Cranium, Jaw, Neck, Clavicle, Scapula, and Brachial Plexus Lecture
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What are the prime movers of cervical extension?
Trapezius
Levator Scapulae
Splenius capitis
Splenius cervicis
What plane and axis does cervical extension occur?
Sagittal plane and frontal axis.
What plane and axis does cervical lateral flexion occur?
Frontal plane and sagittal axis.
What are the prime movers for cervical lateral flexion?
Trapezius
Levator scapulae
Sternocleidomastoid
Scalenes
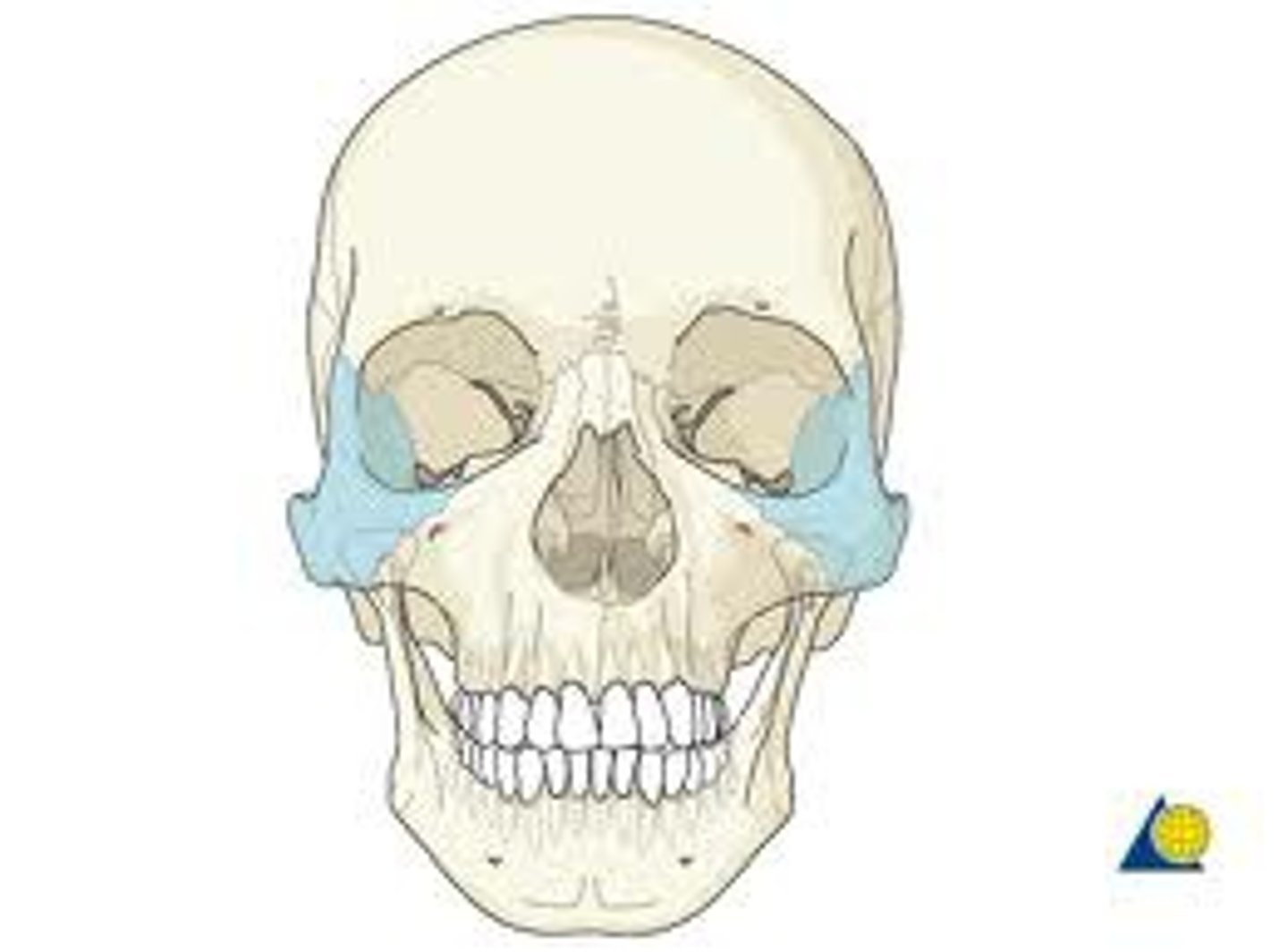
What is the zygomatic arch composed of?
The zygomatic process of the temporal bone and the temporal process of the zygomatic bone.
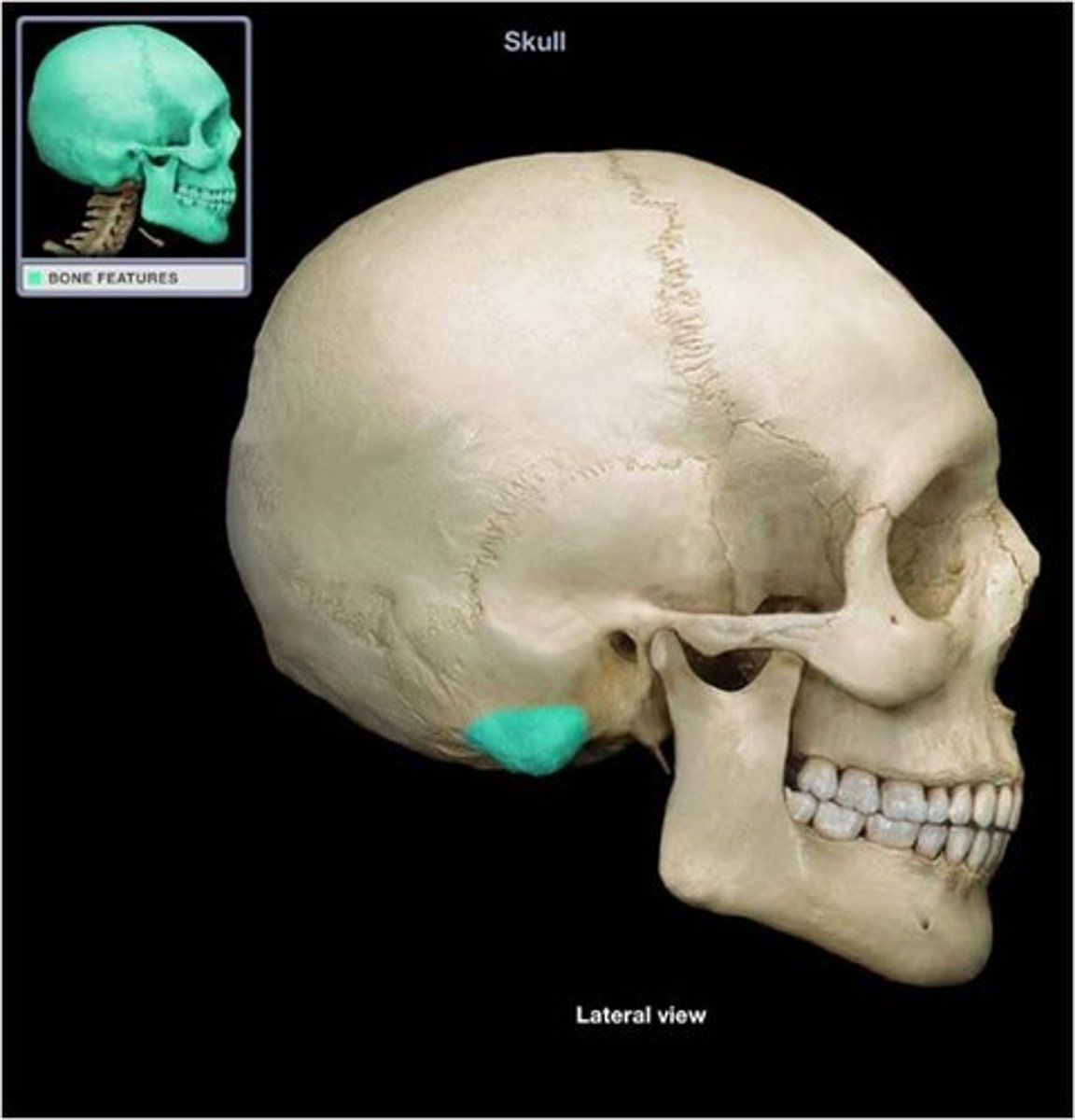
Where is the mastoid process located?
The temporal bone.
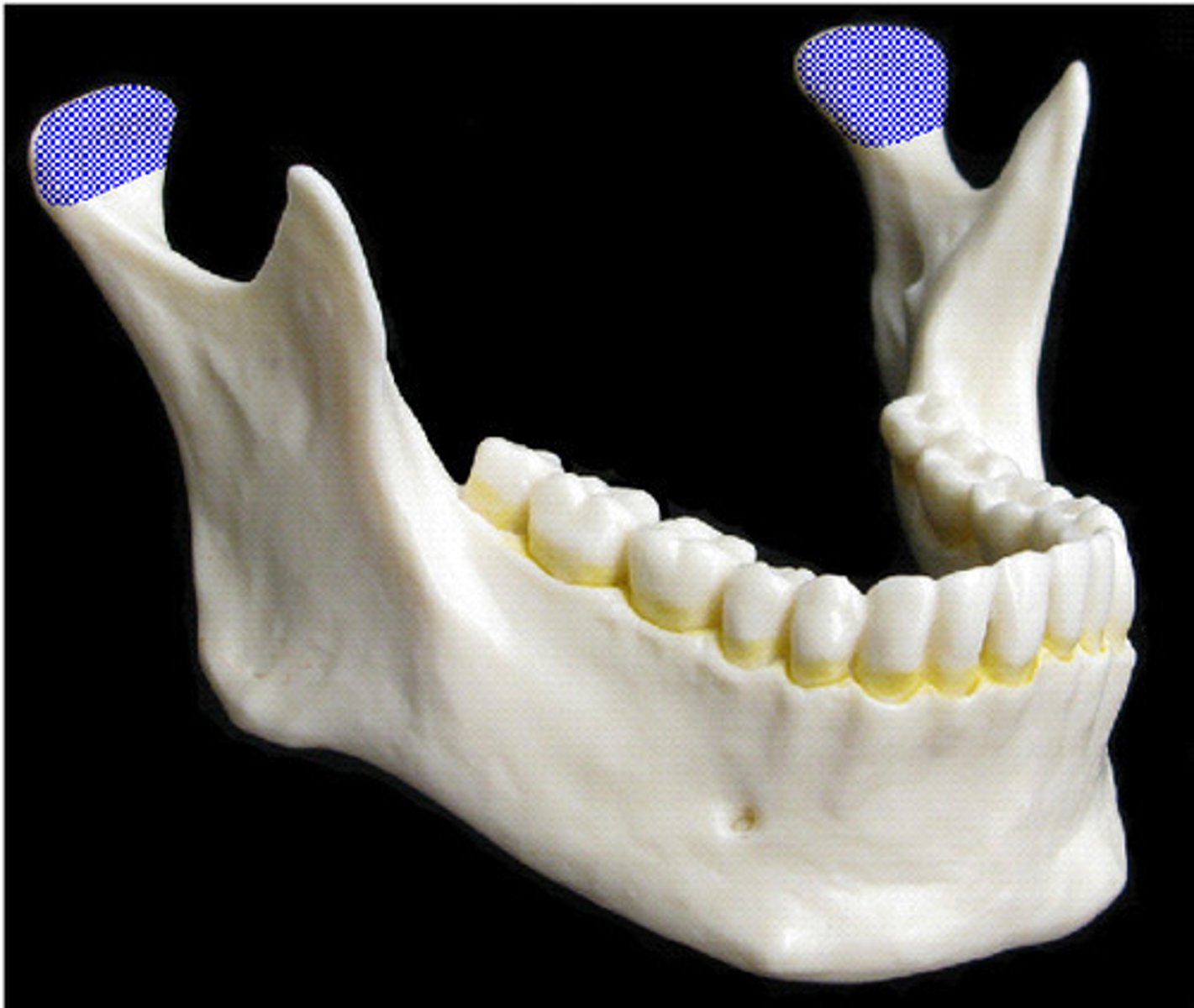
The mandibular condyle forms part of the ___________ joint.
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
What are the externally visible muscles of mastication?
The masseter and temporalis.
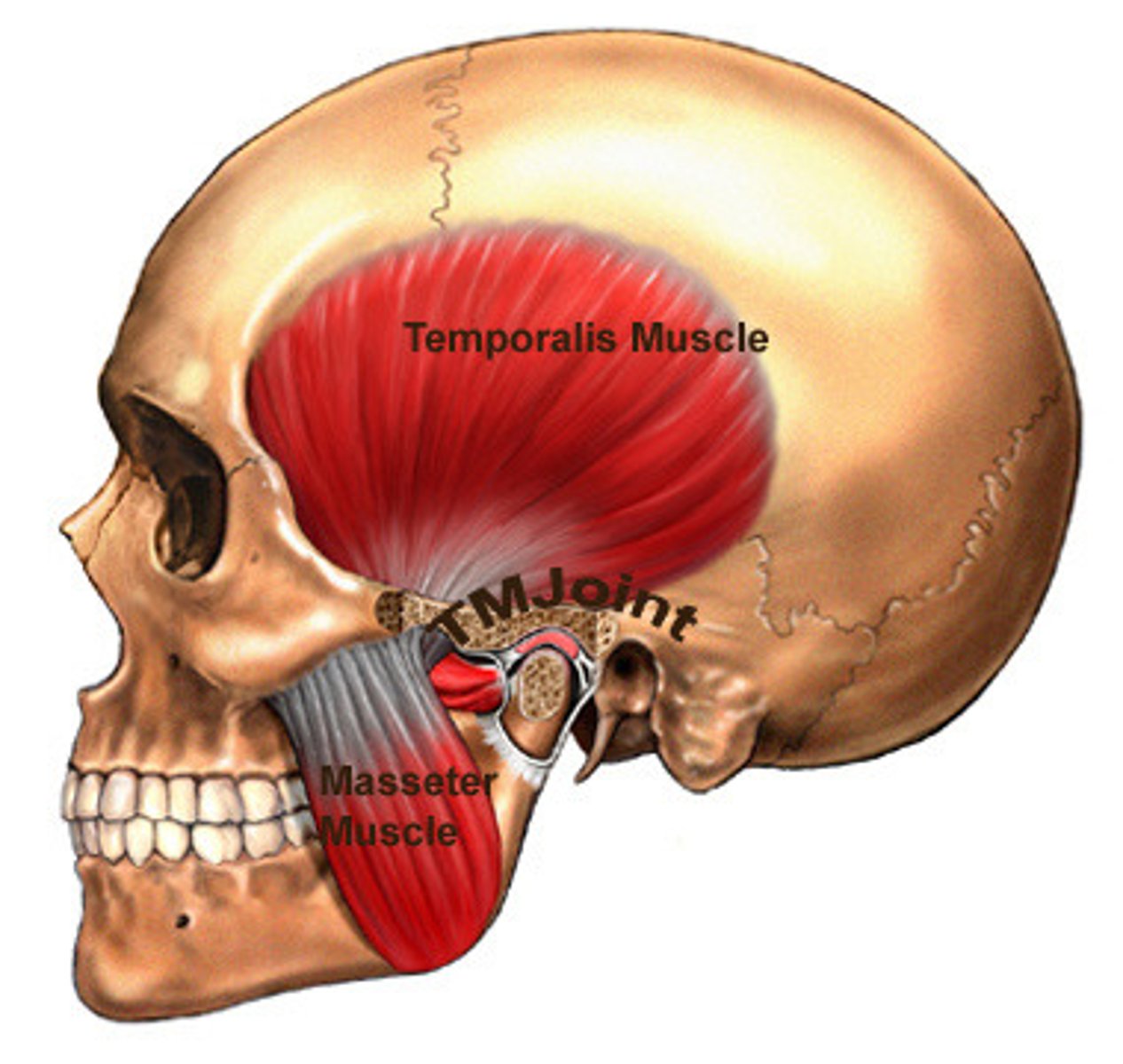
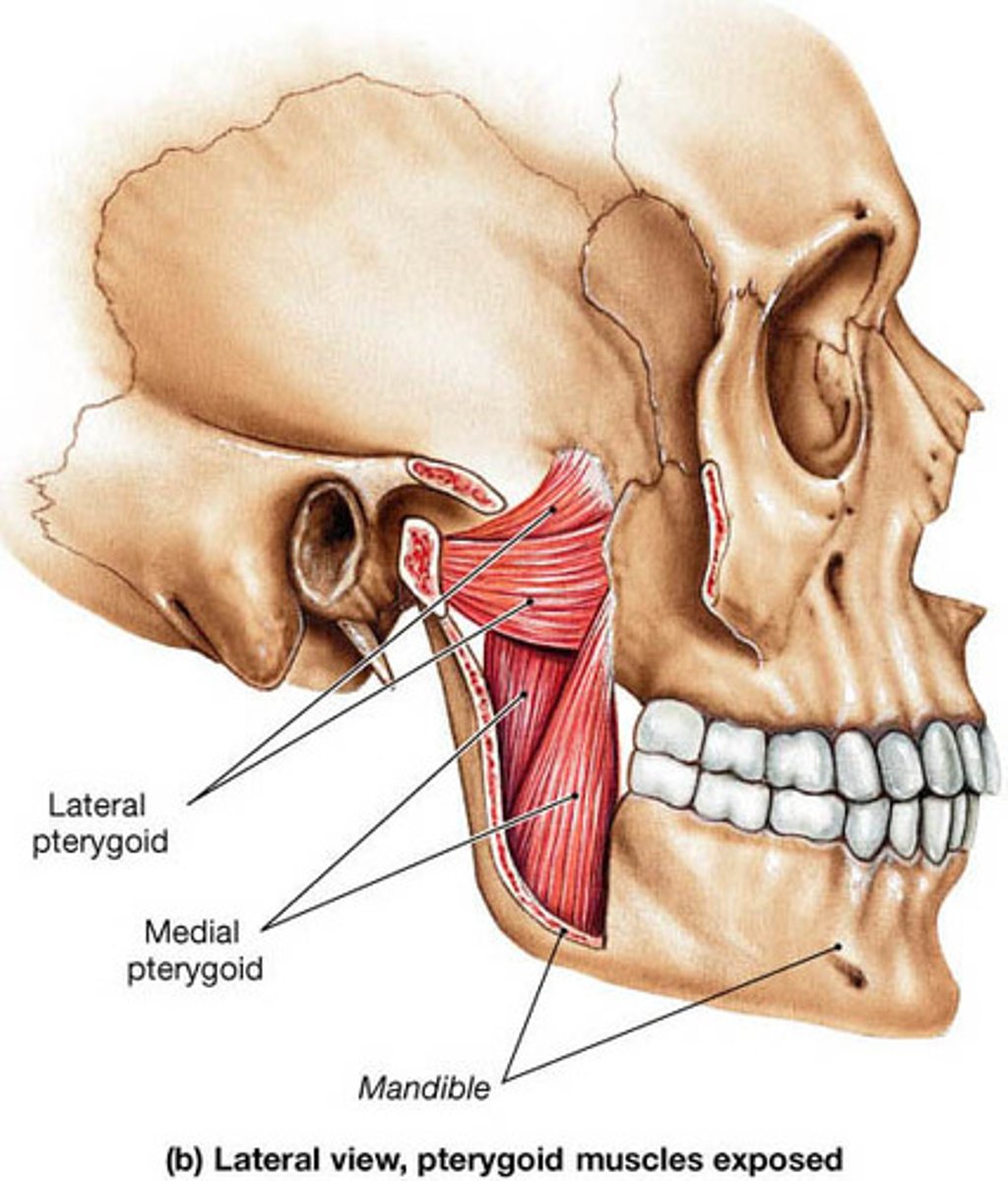
What are the muscles of mastication that are not externally visible?
The medial and lateral pterygoid muscles.
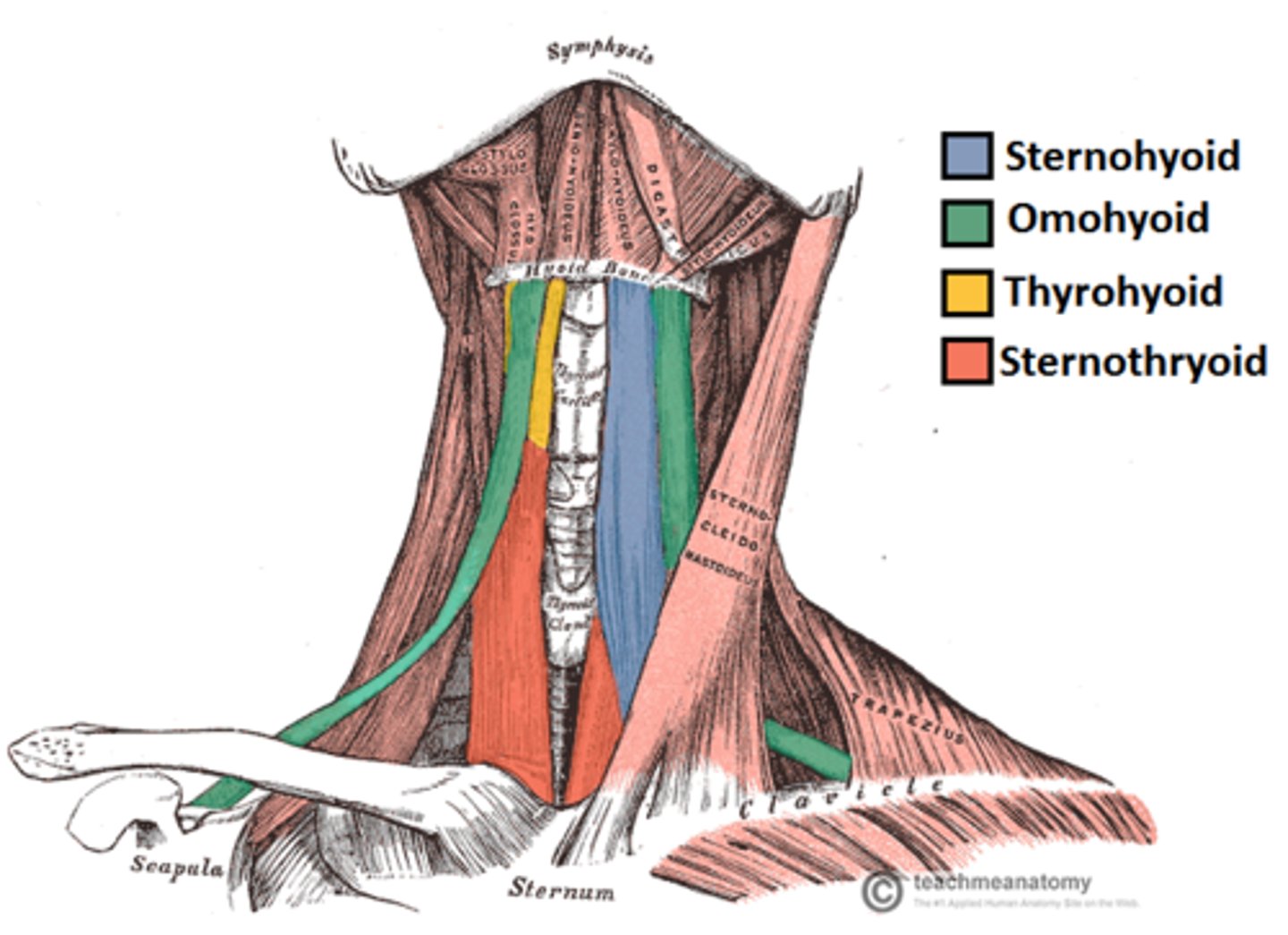
What muscles raise and lower the hyoid bone and larynx?
The strap muscles and digastric muscle.
What plane and axis does cervical rotation occur on?
Transverse plane and vertical axis.
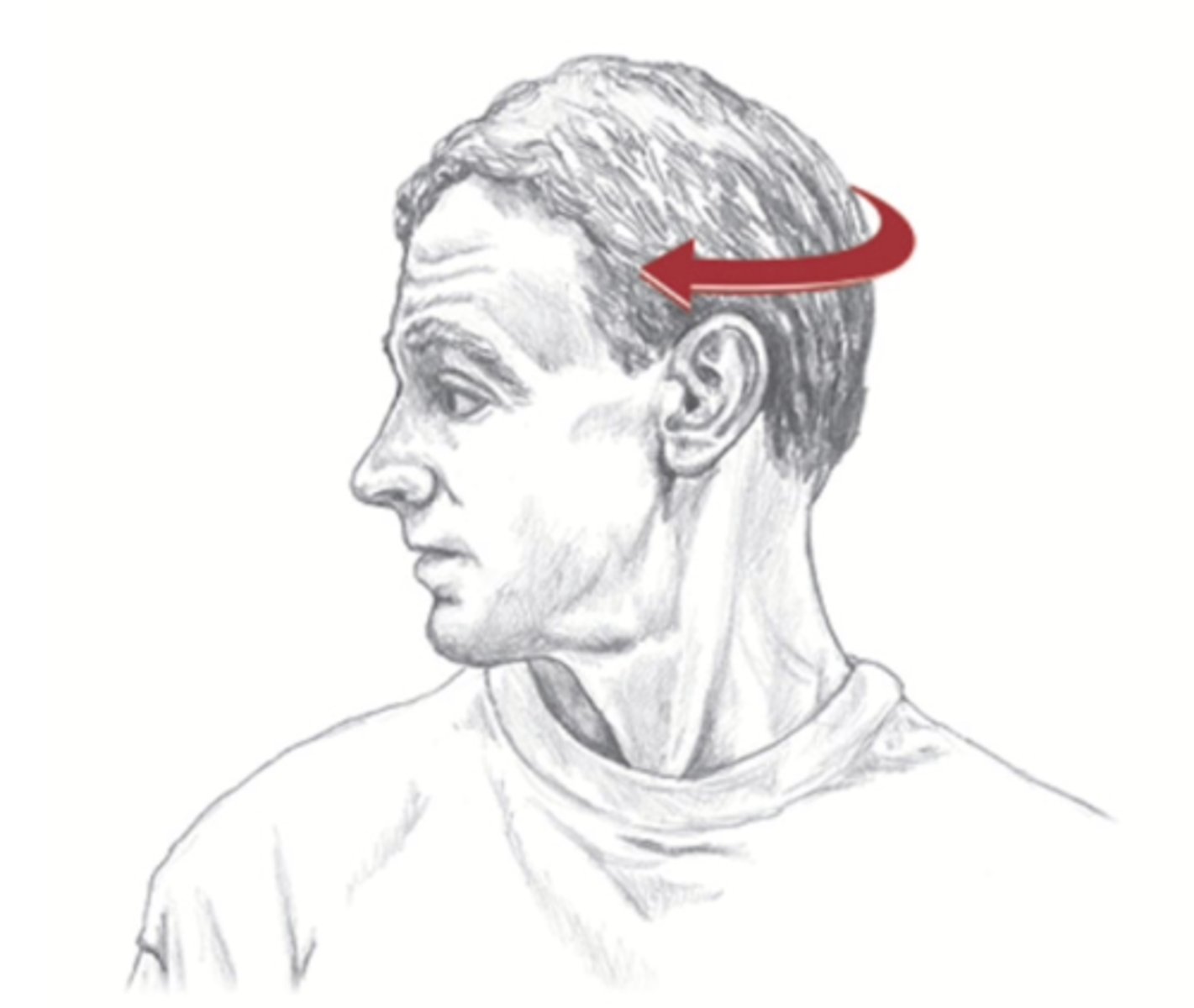
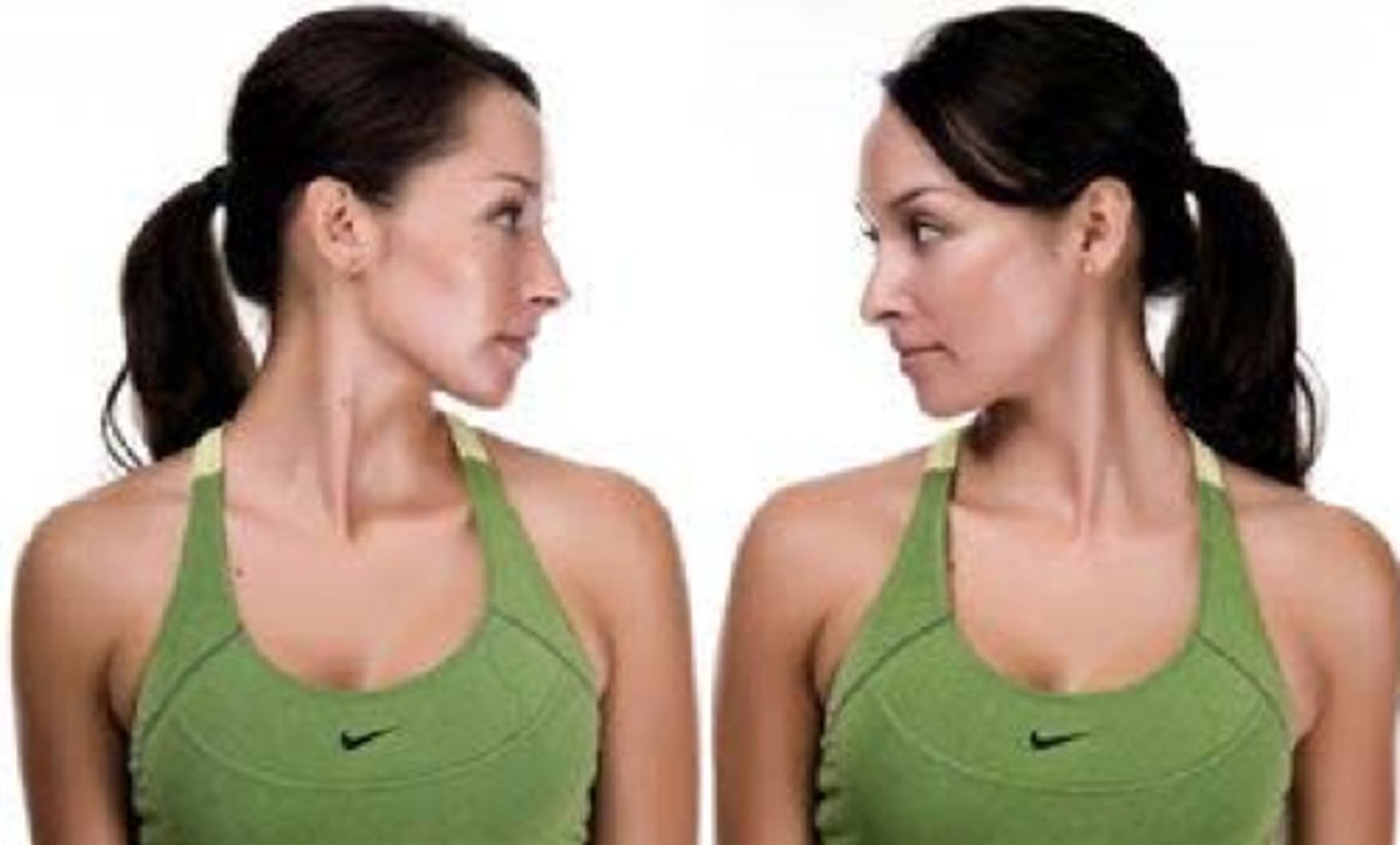
What are the prime movers for cervical rotation?
Sternocleidomastoid
Levator scapulae
Trapezius
Splenius capitis
Splenius cervicis

What nerve is in danger of damage in the lateral cervical region with radical neck injuries?
The accessory nerve
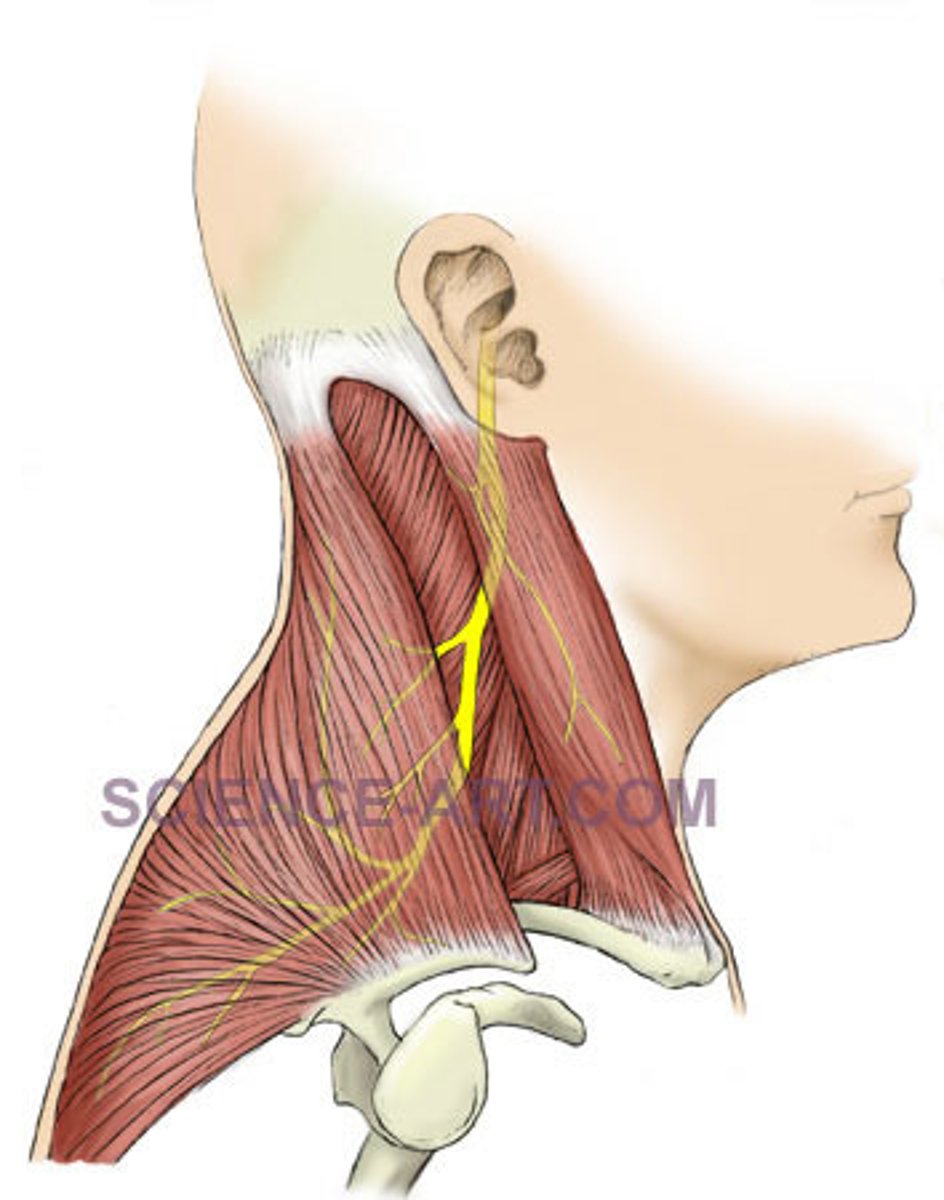
What does the sternocleidomastoid muscle protect?
The internal jugular vein, carotid artery, and the vagus nerve.
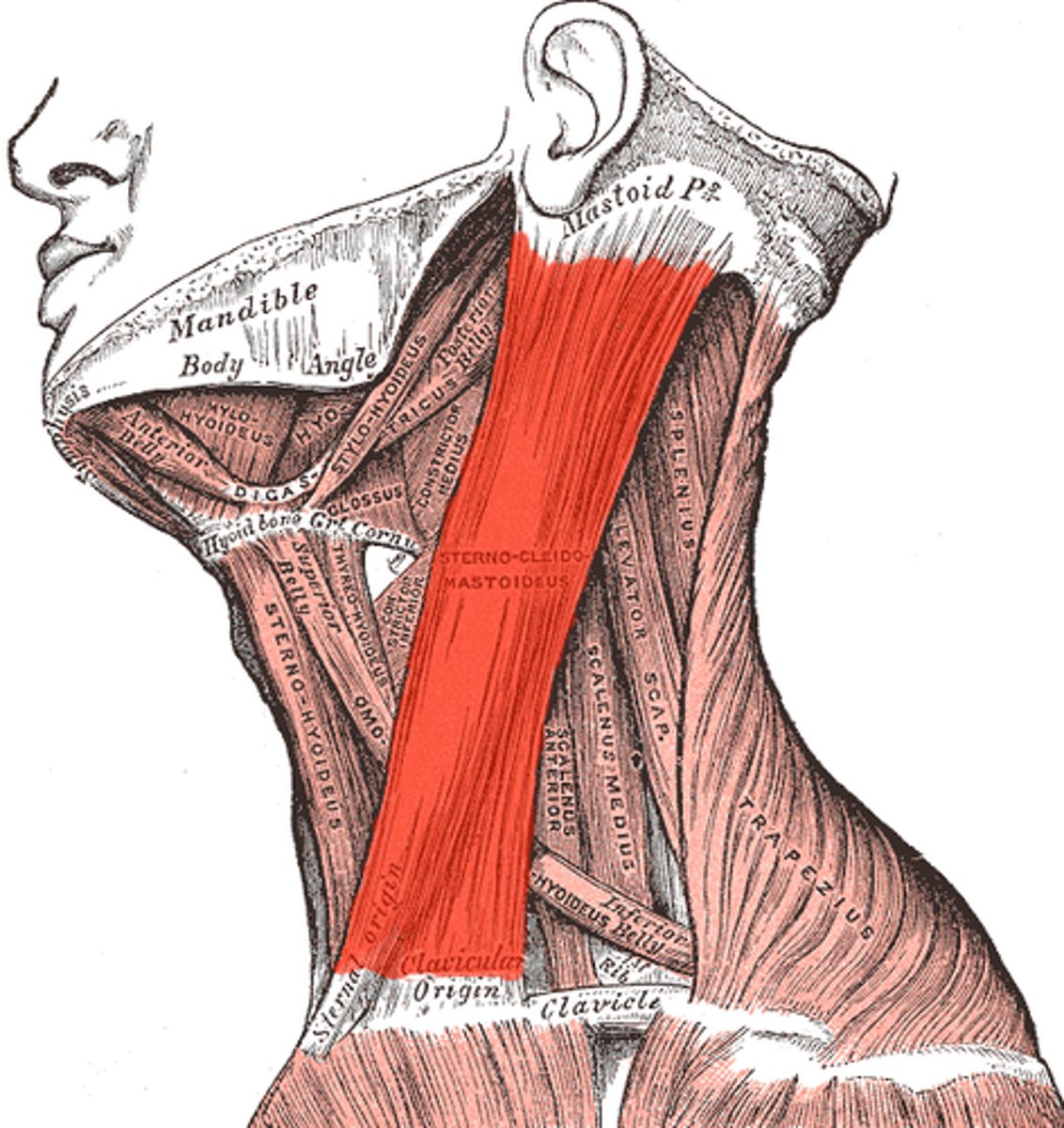
What plane and axis does cervical flexion occur?
The sagittal plane and frontal axis.
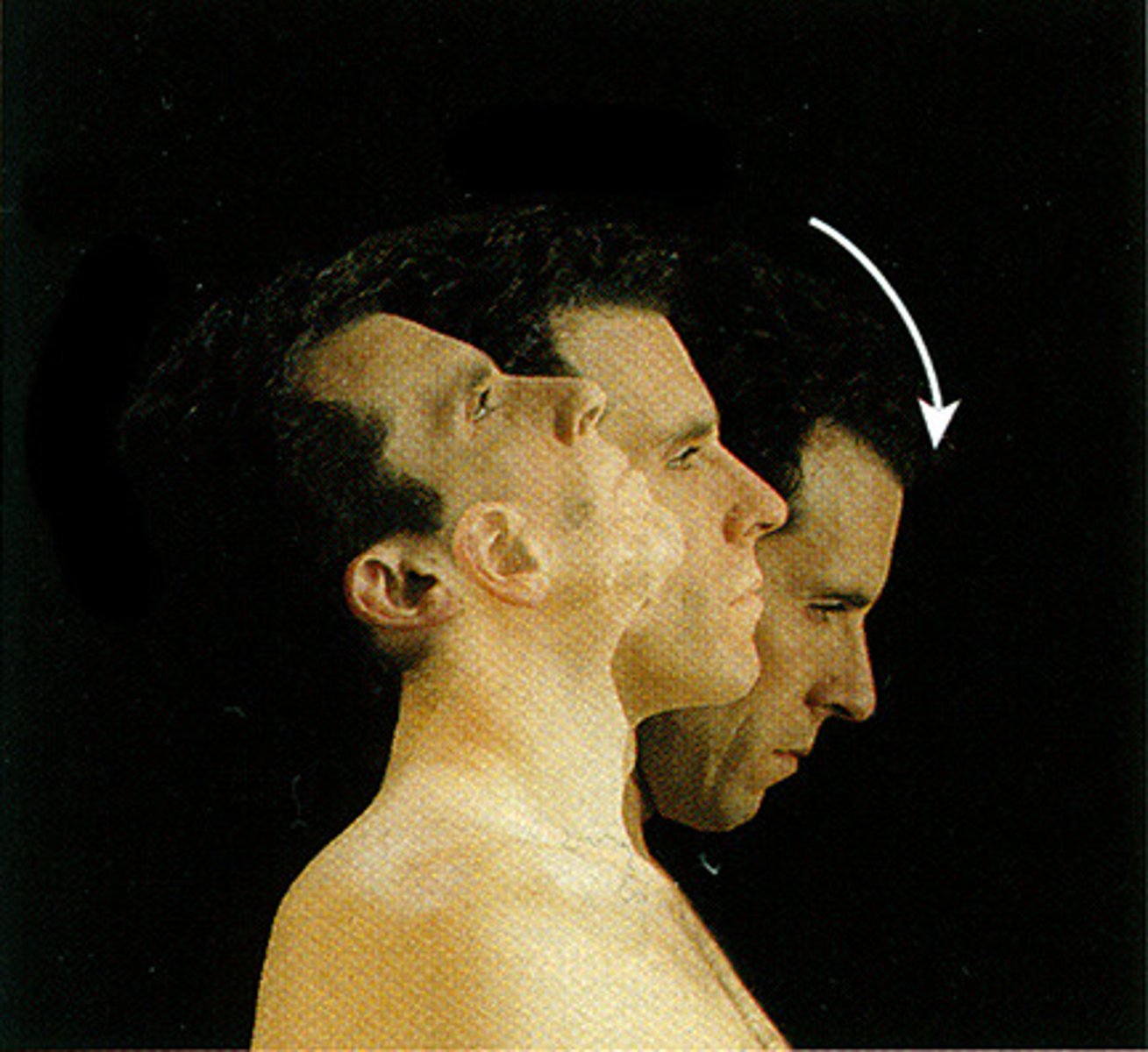
What are the prime movers of cervical flexion?
Sternocleidomastoid
Anterior scalene
Longus capitis
Longus colli
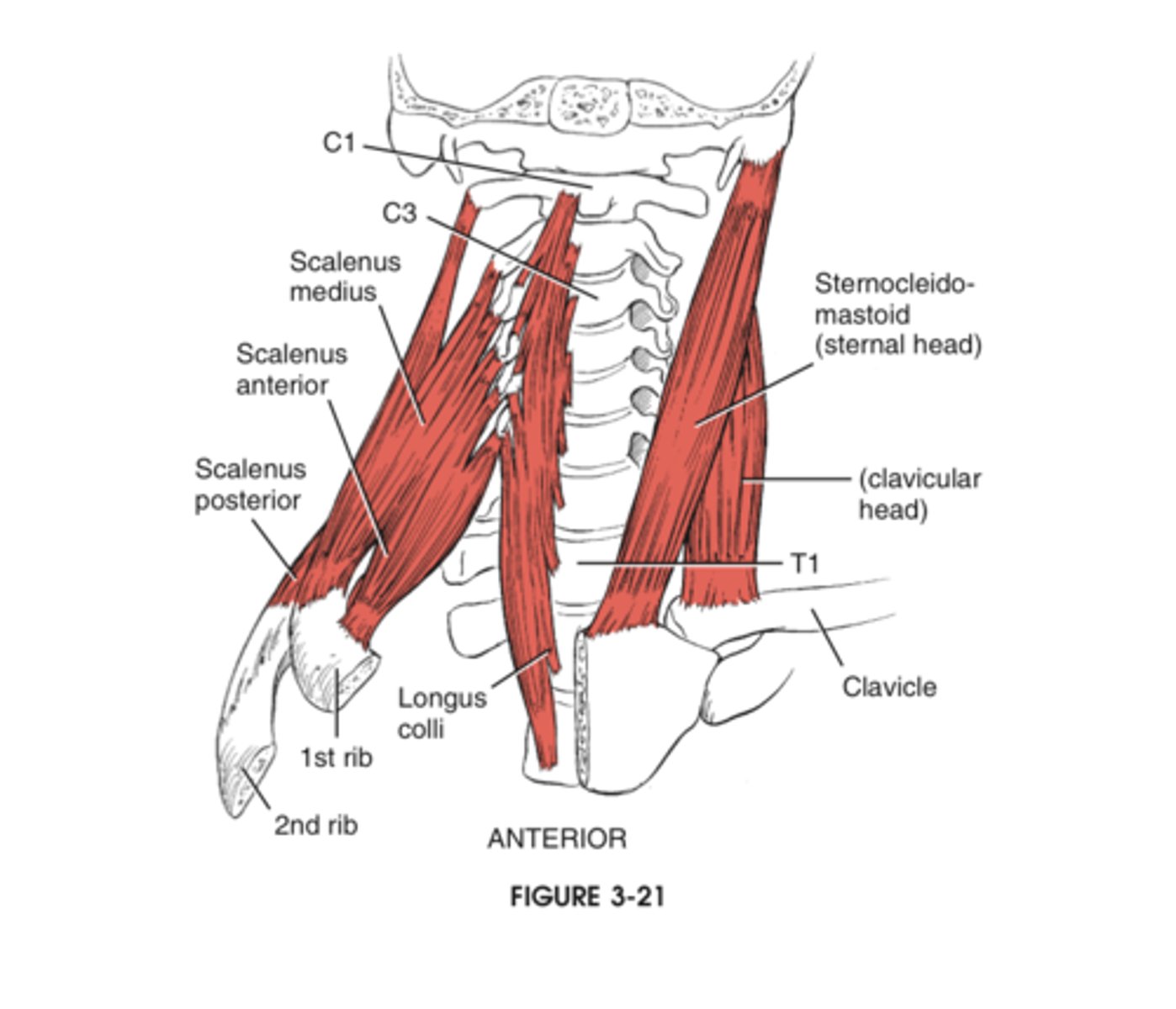
Where do the anterior and middle scalene muscles insert?
The first rib
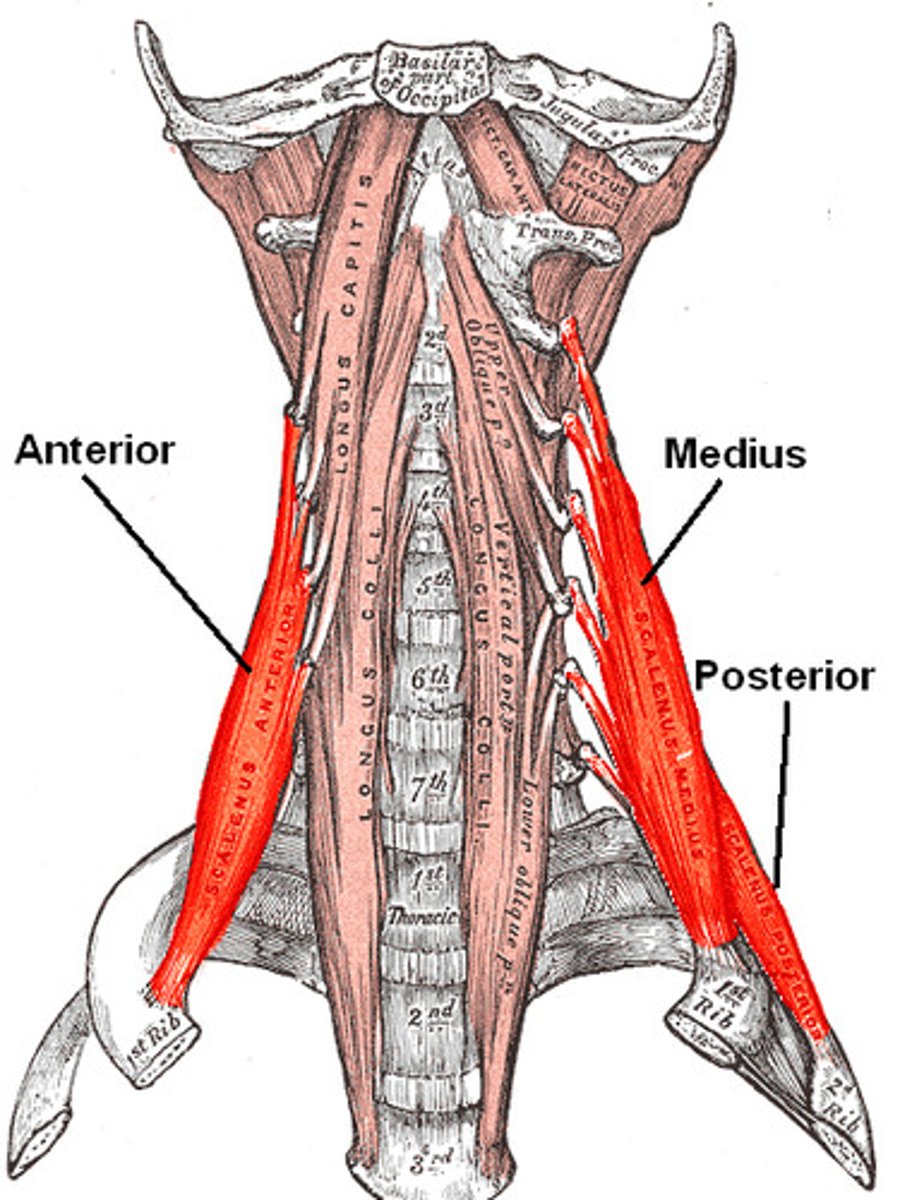
Where does the posterior scalene muscle insert?
The second rib
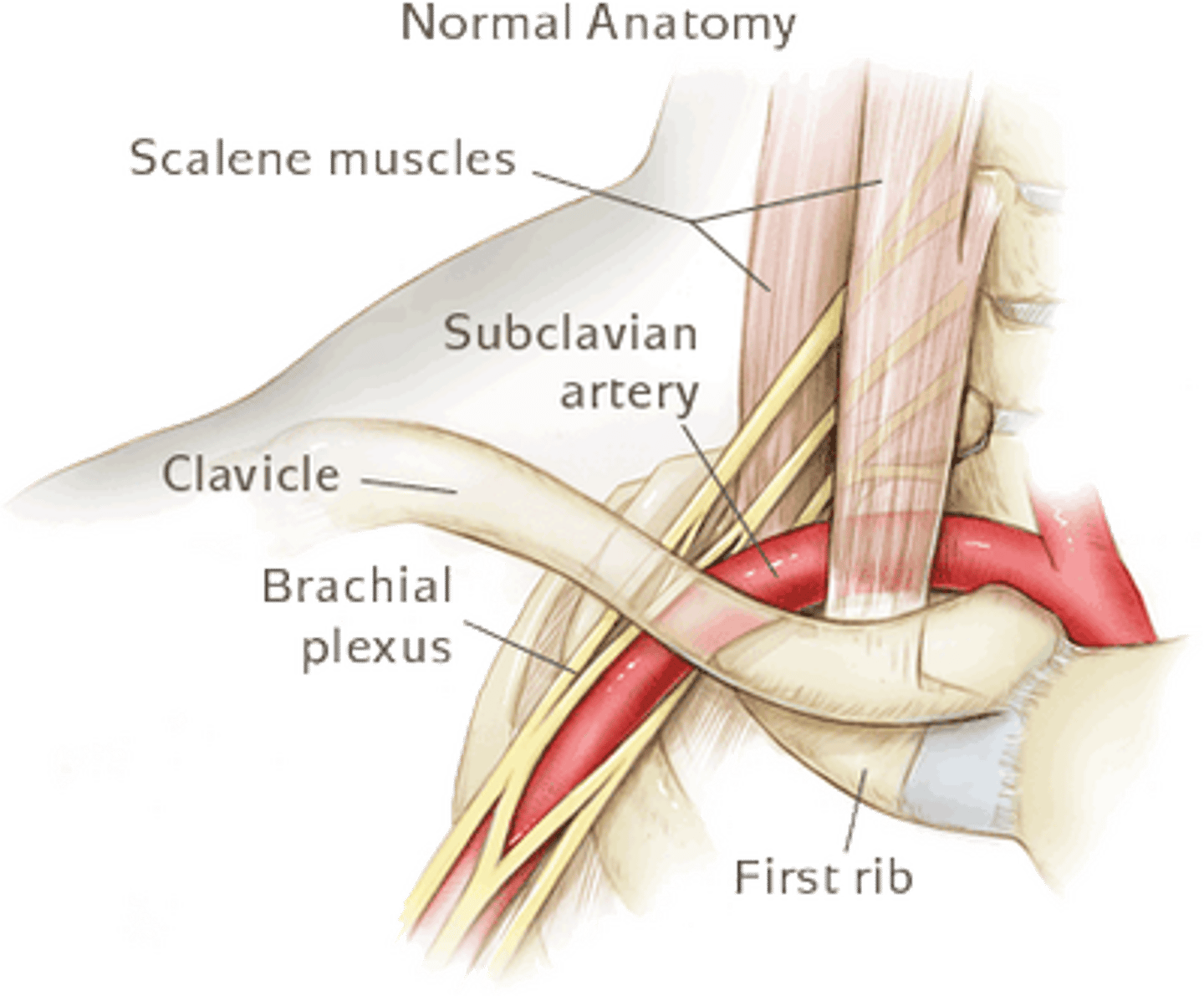
What passes between the anterior and middle scalene muscles?
The brachial plexus and subclavian artery.
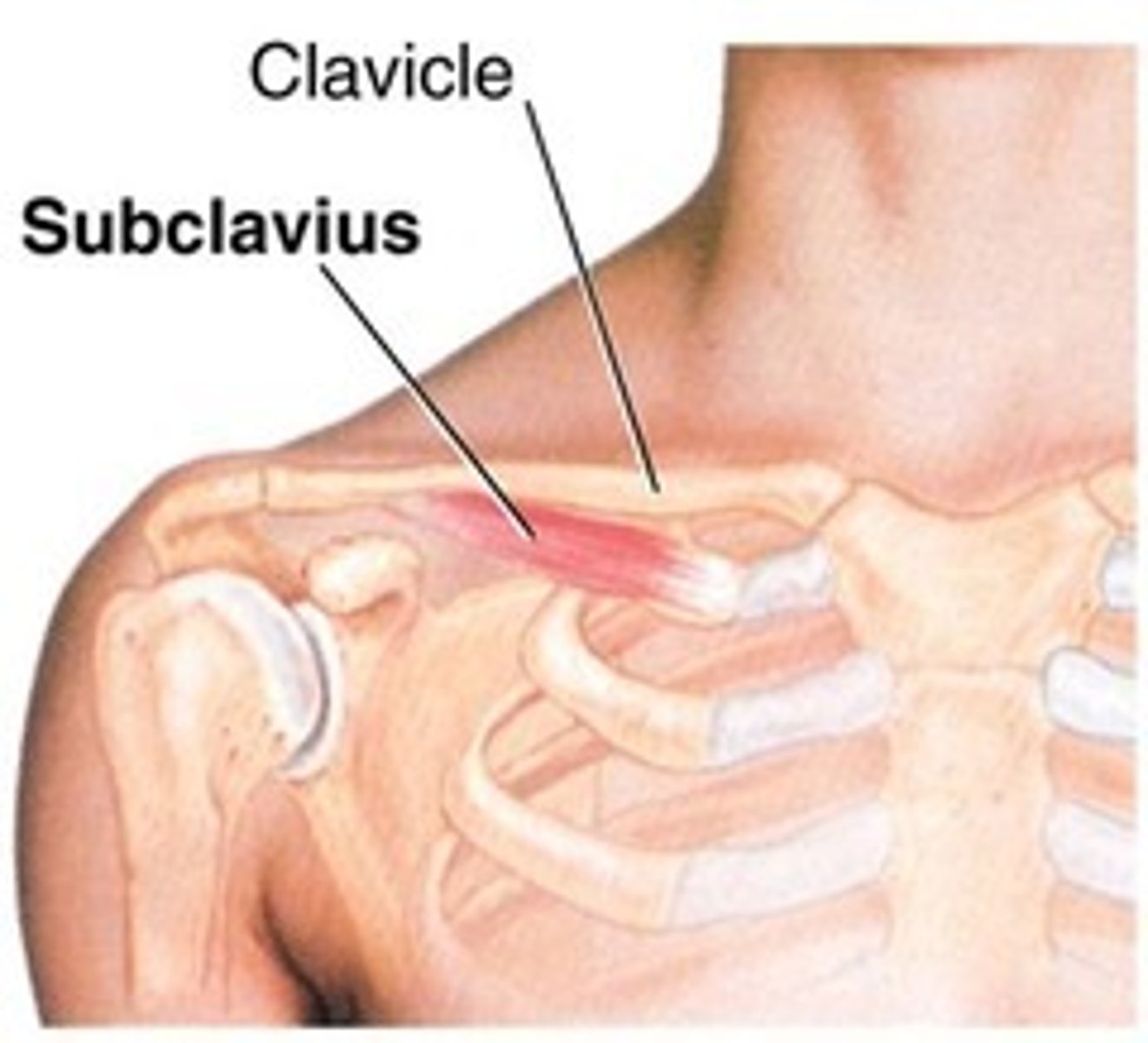
What is the function of the small subclavius muscle?
It helps to anchor and depress the clavicle.
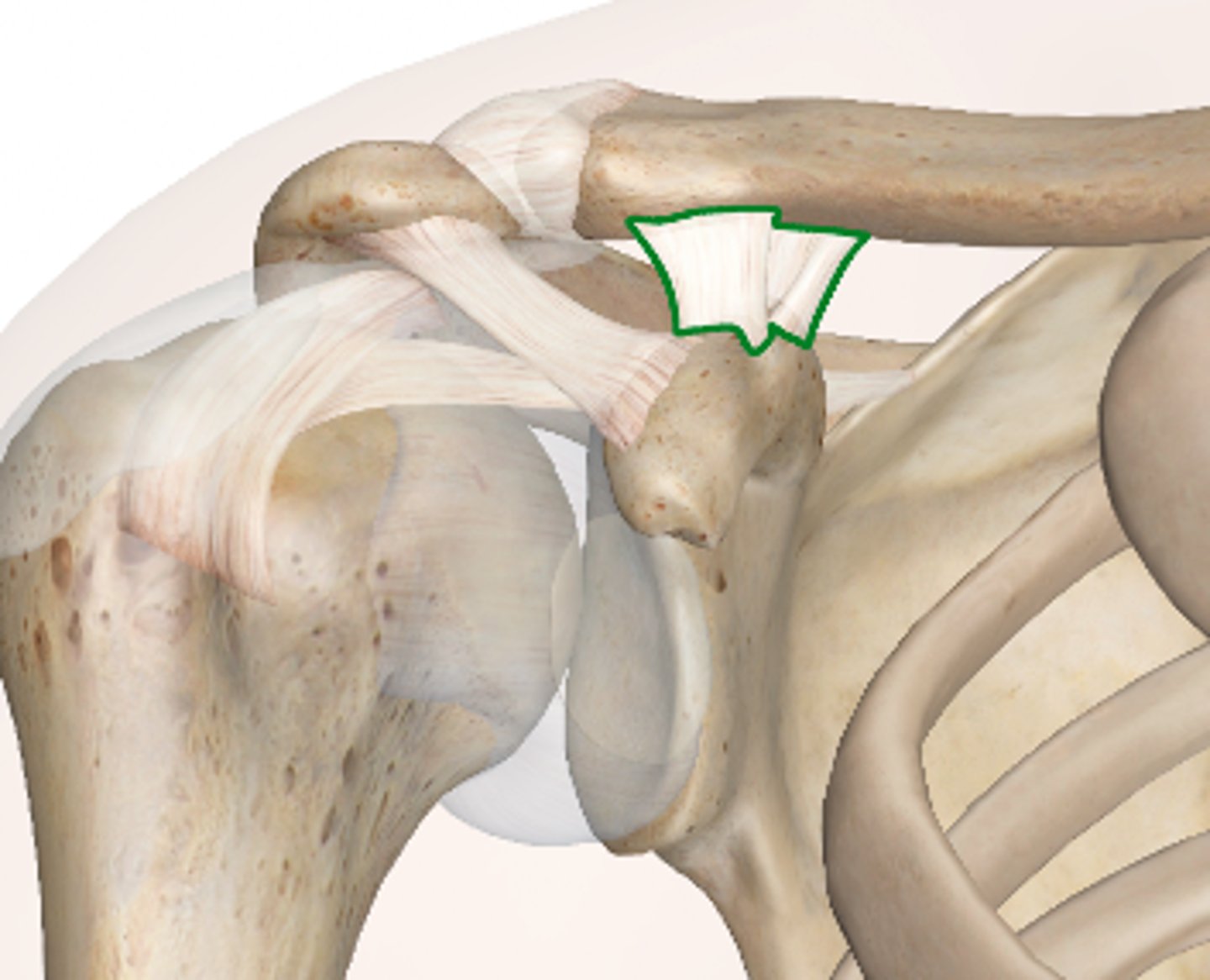
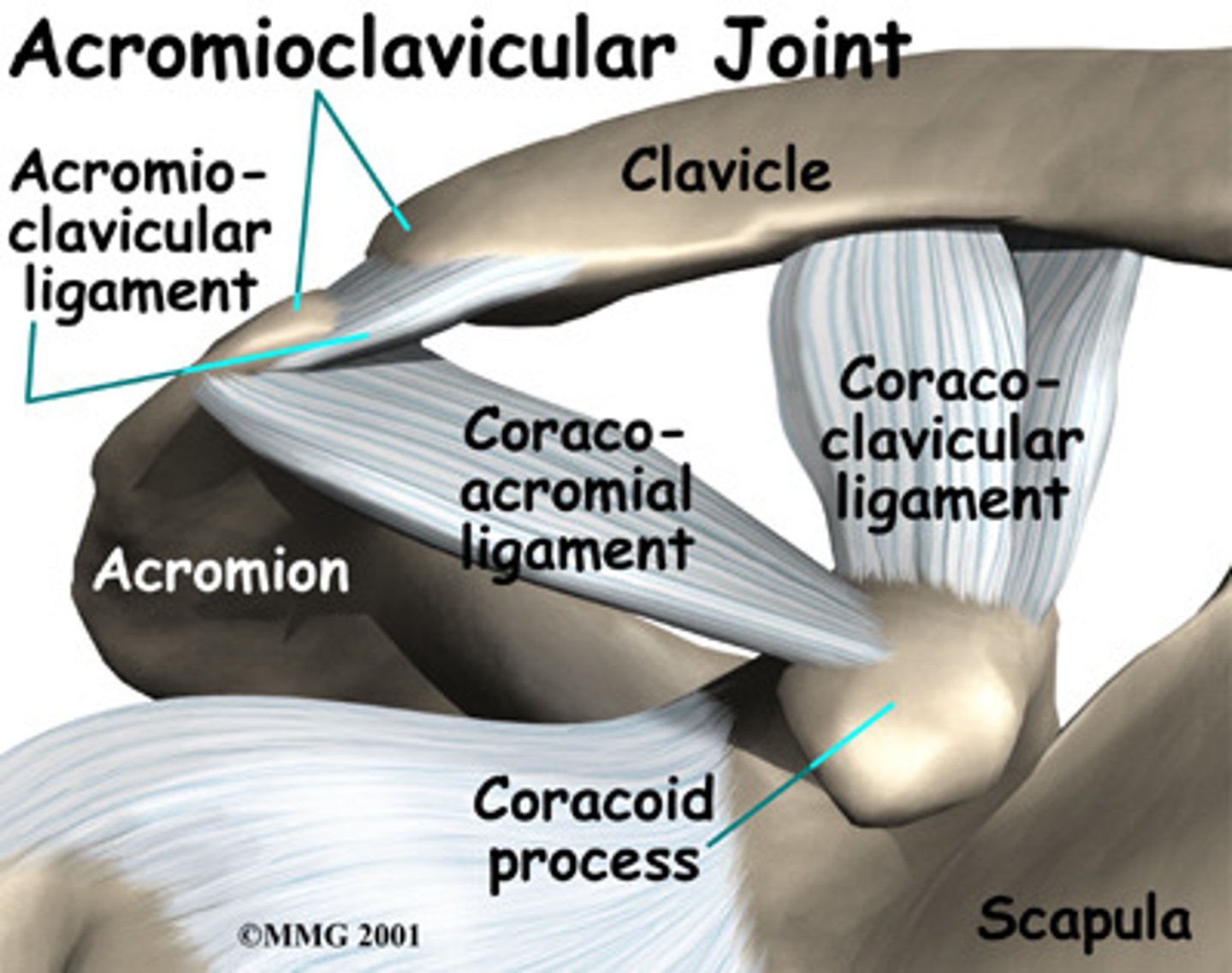
What is the function of the acromioclavicular ligament?
Superiorly strengthens the joint capsule.
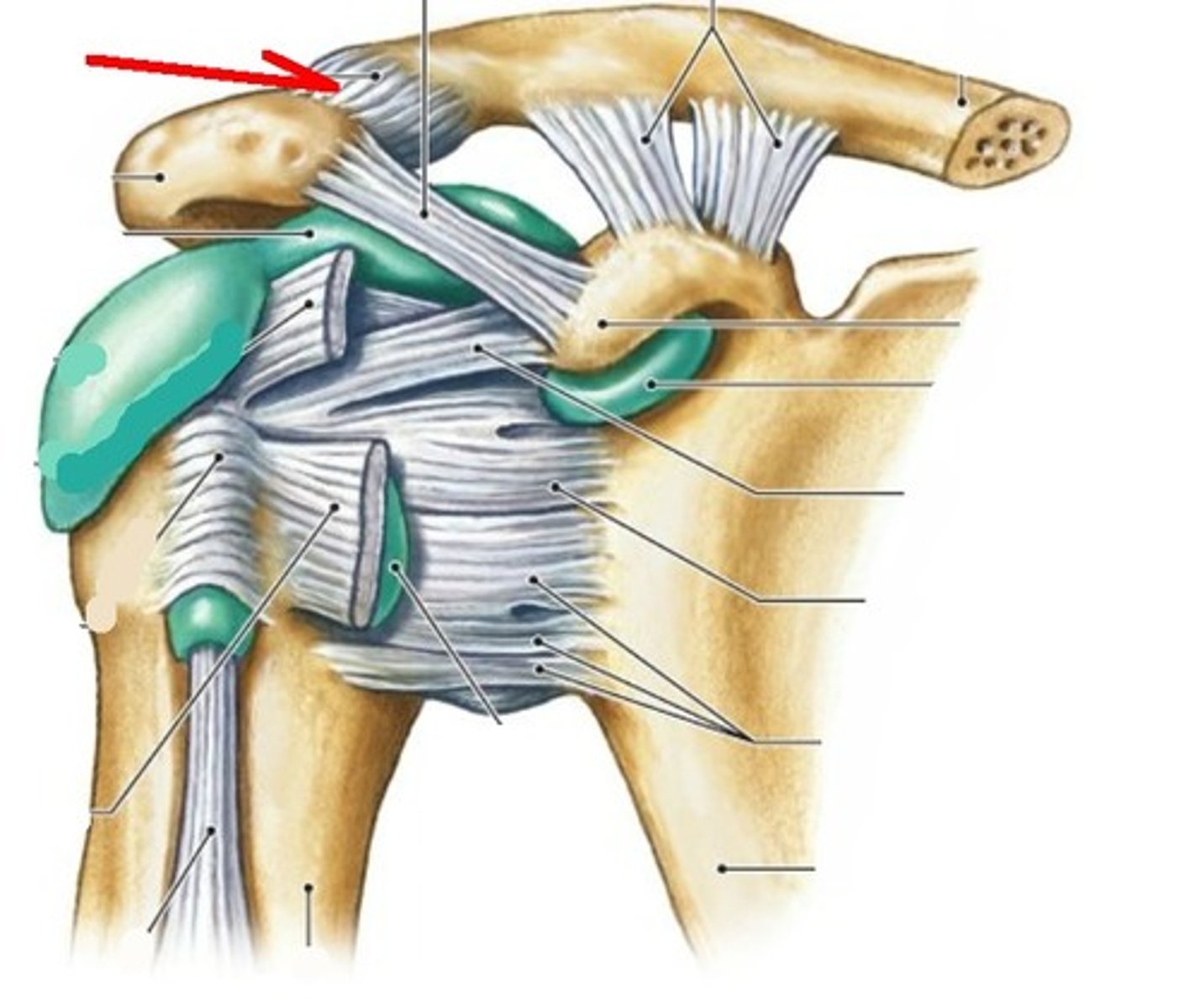
What is the function of the coracoclavicular ligament?
Strengthens the lateral end of the clavicle by attaching to clavicle.
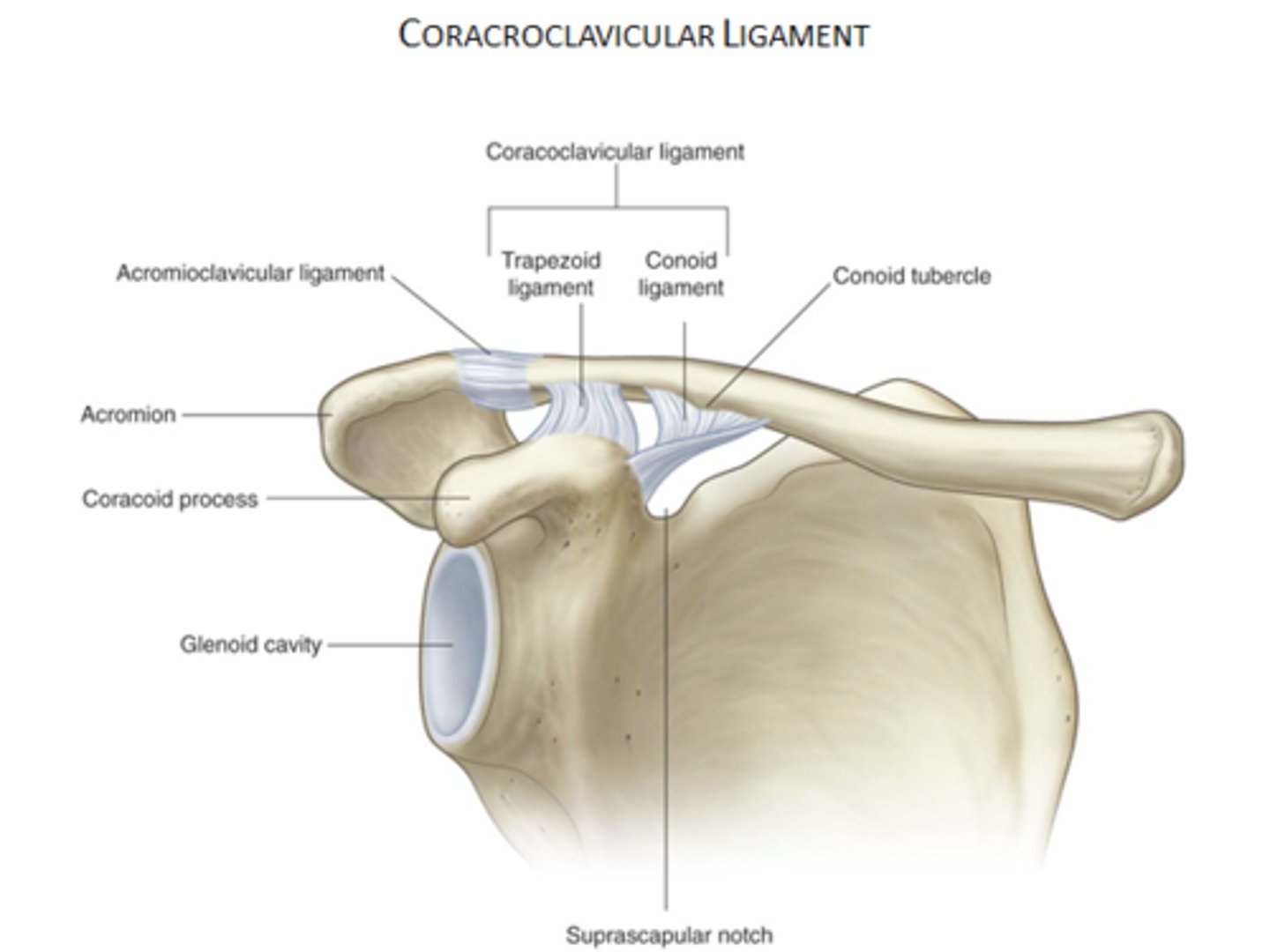
What are the two parts of the coracoclavicular ligament?
The trapezoid and conoid
What supplies blood to the acromioclavicular (AC) joint?
The suprascapular and thoracoacromial arteries.
What is the nerve supply in the acromioclavicular (AC) joint?
The lateral pectoral and axillary nerves.
How many muscles are innervated by the brachial plexus in the shoulder/upper extremity?
32
What are two reasons why the brachial plexus bundles axons?
1. Structural strength
2. Functionality
What is the brachial plexus?
A network of ventral primary rami that combine to form peripheral nerves of the upper extremity.
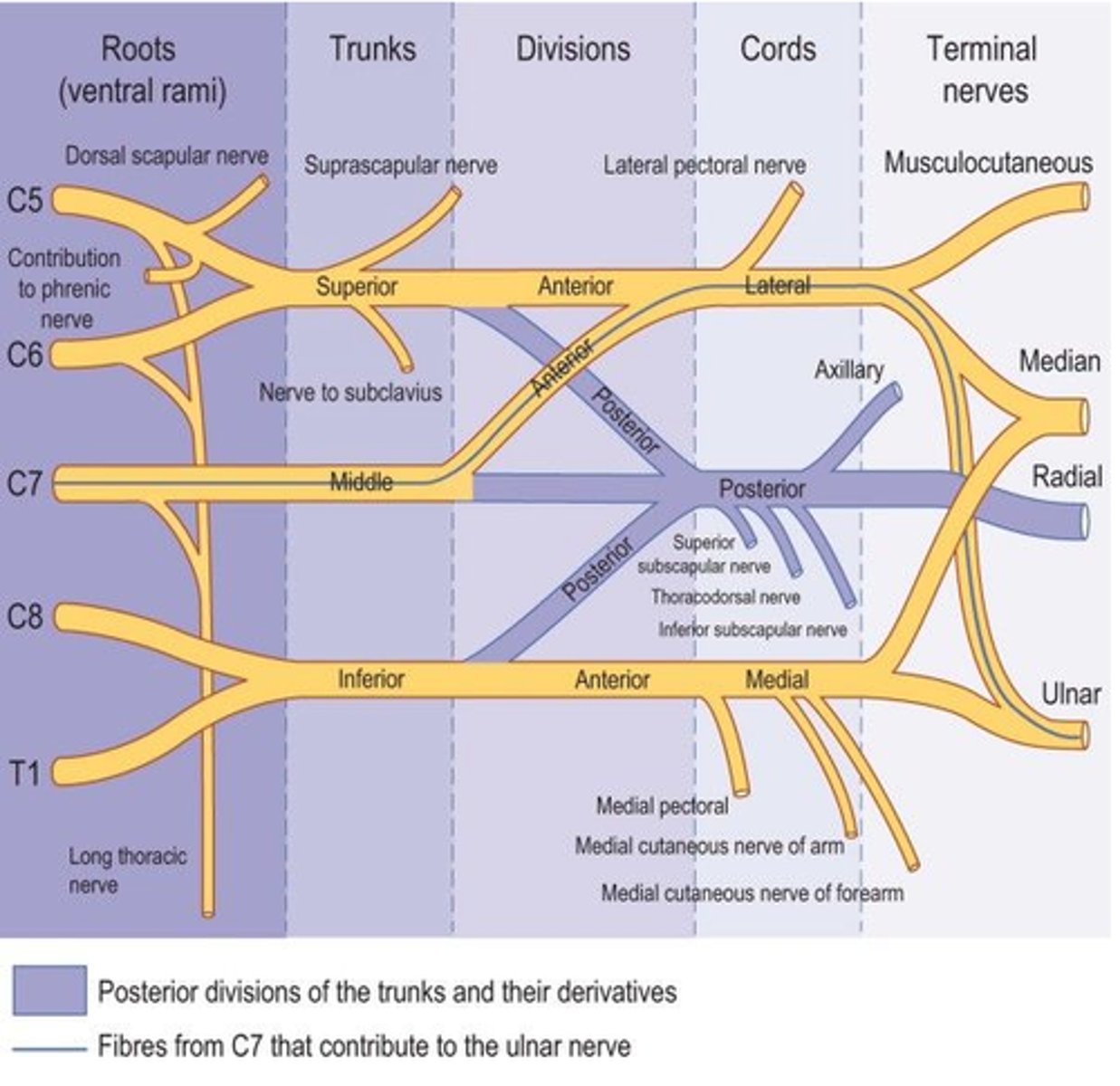
What forms the brachial plexus?
The union of the ventral rami of C5 through C8 and the greater part of the ventral rami of T1.
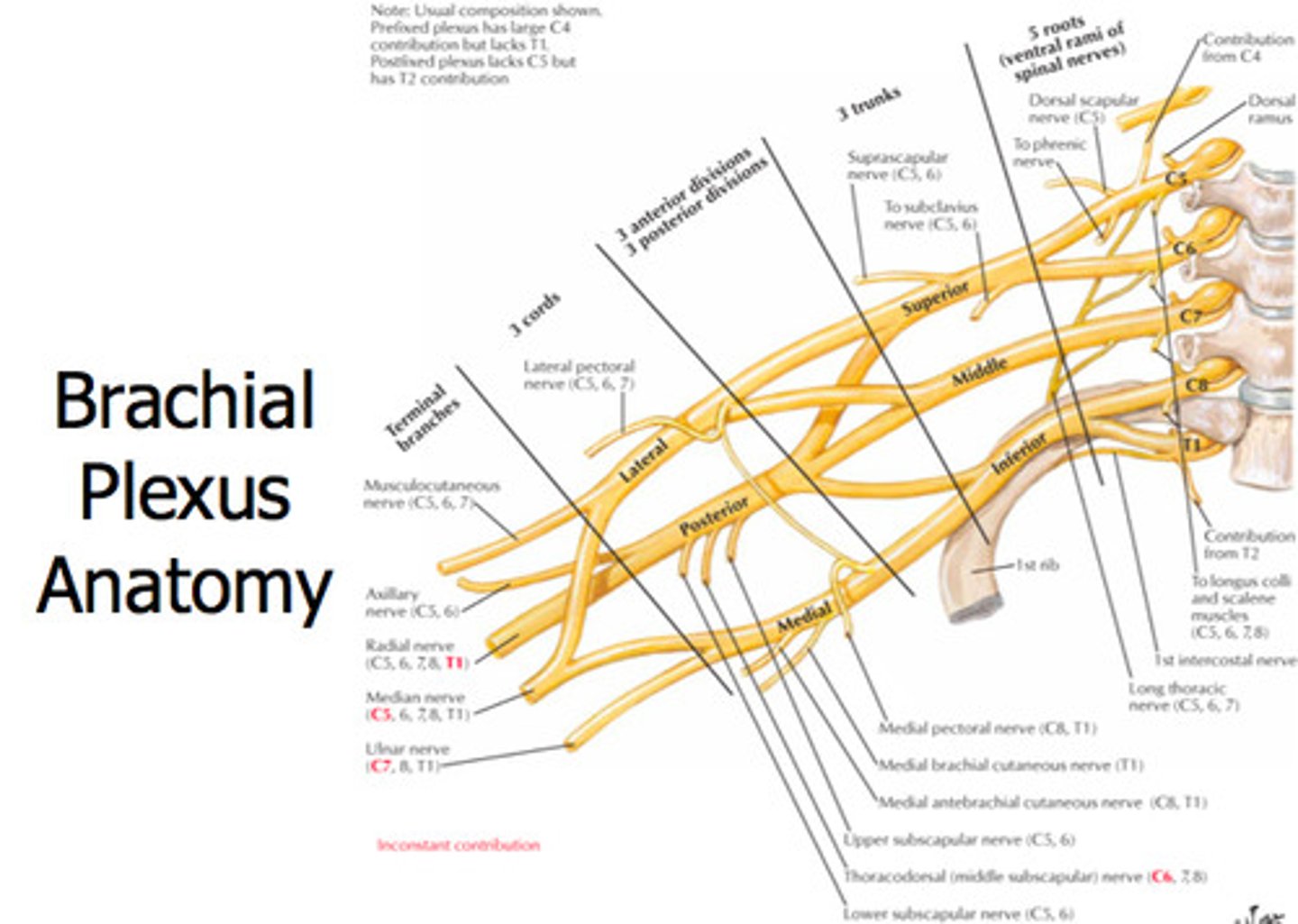
What are the 5 main branches of the brachial plexus?
Axillary
Radial
Ulnar
Median
Musculocutaneous
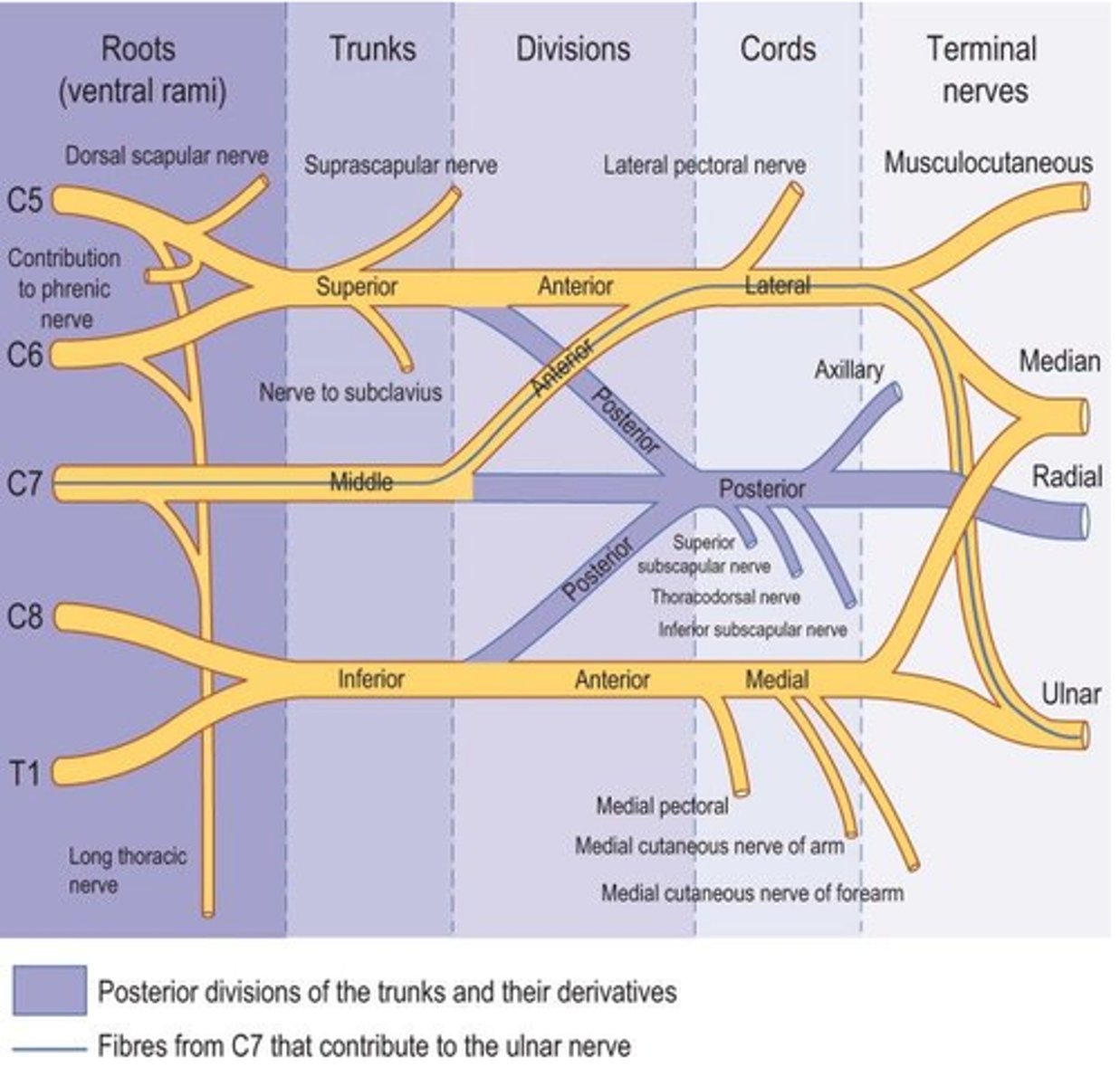
The brachial plexus divisions and cords are accompanied by the ___________ artery.
Axillary
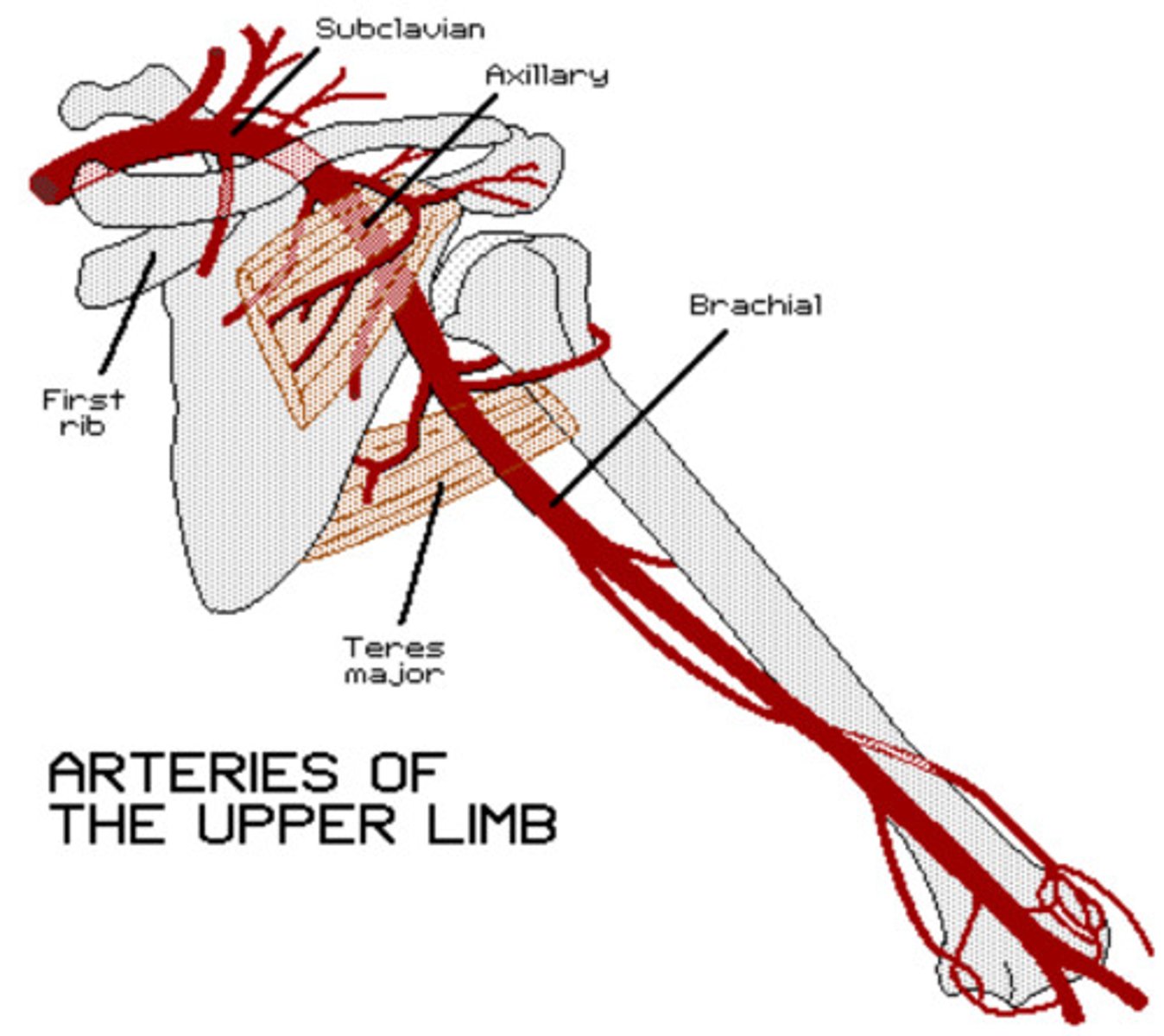
The axillary artery is a continuation of ________________ artery.
Subclavian
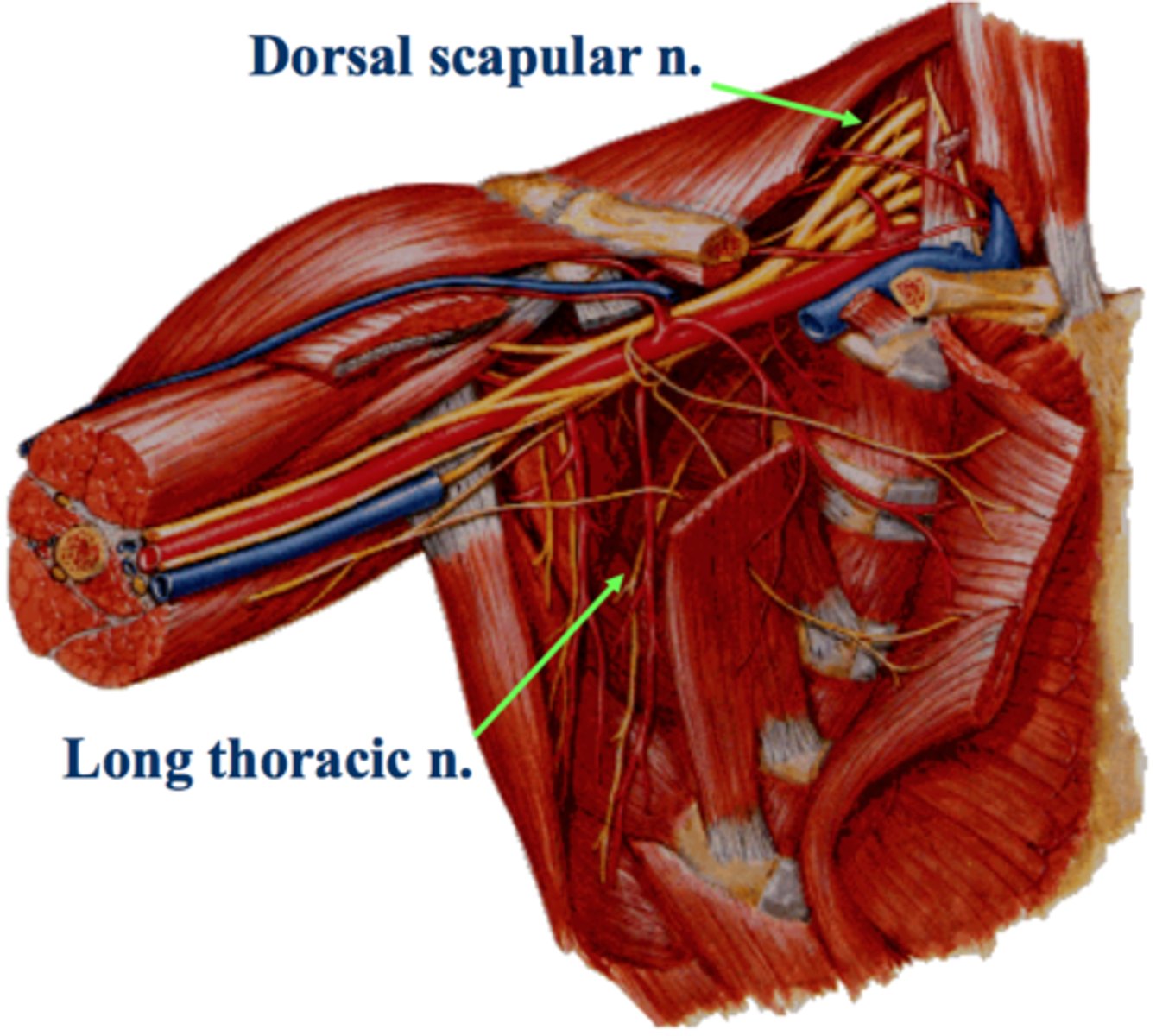
What does the dorsal scapular nerve innervate?
Rhomboid Major Rhomboid Minor
Levator Scapulae
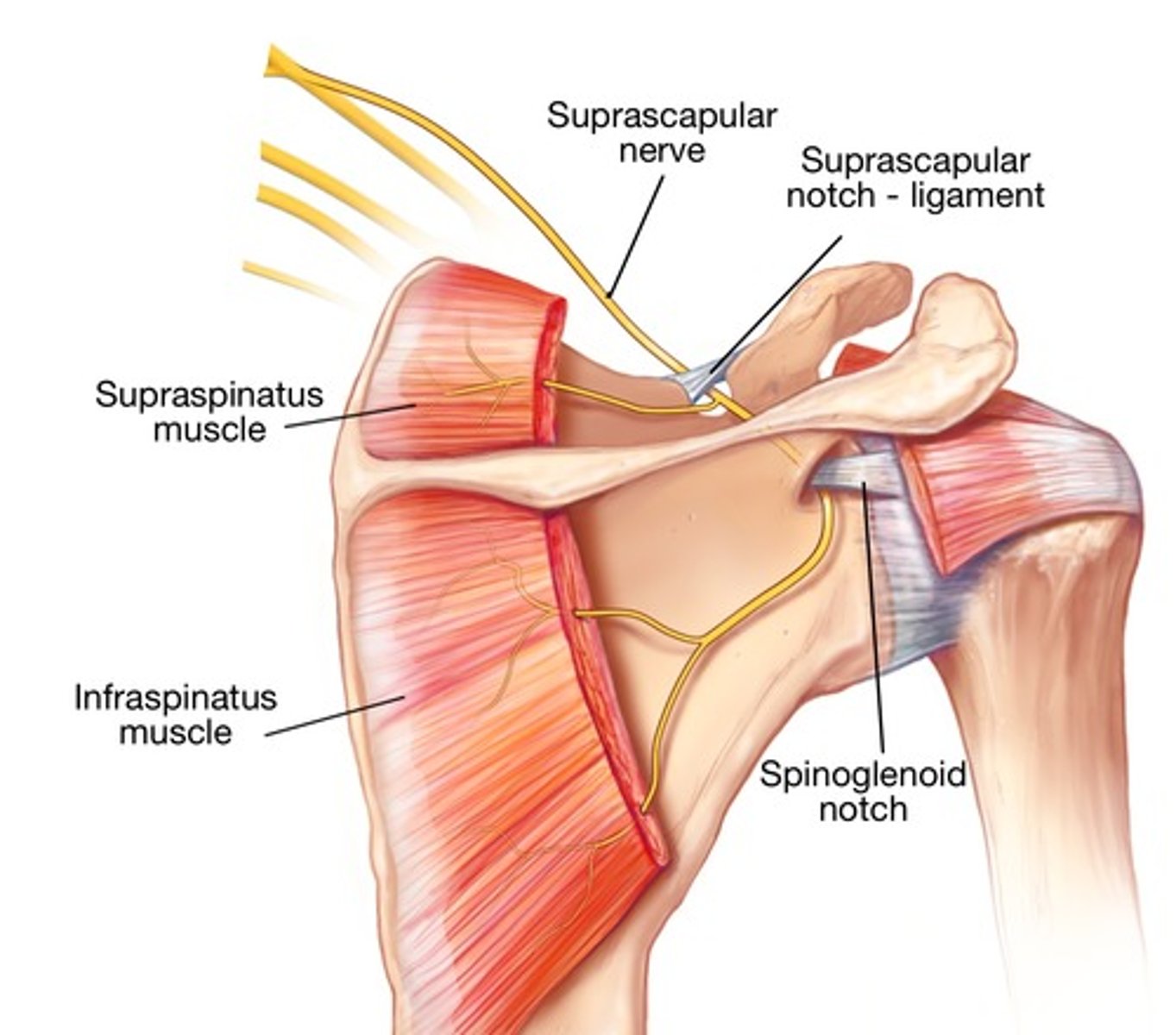
What does the suprascapular nerve innervate?
Supraspinatus Infraspinatus
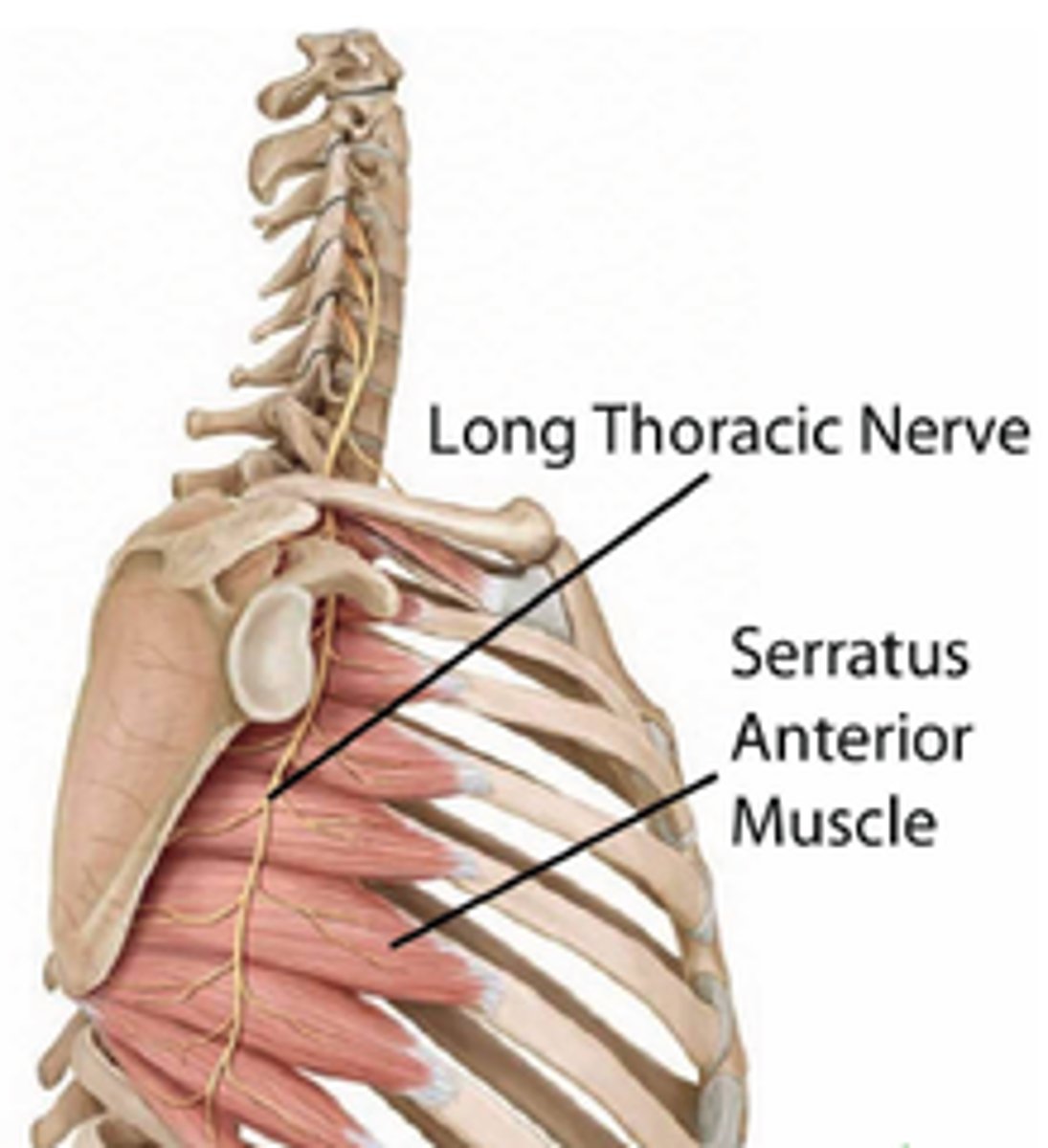
What does the long thoracic nerve innervate?
Serratus Anterior
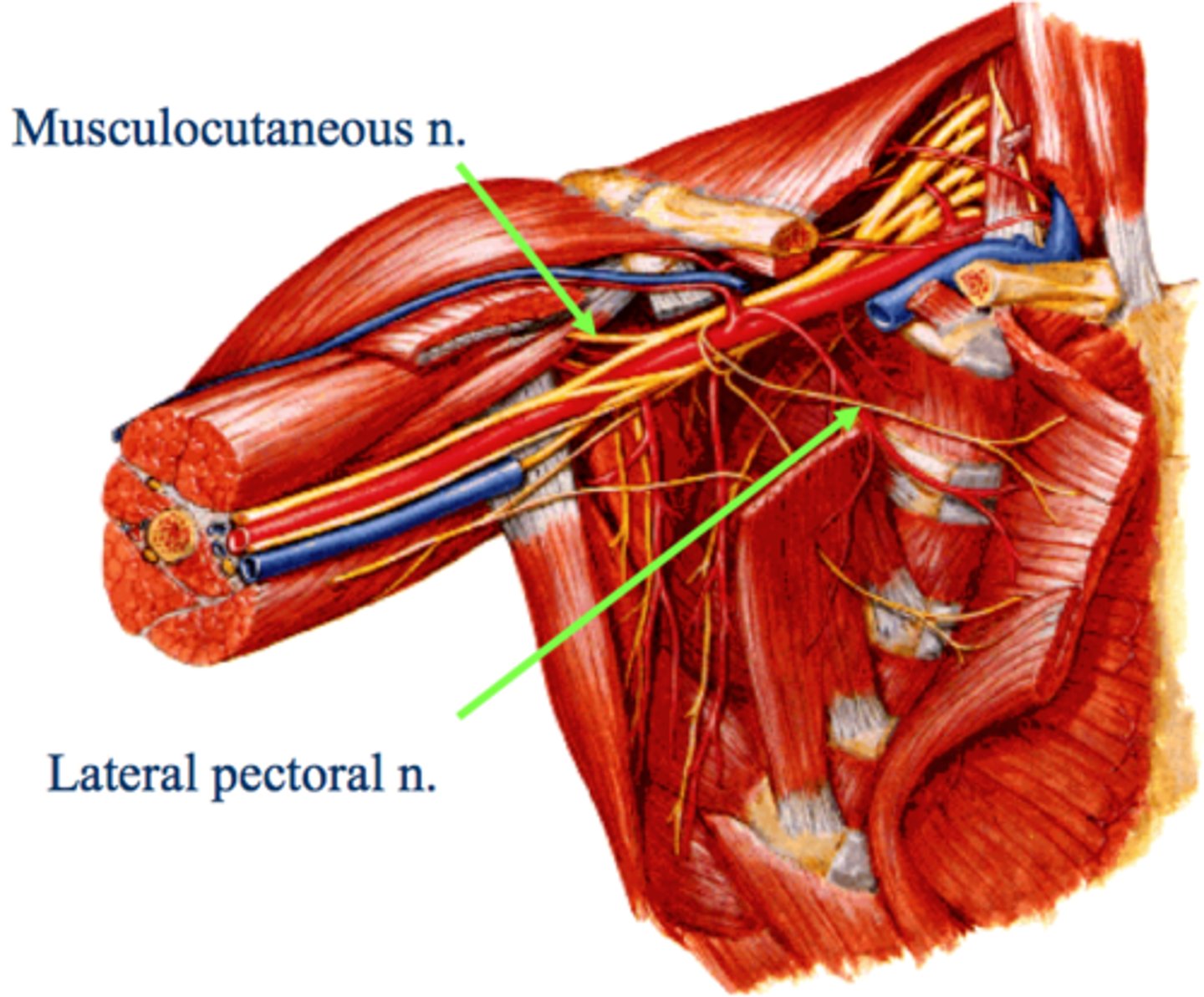
What does the lateral pectoral nerve innervate?
Pectoralis Major
What does the medial pectoral nerve innervate?
Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor
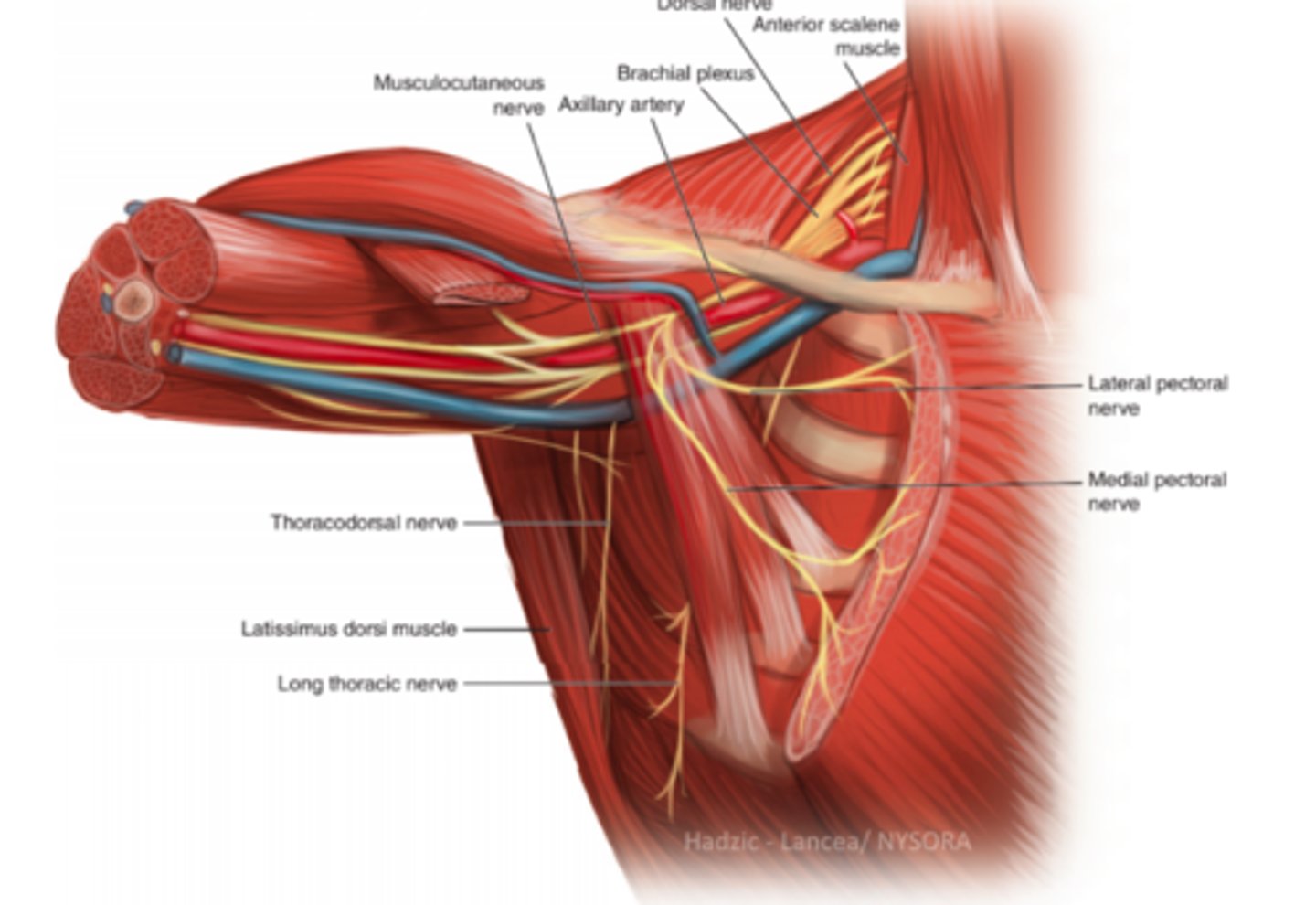
What does the upper subscapular nerve innervate?
Subscapularis
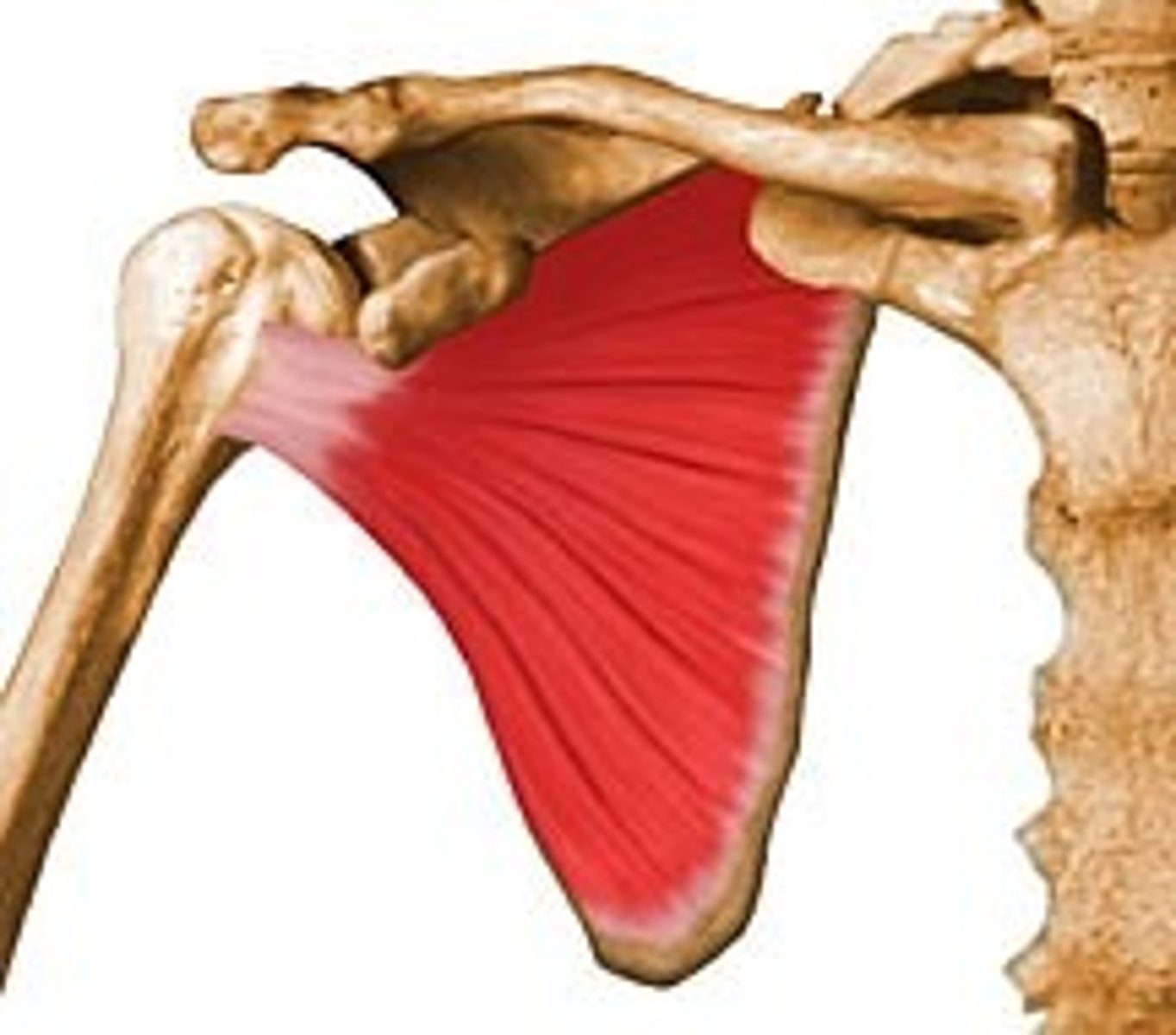
What does the lower subscapular nerve innervate?
Teres Major
Subscapularis
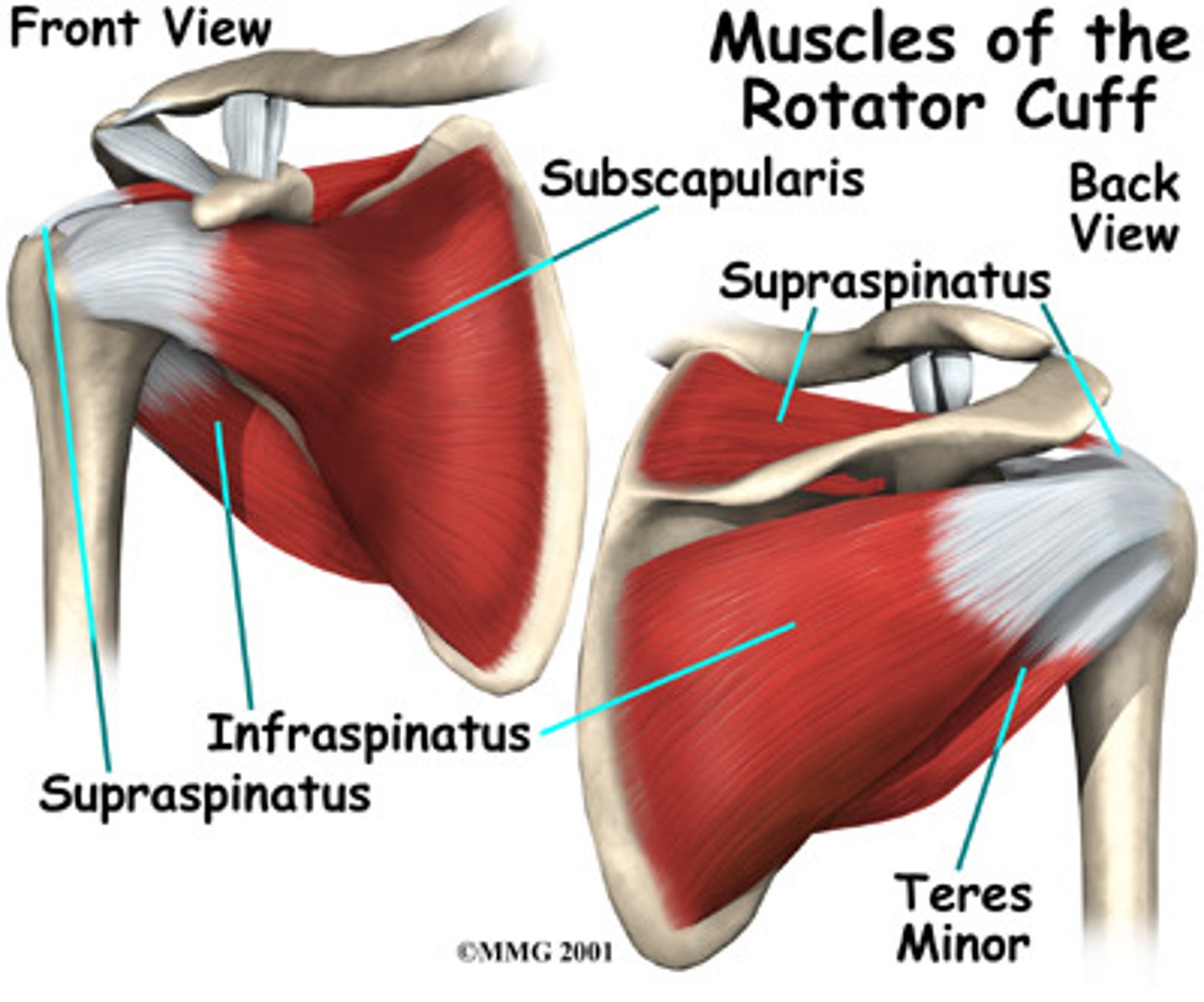
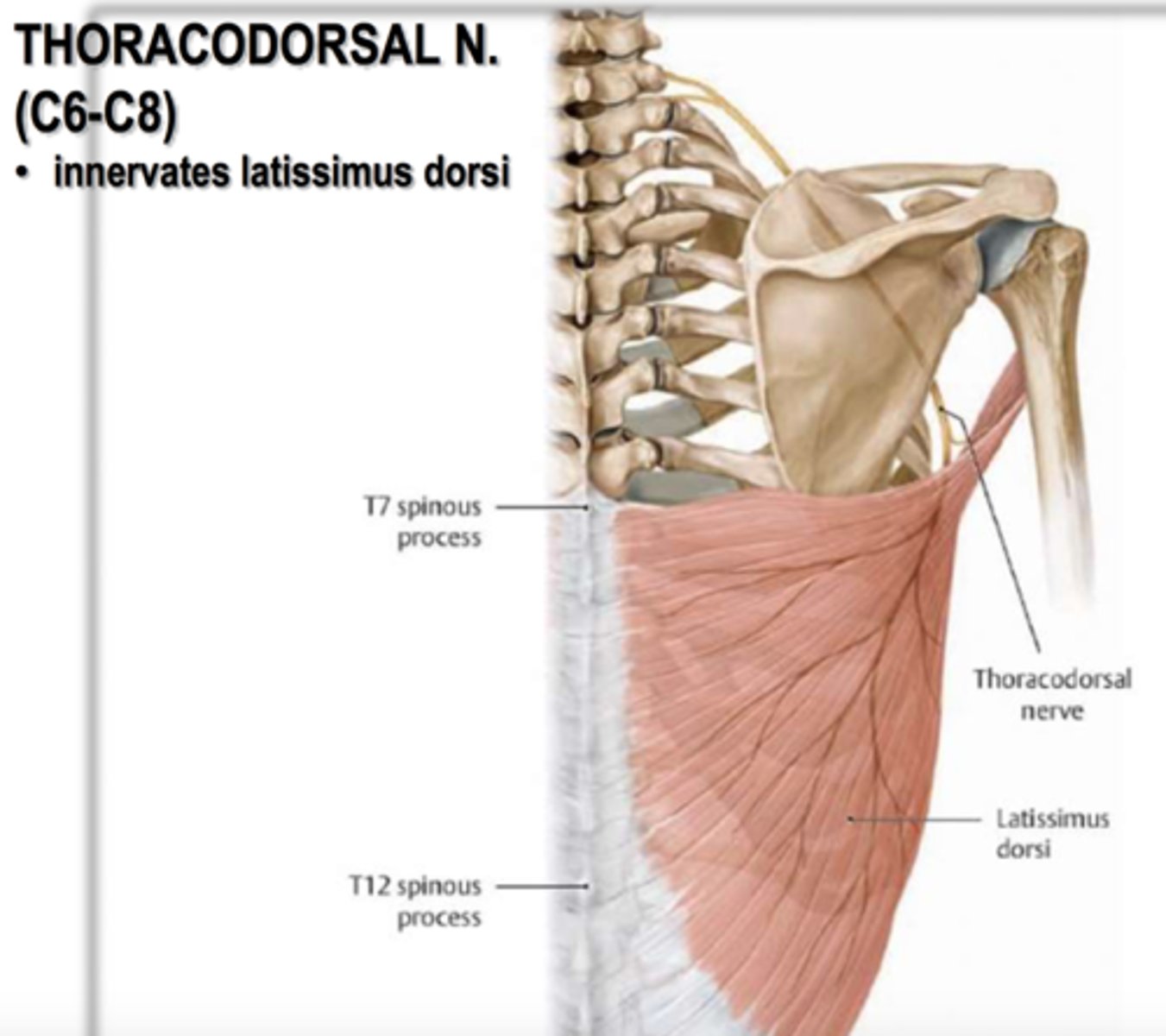
What does the thoracodorsal nerve innervate?
Latissimus Dorsi