Final Paper and Presentation
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Final Paper and Presentation

Hypothesis testing
lIn addition to descriptive statistics, most researchers compute inferential statistics
Mathematical tests to answer RQs
•Define hypotheses
•Choose appropriate statistical test
•Choose significance level and criterion for accepting/rejecting hypothesis
lbinary decision-making process
Hypotheses
lPredictions: expected relationships between variables
lHo: no relationship between variables or groups
lHA: expected result of experimental research
This is what I ask of you in your project
directional vs. non-directional
Briefly…
lCan you state the hypothesis / hypotheses for your proposed study?
•It is expected that…
•It is predicted that…
•Think: is your hypothesis directional or non-directional?
Hypothesis testing
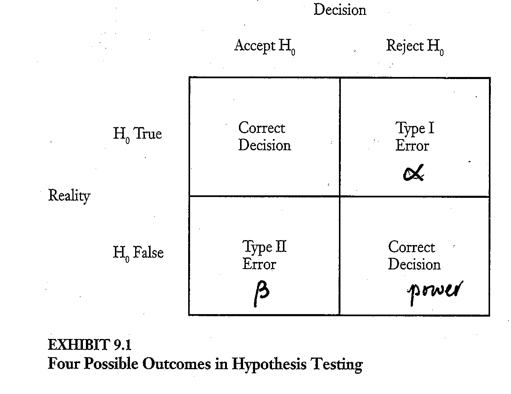
lIn reality, error is always possible
Hypothesis testing
lWe try to minimize error
lSampling and power
sample size (n) determines the power of the statistical tests
•larger sample à more powerful test
•samples with n < 10 are subject to Type II error
power is the probability of rejecting Ho when it is false (a correct decision)
Hypothesis testing
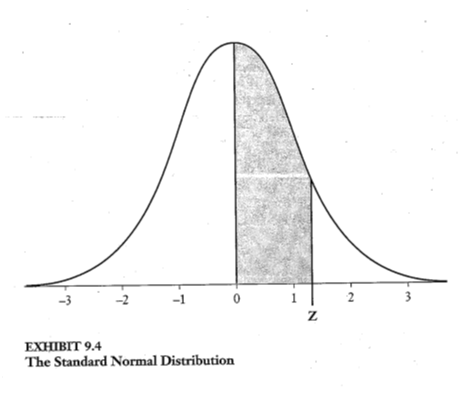
lParametric statistical tests rely upon the normal distribution
model for evaluating data
frequency pattern of scores
•unimodal
•mean and median are centered
Hypothesis testing
Hypothesis testing
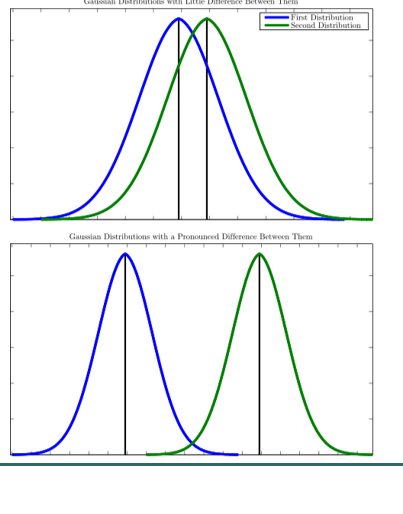
lCentral Limit Theorem (CLT)
•a distribution will be normal if the sample is large enough
(n > 30)
•may not always hold for clinical populations, which are often
•highly variable
•multimodal
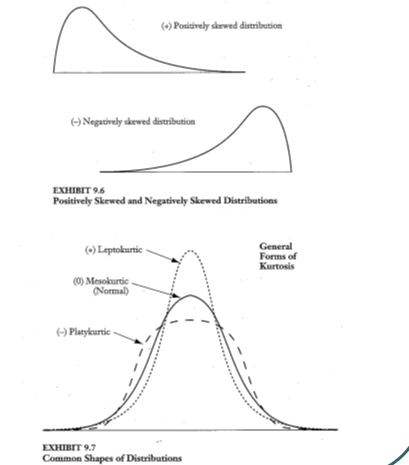
Statistical tests of significance
lParametric vs. non-parametric tests
Assumptions underlying parametric statistics
•Normal population distribution
•Homogenous population variances