Review Questions
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Diffusion is principally driven by three properties within cells. What are they?
Concentration differences, the charges on the ions, and the potential difference between the intracellular and extracellular environments
Define the Nernst potential in 2 words
electrochemical balance
what is the equation to calculate the Nernst potential?
61.5/z * log (co/ci)
what is the equilibrium potential for Na+?
+67 mV
what is the equilibrium potential for K+?
-98 mV
what is the equilibrium potential for Cl-?
-90 mV
what is the equilibrium potential for Ca2+?
+129 mV
Why is the Nernst potential for a K+ a negative value even though it has a positive charge?
It has a high intracellular concentration, which makes the co/ci ratio less than 1. log(<1) = a negative number
what is the difference between the equation for the Nernst potential and the Goldman equation?
the goldman equation accounts for relative permeabilities of each ion and the nernst equation accounts for the charge of the ion.
why does potassium play a major role in the resting membrane potential?
Potassium has a higher permeability than sodium due to the presence of leak channels
For a positively charged ion, if the membrane potential is more negative than the equilibrium potential, then the direction of flux is ___ the cell
into
For a negatively charged ion, if the membrane potential is more positive than the equilibrium potential, then the direction of flux is ___ the cell
into
For a negatively charged ion, if the membrane potential is more negative than the equilibrium potential, then the direction of flux is ___ the cell
out of
For a positively charged ion, if the membrane potential is more positive than the equilibrium potential, then the direction of flux is ___ the cell
out of
The membrane is clamped at +70mV. what direction does a Ca2+ ion move?
into the cell
if an anion has a nernst potential of -90 mV and the voltage is clamped at +10 mV, which direction is the ion flowing?
into the cell
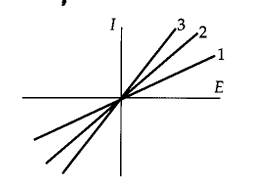
what is changing in this graph?
conductance
a hypothetical neuron which expresses sodium ion channels is grown in culture and is subjected to an experimental drug which blocks sodium channels. What happens to the Nernst potential following the administration of the drug?
the nernst potential does not change (because blocking the sodium channels affects permeability, which is not a factor in the nernst potential.
a hypothetical neuron which expresses sodium ion channels is grown in culture and is subjected to experimental conditions in which additional sodium is added to the extracellular environment. What happens to the Nernst potential following the addition of sodium?
the nernst potential will increase
how does resistance affect the time constant?
resistance and time constant are proportional
how do we define the time constant?
the time it takes for a capacitor to charge up to 63% (or to discharge 37%)
what is the quantity and directionality of ions being pumped by the Na+/K+ pump?
3 Na+ out, 2 K+ in
what is the quantity and directionality of ions being exchanged by the Cl-/K+ exchanger?
1 Cl- out, 1 K+ out
what is the quantity and directionality of ions being exchanged by the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger?
3 Na+ in, 1 Ca2+ out
t/f: it requires energy to maintain the Na/K pump
true
t/f: it requires energy to maintain the Cl/K exchanger or the Na/Ca exchanger
false
rank the following ions by the size of their respective hydration shells: Na+, K+, Ca2+
Ca2+ > Na+ > K+
How come a K+ ion can’t pass through a Na+ channel?
it is too large to fit with a water molecule.
how come a Na+ ion can’t move through a K+ channel?
it is too large to fit while hydrated and too unstable without a water molecule
define the following terms: hypertonic, isotonic, hypotonic.
all refer to the solute concentration outside the cell.
hypertonic - high solute concentration
isotonic - same concentration as inside
hypotonic - low solute concentration
why is saline used instead of water for an IV?
saline is a solution of salt and water. plain water would be hypotonic to the inside of a blood cell, so if water were used, it would enter the blood cells by osmosis, leading to the cells bursting. saline prevents this.
what happens to the capacitance of a cell as the surface area of the membrane increases? when the space between the plasma membrane increases?
increase, decrease
how does the force between 2 charges change if the distance between them is cut in half?
4x
when we are at nernst potential of an ion, are we in a static or dynamic equilibrium state?
dynamic
t/f: the nernst potential of an ion takes only the extra/intracellular concentration of that ion into account.
false, the charge of the ion and the temperature are also taken into account.
if i permanently close all K+ channels, but leave all other channels alone, what will happen to my resting membrane potential?
the permeability of potassium has changed, so the membrane potential would move more towards the Na+ nernst potential.
someone takes a drug that causes Na/K pump to be destroyed, which direction does K+ move?
out of the cell

B
how are voltage and current related?
proportional (V=IR)
how are voltage and resistance related?
proportional (V=IR)
how are resistance and current related?
inverse (I=V/R)
how are capacitance and surface area related?
proportional
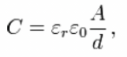
how are capacitance and distance related?
inverse
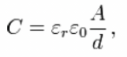
how are the time constant and resistance related?
proportional (t=rc)
how are the time constant and capacitance related?
proportional (t=rc)
how are force and distance between the charges related?
inverse (squared)

if no ions: ___ resistance, ___ conductance
high resistance, low conductance (ions are needed to carry charge)
if some ions: ___ resistance, ___ conductance
moderate, moderate
if many ions: ___ resistance, ___ conductance
low resistance, high conductance
if your circuit has a voltage of 10 and your resistance drops from 4 to 2 ohms, will your current increase or decrease?
increases
when series resistance increases, capacitance ___
decreases
myelination (increases/decreases) capacitance
decrease (because it increases the thickness)
in terms of the time constant equation, C is a more important property for ___
axons
in terms of the time constant equation, R is a more important property for ___
dendrites
resistance is proportional to the number of ___
open channels at rest
If we added myelination to the axon, would τ increase or decrease?
decrease
If we opened K+ leak channels, would τ increase or decrease?
decrease
in a neuronal circuit model, the battery represents the
concentration gradient
the longer side of the battery symbol pointing toward external
K+
the shorter side of the battery symbol pointing toward external
Na+
in the neuronal circuit model, the capacitor represents the
cell membrane
in the neuronal circuit model, the resistors represent the
channels
an arrow across a resistor indicates
variable resistance (which represents gated channels)
in the neuronal circuit model, what is gL?
leak channels (ungated, so no variability → no arrow)
ions move because of ___ difference
concentration difference
a positive Nernst potential means the ion will move ___ the cell
into
a negative Nernst potential means the ion will move ___ the cell
out of
how do you use the goldman equation for anions?
multiply the end result by -1
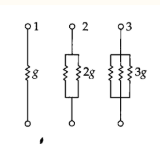
which has the highest conductance?
3, because it has 3 resistors (more channels, lower resistance, higher conductance)
on an IV plot, the slope =
conductance
what change on an IV plot: ion concentrations are changed
shift to left or right (no slope change bc no conductance change)
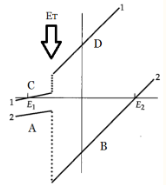
why is there a jump?
the jump represents a change in conductance due to the opening of ion channels (like during an action potential)
if nernst = 0, how will the ions move?
they will not because there is no potential difference.
as R increases, T (tau) ___
increases
what change on an IV plot: more channels open
slope increases