Horace: HIV Background
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
HIV infection leads to which disease if untreated?
AIDS
AIDs is defined as:
CD4 T cell count of < 200
or
< 14% of total T cell count
or
diagnosis of one of the AIDs defingin conditions
first known case of HIV was in ____
1959
what are the three modes of transmission for HIV
sexual
parenteral
perinatal (vertical)
what is the main method of HIV transmission
sexual intercourse
what type of sex causes the most HIV transmission
receptive anal sex
what are the ways that HIV can be transmitted parenterally?
blood transfusions
injection drug use (sharing needles)
skin puncture
mucous membrane contact
how can vertical transmission of HIV occur
through pregnancy, delivery, and breast feeding
the longer the time from membrane rupture to delivery will ____ the risk of vertical transmission of HIV
increse
HIV + moms are instructed to not ____
breast feed
what is the hallmark of untreated HIV infections
profound T cell depletion and severe immunosuppression that puts the pt at a hgih risk for opportunistic infections
what is the main cause of morbidity and mortality in pts with HIV
opportunistic infections in setting without access to antiretroviral drugs
which cells does HIV infect
T-helper lymphocytes, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, and brain microglia
what receptor does HIV particles bind to
CD4
CD4 receptors are found on which cells
T-helper lymphocytes, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, and brain microglia
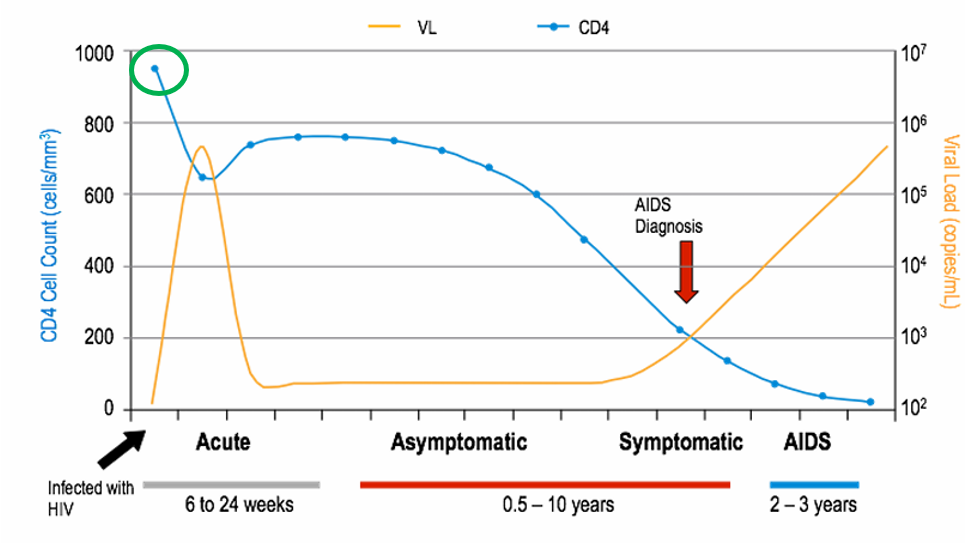
explain what the green circle is representing
this is the highest a pts CD4 cell count will be in their whole life is they never get any tx
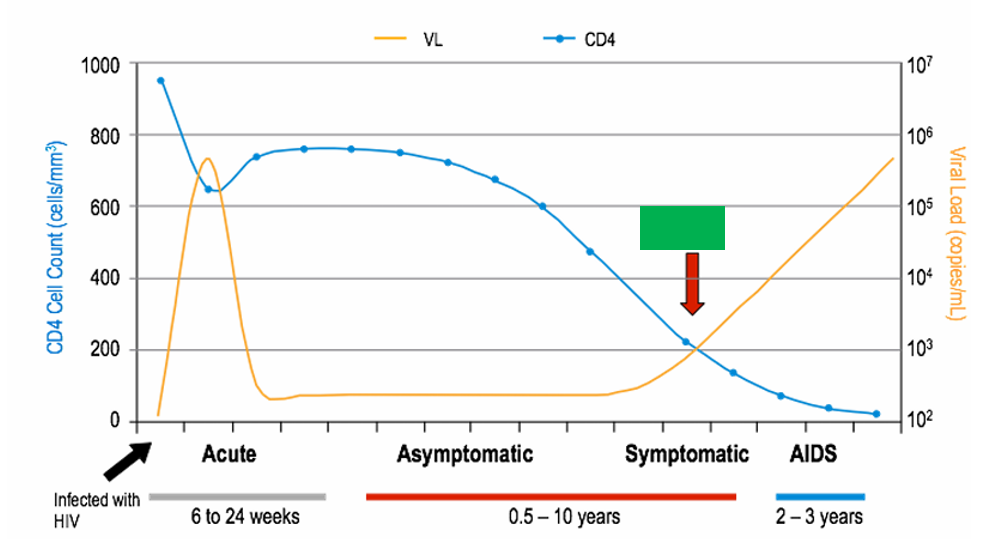
what does the red arrow point to
CD4 level of 200 which is when a person is diagnosed with AIDS
if it takes a person 10 years after an HIV infection to be symptomatic then they are called…
long term non-progressors
long term non-progressor
someone that took 10 years to show any symptoms of HIV infection
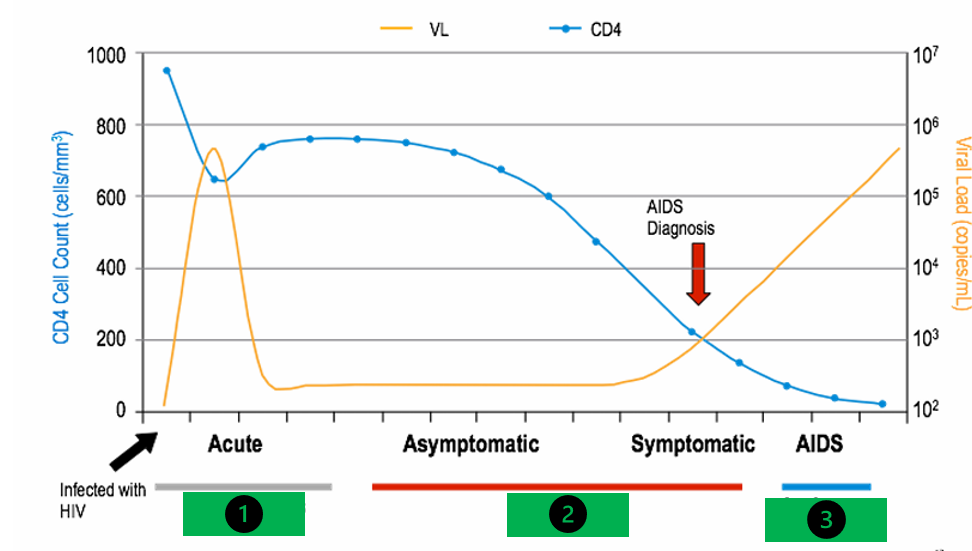
how long is the acute phase of HIV (1)
6 to 24 weeks
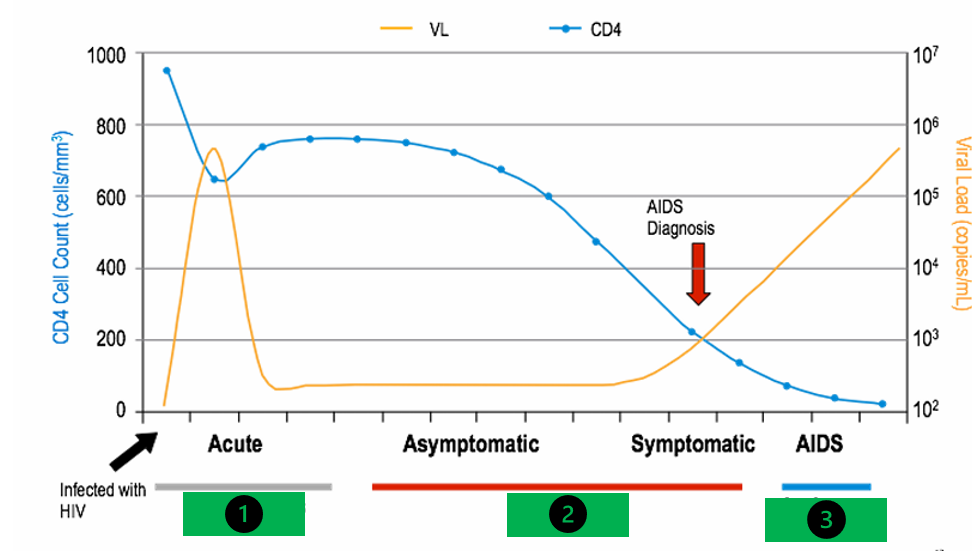
how long is the asymptomatic and symptomatic phase of HIV (2)
½ a year to 10 years
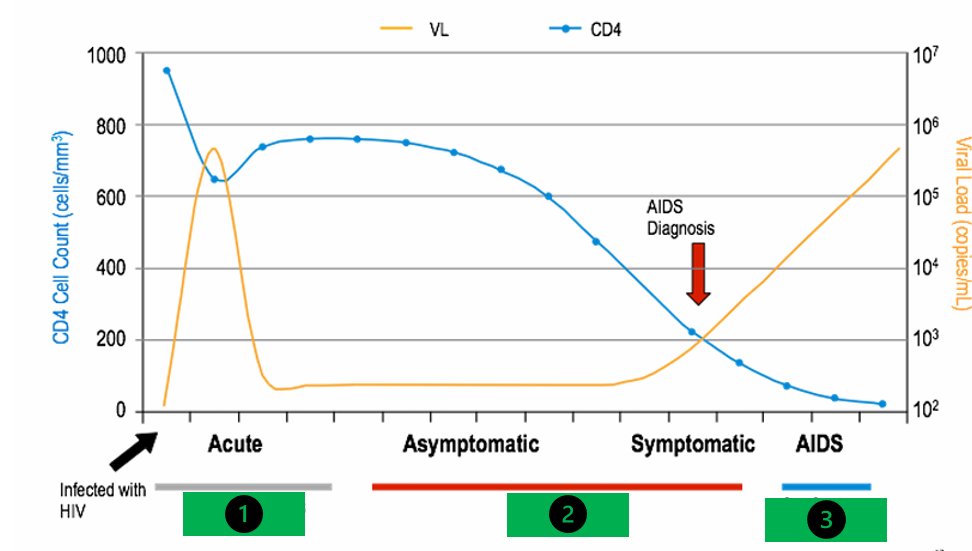
how long is the AIDs phase (3)
2-3 years
who should be tested for HIV
anyone with STIs
high risk pts
all preg ppl
ppl with tuberculosis
pplk with HBV or HepC
anyone between 13-64 yrs of age
who is considered high risk for HIV
ppl with alot of sexual partners, sex workers, and ppl who share partners
anyone aged ____ should be tested for HIV
13-64
anyone with which diseases should always be tested for HIV
tuberculosis, HepB and HepC
what are the two categories of testing that can be done for HIV
antibody testing and confirmatory testing
what are the antibody testing options for HIV
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
Rapid tests like OraQuick
what is the minimum time for antibody production to occur in a pt with HIV
3-4 weeks
what are the confirmatory tests for HIV
western blot
detection of antigens to HIV
HIV-1 RNA testing is used routinely to…
follow progression and response to therapy
what is the goal number of copies of HIV RNA in a person
< 50 copies (suppressed and undetectable)
suppressed/undetectable amount of HIV RNA copies
< 50 copies/mL
low to moderate amount of HIV RNA copies
50-100k copies/mL
high amount of HIV RNA copies
> 100k copies / mL
both CD4 Counts and HIV-1 RNA testing are RARELY used for…
diagnosis
CD4 count testing is used routinely for…
following the progression and response to therapy
normal immune system CD4 count
500 +
weakened immune system CD4 count
200-499
AIDS CD4 count
< 200
anti-retroviral therapy (ART) is rec for ___________ to reduce the risk of disease progression and to prevent transmission
all HIV-infected individuals (regardless of timing)
which two studies changed the guidelines on when to treat a person with HIV
START and TEMPRANO
START and TEMPRANO lead to
changing the guidelines to say that a person should immediately be treated for HIV
at the beginning of an HIV infection it is more likely that the person has which type of virus
wild type
wild type virus
unmutated original copy
what are the goals of HIV tx
To achieve maximal and durable suppression of HIV replication, interpreted to be a sustained plasma viral load less than the lower limit of quantitation
a HIV tx goal is to increase CD4 cells to ____
> 200
a HIV tx goal is to reduce the HIV viral load to ____
< 50 (undetectable)
HIV tx goal is to prevent ____ and decrease the risk of _____
transmission; opportunistic infections
HIV tx goal is to decrease ___ and ____
morbidity and mortality
HIV can be very inflammatory which leads to
increased risk of cardiovascular issues and MI
all pts with HIV should be started on a _____ due to inflammatory nature
statin drug
HIV can lead to which type of pain
neuropathic
HIV can lead to damage to which organ
kidney
Persons starting ART should use another form of prevention with sexual partners for _________ of treatment and until an HIV RNA level of <200 copies/mL has been documented
at least the first 6 months