A&P Unit 2 (Connective)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
T or F; connective tissue is vascularized
true
what are the 3 distinct components of connective tissue?
ground substance
fibers
cells
what is the ground substance?
material that holds everything together
fibroblast
manufactures and secrete both fibers and ground substance
wandering cells
move in and out of connective tissue as needed
white blood cells
leukocytes, move into connective tissue during times of infection
the 2 broad categories of connective tissue are:
loose connective
dense connective
loos connective tissue includes:
areolar
adipose
reticular
areolar tissue
randomly placed fibers and cells suspended in a thick, translucent ground substance
not strong, good for packing and supporting
present in all mucous membranes
areolar make-up
GS: thick & translucent
F: elastic, reticular, collagen
C: fibroblasts
adipose tissue
“fat”
highly vascularized
energy store, thermal insulator, mechanical shock absorber
2 types: white & brown
adipose make-up
GS: thick & translucent
F: elastic, reticular, collagen
C: adipocytes
white adipose tissue
basic fat- contains 7 times more sugar than brown adipose
brown adipose tissue
energy storehouse, like for hibernation- 10 times more energy than white adipose
reticular tissue
resembles areolar tissue
found in a limited number of sites
reticular make-up
GS: supportive
F: reticular
C: fibroblasts
dense connective tissue includes:
regular
irregular
elastic
regular tissue
tightly packed fibers
makes up tendons and ligaments and fascia
tremendous tensile strength
avascular
regular make-up
GS: thick and supportive
F: collagen
C: fibroblasts
irregular tissue
thick bundled of collagen
forms the tough capsule of joints and fibrous coverings of certain organs
irregular make-up
GS: thick and supportive
F: collagen
C: fibroblasts
elastic tissue
few regions in the body, between vertebrae
walls of arteries, stomach, bronchi, bladder, and regions of the heart
elastic rather than collagenous fibers
elastic make-up
GS: thick and supportive
F: elastic with collagen interspersed
C: fibroblasts
cartilage
tough, specialized tissue made of chondroblasts; the type of cartilage is based on the type of fiber in the matrix
3 types of cartilage found in the matrix
hyaline
elastic
fibrocartilage
Hyaline cartilage
densemost common kind in the body
tough but more flexible than bone
composes most of the embryonic skeleton
closely packed collagen fibers
elastic cartilage
dense bundles of elastic fibers
tremendous flexibility
epiglottis and pinnae (external ear)
fibrocartilage
merged with hyaline and dense connective tissue
thick bundles of collagen, less chondrocytes
designed to take compression
between vertebrae
bone, aka
osseous connective tissue
osteoblasts
bone cells
plasma
liquid component of blood
erythrocytes
red blood cells
thrombocytes
platelets
blood make-up
GS: plasma
F: fibrinogen
C: RBC and WBC
membranes, are used to _________ and __________
cover, protect
4 common types of membranes:
mucous
serous
cutaneous
synovial
mucous membranes
mucosae, line organs that have connections to the outside environment
serous membranes
serosae, line the walls and cover the organs that fill closed body cavities
parietal layer
lines and touches the cavity wall
visceral layer
covers and touches the outer surface of the organ
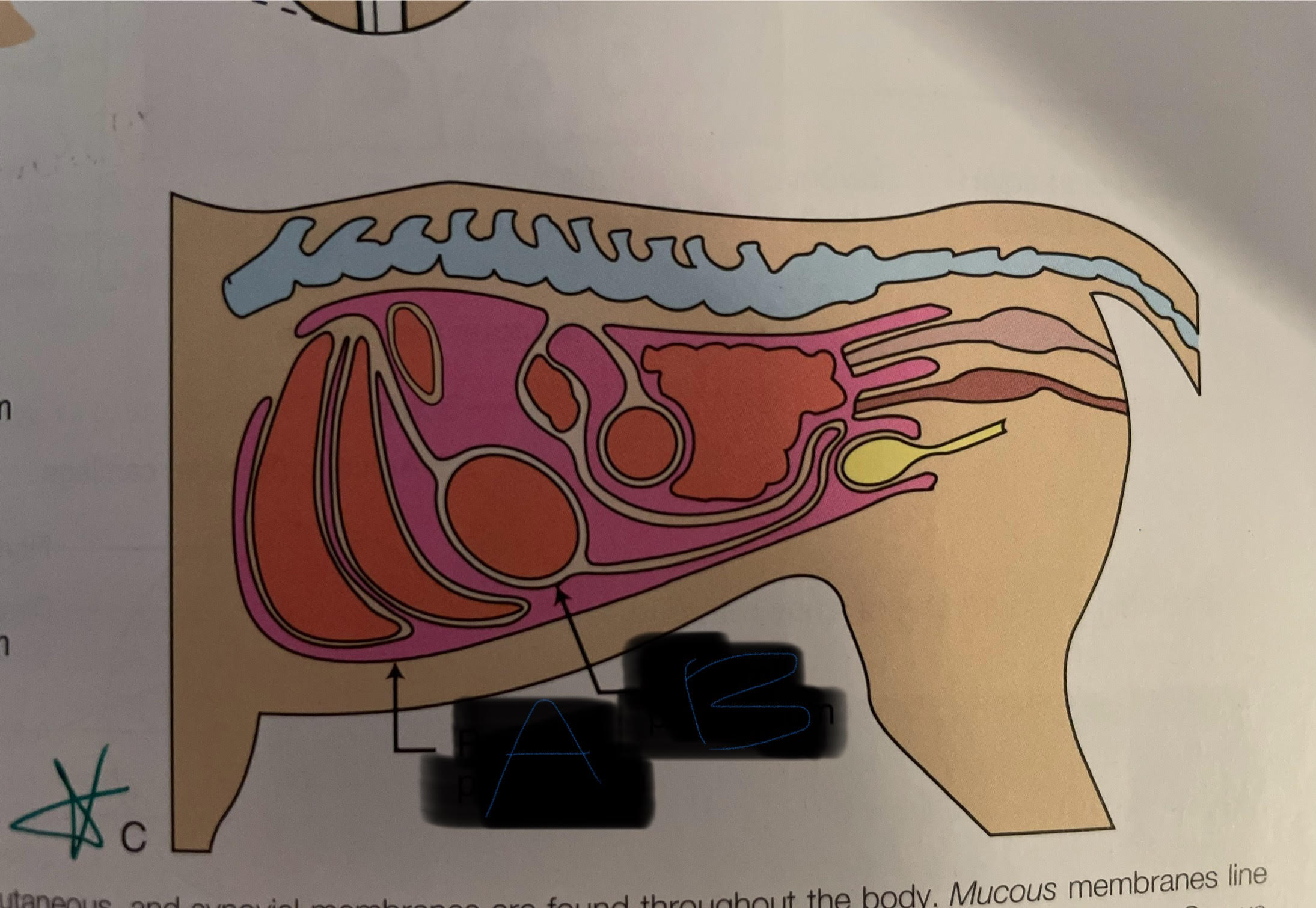
Label blank A and B
A. Parietal
B. Visceral
Effusion
when an abnormally large amount of fluid enters a body cavity
ascites
the presence of an effusion in the peritoneal space of the abdominopelvic cavity
cutaneous membrane
integument (skin), organ that is perpetually exposed to the outside environment
epidermis
outer keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
synovial membranes
lines the cavities of joints, manufacture the synovial fluid that fills the joint spaces
synovial membrane make-up
loose connective tissue and adipose tissue covered by a layer of collagen fibers and fibroblasts