clinical skills group quiz 1 contents
1/768
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
769 Terms
POC ultrasound
bedside ultrasound used as a quick way to assess for pathology
phased array probe

linear probe

curvilinear probe

endocavitary probe
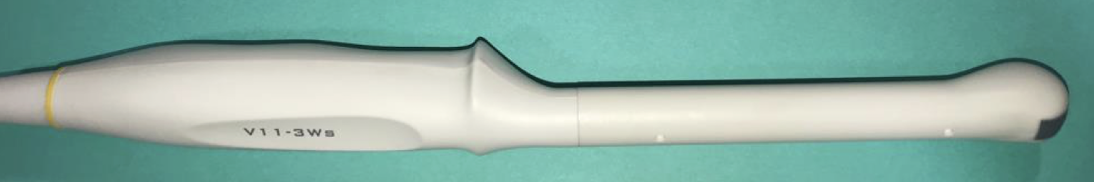
linear probe frequency
5-15 MHz
linear probe uses
soft tissue, MSK, peds, ocular, trachea, thyroid, thoracic, many procedures, DVT, appendicitis, testicular
linear probe depth
superficial
curvilinear probe depth
deep
curvilinear probe frequency
2-5 MHz
curvilinear probe other name
OB/belly probe
curvilinear probe uses
gallbladder, liver, eFAST, renal, aorta, IVC, bladder, bowel, OB/gyn
phased array probe depth
deep
phased array probe frequency
1-5 MHz
phased array probe other name
cardiac probe
phased array probe uses
cardiac, abdominal, eFAST, renal, bladder, bowel, IVC
endocavitary probe frequency
8-13 MHz
endocavitary probe uses
OB/gyn, peritonsillar abscess
general ultrasound indicator location
R on patient, L on screen
cardiac ultrasound indicator location
L on patient, R on screen
anechoic color
black
hypoechoic color
dark
hyperechoic color
bright
anechoic structure
fluid
hypoechoic structure
soft tissue
hyperechoic structure
bone/air
sagittal plane
coronal/frontal plane
transverse plane
sensitivity
ability of a test to result in a true positive
specificity
ability of a test to obtain normal range/negative results for those who do not have the disease
general gold standard
best diagnostic test for diagnosing a particular disease process
reference range
set of values that represent what is considered normal/expected
critical value
indicate an immediate risk to the patient
point of care testing
done near the patient (ex - BG, pregnancy, US)
provider performed microscopy
diagnostics performed by the provider common in vet/rural med (ex - KOH prep)
lab testing indications
dx, screening, risk assessment, monitor disease and therapy
components of CBC
WBC, RBC, Hgb, Hct, MCH, MCHC, MCV, RDW, platelets
components of differential
lymphocytes, neutrophils (bands and segments), eosinophils, basophils, monocytes
components of BMP
Na+, K+, BUN, creatinine, glc, Ca2+, Cl-, bicarb, GFR
WBC normal range
3200-9800 (prickett) or 4000-11000 (everything else on the internet)
WBC sensitivity/specificity
very sensitive, NOT specific
hyperleukocytosis
>100,000, indicates cancer
leukocytosis
generally elevated WBC, can indicate infection, dehydration, stress
leukopenia
decreased WBC
elevated neutrophils
acute bacterial infection
left shift meaning with CBC
elevated
right shift meaning with CBC
decreased
decreased neutrophils
viral infections
elevated eosinophils
allergies, parasitic infections
elevated basophils
inflammation
decreased basophils
stress
elevated monocytes
viral diseases, parasitic
elevated lymphocytes
chronic infections
decreased lymphocytes
HIV
Hgb normal female
12-15
Hgb normal male
13.6-17.7
anemia
low hgb
erythrocytosis
too many RBCs
hematocrit
RBCs/total blood
hematocrit normal female
33-43%
hematocrit normal male
39-49%
platelets
clotting factor
platelet normal range
130,000-400,000
thrombocytosis
elevated platelets
thrombocytopenia
decreased platelets
elevated potassium
hemolysis
decreased potassium
GI loss (vomiting, diarrhea)
creatinine
muscle waste product filtered by kidneys
elevated creatinine
kidney dysfunction
blood urea nitrogen
waste product from protein breakdown
elevated BUN
kidney dysfunction, upper GI bleed
glomerular filtration rate
rate kidneys filter
decreased GFR
kidney dysfunction
components of CMP
all BMP + LFTs
alk phos, alanine transam, aspartate aminotransf, total protein, albumin, bilirubin
denisities on xray dark to light
air, fat, soft tissue/fluid, calcium, metal
x-rays
images produced using ionizing radiation
x-rays advantages
inexpensive, readily accessible
x-rays disadvantages
limited range of densities, limited detail, potential to cause cell mutations/cancer
IVP dye
iodine based dye used for CT
oral contrast
used for gastric bypass patients
barium contrast
used in GI tract
gadolinium contrast
used in MRI
CT scan
rotating x-ray beams and multiple detectors to produce images
CT measurement units
hounsfield units
CT windows
lung, mediastinal, bone
MRI
uses magnets to manipulate hydrogen ions
MRI advantages
more detailed, no radiation
MRI disadvantages
expensive, time consuming, not readily available, closed space
T1 weighted MRI
anatomic, fat realigns quickly
T2 weighted MRI
pathologic, water realigns slowly
T1 MRI colors
bright - fat
dark - water, CSF, infection/demyelination
T2 MRI colors
bright - CSF, fat, water, infection/demyelination
dark - brain white matter
fluoro
uses x-rays, CT, or MRI to perform real time visualization often with contrast
fluoro uses
GI procedures, IR/angiograms
fluoro advantages
can be relatively mobile, assess in real time
fluoro disadvantages
exposure to ionizing radiation higher than x-ray
nuc med
uses radionucleides, radio tracers
nuc med examples
SPEC, PET, HIDA, bone scintigraphy (bone scan)
thyroid nuc med affinity
iodine