CARBONYL AND BENZYLIC NOMENCLATURE
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
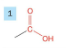
Carboxylic acid
Drop -e from root
add -oic acid at the end
prefix carboxy
Acid Anhydride
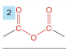
-drop -e from root
-add -oic anhydride
Ester
Establish the alkanoate portion as the root for the ester. The name of the alkanoate is determined by the number of carbons in the chain.
Number the alkyl and alkanoate chains. C-1 of the alkanoate chain is assigned to the CO2 carbon, and C-1 of the alkyl group is assigned to the carbon that is attached to the ester oxygen.
Establish the alkyl portion of the ester.
Write the parent name of the ester in the format alkyl alkanoate. Notice that there is a space between the two portions of the name.
Add the names and locator numbers of the substituents.
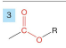
Acid Chloride
-drop -e from root
-add -oyl chloride
-prefix chloro- carbonyl
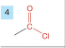
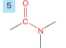
Amide
-drop -e from root
-add amide
-prefix carbonoyl
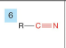
Nitrile
-add nitrile
-prefix cyano
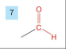
Aldehyde
-drop -e from root
-add al
prefix oxo
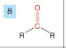
Ketone
-drop -e from root
-add -one
-prefix oxo
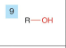
Alcohol
-drop -e from root
-add -ol
-prefix hydroxy
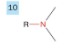
Amine
-drop -e from root
-add amine
-prefix amino
Naming Benzene
establish “benzene” as the root( groups attached to the ring are the substituents)
Numbering (give lowest locator number to the highest priority group)
Add prefixes and locator #s
Disubstituted benzenes
can optionally use a nonnumerical system to designate the locations of the substituents
