Chemistry of Life
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
monosaccharide
A single sugar molecule (monomer) such as glucose or fructose, the simplest type of sugar.
Disaccharide
A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis.
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides
Sugar
-ose
Enzymes
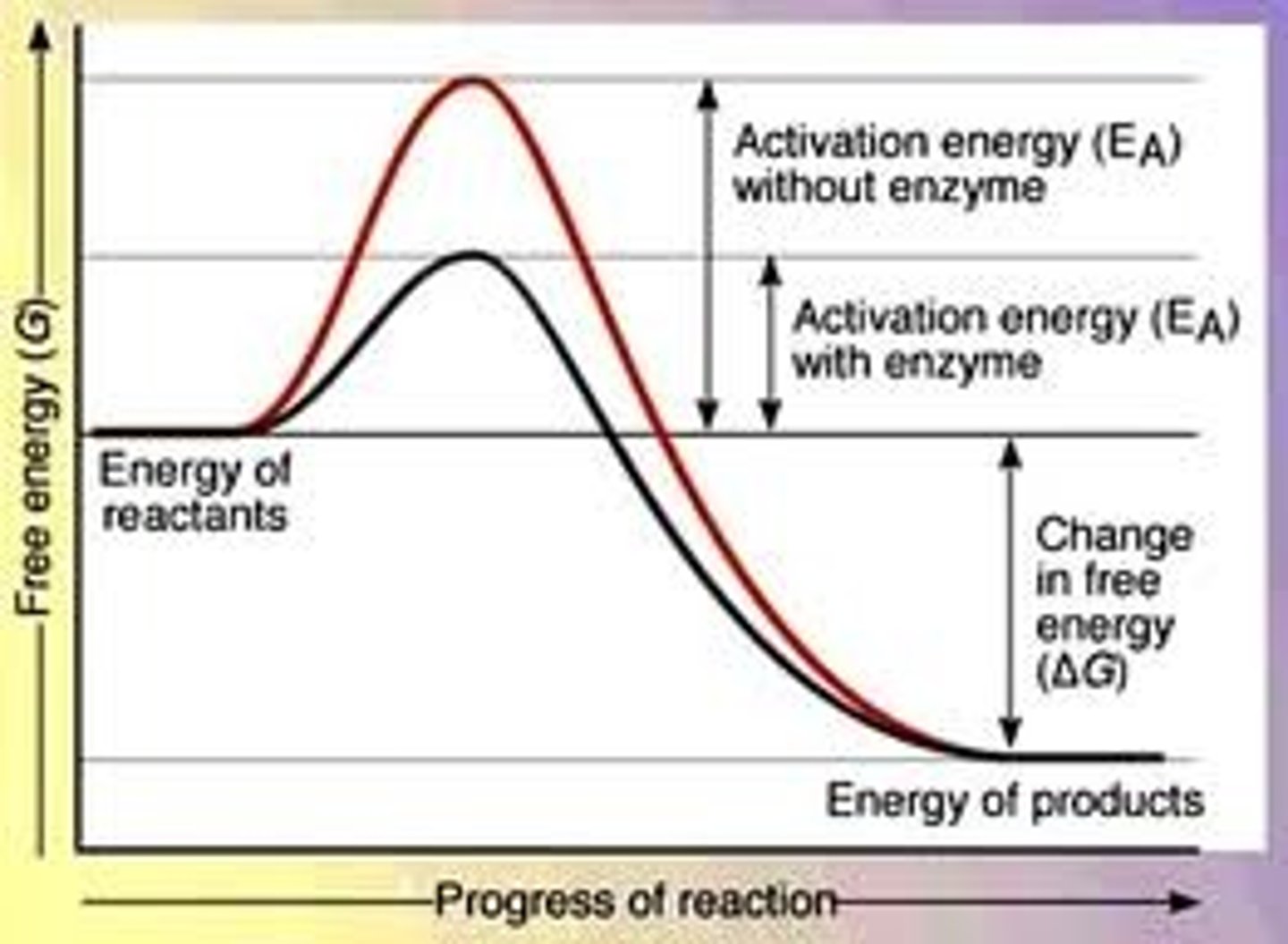
speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy of the reaction (catalysts)
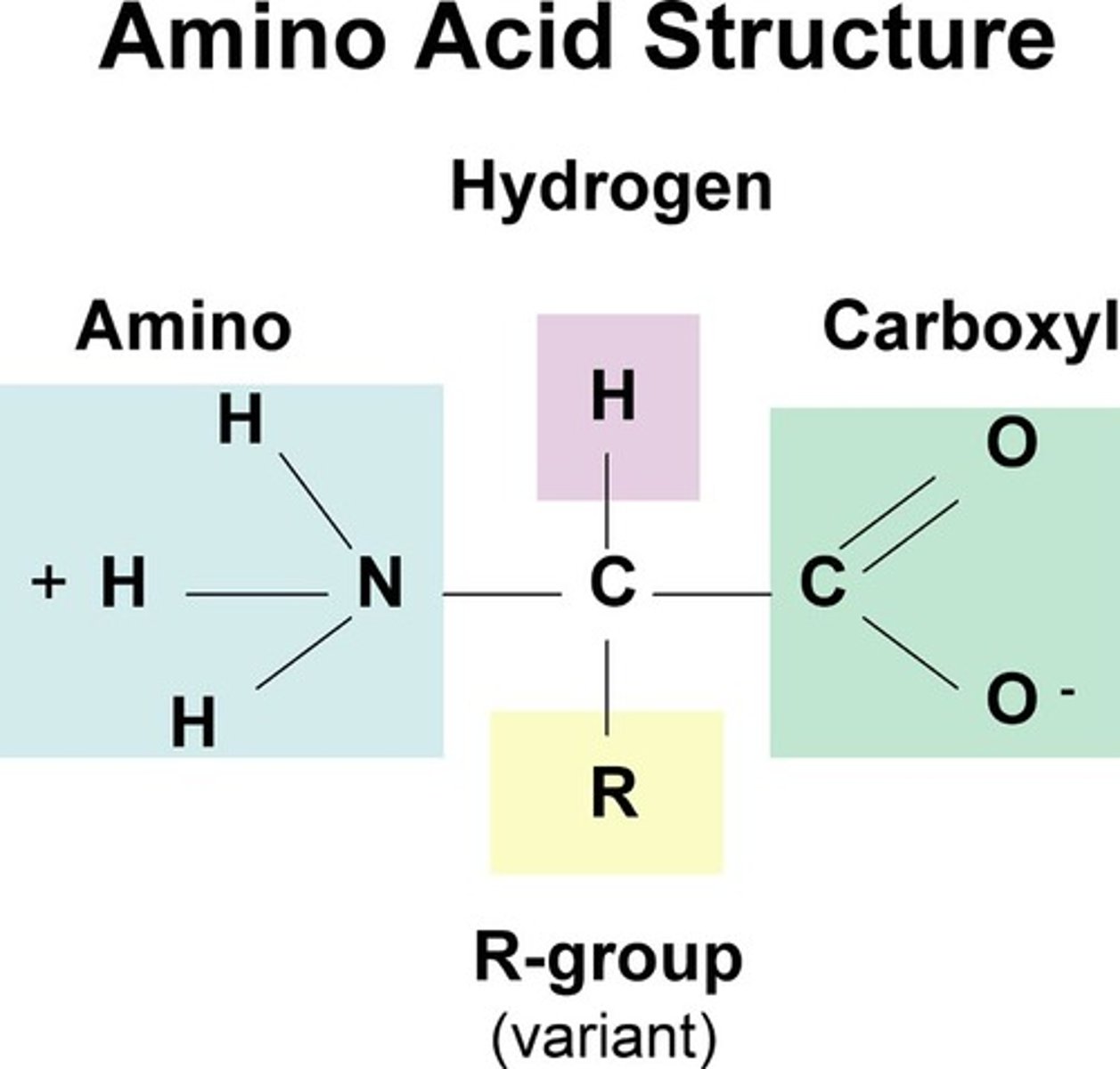
amino acids
building blocks of proteins
Protein
macromolecule that contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen; needed by the body for to fight infections, carry oxygen and makes up many structural components in the body
Lipids
Used for long term energy storage, makes up the cell membrane, pigments like chlorophyll and hormones
glycerol and fatty acids
Building Blocks of Lipids
Glycogen
a polysaccharide made by animal cells to store energy- short term
Starch
A storage polysaccharide in plants consisting entirely of glucose.
Cellulose
A substance (made of sugars) that is common in the cell walls of many organisms
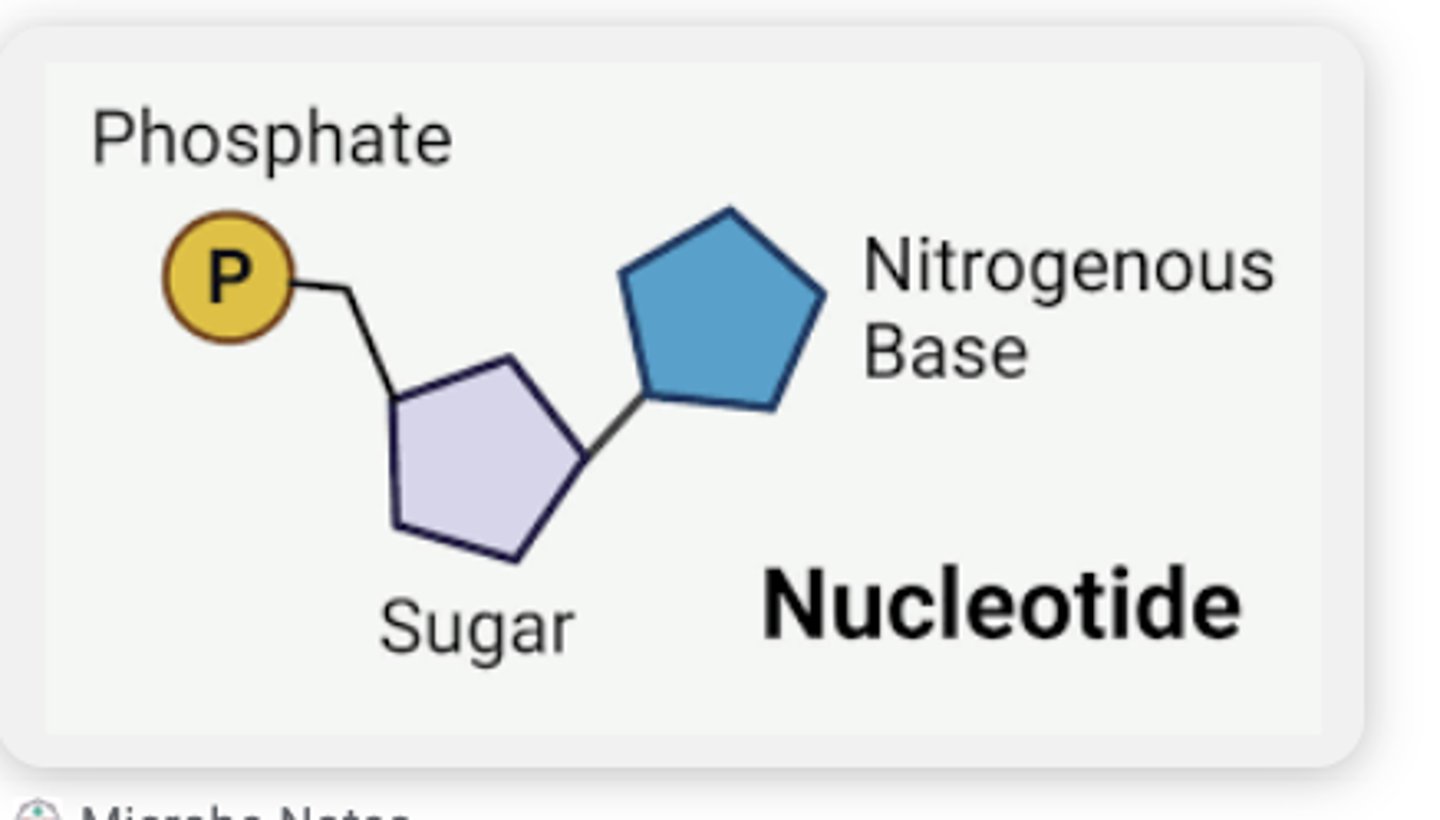
Nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.
RNA
single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose and is involved in protein synthesis
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two monomers or molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule.
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
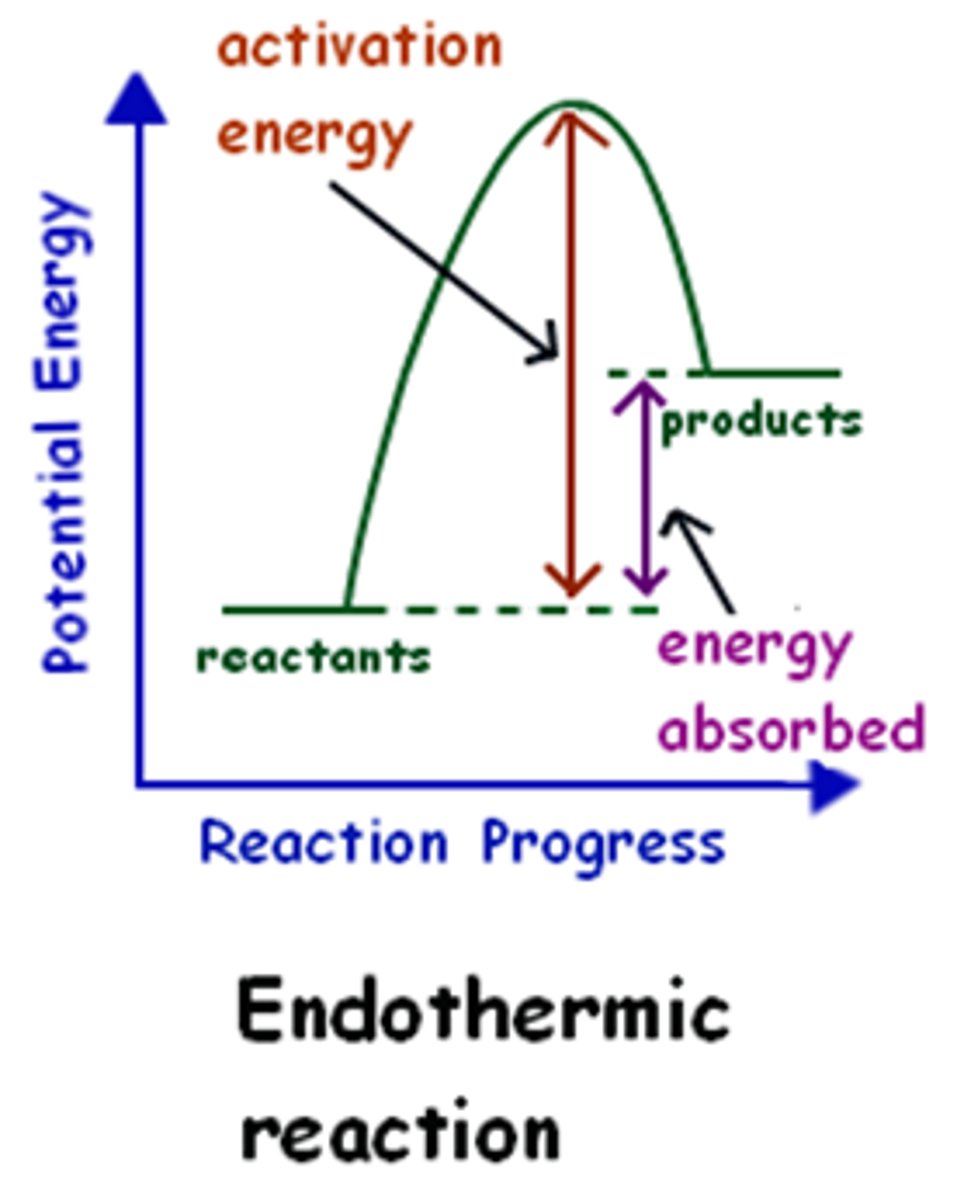
Endothermic
(of a chemical reaction or compound) occurring or formed with absorption of energy
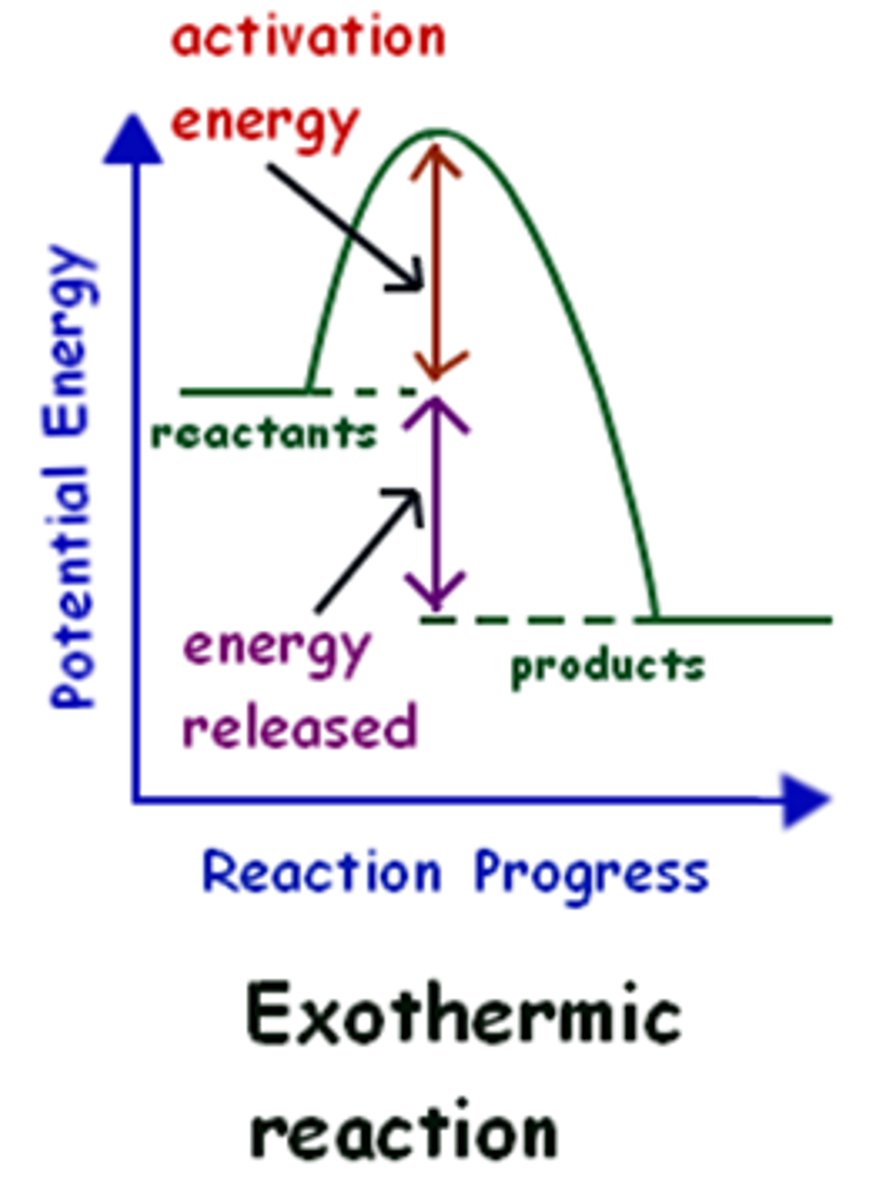
Exothermic
Chemical Reaction in which energy is primarily given off in the form of heat
-ase
enzyme
Substrate
The reactant on which an enzyme works.
Active site
The part of an enzyme where the chemical reaction occurs.
Reactants
A starting material in a chemical reaction
Products
The elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction.
polar molecule
A molecule that has electrically charged areas.
water
polar molecule, universal solvent, high specific heat, forms hydrogen bonds, stabilizes land temps
Atom
Basic unit of matter
compound
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds
Molecule
two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
atomic mass
Number of protons and neutrons
covalent bond
A chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule
ionic bond
the attraction between oppositely charged ions
hydrolysis
A chemical process that splits a molecule by adding water.
dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules are bonded together with the removal of a water molecule.
polymer
molecules composed of many monomers; makes up macromolecules
monomer
Building blocks or a simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers
solution
A homogeneous mixture of two or more substances
solvent
the substance in which the solute dissolves
solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances
capillary action
the combined force of attraction among water molecules and with the molecules of surrounding materials
covalent bond
A chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule
ionic bond
the attraction between oppositely charged ions
ions
charged particles
hydrogen bonds
Very weak bonds; occurs when a hydrogen atom in one molecule is attracted to the electrostatic atom in another molecule
nonpolar covalent bond
a covalent bond in which the electrons are shared equally by the two atoms
Hydrophilic
water loving - salts and other polar molecules like sugar
Hydrophobic
Water fearing
Hemoglobin
iron-containing protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen for delivery to cells
membrane proteins
Embedded proteins that perform specific functions for the cell membrane.
nuicleotide
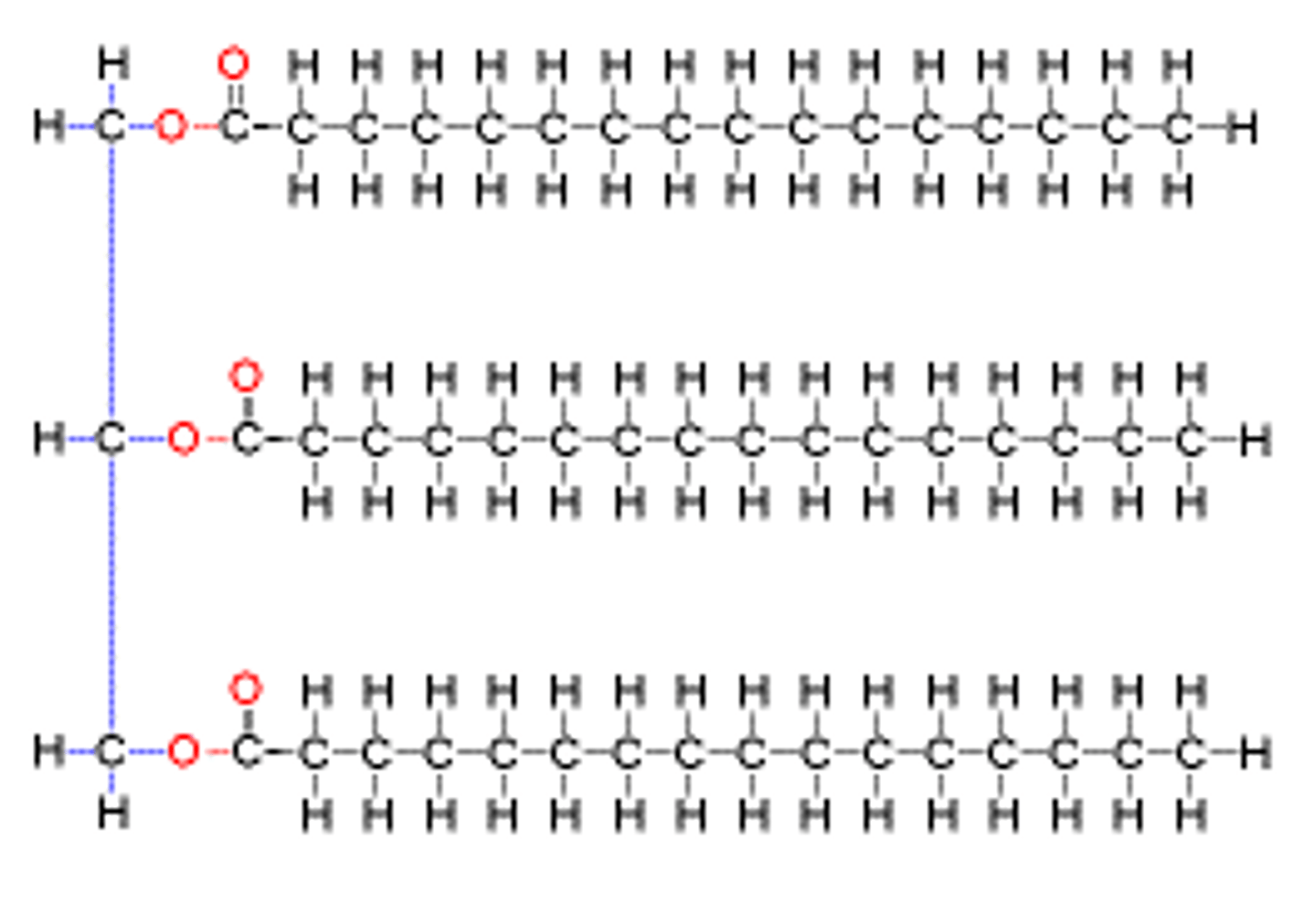
Triglycerides/fats
composed of 1 glycerol + 3 fatty acids
amino acids
building blocks of proteins
Exothermic reaction graph
products have less energy than reactants
endothermic reaction graph
products have more energy than reactants
enzyme graph