Pharm I - Exam II
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
Barbiturates are weak ___ with a pKa around 7.9
Acids
Methohexital (Brevital) is used to a limited degree in the US. Both methohexital and thiopental (Pentothal) are categorized as ____ ____ acting barbiturates with a duration of action of about _-_ mins
Ultra short
39-60
Barbiturates may stimulate ____ release from ___ ___ which may affect bronchial tone as well as blood pressure
Histamine ; mast cells
Barbiturates can precipitate and attack of ___ and they are absolutely contraindicated in those identified with the condition
Porphyria
Distribution half-life (also termed …. half-life) represents the time required for half of the drug to …
Alpha
Reach the receptor AKA achieve onset of symptoms
Elimination half-life (also termed ___ half-life) refers to the time required for 50% of the drug to …
Beta
Be metabolized (cleared)
Arrange the following benzodiazepines in order from shortest to longest distribution half-life (alpha half-life): lorazepam, midazolam, diazepam
Lorazepam (Ativan): 4-5 mins*
Midazolam (Versed): 7-15 mins
Diazepam (Valium): 10-15 mins
*this is why we use Ativan for acute seizure activity
Arrange the following benzodiazepines in order from shortest to longest elimination half-life (beta half-life): lorazepam, midazolam, diazepam
Midazolam (Versed): 2-4 hrs*
Lorazepam (Ativan): 10-16 hrs
Diazepam (Valium): 20-50 hrs
*this is why we used versed during induction; it will wear off quickly after we have induced the patient
Reversal agent for benzodiazepines
Flumazenil (Romazicon)
Which FIVE of the following drugs are >90% protein bound? (Diazepam, lorazepam, midazolam, etomidate, Propofol, ketamine, dexmedetomidine, methohexital, thiopental)
Diazepam: 98%
Lorazepam: 90%
Midazolam: 94%
Propofol: 98%
Dexemedetomidine: 94%
For the average 70kg man, list the average volumes for each of the following fluid compartments: plasma, interstitial fluid (IF), ECF, ICF
Plasma: 4L
IF: 10L
ECF (plasma + IF): 14L
ICF: 28L
The extracellular fluid compartment is comprised of which two other fluid compartments? (Plasma, interstitial fluid, or intracellular fluid?)
Plasma + IF
The more lipid soluble a drug, the ___ the volume of distribution
Higher (greater propensity to enter and disperse into the tissues)
A “large” volume of distribution (Vd) is considered to be >_L/kg?
0.6 L/kg
A “small” volume of distribution (Vd) is considered to be <_L/kg?
0.4 L/kg
A drug with a large Vd (>0.6L/kg) is widely distributed in the … and is likely … soluble?
Body (tissues) ; lipid
A drug with a small Vd (<0.4L/kg) is largely contained in the … and is likely … soluble?
Plasma ; water
Formula for volume of distribution
Vd = (amount of drug in the body) / (plasma drug concentration)
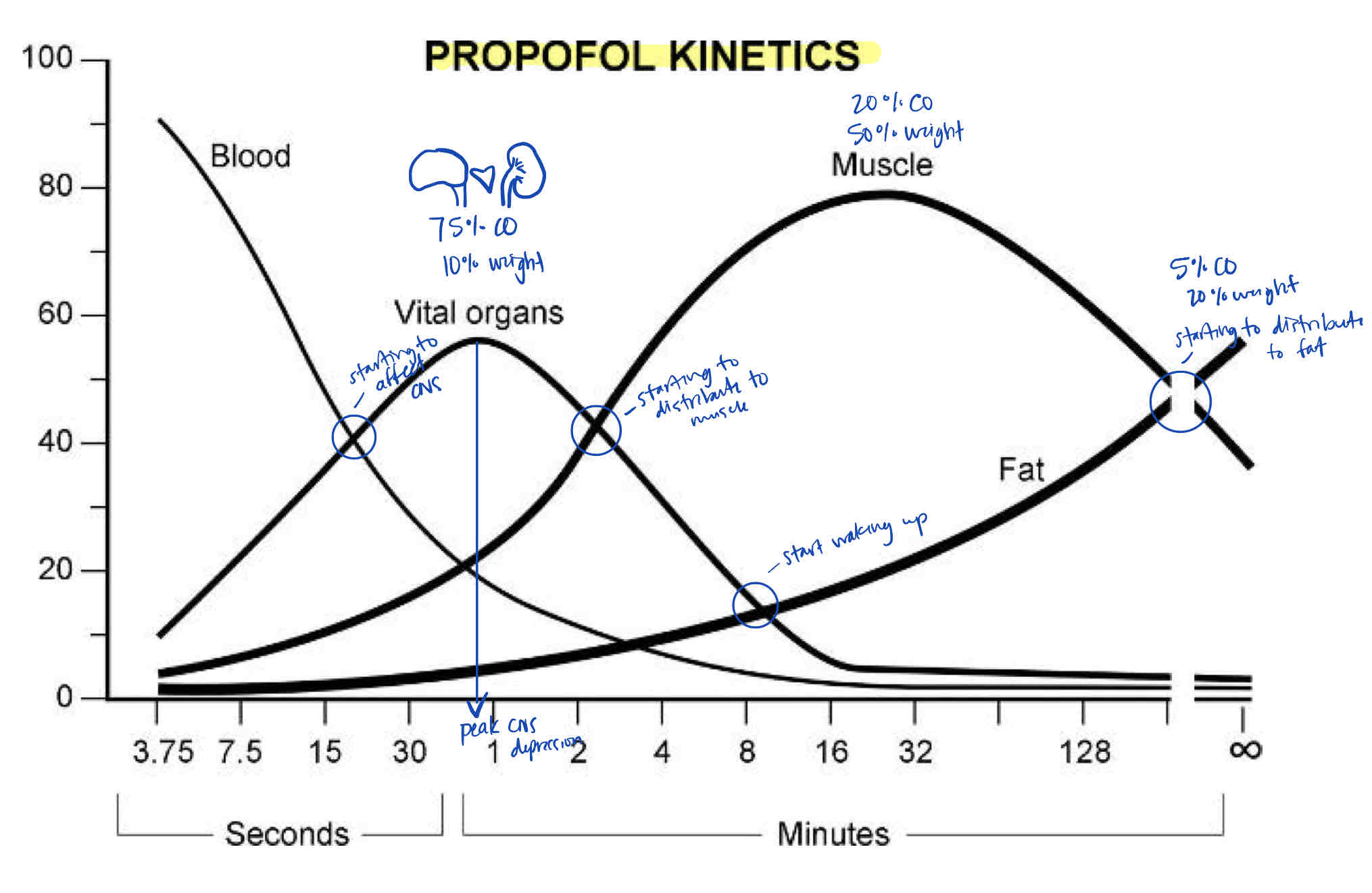
Note the range of CNS effects, peak CNS effects, and especially where the Propofol begins to leave the vital organs group for the fat group. (AKA: why does the patient wake up around 8 mins after a Propofol Bolus?)
Redistribution to the fat group removes Propofol from the CNS (vessel-rich group)
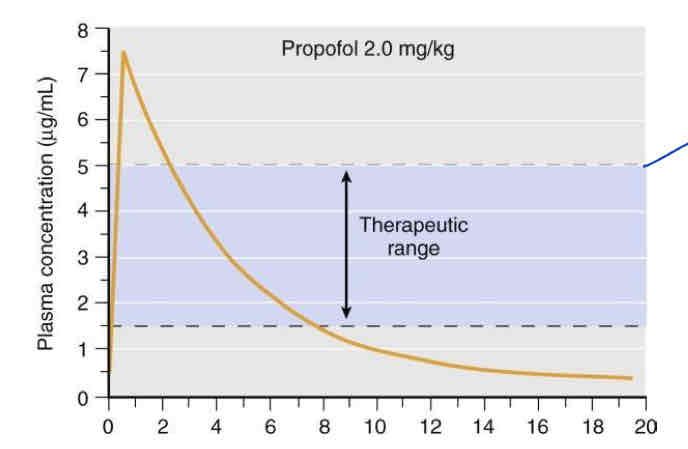
The top of the therapeutic range (5mcg/mL) on this graph represents … half-life. Why?
Distribution (alpha) half-life (per Jess)
Alpha half-life = time required to reach the receptor
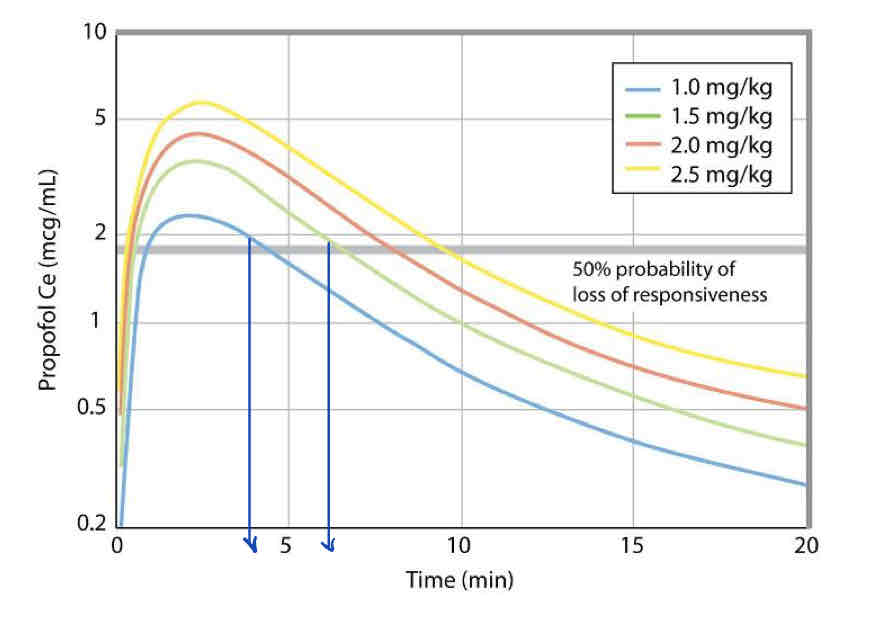
What patient response occurs at the two vertical lines drawn over this graph?
End LOC (patient starts to wake up)
Takeaway: a standard 2mg/kg of Propofol gives you about 7-8 minutes of unconsciousness for intubation
Protein binding >__% is considered significant?
90
Albumin has a … charge and preferentially binds to weak … drugs
Negative ; acid
Alpha 1 acid glycoprotein (AAG) preferentially binds to weak … drugs
Base
A drug that is 99% protein bound and 1% free fraction… suddenly, the drug becomes only 97% protein bound with a 3% free fraction. This increases the unbound (active) drug concentration by ___%
300
Four types of patients that are at risk for adverse effects from highly protein bound drugs
Malnourished
Severe liver disease
Severe kidney disease
3rd trimester of pregnancy
… is a very important receptor in the CNS that has inhibitory effects when agonized
GABA-A
The GABA-A receptor is comprised of which three subunits?
Alpha, beta, gamma
Which ion channel is present on GABA-A receptors and how does it affect the target cell?
Cl- ; when agonized, the Cl- channel on the GABA-A receptor opens and causes in influx of Cl- into the cell, hyperpolarizing it and preventing excitatory stimulation
… is the principal inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS
GABA
… is the principal excitatory neurotransmitter in the CNS
Glutamate
NMDA receptors are activated by the agonist … and co-agonist … when voltage changes displace Mg2+ from the ion channel pore
Glutamate ; glycine
Ketamine is an antagonist to which neurotransmitter?
Glutamate
Which two ion channels are present on the NMDA receptor and what effect do they have on the target cell when activated by glutamate?
Na+ and Ca2+ ; activation of the NMDA receptor by glutamate opens these ion channels, causing an influx of Na+ and Ca2+, depolarizing the cells
Ketamine acts on NMDA receptors primarily by a … … mechanism
Pore-blocking
Ketamine … the NMDA receptor
ANTAGONIZES
Benzodiazepine are … agonists that enhance the effectiveness of GABA
Allosteric
Benzos, Propofol, and etomidate are all … mimetic
GABA
Which of the following is NOT an agonist?: benzos, Propofol, etomidate, ketamine, and dexmedetomidine
Ketamine (NMDA antagonist)
Midazolam only provides … amnesia
Anterograde
Benzos have a sedative effect and an antianxiety effect. With prolonged use, tolerance decreases the patient’s sensitivity to which one of these effects?
Sedative effects (They will still get the anxiolytic property but might not feel as sleepy)
Which GABA-mimetic drug class is used for its hypnotic sleep properties and lacks several pharmacological properties of benzos. What are some examples of this drug class?
Non-benzodiazepine receptor agonists (NBRAs)
Zolpidem (Ambien), Eszopiclone (lunesta), zaleplon (sonata), zopiclone (Imovane)
Z drugs (NBRAs) are selective enough to only act on the alpha … subunit of the GABA receptor. This allows z drugs to produce sleep without relieving … or producing … …
Alpha 1
Anxiety ; muscle relaxation
Chemically, Z drugs are NOT … but they do act on benzodiazepine receptors
Benzodiazepines
GABA-A subunit alpha 1 causes
Sedation
GABA-A subunit alpha 2 and subunit alpha 3 cause
Muscle relaxation and anxiolysis
GABA-A subunit alpha 5 causes
Cognitive effects
All of the following drugs are weak bases EXCEPT…
(Valium, Ativan, versed, etomidate, Propofol, ketamine, dexmedetomidine)
Propofol (weak acid)
Which two induction anesthetics are known to cause pain on injection?
Etomidate and Propofol
Lipid-soluble drugs (Propofol) are difficult to get into IV solutions and require … that can be irritable to veins and cause pain on injection
Solvents
Propofol’s high lipid content increases the risk of … … if it is not used within a certain amount of time after being drawn up or spiked?
Bacterial contamination
(6 hours for syringe and 12 hours for bottle w/tubing)
Propofol’s lecithin content was previously believed to cause reactivity in patients with allergies to …, …, and …
Current evidence shown no contraindications to Propofol use in patients with these allergies
Egg, soy, peanut
… is the ONLY drug that is technically classified as an IV anesthetic by the FDA. Most other induction anesthetics are classified as … …
Ketamine ; sedative hypnotics
Induction dose, onset, and duration for etomidate
Induction dose: 0.2-0.3 mg/kg
Onset: <30 seconds
Duration: 5-10 mins
Induction dose, onset, and duration for Propofol
Induction dose: 1-2 or 1-3 mg/kg
Onset: <30 seconds
Duration: 3-8 mins
Induction dose, onset, and duration for Ketamine
Induction dose: 1-2 mg/kg
Onset: 45-120 seconds
Duration: 60-120 mins
Induction dose, onset, duration for dexmedetomidine
Induction dose: 0.5-1 mcg/kg over 10 mins followed by continuous infusion of 0.2-0.7 mcg/kg/hr
Onset: 2-5 mins
Duration: 10-30 mins
The brain has a high metabolic rate and receives approximately ..% of cardiac output
15
…% of the brain’s energy consumption is used to support electro physiologic functions
60
CBF is … correlated with local cerebral metabolism
Directly (“tightly coupled”)
CBF is autoregulate and held constant over a MAP range between … and … mmHg
65-150 mmHg
Beyond doses of _ MAC, direct cerebral vasodilation results in an increase in CBF and cerebral blood volume
1 MAC
Ketamine has what effect on CMR and CBF
Increases both
Barbs, Propofol, ketamine, volatiles, and xenon have neuroprotective efficacy and can reduce … … …
Ischemic cerebral injury
Which anesthetic is associated with regional reductions in blood flow and can exacerbate ischemic brain injury?
Etomidate
In patients with rapidly elevated ICP, … provides the greatest margin of safety and ability to reduce ICP. Care must be taken not to compromise CPP through …
Propofol ; hypotension
… or … … is effective for controlling raised ICP after severe head injury
Mannitol or hypertonic saline
Prophylactic long-term hyperventilation in the first 24 hrs after severe TBI should be avoided because it can compromise …
Cerebral blood flow (can be used acutely for neurological deterioration or in surgery)
WHAT IS THE PRIMARY MECHANISM BY WHICH PROPOFOL CAUSES CV DEPRESSION?
Decreased SVR (through venodilation)
Five mechanisms of anesthetics that cause a decrease in BP
CNS depression
Direct cardiac depression
Decreased SVR
Baroreceptor depression
Hormonal changes (renin?)
Which IV anesthetic has more respiratory depressive side effects, prop or etomidate?
Propofol
Which IV anesthetic maintains airway reflexes, respirations, and is a SIGNIFICANT bronchodilator?
Ketamine
Small doses of IV … at the end of a procedure can help prevent bronchospasm/larygnospasm
Ketamine (d/t bronchodilatory effects)
Overall effect of IV anesthetics on renal and GI function
Transient depression
Etomidate may cause enzyme induction of … and suppress the enzyme …
ALA synthetase (in porphyria)
11-beta hydroxylase (important in the pathway for cortisol and aldosterone production)
Which medication can cause a low APGAR score if administered too soon before delivery?
Propofol
Risk factors for Propofol infusion syndrome (PRIS):
Young age, doses >4-5 mg/kg/hr for >48 hrs, critical illness, high fat/low carb intake, inborn errors of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation, concomitant catecholamine infusion, steroid administration
S/s of Propofol infusion syndrome (PRIS):
CV: hypotension, wide QRS, bradycardia, VT/VF/asystole
Resp: hypoxia
Renal: AKI, hyperkalemia, green pee
Musc: rhabdomyolysis
Metabolic: hyperthermia, metabolic acidosis
Hepatic: hepatomegaly, transaminitis, steatosis, hypertriglyceridemia, lipidemia
Administering Ketamine is pretty much like giving our patients which two street drugs?
PCP and LSD
Which IV anesthetic will NOT cause the patient to go through the normal stages of anesthesia?
Ketamine (d/t lack of action on the GABA receptor)
Ketamine causes an unconscious and amnestic state referred to as … …
Dissociative anesthesia
Effects of ketamine on the eyes
Nystagmus and increase IOP
Like N2O, Ketamine has an … effect
Analgesic
When giving Ketamine, consider administering a … to prevent emergence delirium, nightmares, and hallucinations
Benzodiazepine (versed)
Ketamine increases salivation and respiratory secretions and might warrant the administration of …
Glycopyrrolate (Robinul)
Ketamine should be administered with caution in patients with:
HTN, angina, CHF, increased ICP/IOP, psychiatric disorders, airway problems? (I guess with secretions? Like CF?)
What are some clinical uses of ketamine in anesthesia practice?
Shock/CV instability
Severe dehydration/hypovolemia
Bronchospasm
Supplement an inadequate block/spinal
Low dose analgesia
Induction
Which IV anesthetic causes sedation that resembles natural sleep?
Dexmedetomidine
Which two IV anesthetics act as mild antiemetics?
Propofol and dexmedetomidine
Where are alpha-2 receptors located?
Presynaptic neurons (served as negative feedback loop for NE to decrease SNS activity)
Vascular smooth muscle (cause vasoconstriction, but to a lesser degree than the sympatholytic effects in the presynaptic neuron)
Mechanism of action of dexmedetomidine
Alpha-2 agonist
Dexmedetomidine prefers … receptors over … receptors
Alpha2 over alpha1
Precedex is a highly selective alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist that confers sedative, anxiolytic, analgesic, and sympatholytic properties; importantly, these effects are achieved with little to no observed … …
Respiratory depression
Which has a greater affinity for the alpha-2 receptor, dexmedetomidine or clonidine?
Dexmedetomidine
Which IV anesthetic agent can be added to a nerve block to prolong its duration of efficacy?
Dexmedetomidine
Which IV anesthetic agent can be administered near the end of a case to prevent emergence delirium?
Dexmedetomidine
… can be used as an adjuvant medication in locoregional technique and has been effectively administered as part of peripheral nerve blocks, IV regional analgesia, and central neuraxial anesthesia
Dexmedetomidine
Benefits of using dexmedetomidine with locoregional techniques? (I.e. regional blocks)
Hasten block onset
Prolong block duration
Reduce pain scores
Reduce early postoperative opioid consumption either with neuraxial blocks or peripheral nerve blocks
Dexmedetomidine was shown to cause … with all types of neuraxial routes, peripheral nerve blocks, and transverse abdominis plane block
Bradycardia
Dexmedetomidine can be used to treat/prevent postop shivering, but seems to be no more effective than standard management techniques like … and …
Forced air warming blankets and opioids
(Dex increases cost of care and potentially prolongs the need for monitoring and observation)