NCM 118: RLE Module 6F: Mechanical Ventilation, Pace Making and ECG Interpretation
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
a positive or negative pressure breathing device that can maintain ventilation and oxygen delivery for a prolonged period
Mechanical Ventilation
Exerts positive pressure on the airway, pushing air in, similar to a bellows mechanism, and forcing the alveoli to expand during inspiration
Positive Pressure
generated on the outside of the chest and transmitted to the interior to expand the lungs and allow air to flow in
Negative Pressure
The ventilator forces a breath into the lungs whether or not the patient tries to breathe
Mandatory Breath
The patient breathes on their own using their muscles.
Air moves in and out naturally, without help from a machine.
Spontaneous Breath
A small device that sends electrical signals to make the heart beat if it’s too slow or irregular
Pacemaker
The wire that carries the signal from the pacemaker to the heart.
Pacemaker Lead
When the pacemaker’s signal successfully makes the heart beat.
Capture
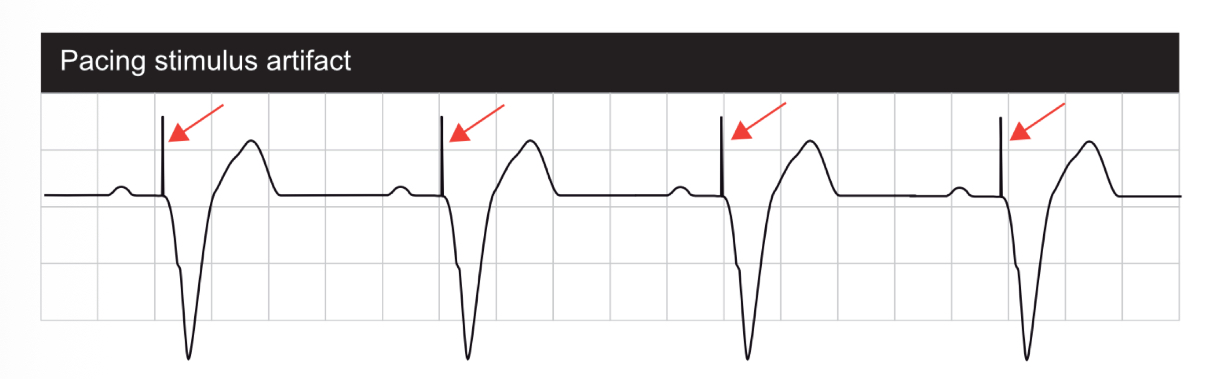
The spike on ECG showing the pacemaker sent a signal
Pacing Artifact
Tiny amount of electric current; 1 mA = 1/1000 of an ampere.
Milliampere (mA)
Pacemaker can detect the heart’s natural beats
Sense
How strong a signal the pacemaker needs to notice a heartbeat
Sensitivity
The minimum signal level needed to make the pacemaker fire a beat. Think: the “trigger point.”
Threshold
The test that records heart’s rhythm and electrical activity.
Electrocardiography (ECG)
the instrument used to record the heart's electrical activity, while an
the recording or tracing produced by that instrument
Electrocardiograph
Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG)
A procedure to study and treat serious heart rhythm problems.
Electrophysiology
Sensors that pick up the heart’s electrical signals
Electrodes
Wires that connect devices like pacemakers or ECGs to the heart.
Lead
Ability of cardiac cells to initiate electrical impulses on their own.
Automaticity
Ability of a cell to respond to stimulation by rapid changes in membrane potential via ion fluxes
Excitability
give 2 purposes, indications and contraindications of mechanical ventilation
Helps the patient to have adequate oxygen
To prevent injury from aspiration
Cardiac arrest/ Sepsis
Asthma
Tension Pneumothorax
Hypovolemic shock
give 2 purposes, indications and contraindications of pace making
To deliver electrical impulses to the cardiac muscle
Aids in managing heart failure
Slower-than-normal
impulse formation
Asymptomatic atrioventricular block
Severe bleeding
Active anticoagulation therapy
give 2 purposes, indications and contraindications of ECG analysis and interpretation
Evaluate how the heart is functioning
Diagnose heart illnesses
Palpitations
Cyanosis
Allergic to adhesive used to affix leads
Patient’s refusal
practice of gradually lowering and eventually discontinuing a patient's mechanical ventilation support
Weaning procedure
Methods of Weaning
Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation (SIMV)
Pressure-Support Ventilation (PSV)
Unsupported Spontaneous Breathing Trial
Methods of Weaning
Patient’s own breaths are synchronized with the decreasing machine breaths
Think: “Machine and patient breathe together, but machine slowly backs off.”
Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation (SIMV)
Methods of Weaning
All breaths are initiated by the patient.
Ventilator gives just enough pressure support to assist.
Think: “Patient leads, machine helps a little.”
Pressure-Support Ventilation (PSV)
Methods of Weaning
Patient breathes on their own.
Ventilator support is removed intermittently; a T-Piece or CPAP is used for short rest periods.
Unsupported Spontaneous Breathing Trial
Common PPV Modes
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
BiLevel Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP)
High-Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation (HFOV)
Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation (IMV)
Common NPV Devices
Iron Lung
Chest Cuirass