TOPIC 7: Biochemical Tests
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards based on those created by @maledine
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Biochemical Tests (Conventional)
One the most important methods in identifying bacteria
Used to determine the nutritional and metabolic capabilities of isolated bacteria.
Used to determine genus and species of organism.
Used to determine ability to survive salts, toxins
Involves enzyme-based tests, presence of metabolic pathways, inhibitor profiles.
Enzyme-based test
Biochemical tests using the catalytic activity of the enzymes
Presence of Metabolic Pathways
Incorporating biochemistry in identifying organisms (ex: amination of lysine)
Inhibitor Profiles
Example of this is that some bacteria can survive with high salt concentration but some cannot
IMViC Test
What is an example of a biochemical test, which uses four biochemical tests respectively involving Indole, Methyl Red, Voges-Proskauer, or Citrate?
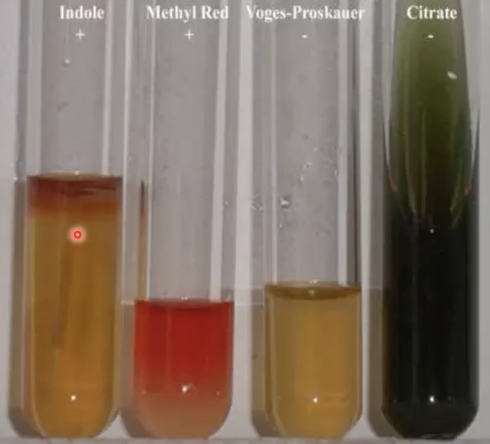

Indole
Methyl Red
Voges-Proskauer
Citrate
What are the reagents used in IMViC Test (what is stands for)?
Indole
In the IMViC Test, what reagent uses enzymes and is the test for motility?
Methyl Red
In the IMViC Test, what reagent can elicit a change in color and is an example of an pH indicator dye?
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
Tests for Detecting Antibacterial Resistance in Broth Dilution
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
(Tests for Detecting Antibacterial Resistance in Broth Dilution)
This is the lowest concentration of an antimicrobial like antifungal, antibiotic or bacteria static drug that will inhibit the visible growth of a microorganism after overnight incubation.
Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
(Tests for Detecting Antibacterial Resistance in Broth Dilution)
This is the lowest concentration of an antibacterial agent required to kill a particular bacterium.
Agar Dilution
To detect antibacteria resistance in this kind of medium, it involves the incorporation of different concentrations of the antimicrobial substance into the agar medium
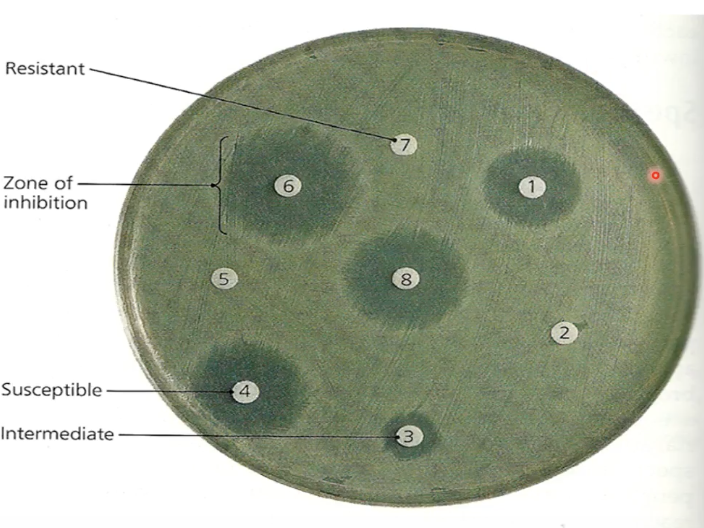
Disk Diffusion/Kirby Bauer Test
Tthe most widely used antibiotic susceptibility test in determining what choice of antibiotics should be used when treating an infection.
Kirby Bauer Test
What is Disk Diffusion also known as?
The inhibition of bacterial growth measured under standard conditions
What does Disk Diffusion test rely on?
Mueller Hinton Agar
Culture medium used in the Disk Diffusion test because it is thoroughly tested for its composition and its pH level that is inoculated with the test microorganism
Filter paper discs with impregnated discs are then placed in this medium
There will be no growth/large zone of inhibition around the disk containing the antibiotic.
(disk diffusion test)
If the Organism is susceptible to a particular antibiotic…
Zone of Inhibitions
(disk diffusion test)
What do you observe in the culture medium to determine antibiotic susceptibility?
Bacteria are susceptible to that antibiotic.
(disk diffusion test)
What does a clear zone (hollow) around the antibiotic disk indicate?
Kirby Bauer chart
(disk diffusion test)
What chart is used to interpret the size of the zone of inhibition?
Compare measurement of zone of inhibition to this
Resistant
Intermediate
Susceptible
(disk diffusion test)
How is the organism classified in relation to the antibiotic after measuring the zone of inhibition?
Intermediate
(disk diffusion test)
Zone of inhibition that means little effectiveness of the antibiotic
Susceptible
(disk diffusion test)
Zone of inhibition that means effective antibiotic to kill the bacteria
Resistant
(disk diffusion test)
No zone of inhibition so antibiotic or this specified concentration of antibiotic in this filter paper disk cannot kill these bacteria
Nucleic Acid-Based Tests
Non Nucleic Acid-Based Tests
2 Categories of Molecular Methods to Identify Bacteria and DNA sequencies
Nucleic acid hybridization
(nucleic acid based test)
when 2 single stranded nucleic acid molecules of complementary base sequence form a double stranded hybrid.
Must be single stranded
If DNA, which is double stranded, it must be denatured and become single-stranded
What is requirement of the nucleic acid in Nucleic Acid Hybridization?

unstable or stable
In Nucleic Acid Hybridization, the hybrid form can either be ___ or ___.

Stable Hybrid Form
What is the hybrid formed called when there is a high degree of complementary base pairing between the two strands?
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
What process is Nucleic Acid Hybridization mainly used for?
Detection of a specific DNA sequence in a mixture of DNA fragments or total cell DNA
What is the purpose of Nucleic Acid Hybridization?
Probe
In nucleic acid hybridization, this is the labelled molecule that binds specifically to the molecule of interest (ex.target sequence DNA/RNA) that can either be a radioactive atom, fluorescent tag, or enzyme helping identify the target sequence.
PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
(nucleic acid based test)
It amplifies target nucleic acid, making many copies of a specific DNA or RNA segment.
Chromatography
Electrophoretic protein analysis (electrophoresis)
Non-Nucleic Acid based analytic methods
Chromatography
(Non-nucleic acid based analytic methods)
A technique for separating the components of a mixture based on the differences in their interactions with surrounding substances (based on their differential affinity for a stationary and mobile phase)
Electrophoretic Protein Analysis/Electrophoresis
(Non-nucleic acid based analytic methods)
This is the migration of charged particles or molecules in a medium under the influence of an applied electrical field.