Linear algebra - Chapter 4
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What three conditions must a subset satisfy to be a subspace?
1) Contains the zero vector, 2) Closed under addition, 3) Closed under scalar multiplication.
What is the null space of a matrix A?
The set of all solutions to Ax = 0.
How do you find the null space of a matrix?
solve Ax = 0, Row reduce A to RREF, express the solution set in parametric form.
How do you calculate if a vector is in the Nulspace?
Multiple the vector by Matrix A, if the result is the zero vector it. is in the Nulspace
What is the column space of A?
The set of all linear combinations of the columns of A.
How do you determine if a vector b is in Col(A)?
Check if Ax = b is consistent.
What does it mean for a transformation T to be one-to-one?
T(x) = 0 has only the trivial solution; Nulspace = {0}.
What does it mean for T to be onto?
The range of T equals the codomain.
What is a basis for a vector space?
A linearly independent set that spans the enite space.
What two conditions define a basis?
1) The vectors are linearly independent, 2) They span the space.
What is the dimension of a vector space?
The number of basis vectors.
What is the dimension of the null space?
The number of free variables in the solution to Ax = 0.
What is the dimension of the column space?
The dimension of the column space (number of pivot columns).
What is the Rank Theorem?
rank(A) + nullity(A) = number of columns of A.
What does the Rank Theorem imply about solutions to Ax = b?
If rank < number of columns, infinitely many solutions; if rank = number of columns, unique solution (if consistent).
What is the basis theorem?
Every linearly independent set in an n-dimensional vector space contains at most n vectors; any spanning set must contain at least n.
How do you convert x to its coordinate vector [x]ᴮ?
Form an augmented matric with the basis vectors and x; row reduced to idenity matrix, resulting x is the co-ordinates of X in terms of B.
Are invertible matrixes singular or non-singular?
non-singular means it’s an invertible matrix
singular means non-invertible matrix
What is the defining formaular for an invertible Matrix?
A dot A-1 = A-1 dot A = Identiy Matrix
How do you calculate the inverse for a 2 by 2 matrix?
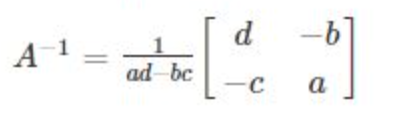
How do you calculate the inverse for a 3 by 3 non-triangular matrix?
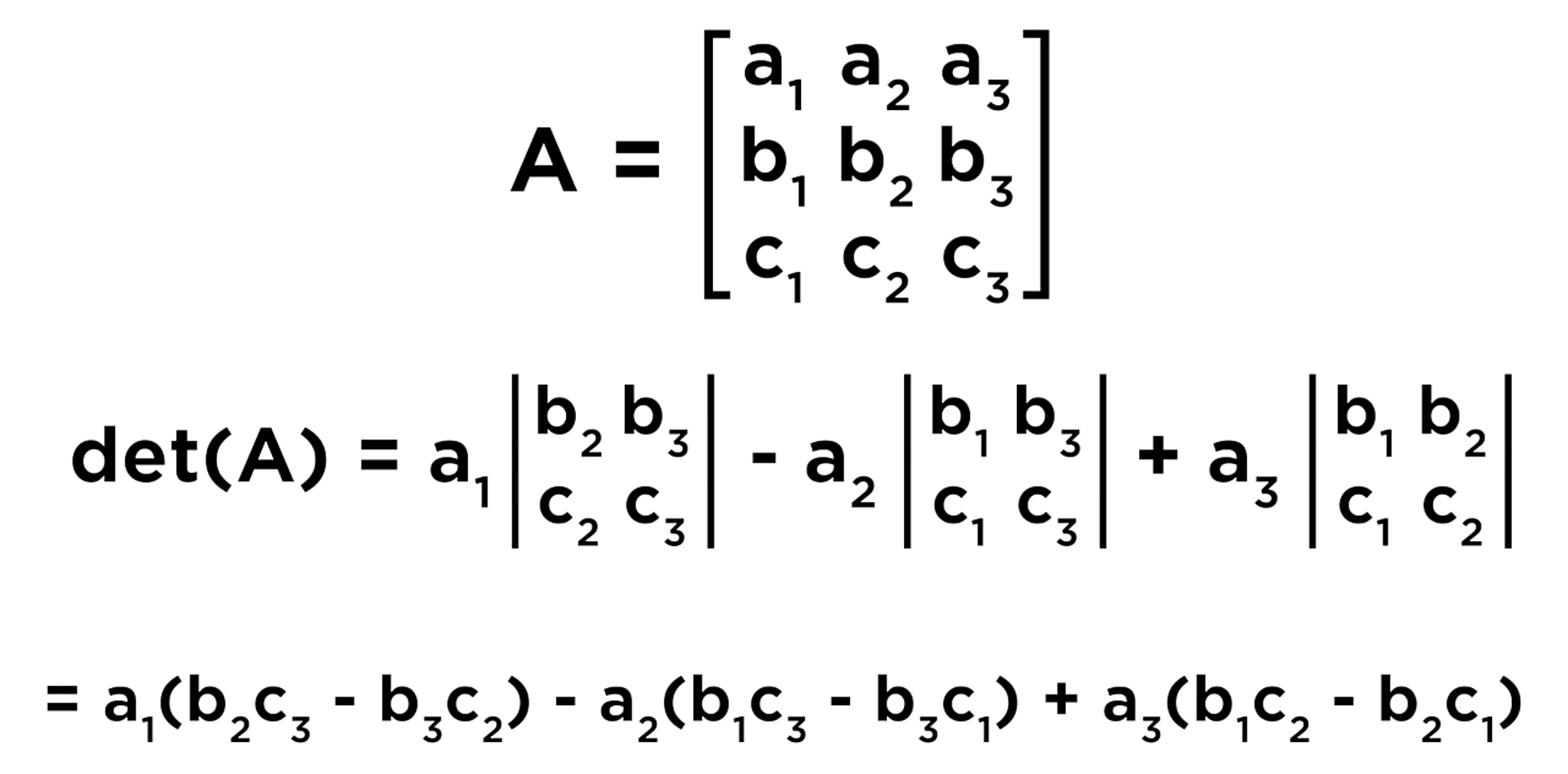
What does it mean for two vector spaces to be isomorphic?
They have the same structure and same dimension but different co-ordinates
When is a tranformation isomorpshic
A tranformation is sisomorphic when it’s one-to-one, onto and linear
How do you convert a coordinate vector [x]ᴮ back into the original vector x?
Multiply the basis matrix B by [x]ᴮ.
What are 4 things to remember when manipulating linear equations:
The identity matrix acts like the unit 1
Never divide instead multiple a matrix by it’s inverse to move to the other side
Multiply on the correct side
What would be a basis for:
A line through R³
The entire R³ subspace
(1 0 0) or (0 0 1) or (0 1 0)
{(1 0 0), (0 0 1), (1 0 0)}
What is a co-ordinate?
Coordinates are the unique scalar weights that specify how much of each basis vector is required to form a particular vector.
What does it imply if two matrices are row equivalent?
Their row spaces are the same
If B is in echelon form. the non-zero rows of B form a basis for the row space of A