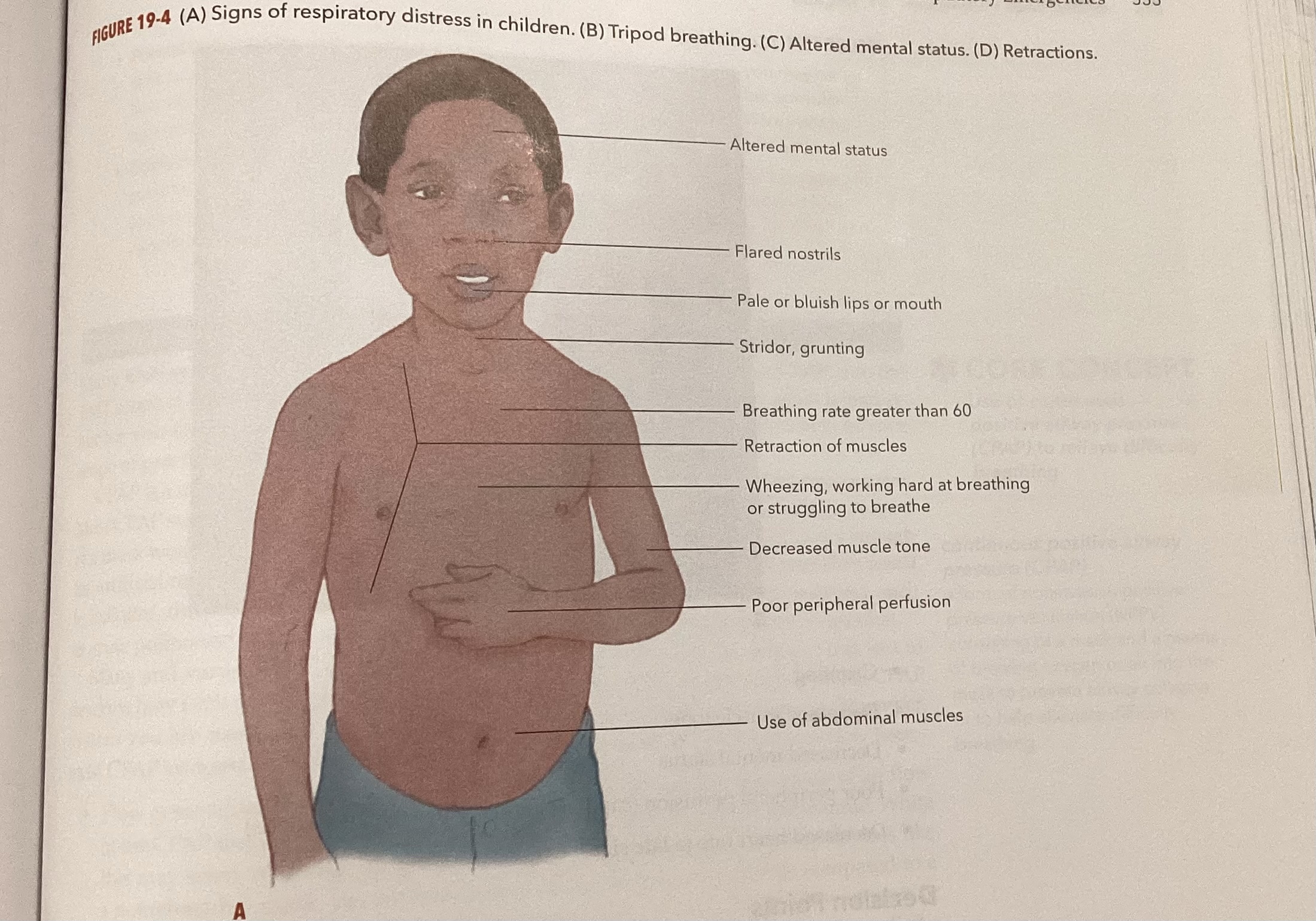
Signs of inadequate breathing/airway
Mental status changes, cyanosis, rapid heart rate, rapid breathing, sweaty skin, fats respiratory rate, slowing or irregular respirations, inability to speak, no lung sounds, low oxygen saturation, dying respirations, irregular rate, breath sounds may be diminished or absent, tidal volume will be inadequate or shallow, chest expansion may be inadequate or unequal, and respiratory effort is increased
BVM
Positive pressure ventilation
Positive pressure: air is pushed into lungs, increases pressure inside airway, and used when patient can’t breathe well on their own
EX. BVM, ventilator, CPAP
Negative Pressure: air is pulled into lungs, lowers pressure inside chest, used when normal healthy breathing
EX. Normal breathing
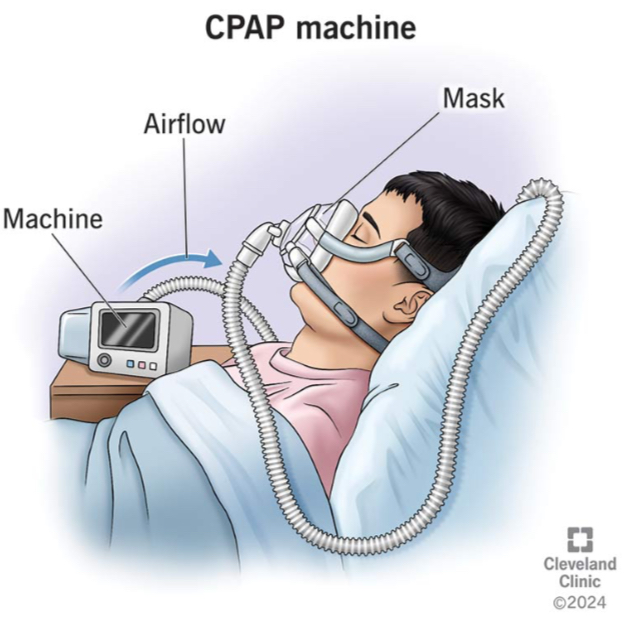
CPAP
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
Most common problem of middle age or older patients
Smoking ciagarette causes most of cases
MDI and Nebulizer
pulmonary edema
fluid in the air sacs and bronchioles (lungs)
COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
A group of lung diseases that block airflow and make it difficult to breathe.
2 types of COPD
emphysema (damage to lungs overtime) and chronic bronchitis (long term couch with mucus)
pneumonia
Bacterial infection of the lungs
Epiglottis
A flap of tissue that seals off the windpipe and prevents food from entering.
pneumothorax
air in the pleural cavity caused by a puncture of the lung or chest wall
coronary arteries
blood vessels that branch from the aorta and carry oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle
ACS (acute coronary syndrome)
group of conditions caused by decreased blood flow through the coronary arteries (STEMI, NSTEMI, unstable angina)
Palpations
left ventricle
Pumps oxygenated blood into the aorta
croup
an acute respiratory syndrome in children and infants characterized by obstruction of the larynx, hoarseness, and a barking cough
Nitroglycerin
nitrate drug used in the treatment of angina, vasodilator
Aspirin
coronary artery disease CAD
a condition affecting arteries of the heart that reduces the flow of blood and the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the myocardium; most often caused by atherosclerosis
aneurysm
a localized weak spot or balloon-like enlargement of the wall of an artery
Angina vs MI
angina (low oxygen to heart tissues) = no dead heart tissues. MI=
dead heart tissue present.
CHF (congestive heart failure)
condition in which the heart cannot pump enough blood to the rest of the body
Chain of survival
Most important actions needed to treat life threatening emergencies
- Early Access, Early CPR, Early Defibrillation, Early Advanced Care
V-fib
ventricular fibrillation
When to transport to cardiac center
Child vs. adult cardiac arrest
High performance CPR
Providing high-quality chest compressions as part of a well-organized team response to a cardiac arrest.
When to stop CPR
S- patient starts breathing and has a pulse
T- patient transferred to another person trained in BLS
O- out of strength to continue
P- a physician is present or providing online direction and assumes responsibility of the patient, gives direction to stop
When to switch roles in CPR
Every five cycles or 2 minutes
Communication with family during cardiac arrest
AED Operation
1. Turn on AED
2. Follow voice command
3. Remove Pads from pad pack
4. Place Pads
5. Let AED analyze
6. Shock if necessary (not follow AED's command)
7. Do not Turn OFF AED until PAX is removed from A/C
No Shock Advised what you should do
Pad placement and pace makers
Dyspnea
difficult or labored breathing
Bradycardia
slow heart rate (less than 60 bpm)
Tachycardia
A rapid heart rate, more than 100 beats/min.
Insulin
A hormone produced by the pancreas or taken as a medication by many diabetics
apnea
absence of breathing
aura
a sensation experienced by a seizure patient right before the seizure, which might be a smell, sound, or general feeling
3 phases of a seizure
Tonic (tensing), clonic (jerks violently), and postictal (recovery)
Hypoglycemia
hyperglycemia
3 P's
polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia
stroke
A sudden attack of weakness or paralysis that occurs when blood flow to an area of the brain is interrupted
Thrombolyotic drug
Lyme disease
Tick-borne disease caused by the spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi.
Syncope/dizziness
"Passing out", loss of consciousness or fainting
allergic rxn vs anaphylaxis
febrile seizures
Seizures that result from sudden high fevers, particularly in children.
Histamine
Chemical stored in mast cells that triggers dilation and increased permeability of capillaries.
Allergies and antibodies
How and when to give epi pen
Lyme disease
Sepsis
infection (local), sepsis (systematic), and septic shock (systematic with hypotension)
Meningitis
inflammation of the meninges of the brain and spinal cord
EMS role in new diseases
carbon monoxide
a colorless, odorless, and poisonous gas
Poison
When to not enter with poison
Activated Charcoal
a substance that absorbs many poisons and prevents them from being absorbed by the body
Alcohol use
Opioid triad
coma, depressed respiration, pinpoint pupils
uppers
stimulants such as amphetamines that affect the central nervous system to excite the user
Downers
depressants, such as barbiturates, that depress the central nervous system, which are often used to bring on a more relaxed state of mind
referred pain
pain that is felt in a location other than where the pain originates
radiating pain
pain felt at the site of tissue damage and in nearby areas
(Spread)
Cholecystitis
Abdominal pain, portion of comfort, guarding,
Major abdominal cpmplaints based on quadrants
Behavioral emergency
when a patient's behavior is not typical for the situation; when the patient's behavior is unacceptable or intolerable to the patient, his family, or the community; or when the patient may harm himself or others
Safety on behavioral emergency
Same sex standard for treating behavioral pt.
Signs of violence on scene/ when to never leave
Anemia
A condition in which the blood is deficient in red blood cells, in hemoglobin, or in total volume.
hemodialysis
the process by which waste products are filtered directly from the patient's blood
spleen
Organ near the stomach that produces, stores, and eliminates blood cells
liver
produces bile
Pancreas
Regulates the level of sugar in the blood
kidneys
Filter blood from the renal arteries and produce urine as waste
Gallbladder
A muscular sac attached to the liver that secretes bile and stores it until needed for digestion
stomach
large muscular sac that continues the mechanical and chemical digestion of food
excited delirium
A serious behavioral condition in which a person exhibits agitated behavior combined with disorientation, hallucinations, or delusions; also called agitated delirium or exhaustive mania.
Perineum dialysis
Role of potassium in dialysis