Unit 6 -responses to internal and external environment
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Define: stimulus/receptor/coordinator/effector/response
Stimulus- change in internal/external environment of an organism that leads to a response
Receptor- detects stimulus, specific to one type of stimulus
Coordinator- formulates a suitable response to a stimulus ( nervous system)
Effector- muscle/gland that produces response to stimulus
Response- change brought due to stimulus
What is tropism give examples
Growth movement of a plant in response to directional stimulus ( away or towards)
phototropism/ gravitropism/hydrotropism
Describe how IAA results in phototropism in shoots
IAA produced in meristems of shoot tips/ root tips
IAA detects light due to receptors
IAA diffuses to the shaded region so there’s a higher concentration of IAA
Causes more cell elongation
Shoot bends towards the light
Outline the acid growth hypothesis
Auxin promotes the active transport of H+ ions
H+ ions lower the PH
Optimum conditions for expansin enzymes to break the H bonds in cellulose
Reduces rigidity
Describe how IAA results in gravitropism in roots
IAA produced in meristems in shoot tips
IAA accumulates on the lower side
Inhibits cell elongation so cells elongates faster on the upper side
Root curves downwards towards gravity
Define Taxes and Kinesis
Taxes: Directional response by organisms who move towards a favourable stimulus or away from an unfavourable one
Kinesis: Non-directional response by organisms who change the speed of movement or the rate of direction change in response to a non-directional stimulus
Why is taxis important
survival from harmful stimuli + favourable environment
Find food
Mating
Why is positive photo taxis in algae useful
increases rate of light-dependent reaction/
Increases rate of independent reaction as more ATP/NADPH
More glucose produced
More respiration
What statistical test is used for choice hammer practical
Chi-squared,to see if there’s a significant difference between the observed and expected number of maggots in each chamber
How can we keep maggots similiar
same previous treatment ( environment/feeding)
Same size/age
Same species
How are neurones different from other cells
Dendrites bring information to cell body + axon carries information away from cell body
Communicate with other cells via electrochemical processes
Specialised structures (NT
What is a reflex
Involuntary actions that are fast and automatic, don’t involve the brain
protect us from harmful stimuli
Effective from birth, not learned
Fast as neurone pathway is short few synapses
What is an action potential + resting potential
Resting potential: difference in electrical charge maintained across the membrane of the axon of a neurone when not stimulated
- (-70mv)
Action potential; changed that occur in the electrical charge across the membrane of an axon when its stimulated and a nerve impulse passes
-(+40mv)
Define depolarisation + generator potential
Depolarisation: temporary reversal of charges on the cell-surface membrane of a neurone that takes place when a nerve impulse is transmitted
Generator potential: depolarisation of the membrane of a receptor cell as a result of a stimulus which changes the PD
Describe how a resting potential is established
Active transport of Na+ out of axon and K+ into the axon by sodium-potassium pump
3 Na+ out and 2 K+ in
Membrane more permeable to K+ ions (K+ channels open) k+ diffuse out
Membrane less permeable to Na+ (Na+ channels closed)
How is the Resting potential maintained
Higher concentration of K+ inside axon + Higher concentration of Na+ outside neurone
Membrane less permeable to Na+ (Na+ channels closed)
Na+ actively transported out axon 3Na+ out 2K+ in by sodium-potassium pump
Inside axon more negative compared to outside
Diffusion of K+ ion out of neurone- maintains electrochemical gradient
Name each stage of the generation of action potential
Stimulus
Depolarisation
Repolarisation
Hyperpolarisation
Resign potential
What happens during depolarisation
Stimulus causes the sodium ion channels in axon membrane to open
Na+ diffuses into the axon down the electrochemical gradient
Inside the axon is less negative as p.d reduced
If threshold of -55mv is reached, more sodium channels open so more Na+ enter
Axon reaches action potential +40mv
What happens during repolarisation
Sodium ion voltage-gated channels close
Potassium ion voltage-gated channels open K+ diffuse or of axon down concentration gradient
Sodium potassium pump actively transports 3 Na+ out for every 2 K+ in (original distribution of ions)
Hyerpolarisation period axon becomes more negative than R.P
Potassium ion voltage-gated channels close returning to R.P -70mv
What is a refractory period and why is it important
Period where the cell is recovering, no action potential generated/ restores axon to R.P ( sodium ion channels not activated)
ensures action potential is propagated in one direction
Limits the frequency of A.P (prevents overstimulation)
Produces separate impulses
Describe the All or nothing principle
if threshold p.d (-55mv) is reached an action potential will fire → ALL
If threshold p.d not reached, no action potential generated → NOTHING
→ bigger stimulus causes more frequent action potentials not bigger A.P (all +40mv)
Describe the propagation of an action potential
As one region of axon produces A.P becomes depolarised, acts as stimulus for next region to be depolarised
Previous region becomes repolarised + returns to R.P
Describe the role of Schwann cells
forms multilayered lipoprotein coat (forming myelin sheath) with node of ranvier at either end
Provides electrical insulation → carry out phagocytosis + plays a role in nerve regeneration
Myelin sheath is an electrical conductor, prevents A.P forming in and on myelination
What is meant by saltatory conduction, is conduction faster in myelinated or non-myelinated sheaths
A.P can only occur at node of ranvier so A.P jumps from node to node
Faster speed of conductance in myelinated sheath
A.P in non-myelinated sheath travels the entire length of axon
What factors affect the speed of conductance
presence of myelin sheath
Diameter of axon
→ greater diameter→ less resistance → less collisions → increase speed
Temperature
→ faster rate of ion diffusion/ increase Ke beyond optimum → sodium potassium ion channels denature (proteins)
Describe the sequence of events that allows information to pass from one neurone to the ext neurone across a cholinergic synapse
Action potential reaches the presynaptic knob and calcium channels open
Ca²+ ions diffuse into pre-synaptic neurone
Vesicles fuse with presynaptic membrane
Acetylcholine released into the synaptic cleft and diffuses across the synapse
Ach binds to receptors on post synaptic membrane
Sodium ions enter the postsynaptic neurone
Depolarisation of postsynaptic membrane
If above threshold, an A.P is produced
Explain why an A.P is less likely to be generated when GABA is released
NT (GABA) cause chloride ion channels to open
Chloride ions move into axon by diffusion
More K+ ions move out of the axon
Inside of the neurone more negative than usual
Hyperpolarisation so A.P cant be generated
What’s the structure of the Pacinian Corpuscle?
Mechanoreceptors found deep in the skin, detect strong pressures (not light touch)
Contain stretch mediated sodium ion channels
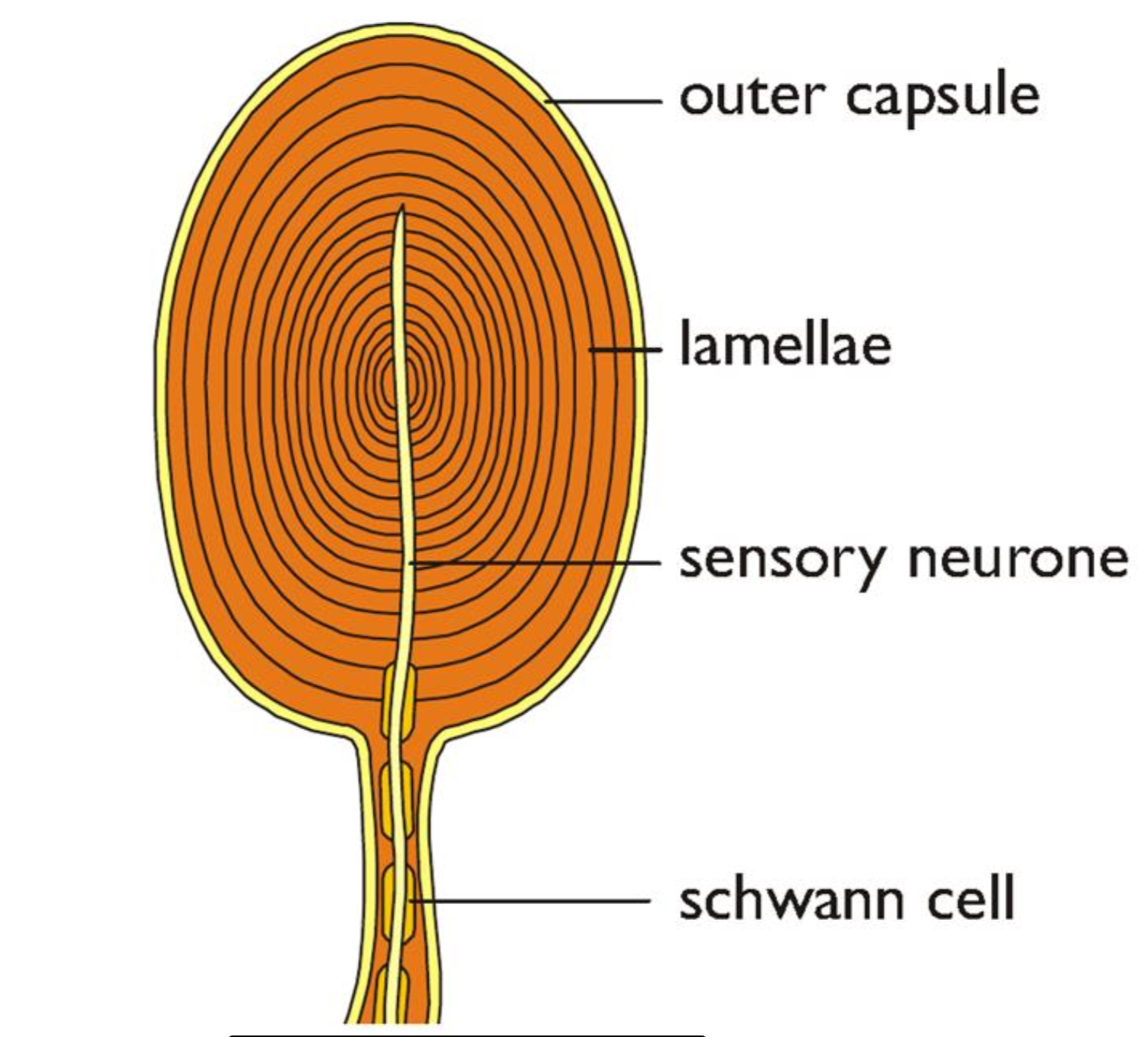
How does the Pacinian Corpsucle cause an A.P
At rest, more sodium ions on the outside than the inside
Pressure distorts the neurone cell membrane, opens the stretch mediated sodium ion channels
Stronger pressure → more Na+ channels open
Na+ diffuses in causing depolarisation allowing generator potential to be established
If threshold is reached, A.P is generated
What does the P.C illustrate
Receptors respond to specific stimuli
P.C responds to mechanical pressure
When a receptor is stimulated leads to generator potential being reached
All or nothing principle, when threshold is reached A.P generated
Describe the two types of summation
Temporal summation: two impulses/ NT are sent in quick succession from the same presynaptic neurone → cone cells
Spatial summation: impulses from different pre synaptic neurones that act on synapses on the same postsynaptic neurone → rod cells
Describe the structure of the retina
Retina contains photoreceptors
Blind spot where optic nerve attaches → no receptors
Fovea → greater density of photoreceptors
How does the breakdown of rhodopsin lead to a generator potential being reached
Rhodopsin (opsin + retianal)
light energy causes retinal to change shape no longer biding to opsin so breaks down
Breakdown causes membrane to be more permeable to Na+ ions
Change in distribution of Na+, change in p.d across rod membrane → generator potential
Rhodopsin resynthesised using energy from hydrolysis of ATP by mitochondria n inner segments
Define visual acuity and explain why rod cells have low visual acuity but high sensitivity
Ability of the eye to distinguish between different shapes + details at a given distance
many rod cells joined to the same bipolar neurone, only a single impulse stimulated
→ cant distinguish separate sources of light that stimulate them
high sensitivity as enough NT to reach the threshold

Why do cone cells have high visual acuity and low sensitivity to light
Has blue/green/red light sensing cells
Each cone cell connected to one bipolar neurone, sends separate sets of impulses to the brain
Requires temporal summation not enough NT released so threshold not reached
Stimulation f different combinations of cones gives range of colour perception
What is meant by myogenic and neurogenic
Cardiac muscles are myogenic → contractions initiated from within as opposed to to by nerve cells (neurogenic)
SAN sinoatrial nodes
Describe how the cardiac cycle is controlled by the SAN and the AVN
SAN conducts an electrical impulse
atria contract at the same time
AVN passes electrical activity after a short delay to allow atria to fully contract
Via purkyne tissue and bundle of His
Ventricles contract from the base upwards
What receptors are involved in controlling heart rate
Chemoreceptors detect rise in CO2/ H+/ carbonic acid
Baroreceptors detect rise in bp → arteries stretch
Found in carotid artery
changes to HR controlled by medulla oblangata in cardioregulatory centre
Explain how increased exercise leads to decreased heart rate
High levels of CO2 dissolve in blood form carbonic acid to lower PH
Chemoreceptors in the aorta detect, sends more impulse to CV centre in medulla
Medulla end more impulses to SAN via sympathetic nervous system
SAN send more impulses so heart rate increases → CO2 removed
Signals medulla to send more impulses to SAN via parasympathetic NS to slow down HR
Explain how a rise in bp results in decrease in rate of a heartbeat
Increased HR increases muscle contraction so SV increases
Carotid arteries stretch which stimulates baroreceptors
send more impulses to medulla oblongata
sends more impulses to SAN via parasympathetic NS
SAN send less impulses so less heart contractions to decrease bp
What are the three types of muscle
cardiac muscle
Skeletal muscle → many nuclei
Smooth muscle cells → involuntary movements
advantage of antagonistic muscles
muscles can only pull
When one muscle contracts the other muscle is pulled out
Maintains posture
describe the structure of skeletal muscles
Divided into muscle fibres (myofibrils) → thin and thick filaments
Repeated units of of muscle fibres → sarcomere
Muscle fibres covered with cell surface membrane → sarcolemma
Cytoplasm → sarcoplasm
Sarcoplasmic reticulum → (SER) store and release calcium ions
Describe structure of thin and thick filaments
contains 2 actin strands that twist around each other
Troponin + tropomyosin proteins
Myosin: myosin tails form a central stalk
Globular heads attach to specific sites on actin + have ATpase
label different regions of a sarcomere
I-band: only actin
H-band: only myosin
A-band: actin and myosin so appears darker
M-line → middle line
Z-line → start and end of one sarcomere
what happens during contraction of sarcomere
I band shortens
H band shortens
A band the same as myosin does not move
Z lines move closer together
Myosin+ actin filaments slide over each other
what is a neuromuscular junction and what are differences of NMJ compare to cholinergic synapses
where motor neurone meets the muscle fibre stimulated by action potential
Only excitatory
A.P ends here
Ach binds to receptors of muscle fibres not post-synaptic neurone
Only links neurones to muscles
Only involves motor neurones no sensory/relay
describe the roles of calcium ions and ATP in the contraction of a myofibril
A.p reaches muscles via T tubules that branch throughput the sarcoplasm, tubules are in contact with sarcoplasmic reticulum
A.P opens Ca2+ ion channels and Ca2+ diffuses into myofibrils from sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ca2+ cause movement of tropomyosin on actin
Exposes binding sites of actin
Myosin heads attach to binding sites on actin → cross-bridge
Hydrolysis of ATP
Myosin heads bend to perform power stroke
What’s the role of phosphocreatine in providing energy for muscle contraction
phosphocreatine provides phosphate/ phosphorylates ADP to make ATP
Generates ATP quickly, anaerobic + alactic
ADP + CP→ ATP + Cr
Differences between fast and slow twitch muscle fibres
Slow twitch→ aerobic respiration
Dense network of capillaries + large store of Ca²+
fast twitch → anaerobic (glycolysis)
High rate of ATP hydrolysis in myosin head
What is homeostasis
Maintenance of constant internal conditions despite fluctuations in both the body’s activities and external environment
Controlled by nervous system + endocrine system or a combination
Importance of maintaining core body temperature, pH, blood glucose and water potential
Temperature: low→ fewer collisions/ high → bonds in tertiary structure break → active site denatures (less E-S complex)
PH: Bonds in tertiary structure Hb- active site changes denature
Blood glucose: Low water potential→ water moves out of cells→ cell shrinks no metabolic reactions
Respiratory substrate
Water potential: cell bursts/shrink
Water is a metabolite + solvent for reactions
What’s meant by negative and positive feedback
negative feedback: change is detected by receptors and effectors return the system to its original state
Positive feedback: corrective mechanism stays on, system deviates even more from the original level
What are ectotherms and what are some advantages/disadantages
Animals that cant control body temperature, rely o external sources of heat
survive longer periods without food
More energy used for growth
Slower metabolic reactions
Less active in cooler temperature→ risk of predation
What are hormones
Chemicals that are released by glands and travel in the blood to certain target cells
target cells have specific receptors on the cell surface + complementary shape to the hormone
What groups of tissues are involved in maintaining blood-glucose concentrations
group of cells Islets of Langerhans
Alpha cells → glucagon
Beta cells → insulin
Good capillary blood supply enables them to be secreted directly into the blood
How does insulin work to reduce blood glucose concentration
Glucose is absorbed by the beta cells via carrier proteins
Vesicles containing insulin move towards cell-surface membrane and release insulin into capillaries
Insulin binds to receptor molecules( liver/muscle/adipose tissues)
More carrier proteins join to the membranes
Increases permeability to glucose → uptake
Enzymes convert glucose to glycogen
What happens when there’s a fall in blood glucose concentration
detected by alpha cells
Alpha cells secrete glucagon
Glucagon binds to receptors
Increased Glycogenolysis glycogen → glucose
Increased gluconeogenesis fats + A.A → glucose
(Cells respire less)
Describe the livers role in carbohydrate metabolism
glycogenesis: glucose → glycogen
Glycogenolysis: glycogen → glucose
Gluconeognesis → production of glucose from sources other than carbohydrates (fats/amino acids)
Describe the role of adrenaline in control of glucose
Amino acid derived hormone produced in adrenal glands
Stimulate glycogenolysis glycogen → glucose
Inhibits insulin+ action of gut/ increase HR + SV
Lipid-insoluble proteins → cant diffuse through phospholipid bilayer
Explain the second messenger model
Adrenaline binds to receptors on liver cell-surface membrane
Causes conformational change in shape of receptor
Activates adenylate cyclase enzyme converts ATP → cAMP
cAMP activates protein kinase converts glycogen → glucose
Increased facilitated diffusion of glucose into the blood
Function of kidneys
ultrafiltration of blood
Selective reabsorption of all glucose some ions and water
Excretes toxic urea, excess ions, water as urine
A.A → ammonia → urea
How does blood enter the glomerulus
Blood enters into glomerulus via Afferent arteriole
Smaller diameter of efferent arteriole causes higher hydrostatic pressure
Describe the three filters of ultrafiltration
endothelium: narrow gaps allows small molecules to pass through
Basement membrane: fine mesh of collagen fibres + glycoproteins, stops larger molecules getting through (proteins + RBC)
Podocytes: epithelial cells with finger like projections (microvilli) allows fluid to pass into lumen of bowman’s capsule
Describe process of ultrafiltration (4 marks)
Blood enters Bowman’s capsule (mass of capillary) via afferent arteriole
High hydrostatic pressure caused by smaller diameter of efferent arteriole
Small molecules pass through basement membrane acts as a filter (glucose, ions, water)
RBC + proteins too large so remain in capillaries and carried by efferent arteriole
Pores between podocytes allow substances to dissolve in blood plasma to pass into lumen of bowman’s capsule
Describe the reabsorption of water by the proximal convoluted tube (5 marks)
Na+ actively transported into capillary from epithelial cell
Lowers concentration of Na+ in cell + maintains diffusion gradient of Na+
Na+ moves into epithelial cell from Proximal convoluted tubule via f.d
Co-transport of glucose/ amino acids/ Cl- against its concentration gradient
Glucose/ amino acids/Cl- move into capillary by f.d
Lower water potential in the capillary so water moves into capillary by osmosis (reabsorbed)
Why might a person with diabetes have glucose present in their urine
Higher concentration of glucose in filtrate
Carrier proteins are saturated
Not all lactose is reabsorbed into blood
Explain the role of the loop of henle in the absorption of water from the filtrate (6 marks)
Na+ actively transported out of the ascending limb into medulla
Ascending limb is impermeable to water
Lowers water potential in the medulla
Water moves out of descending limb by osmosis into medulla
Na+ diffuses into descending limb to recycle in loop of henle
Longer loop= lower water potential in the henle
→ counter current: filtrate in ascending + descending limb flow in opposite directions
How does the length of loop of henle affect water absorption ?
longer loop of henle = more water reabsorbed
Lower water potential in medulla
More water moves into descending loop via osmosis
Concentration gradient maintained for a longer period of time
What is osmoregulation and osmoreceptors
Process by which organisms regulate the water content of the body
osmoreceptors in hypothalamus monitor the water potential of blood
Posterior pituitary gland secretes ADH
How does ADH cause more water or be reabsorbed
ADH binds to receptors on cell-surface membrane of distal convoluted tubule
Activates phosphorylase which converts ATP → CAMP
Vesicles fuse with cell-surface membrane
Contains aquaporin + fuses to cell-surface membrane
Increases permeability to water so more water reabsorbed
→ decreases volume of urine + increases concentration
Describe the process i which concentrated urine is produced in kidneys
Osmoreceptors in hypothalamus detect the low water potential of blood
→ change shape/ impulses to posterior pituitary gland
Posterior pituitary gland secretes more ADH into blood
More aquaporin channels on cell surface membrane
Increases permeability to water So more water reabsorbed by osmosis down water potential gradient