Medical Interventions and Genetics: Key Concepts and Techniques
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What is a pathogen?
A specific causative agent of a disease.
What is an outbreak?
A sudden rise in the incidence of a disease.
What did our ELISA test check for?
Antibody concentrations.
What are symptoms of meningitis?
Chills and fever, malaise/fatigue, headaches, and a stiff neck.
What does an epidemiologist do?
Searches for patterns in disease outbreaks.
What does each colored peak on a graph represent?
The nucleotides
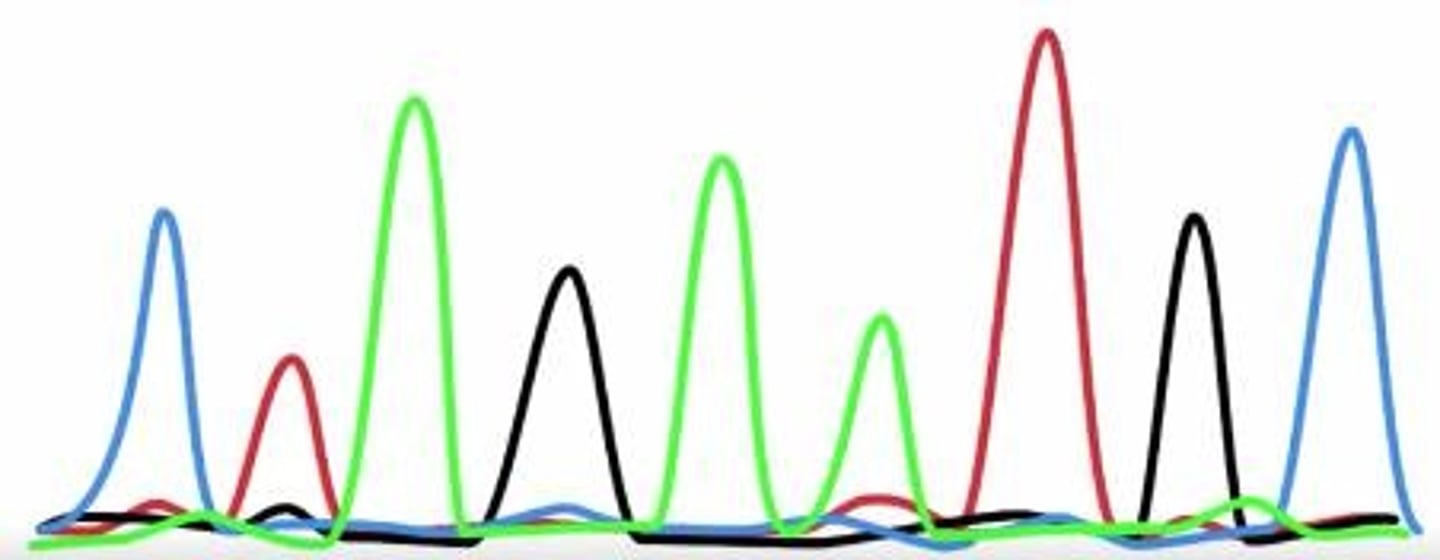
What sort of BLAST did we do?
Nucleotide blast.
What is an organism's genes?
Genome.
What is bioinformatics?
The field of science that combines biology, computers, and information technology to store and analyze genetic data.
Why is PCR used in genetic sequencing?
To make enough copies of the DNA that it can be tested and measured.
What is transduction?
When a virus called a bacteriophage moves fragments of DNA between bacterial cells.
What is a plasmid?
A small circle of DNA that can contain genes to create antibiotic resistance.
What is 'naked' DNA?
Pieces of genetic material outside the bacterium.
What number represents the inner ear in the image?
7.
What number represents the pinna in the image?
8.
What part contains fluid and tiny sensory hairs to detect sound?
The cochlea.
What percentage of nucleotide base pairs is similar between humans?
More than 99%.
What happens to DNA when the sample is heated in thermal cycling?
It denatures.
What happens to DNA when the sample is cooled in thermal cycling?
It anneals.
What is PTC?
Phenylthiocarbamide, tastes bitter to some individuals.
What career involves speaking with people about their genetic information?
Genetic counselor.
What is the Human Genome Project?
The project that sequenced all the human genes.
What is a characteristic of a genetic disease?
It is the result of mutations in the genes and can be inherited.
How is a mother tested for gestational diabetes?
Through a glucose tolerance test after fasting.
Urine test after 24 hours of fasting
A diagnostic test used to assess metabolic function and glucose levels after fasting.
Amniocentesis
A procedure that involves using a large needle to extract and test amniotic fluid for genetic abnormalities.
Alpha Fetoprotein (AFP) test
A second-trimester blood test that helps determine the risk of neural tube defects such as spina bifida and anencephaly.
Glucose tolerance test
A test where blood glucose levels are measured after fasting and then after consuming a glucose-rich drink.
Karyotype
An image of the chromosomes in a cell, used to identify chromosomal abnormalities.
Single Gene Disorders
Disorders caused by changes or mutations in the DNA sequence of one gene, resulting in non-functional proteins.
Multifactorial Disorders
Disorders caused by a combination of environmental factors and mutations in multiple genes, leading to common chronic illnesses.
Chromosomal Disorders
Disorders caused by missing or extra copies of genes, or structural changes in chromosomes.
Mitochondrial Disorders
Disorders caused by mutations in non-chromosomal DNA passed from mother to child.
SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism)
A variation in a single nucleotide that occurs at a specific position in the genome.
Carrier screening
A test to determine if an individual carries a gene for a genetic disorder, even if they do not show symptoms.
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
A technique used to amplify small segments of DNA for analysis.
Taq polymerase
A heat-stable enzyme used in PCR to synthesize new DNA strands.
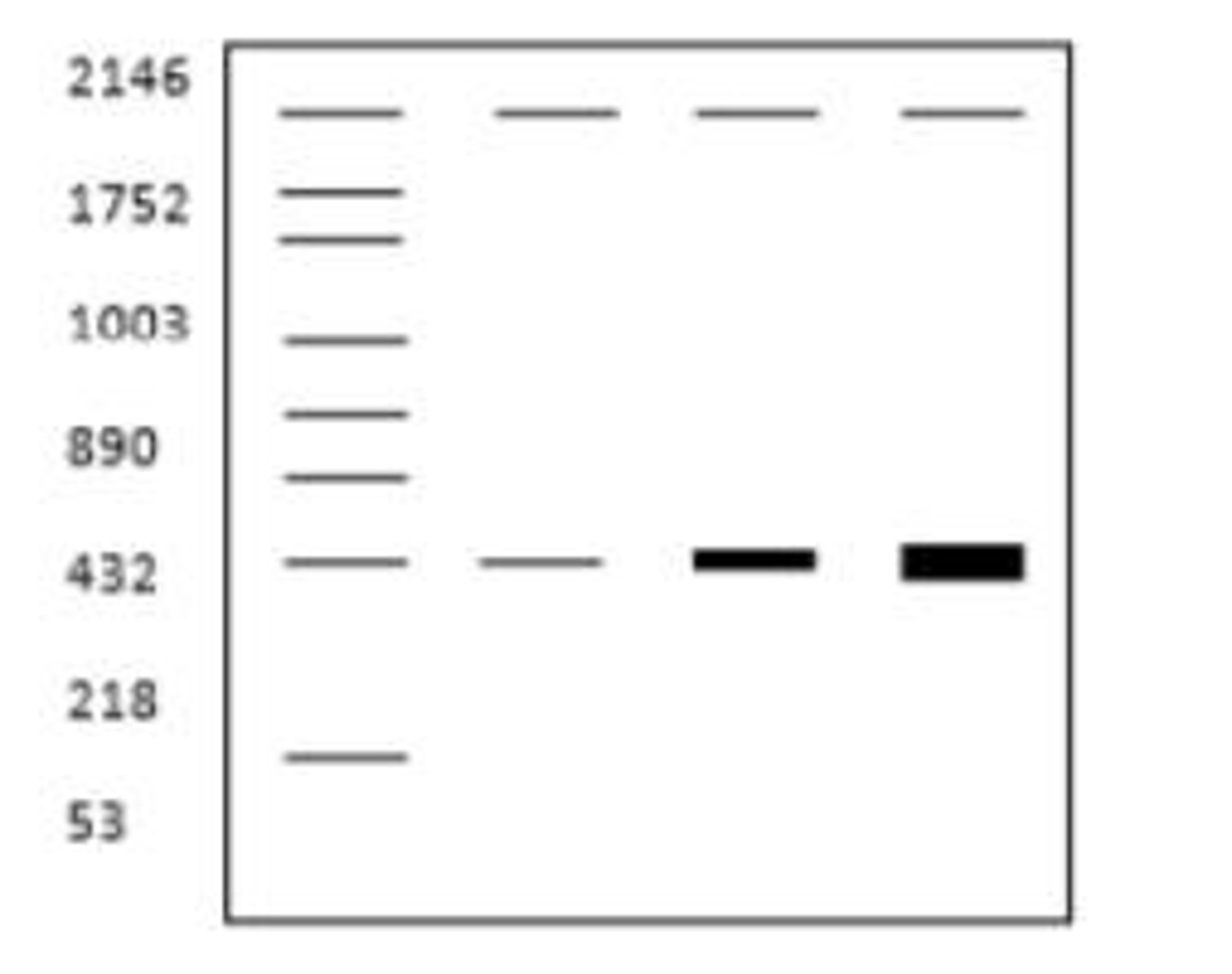
Gel electrophoresis
A laboratory method used to separate DNA fragments based on their size.
Dominant gene
A gene that expresses its trait even when only one copy is present in the genotype.
Homozygous recessive
An individual with two copies of the recessive allele for a particular gene.
Heterozygous
An individual with one dominant and one recessive allele for a particular gene.
Restriction enzyme
An enzyme that cuts DNA at specific sequences, used in genetic engineering and analysis.
Gene therapy
A technique that modifies a person's genes to treat or prevent disease.
CRISPR
A gene-editing technology that uses a guide RNA and Cas9 protein to target and modify specific DNA sequences.
In-vitro fertilization
A reproductive technology that involves fertilizing an egg outside the body and implanting it into the uterus.
Reproductive cloning
A process used to create a genetically identical copy of an organism.
Vector in gene therapy
A carrier used to deliver genetic material into cells, which can include viruses like retroviruses.