PLTW- Biomed End of Course Final Review
1/208
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
209 Terms
How quickly does the body lose heat after death?
Approximately 1.5 degrees Fahrenheit per hour until it reaches surrounding environment temp
Who did the fingerprint at the crime scene belong to?
Alex Garcia
What is rigor mortis?
stiffening of the muscles after death
What is lividity?
Pooling of the blood after death
What is algor mortis?
Cooling of the body after death
What causes your muscles to become stiff after death, or rigor mortis?
The loss of ATP which lasts for about 3 hours after death
What are the 5 manner of death possibilities?
Homocide, suicide, natural, accident, or undetermined
What does a crime scene sketch include?
Sketch, key, and scale
What are antigens?
proteins found on the surface of red blood cells
What are the 8 different blood types?
A+, A-, B+, B-, AB+, AB-, O+, O-
What is blood composed of?
liquid plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, antigens and antibodies
What protein is hair composed of?
Keratin
What are the 4 main fingerprints?
arch, loop, whorl, tented arch
What are minutiae?
Specific ridge marks in the fingertips
What is an arch fingerprint?
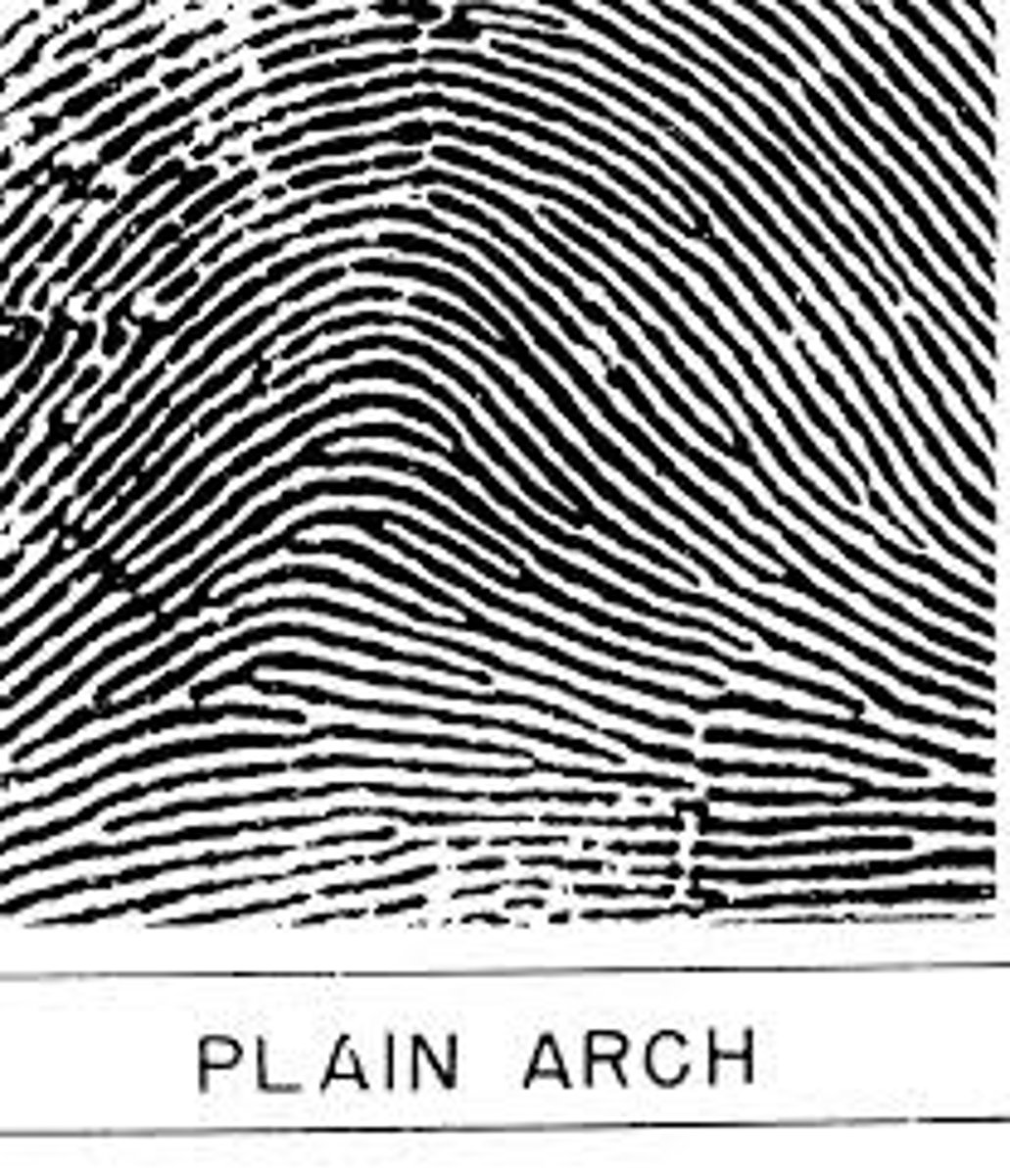

What is a loop fingerprint?
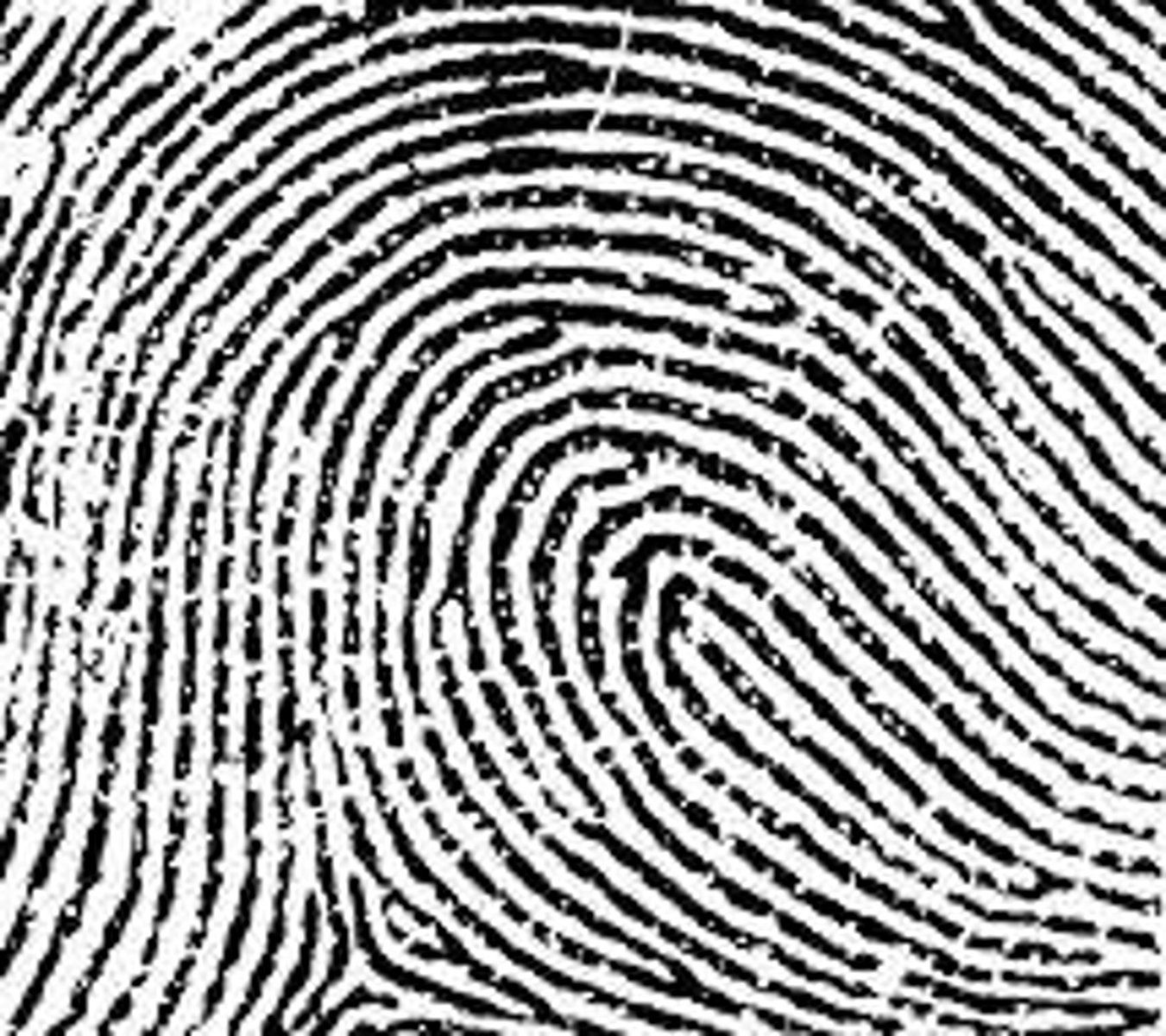

What is a whorl fingerprint?

What is a tented arch fingerprint?

Do red blood cells have DNA?
NO
What shape is DNA in?
a double helix
How many bonds do adenine and thymine need?
2 hydrogen bonds
How many bonds do Guanine and cytosine need?
3 hydrogen bonds
Which was does DNA run
negative
Which two nitrogen bases are purines
Adenine and Guanine
Which two nitrogen bases are pyrimidines
Thymine and Cytosine
Approximately how many nucleotides are in a strand of DNA?
over 3 billion
How is DNA packaged?
DNA is packaged as chromosomes, that contain numerous segments of DNA called genes
Why is HIPPA important?
it keeps our medical information safe and confidential
When should HIPPA be broken?
if it could harm the public, epidemic, child abuse, or emergency
What is acetylsalicylic acid used to treat?
Prescribed to prevent high cholesterol and diabetes
What does HIPPA stand for?
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
What kind of diabetes did Anna have?
Type 1 diabetes
What does type 1 diabetes mean?
The pancreas of a person with type 1 diabetes will no longer produce insulin
What does type 2 diabetes mean?
A person with type 2 diabetes will have damaged insulin receptor sites so they are not getting the insulin they need
What would a glucose and insulin chart of a person with type 1 diabetes look like?
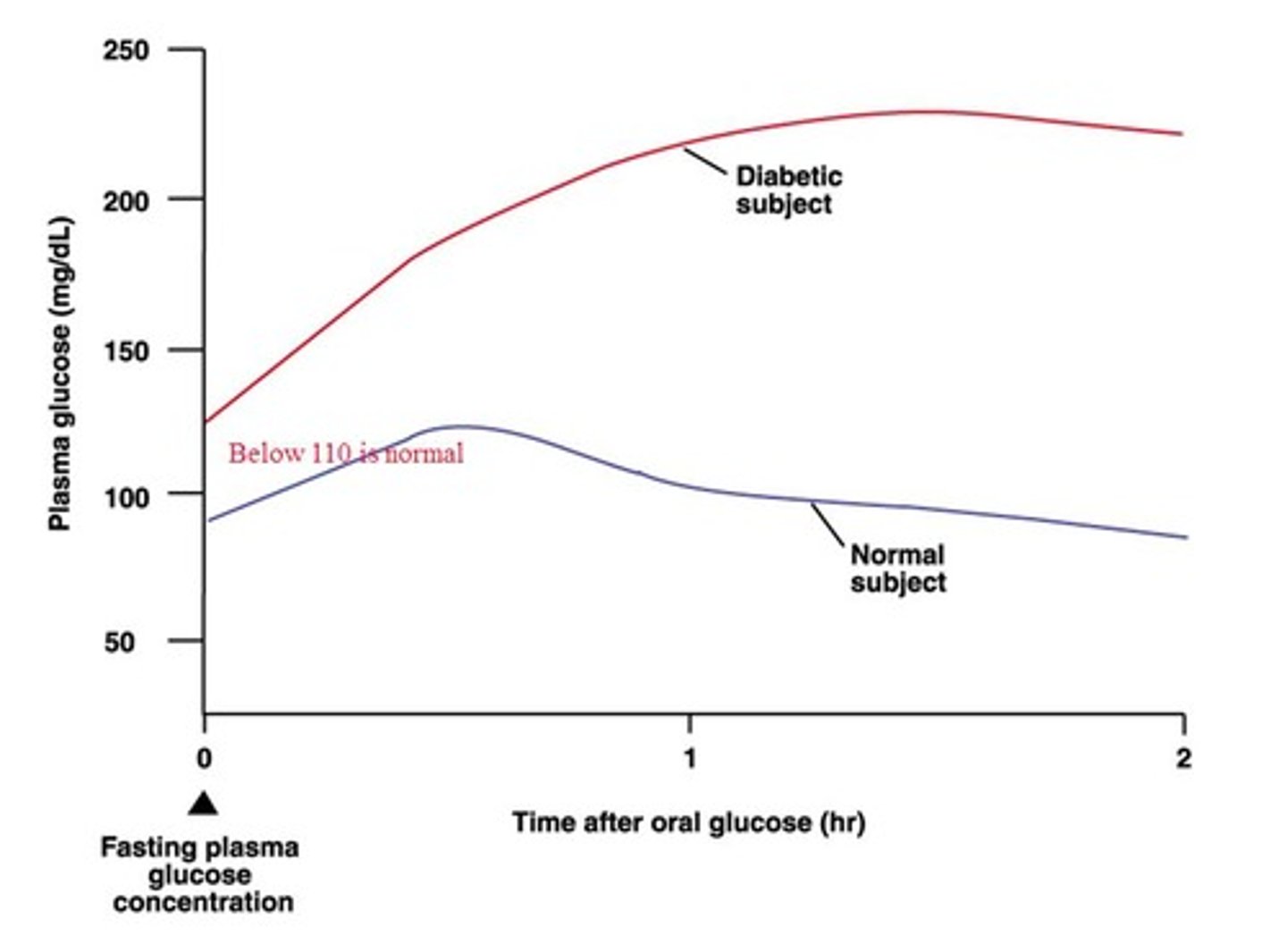
What is benedicts solution used for?
Used to test for sugar/glucose, normally light blue, when heated with presence of sugars it turns green, yellow, orange or red
What is lugols iodine used for?
indicates starch (carbohydrates), normally yellow or light brown, in the presence of starch it turns dark purple or black
What is biurets solution used for?
indicates protein, normally light blue, changes to violet/purple in presence of protein
What does Chargaff's rule state?
That adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine
What is sickle cell disease?
Individuals who are homozygous for the gene controlling hemoglobin S. The disease is characterized by the destruction of red blood cells and by episodic blocking of blood vessels because of the shape of the blood cells.
How any nucleotides code for 1 amino acid?
3
What is a protein?
A chain of amino acids bonded by peptide bonds
What is the general structure of an amino acid?
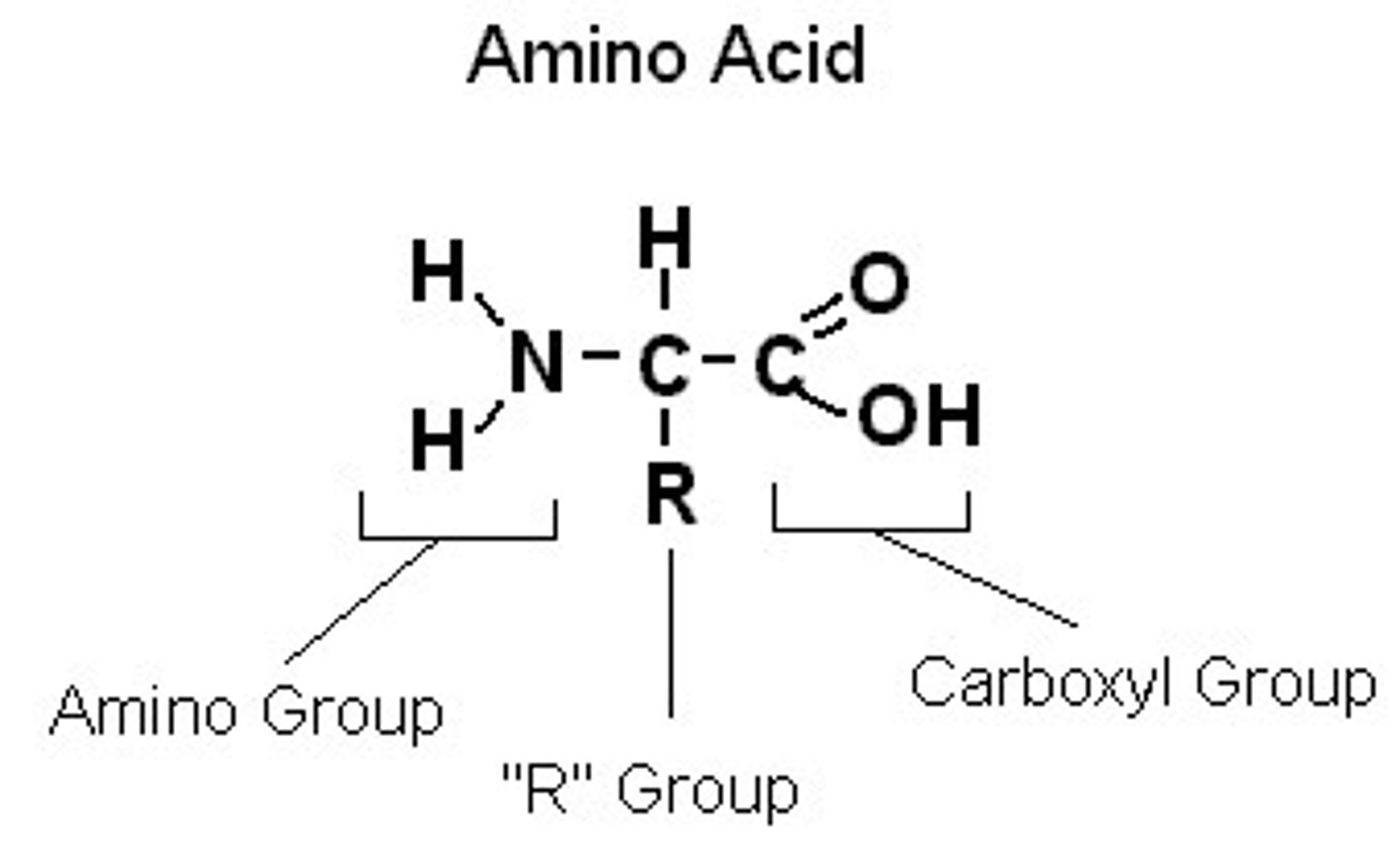
How does DNA replicate?
the Helicase enzyme breaks the hydrogen bonds so the DNA unzips and forms a copy
What are the steps in making a protein?
1. DNA in nucleus is unzipped by enzyme of helicase(protein)
2. Transcription: messenger RNA copies instructions from DNA and carries the code to the ribosome in the cytoplasm *code is carried in groups of 3 amino acids called a codon
3. Translation: TRNA brings the amino acids to the ribosome
4. Synthesis: proteins are put together by ribosomal RNA
What is the overall charge of DNA?
negative
How does DNA always start?
Always start with AUG or Met
What is a genetic mutation?
an inheritable change in the nucleotide sequence of an organisms DNA that ultimately serves as a source of genetic diversity
What are some causes of a genetic mutation?
-DNA fails to copy accurately
-external influences (chemicals, radiation)
*most mutations are naturally occurring
What is sickle cell disease caused by?
A point mutation on chromosome 11
The outside backbone of the DNA molecule is made of alternating molecules of what?
phosphate and sugar
When isolating DNA, what was the purpose of the detergent component of the lysis buffer solution?
to break the nuclear and cell membranes
What does the alcohol do when you are isolating DNA?
It precipitates the DNA out of the solution
What act as molecular scissors to cut DNA at specific locations?
Restriction enzymes
What does the polymerase chain reaction do?
it enables scientists to produce millions of copies of a specific DNA sequence from a small amount of DNA
What is the leading cause of death in the US?
Heart disease
What is the normal amount of blood in a human body?
5.6 liters
What forms and replaces your blood cells?
bone marrow
What is the role of blood plasma?
carries nutrients and platelets
What is the role of red blood cells?
carries oxygen to all parts of your body
What is the role of white blood cells?
they fight off infections
What is the role of platelets?
clots the blood to stop bleeding
What is the name for platelets?
thrombocytes
What is the name for red blood cells?
erythrocytes
What is the name for white blood cells?
leukocytes
What is hemoglobin?
the amount of red blood cells in the blood
What are some things that could cause a sickle cell crisis?
certain medications, high altitudes, and strenuous exercise
What are some symptoms of a sickle cell crisis?
fever, pain, weakness or fatigue, abdominal pain and swelling or headaches
When does sickle cell hemoglobin happen?
when glutamic acid is substituted with valine because of a point mutation on the 6th codon after AUG or the 7th codon of the entire beta-hemoglobin
What is insulin?
a type of protein called a hormone
What is the function of insulin?
functions to control glucose levels in the plasma, opening the cell channels
What can diabetes lead to?
-amputations
-kidney diseases
-vision loss
-billions of dollars spent
What is the normal glucose levels?
70 mg/dL - 115 mg/dL
What was Anna's glucose level?
425 mg/dL
What are some symptoms and effects of diabetes?
-frequent urination
-unusual thirst
-extreme hunger
-fatigue
-cuts/bruises slow to heal
-tingling/ numb hands or feet
-weight loss
-frequent infections
Describe type 1 diabetes:
1. stomach changes food into glucose
2. glucose enters bloodstream
3. pancreas makes little to no insulin
4. little or no insulin enters the blood
5. glucose builds up in the blood
Describe type 2 diabetes:
1. stomach changes food into glucose
2. glucose enters blood
3. pancreas makes insulin
4. insulin enters blood
5. glucose cant get into the cells of the body
6. glucose builds up in the blood
What is the treatment for type 1 diabetes?
-take insulin
-carb counting
-frequent blood sugar monitoring
-healthy eating and exercise
*they need to take insulin*
What is the treatment for type 2 diabetes?
-healthy eating
-exercise
-possibly medication or insulin therapy
-blood sugar monitoring
*metformin improves sensitivity of insulin receptors on body's cells*
What is a positive feedback loop, and give an example?
causes a reinforcement of the original action, so the input causes the action to increase, production of oxytocin for labor
What is a negative feedback loop, and give an example?
causes the system to stop doing the original action and to either take no action or to perform an opposite action, production of insulin to regulate glucose levels
What kind of feedback loop is the glucose insulin feedback loop?
negative feedback loop
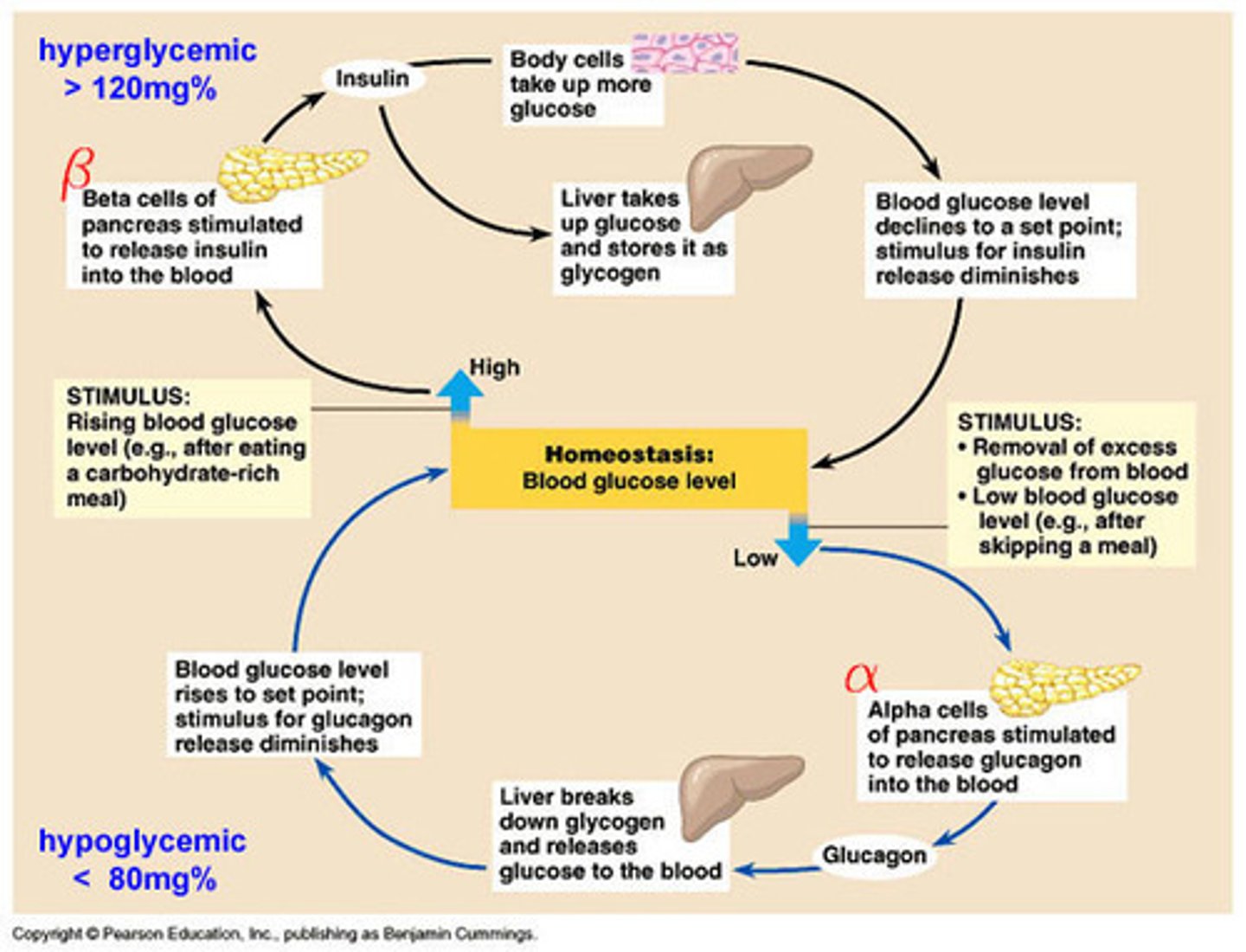
What do alpha cells do?
produce glucagon sent to the liver
What do beta cells do?
produce insulin sent to blood and liver
What can excessive glucose in the blood result in?
reduced blood flow to hands and feet, constriction of blood vessels, necrosis, and neuropathy
What is insulin considered to be?
protein, hormone, and a signal molecule
What is the job of the glut-4 vessels?
allows glucose to pass from blood plasma into cell cytoplasm
Around 10 am and 3 pm, you become hungry because your stomach is empty. Then, your energy level drops. If you do not have access to food, how does your body get energy to keep you going until dinner?
your pancreas secretes glucagon which is transported to the liver and is used to convert glycogen back into glucose and the ATP for energy
When you tested the food in Anna's stomach from the autopsy you found her diet on the morning of her death to contain what?
glucose, carbohydrates, lipids/fats, NO PROTEINS
Describe a glucose tolerance test?
fast for 8-12 hours, have blood drawn for a baseline glucose level and every 30 minutes for 2 hours
When a person has type 1 diabetes, what is wrong with their beta cells?
their beta cells are not functioning
What is hyperglycemia?
the medical term for high blood sugar levels
What is hypoglycemia?
medical term for low blood sugar
hypotonic solution
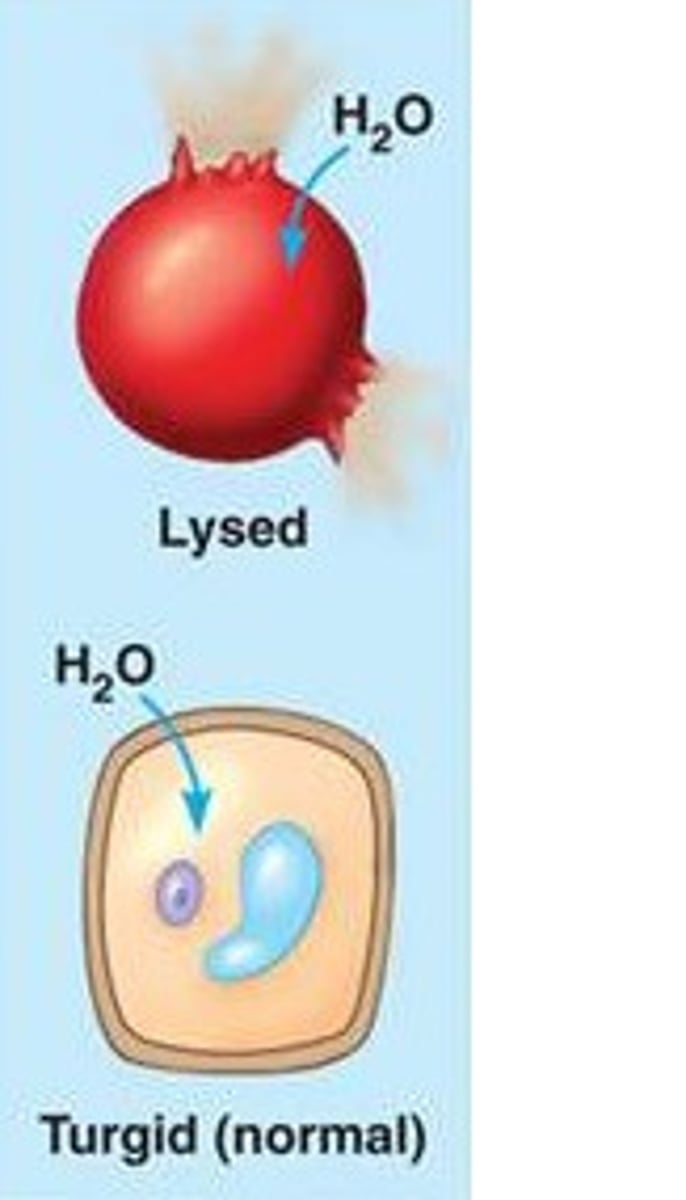
hypertonic solution
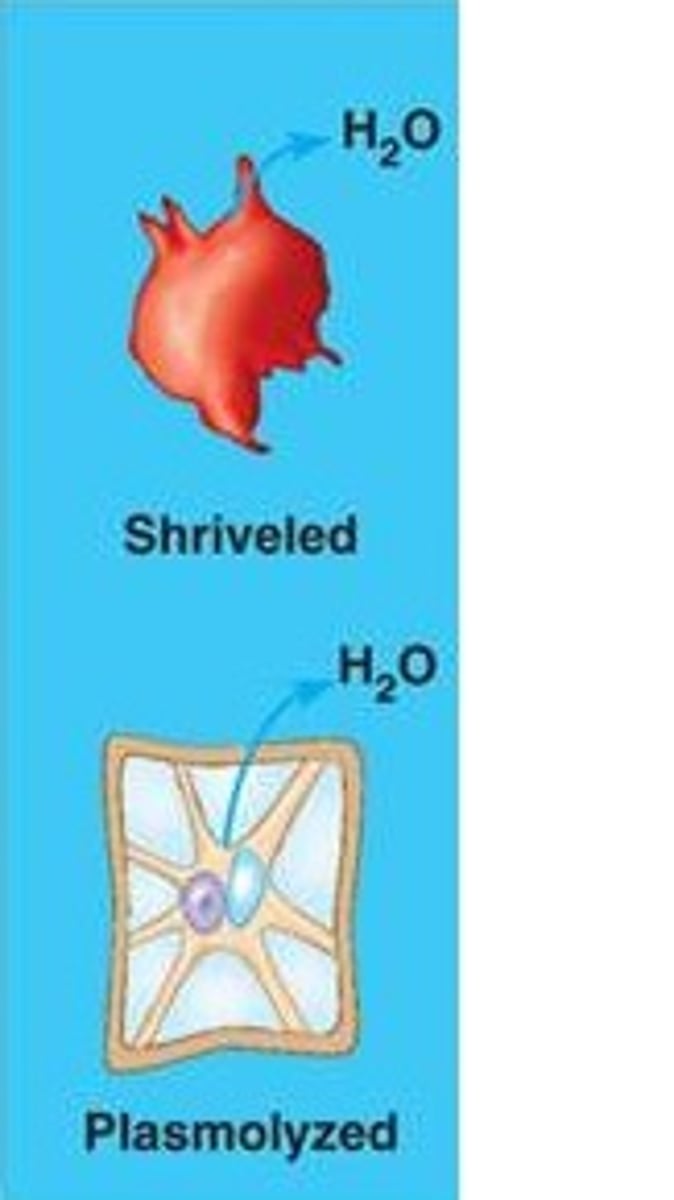
isotonic solution
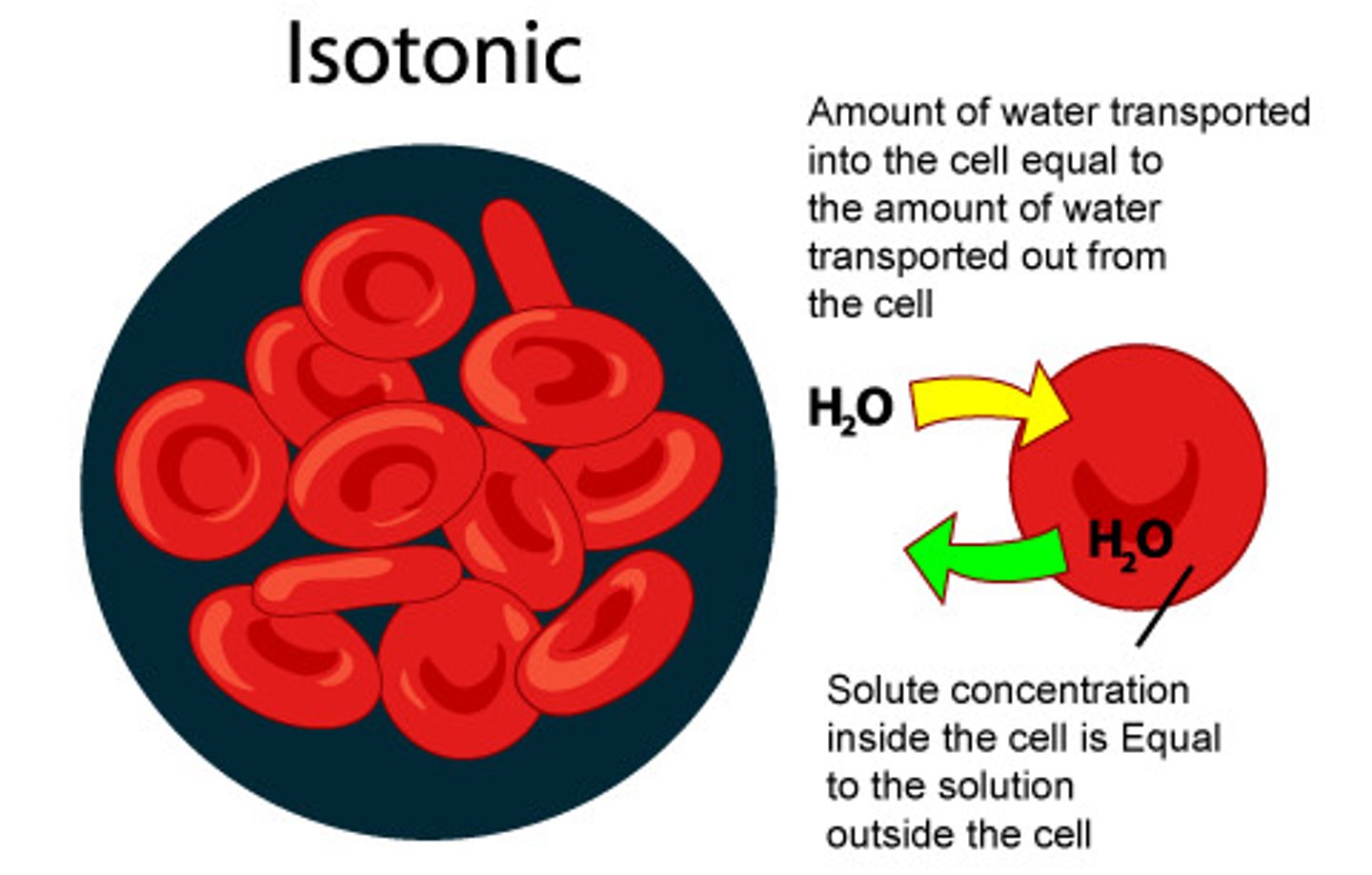
What are monomers?
small molecules which may be joined together in a repeating fashion to form more complex molecules called polymers
What are polymers?
made up of many molecules all strung together to form really long chains
How is anemia diagnosed?
a hematocrit test
What is the normal hematocrit level for females? males?
female: 35-46
male: 42-54