Part 3- HUSSEIN EXAM 1
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BASED ON AND ONLY ON THE SG!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
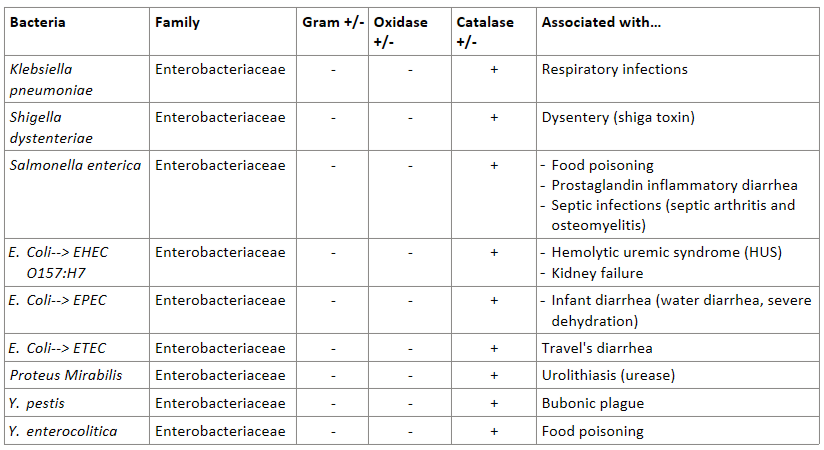
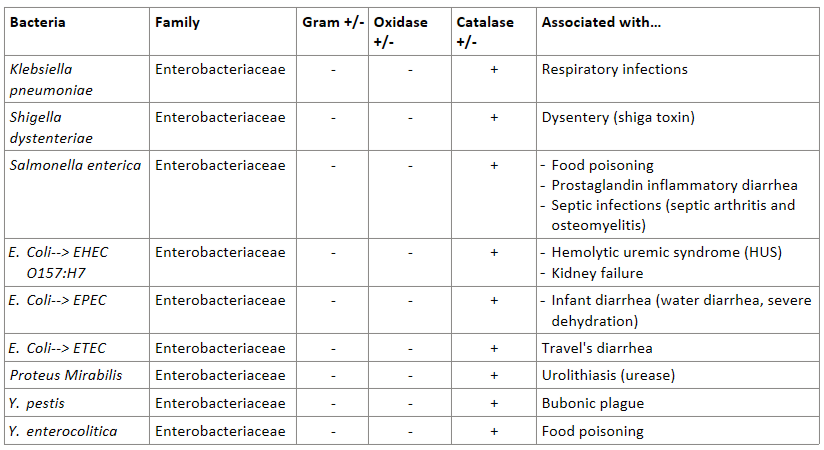
Enterobacteriaceae is a specific family of gram _______ rod/bacillus bacteria.
a. positive
b negative
b
What are some examples of Enterobacteriaceae?
(FYI!!!!!!!)
E. coli
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Salmonella enterica
Shigella sonnei, Shigella flexneri
Yersinia
Enterobacteriaceae is…
catalase + or -
oxidase + or - and all other Gram- are …
catalase +
oxidase -, ALL other gram - are oxidase positive
Enterobacteriaceae bacteria have what in its cell wall that acts a virulence factor?
O antigen in the LPS
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a cause of _________________.
respiratory infections
Answer the following about Shigella Dysenteriae (g- bacillus):
has what virulence factor that causes what?
the infective dose of this bacteria is ______.
shiga toxin—> causes dystentery
infective dose is LOW—> only need 200 bacteria to cause an infection
Answer the following about Salmonella enterica (g- bacillus):
humans can act as a ____________.
associated with what infections?
humans can act as reservoir (aka carry the bacteria but no symptoms)
infections:
food poisoning
prostaglandin inflammatory diarrhea
septic infections like septic arthritis and osteomyelitis
Answer the following about E. coli:
How does it acquire iron?
How can it become uropathogenic? What does that lead to?
iron acquisition with enterobactin/chelin
uropathogenic with P-pilus
leads to cystitis (in young females), UTI, pyelonephritis
There are many different “virotypes” of E. coli (g- bacillus /enterobacteriaceae).
Answer the following about the EHEC O157:H7 (enterohemorrhagic) virotype:
associated with what? (transmission wise)
can cause what syndrome? this leads to?
associated with petting zoos and undercooked hamburger
can cause hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) which can lead to kidney failure
There are many different “virotypes” of E. coli (g- bacillus /enterobacteriaceae).
Answer the following about the EPEC virotype:
causes _____________ in developing countries
leads to severe ____________
high/low mortality rates?
causes infant watery diarrhea in developing countries
leads to severe dehydration
HIGH mortality rates
There are many different “virotypes” of E. coli (g- bacillus/ enterobacteriaceae).
Answer the following about the ETEC virotype:
often associated with what?
traveler’s diarrhea
The enterobacteriaceae Proteus mirabilis is highly mobile and produces what enzyme? what is the result?
produces the enzyme urease—> leads to urolithiasis (urinary stones)
Answer the following about Y. pestis (g- bacillus/enterobacteriaceae):
associated with WHAT DISEASE?
how is it transmitted?
bubonic plague
transmission:
through rat fleas
pulmonary plague spreads from person to person
Answer the following about Y. enterocolitica (g- bacillus/enterobacteriaceae):
associated with what?
can survive at what temperature?
associated with food poisoning
can survive at 4 celcius (allows it to survive/multiple in food stored in the fridge)
ENTEROBACTERIACEAE REVIEW
Haemophilus aegyptius causes what disease?
Brazilian purpuric fever
Haemophilus ducreyi causes an STI known as a chancroid. What is the hallmark symptom of this?
painful necrotic ulcer
Answer the following about Haemophilus influenzae type B (HiB):
causes what disease/infection? in what patient population?
virulence factor?
vaccine type
causes meningitis in <2 years old
virulence factor—> PRRP CAPSULE
conjugate vaccine
Answer the following about Haemophilus influenzae type A (HiA):
causes what disease/infection? in what patient population?
does it have the same virulence factor as HiB?
causes:
otitis media in kids
sinusitis in adults
NO CAPSULE!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!—> result= can’t be typed (further classified)
Answer the following about Pseudomonas aeruginosa:
oxidase ±?
causes what infection?
known for infecting ________ wounds
highly __________
oxidase +
causes lung infection in cystic fibrosis
known for infecting BURN wounds
highly resistant
How is each of the following transmitted?
Vibrio cholerae
Vibrio vulnificus
Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Vibrio cholerae: fecal-oral route, leafy veggies
Vibrio vulnificus- shellfish
Vibrio parahaemolyticus- fecal-oral route, shellfish, oysters
Each of the following is associated with what symptom/infection?
Vibrio cholerae
Vibrio vulnificus
Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Vibrio cholerae- rice water diarrhea
Vibrio vulnificus- gastroenteritis, sepsis, wound infection
Vibrio parahaemolyticus- wound infection

Vibrio cholerae is associated with epidemic/pandemics. What enzyme is produced by this bacteria?
adenylate cyclase
What infection is Bordetella pertussis associated with?
How is it transmitted?
What vaccine is available for prevention?
WHOOPING COUGH in CHILDREN
transmitted through aerosols, droplets
DPT vaccine available
Legionella pneumophila is associated with what disease? How is it transmitted?
associated with Legionnaire’s disease (respiratory—> severe form of pneumonia)
transmitted by aerosols, ex: air-conditioning
Mycobacterium are a family of rod shaped bacteria.
What are some examples?
(FYI—> do not memorize)
M. tuberculosis
M. kansasii
M. avium
M. leprae
M. ulcerans
Answer the following about M. tuberculosis:
associated with what infection? more specific?
transmission
what route of infection?
People with underlying disease are more likely to have…
symptoms
virulence factor?
TB!!!!!!
MILITARY TB (widespread infection in body)
transmission: aerosols
hematogenous route of infection (enters bloodstream)
REACTIVATION TB—> more likely in ppl with underlying disease, old age, et.c
symptoms: hemoptysis (coughing up blood)
virulence—> CORD FACTOR, bind to mitochondria, prevents phagosome lysosome fusion
What is the 1st and 2nd line tx for tuberculosis caused by M. tuberculosis? Why would we use 2 drugs?
1st line- Isoniazid, Ethambutol, Rifampin, Pyrazinamide, Streptomycin
2nd line- Para-aminosalicylic acid, ethionamide, Cycloserine, fluoroquinolones, kanamycin
use 2 drugs bc it prevents resistance
Answer the following about M. kansasii:
what happens when this bacteria is exposed to light?
sometimes it can cause a false positive for what test?
photochromogenic (produces pigment when exposed to light)
can “mimic” TB and cause a FALSE POSITIVE ON PPD test
Answer the following about M. avium:
intra or extracellular?
results of acid-fast test
opportunistic in what pt. populations?
bc of low _____
intracellular
positive acid-fast test
opportunistic—> in immunocompromised and AIDs
bc of low CD4
Answer the following about M. leprae:
where does this bacteria grow?
caused what disease? symptoms?
Tx?
grows in foot pad of armadillo or mouse (cannot grow in agar/culture—> requires living host!!!!!)
causes:
tuberculoid LEPROSY—> patchy anesthesia
lepromatous LEPROSY—> severe, contagious, cell-mediated immunity defective
tx: DAPASONE—> take long term
Answer the following about M. ulcerans:
causes what skin disease?
is our immune response responsible for tissue destruction?
causes Buruli ulcer—> a chronic necrotizing skin disease
our immune response is NOT responsible for tissue destruction
Answer the following about Borrelia recurrentis:
what transmission method causes epidemics?
what transmission method causes endemics?
when must testing for this bacteria occur?
Louse/Lice—> causes epidemics with relapsing fever
ticks—> cause endemics
specimens for testing collected during FEBRILE PEROID
Answer the following about Borrelia burgedorferi:
what is the HALLMARK symptom?
causes what disease?
transmission?
symptom—> BULLS EYE RASH (aka erythematous migrans)
causes LYMES disease
transmitted by tick
Answer the following about Leptospira interrogans:
transmission by…
can survive in what?
symptoms of infection?
transmission by dogs, puppies
can survive in brackish water and at 4 degrees C
symptoms—> jaundice, hepatitis, infected spleen
What bacteria causes syphilis?
T. pallidum
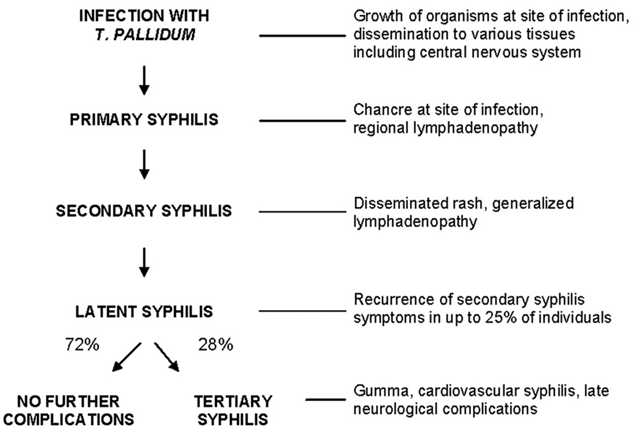
Answer the following about T. pallidum:
causes what infection?
what are the stages of infection?
what type of transmission?
What test identifies this bacteria?
T. pallidum
Stages infection:
Infection with T. pallidum
primary syphilis—> chancroid (painless ulcer)
secondary syphilis (systemic spread of bacteria)
latent syphilis (asymptomatic)
tertiary syphilis—> GUMMAS, CNS, paralysis, blindness
VERTICAL transmission (aka can be passed mom—> fetus)
VDRL test—> for T. pallidum and other spirochetes