2. Structure and Function of the Hippocampus
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What does the hippocampus look like?
a slice through looks like onion rings
along tis length the hippocampus shows distinct cell fields that are tightly folded
What is involved in the loop which occurs within the hippocampus?
within the hippocampus
inputs via dentate gyrus
associations between CA1 and CA3 fields
outputs via subiculum
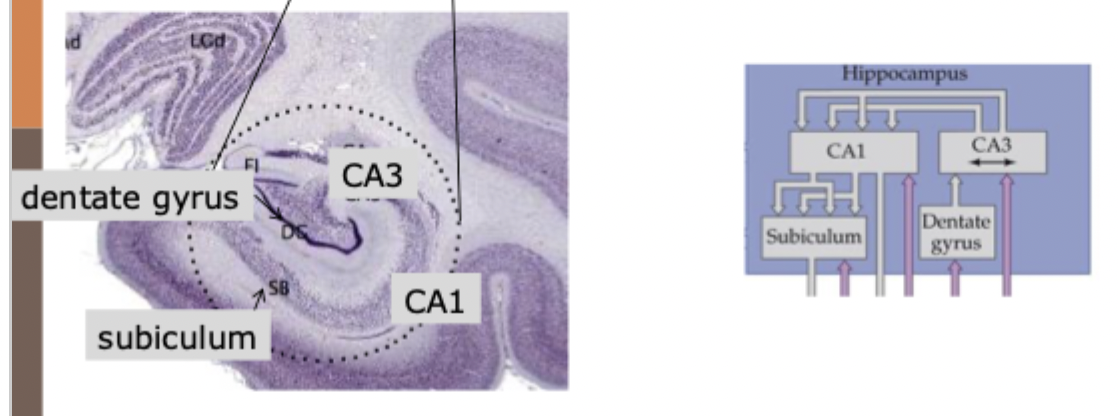
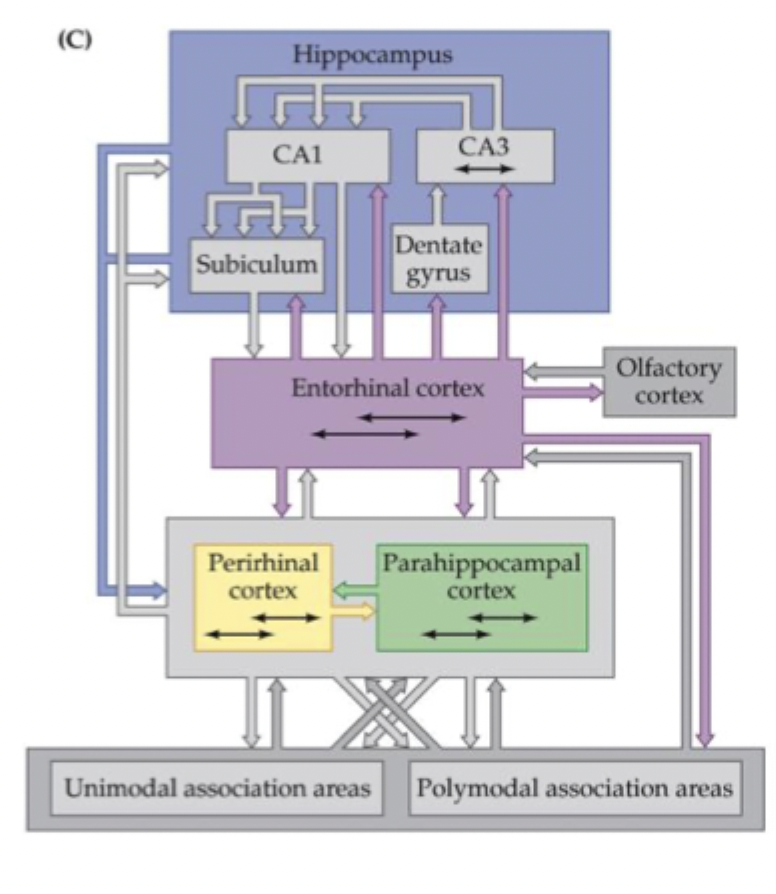
What are the 4 structures adjacent to the hippocampus and what are their key functions?
entorhinal cortex
rhinal sulcus
perirhinal cortex
parahippocampal cortex
What is the key function of the entorhinal cortex?
gateway between hippocampus and cortex
what is the function of the perirhinal cortex?
important for object recognition
what is the parahippocampal cortex important for?
spatial layout coding
What is the Hippocampus’ role in Eichenbaum’s relational theory?
hippocampus forms associations e.g. between what and where
it’s where the binding process takes place between diverse inputs
the adjacent perirhinal and parahippocampal cortex learn about familiar objects and locations
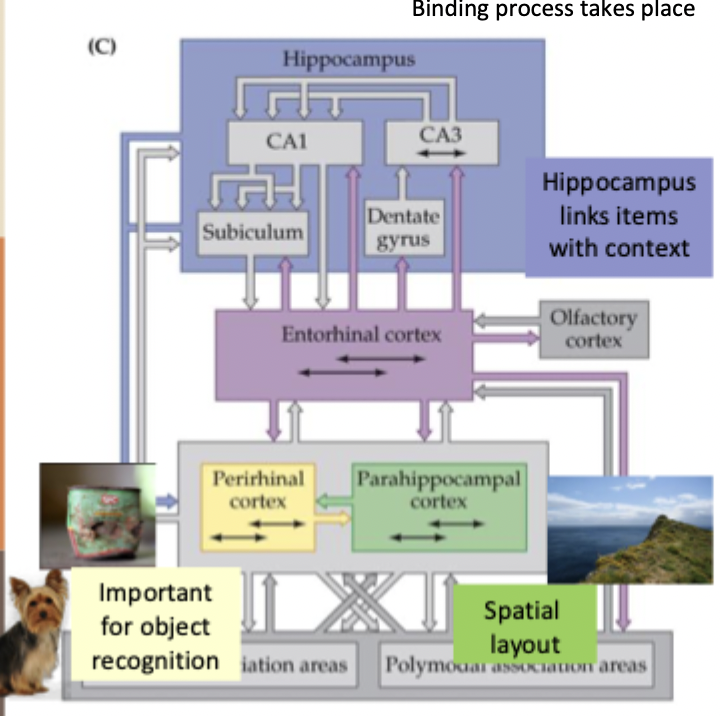
How does the posterior hippocampus differ from the anterior?
greater input from parahippocampal cortex: spatial memory
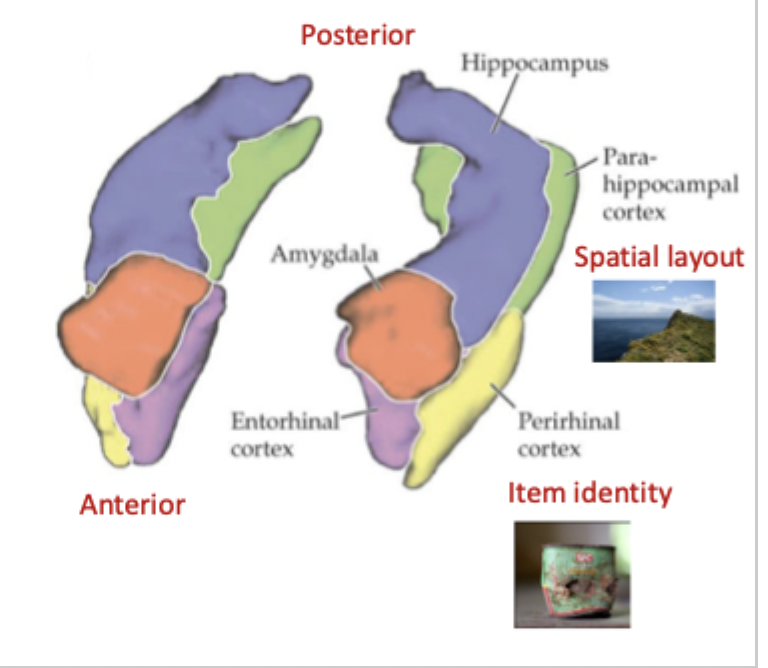
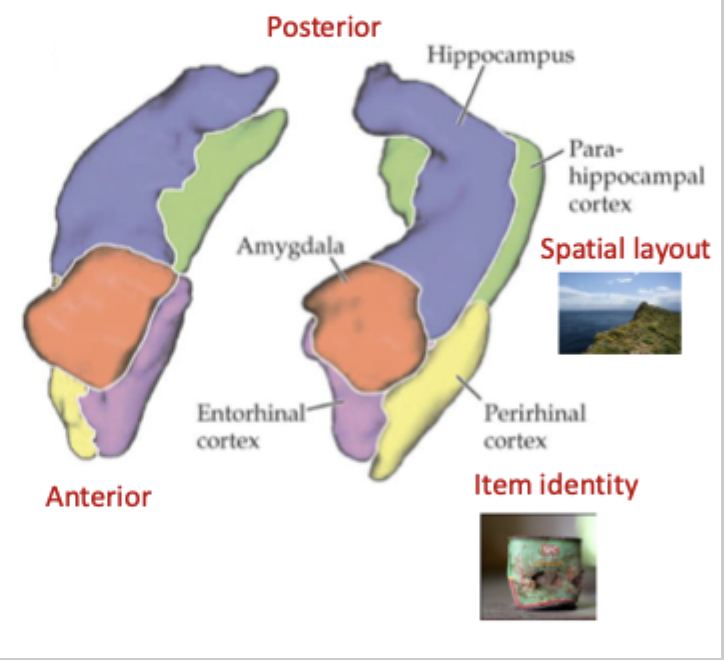
How does the anterior hippocampus differ from the posterior?
greater input from the amygdala and perirhinal cortex: emotional memories, item familiarity/ salience
Features of the hippocampus that supports multi-modal associative memory
received connections from all modalities - e.g., vision, sound, smell, emotions → memories are multisensory
contains multiple nested feedback loops/ multiple pathways information can flow through → ideal for associative learning
neurons have special properties that support memory
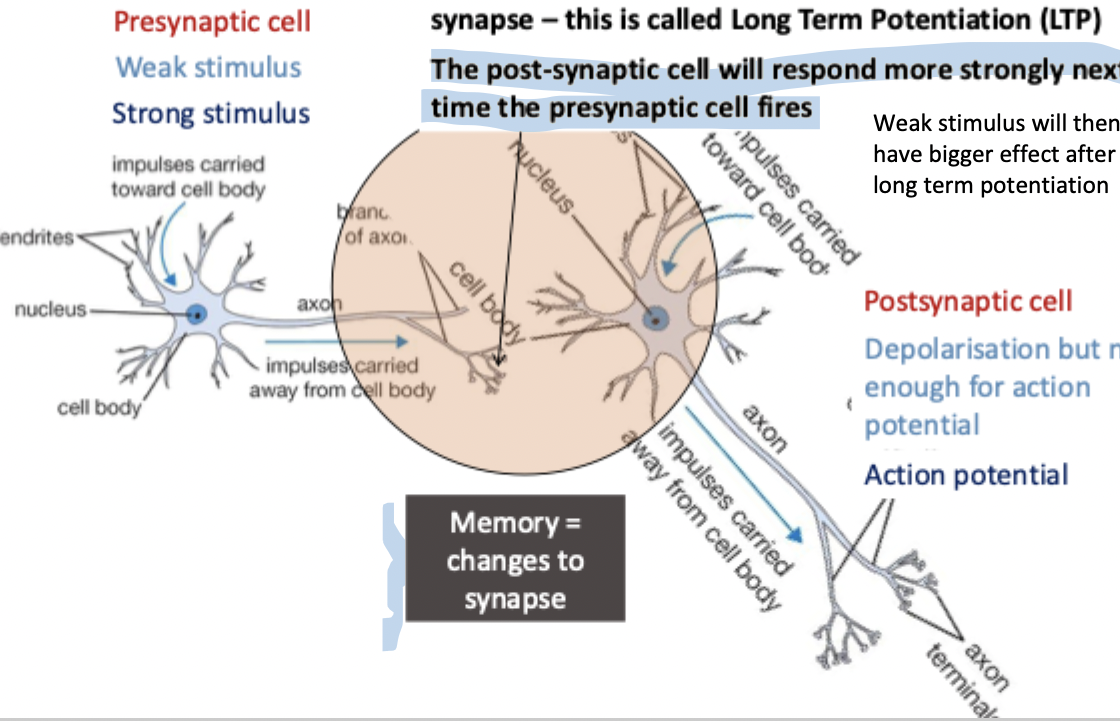
Long-term memory at the level of individual neurons…
reflects structural changes at the synapse
What was Donal Hebb’s suggestion regarding how synaptic changes underpin memory? (1949)
Memories are stored in connections between neurons (“cell assemblies”)
LTM through Hebbian learning: “cells that fire together, wire together”
in the brain, this happens because of long-term potentiation (LTP)
What happens in order for long-term potentiation to occur?
memory = changes to synapse
release of some glutamate (excitatory neurotransmitter) by presynaptic neuron, some Na+ channels open briefly
release lots of glutamate, ion channels in post synaptic cell open for longer, large influx of Na+ ions
this strengthens communication at this particular synapse - this is called long term potentiation
the post-synaptic cell will respond more strongly next time the presynaptic cell fires
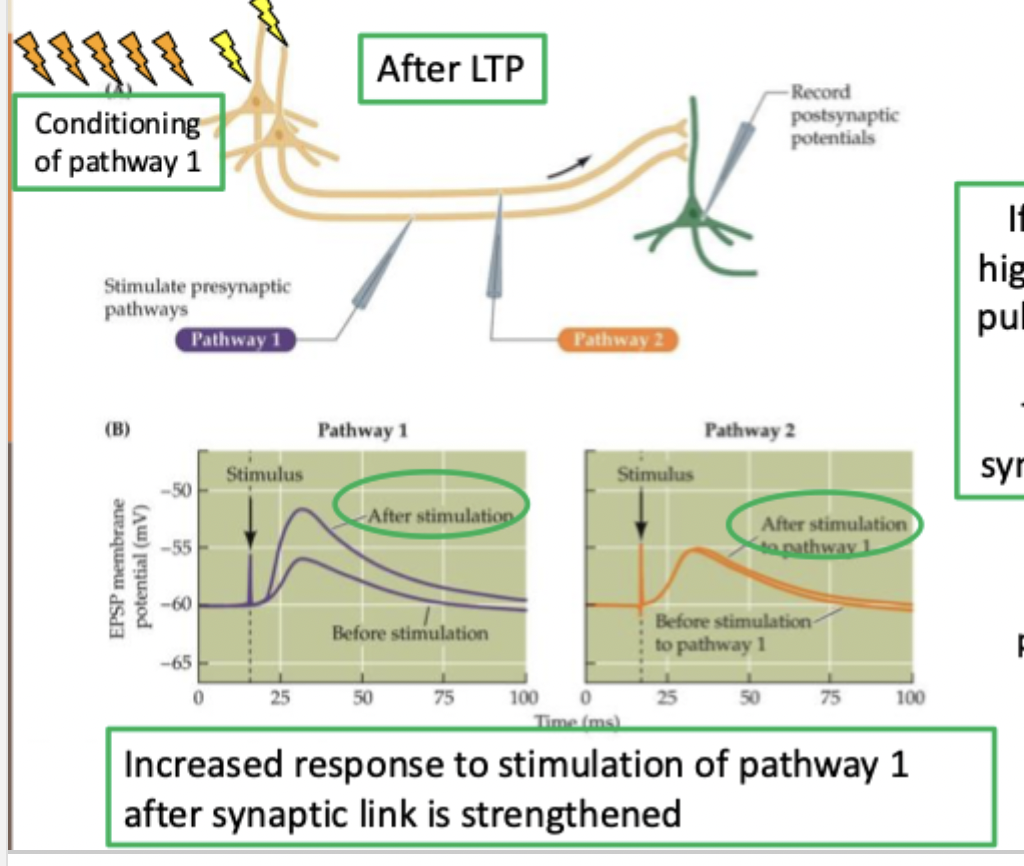
What did Bliss and Lomo find regarding LTP in rabbit hippocamus?
before LTP a single pulse to pathways 1 and 2 triggers slight depolarisation in post synaptic cell
If pathway 1 is conditioned with high frequency stimulation, a single pulse now drives a bigger response. Pathway 2 does not change. The connection at this specific synapse has been enhance by LTP
What is the role of NMDA receptors in long term potentiation?
LTP occurs across the brain but hippocampal cells are particularly rich in NMDA receptors
in CA3 and CA1 hippocampus subsections, there are two types of glutamate receptors
if there’s enough sodium, magnesium will be pushed out of the way, no longer blocking NMDA channel → bigger action potential
calcium can only enter post-synaptic cell if action potential has already taken place as it can get through unblocked NMDA receptors
What are the changes in synaptic function and morphology associated with LTP maintenance?
structural changes = “synaptic consolidation”
increases in receptor density
increases in neurotransmitter release
enlargement of synapse
division of synapse
formation of new dendritic spines
In the hippocampus associations of a variety of inputs may be formed by…
LTP between the CA1 and CA3 hippocampal neurons
Due to LTP, how is memory for a single event possible?
LTP can be induced by a single high frequency train
What determines how long the synaptic changes last?
LTP elicits changes that last for weeks - “synaptic consolidation”: makes memories durable
What is the consequence of LTP specificity?
Only synapses active during the stimulation are increased; inactive pathways to the same neuron are not
doesn’t change the whole neuron but only the synapse
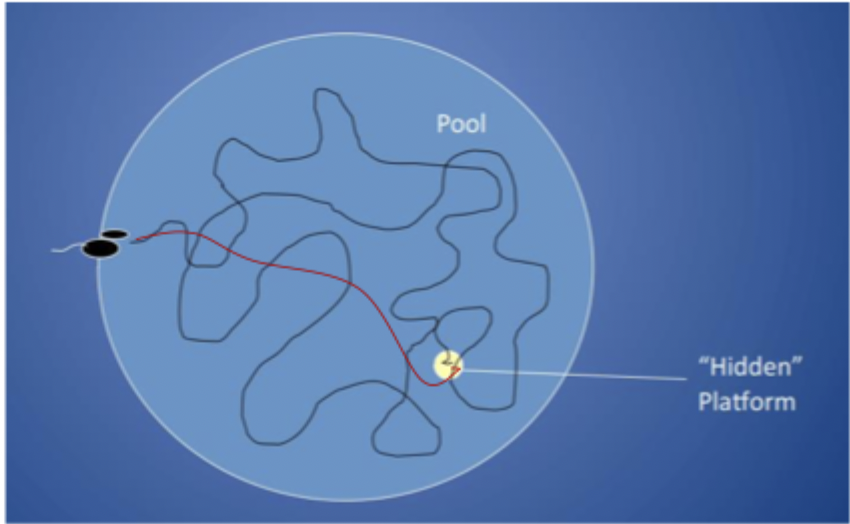
What is the procedure of the Morris water maze?
trial 1: rat searches for way out and discovers hidden platform
trial 2: rat remembers location of platform. Swims there much faster, using landmarks around room to navigate
What can be concluded from studies of hippocampal lesions in rats?
shows role of hippocampus in memory tasks
posterior hippocampus is more important for spatial memory
these studies do not show the contribution of specific processes like LTP
What could be concluded from pharmacological studies, bathing hippocampus of rats in NMDA receptor antagonists (blocks glutamate binding site)
shows importance of LTP in hippocampus- but doesn’t reveal importance of NMDA receptors specifically
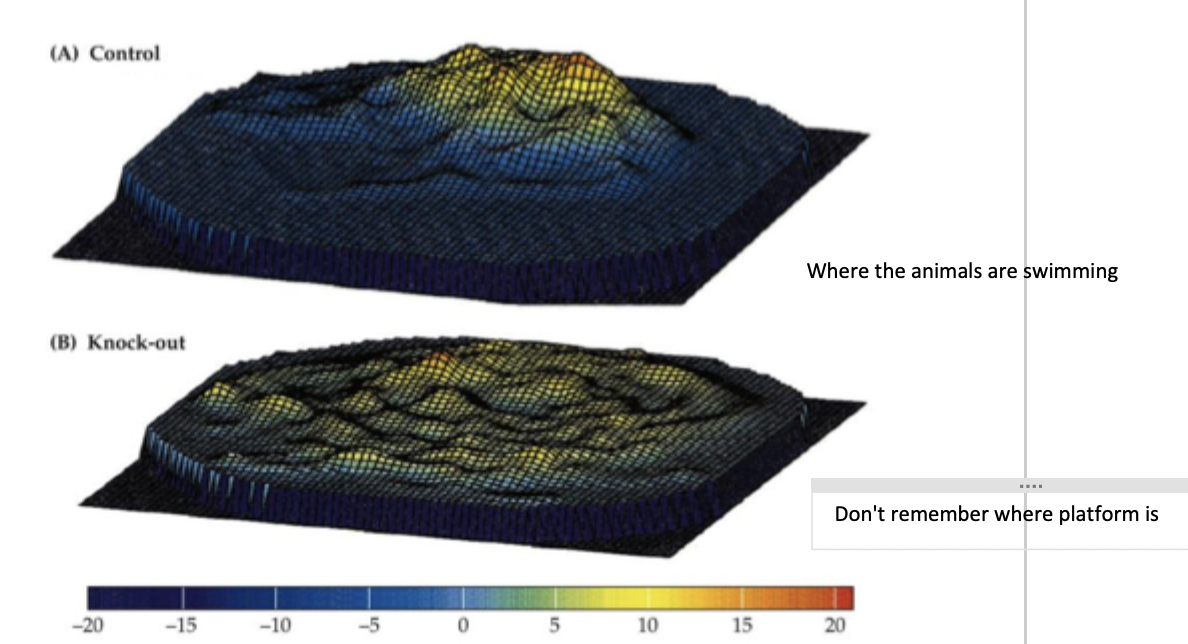
What was found from Tonegawa’s study of transgenic mice that lack NMDA receptor in CA1?
gene-splicing used to create strain of knockout mice that lack NMDA receptor in CA1
impaired in spatial learning
in morris water maze - don’t remember where platform is
other forms of learning such as classical conditioning preserved (cf. amnesia)
conclusion: LTP in CA1 field is critical for spatial memory
How could researchers prove the knockout mice spatial learning learning results is spatial not procedural learning?
release the rat in a different position on each trial
What are place cells in the context of rat studies?
Cells in CA1 that become active when the rat is in a particular place
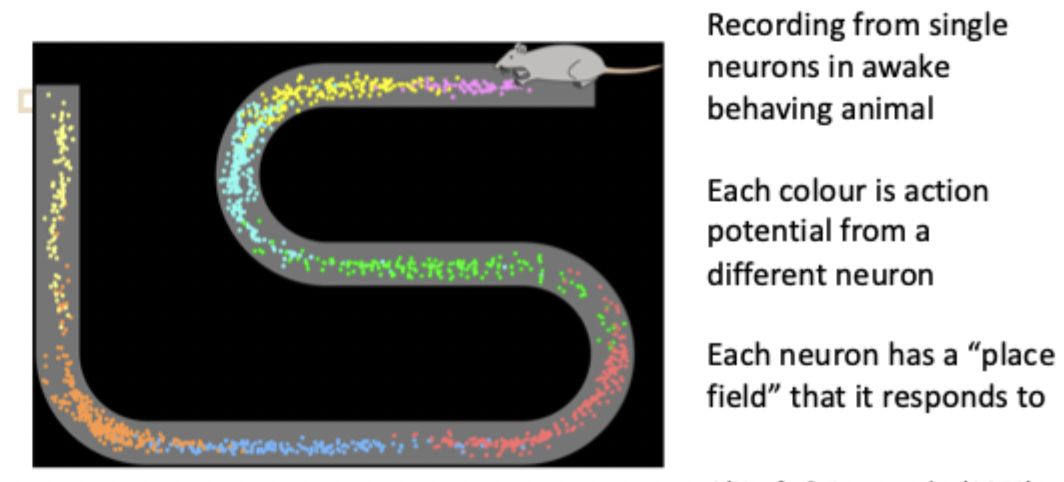
What is the theory of Cognitive Maps? (John O’Keefe and Lynn Nadel)
hippocampus provides an internal map that codes for spatial relation between objects in the environment
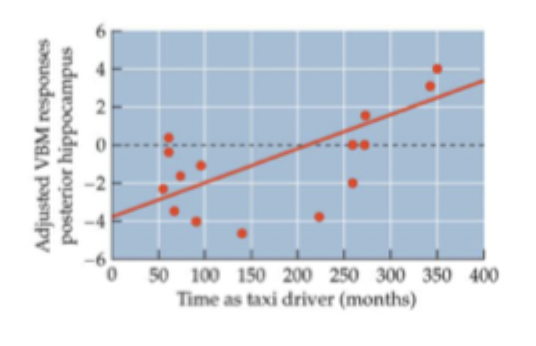
What evidence did Maguire find regarding Hippocampus and spatial memory in humans?
voxel-based morphometry (VBM) measure size of brain structures
experienced taxi drivers have (slightly) more voxels in posterior hippocampus
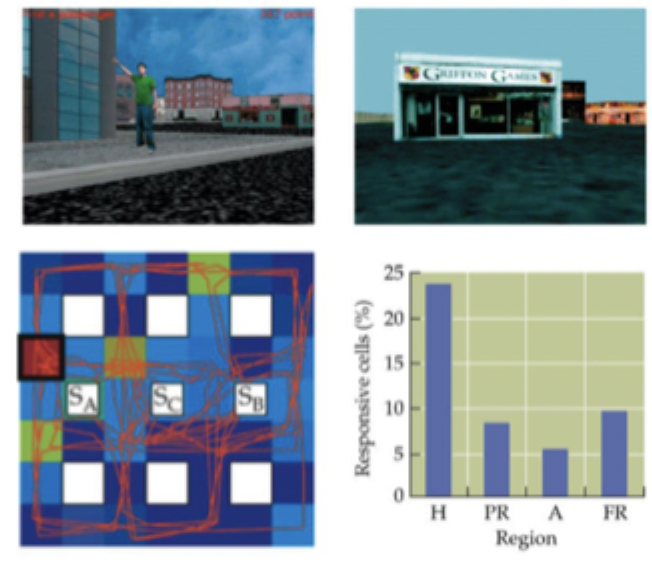
What did Ekstrom et al find regarding place cells in epileptic patients?
microelectrode arrays implanted prior to epilepsy surgery - allows recording from single neurons in human hippocampus
navigation through virtual reality environment - proportion of neurons that fire in response to a specific location in hippocampus, parahippocampal cortex, amygdala and frontal cortex
most responsive cells in hippocampus
How do we see the role of place cells in the spatial deficits of amnesia?
amnesic patients show deficits in tasks that don’t appear to have a spatial dimension - e.g. word lists
yet all episodic memories are encoded and recalled in a spatial location
mental time travel involves reconstructing environment; spatial location is a profound cue to recall
amnesic patients often have spatial deficit - HM couldn’t learn his way to the bathroom
both episodic memory and spatial learning require relational code
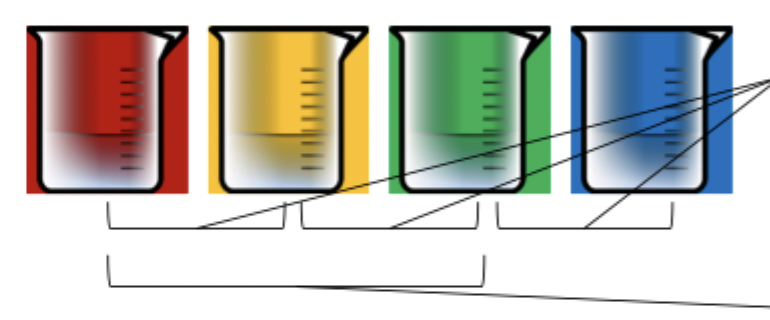
How was the theory of relational memory tested with rats and what was found?
rats with hippocampal lesions can remember individual association but cannot infer relations
tested using transitive inference task - colours depict different odours
rat can learn which cup out of each pair is rewarded with buried food but cannot infer best cup to search when both cups have been rewarded previously - need relational framework
What does the theory of recollection vs familiarity outline?
unique role of hippocampus in mental time travel

recollection involves relations between items and contexts
familiarity is a form of declarative memory (feeling of familiarity is conscious) → related to priming in perirhinal cortex (which shows strong response to novelty)