C2 : Bonding, Structure and the Properties of Matter
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
What are the 3 types of bonds?
Ionic
Covelant
Metallic
When is an ion formed + why does this happen?
When an atom gains or loses electrons to gain a full outer shell and become stable
What does ionic bonding occur between + what is formed in terms of ions?
Metals and non-metals react together
The metal loses electrons forming a positive ion + the non-metal gains electrons forming a negative ion
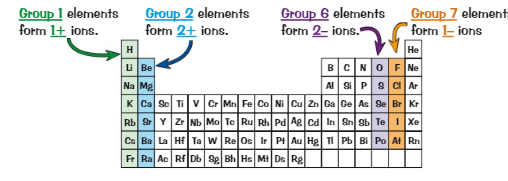
Which groups are most likely to form ions?
1,2,6,7
What are group 1 + 2 elements, do they gain or lose electrons + what do they form?
Metals
Lose electrons
Positive ions
What is a positive ion called?
Cation
What are group 6 + 7 elements, do they gain or lose electrons + what do they form?
Non-metals
Gain electrons
Negative ions
What are negative ions called?
Anions
What charge ions do groups 1,2,6,7 form? (4)
Group 1 → 1+ ions
Group 2 → 2+ ions
Group 6 → 2- ions
Group 7 → 1- ions
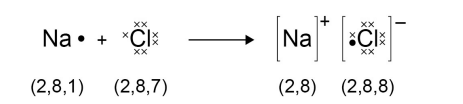
Write the half equation for sodium gaining a full outer shell (Na → group 1)
Na → Na+ + e-
Write the half equation for magnesium gaining a full outer shell (Mg → group 2)
Mg → Mg2+ + 2e-
Write the half equation for chlorine gaining a full outer shell (Cl → group 7)
Cl + e- → Cl-
Write the half equation for oxygen gaining a full outer shell (O → group 6)
O + 2e- → O2-
What happens to the electrons in ionic bonding?
Electrons are transferred
What diagram represents ionic bonding?
Dot and cross diagrams
Draw a dot and cross diagram for sodium chloride (NaCl)
(Na → group 1) (Cl → group 7)
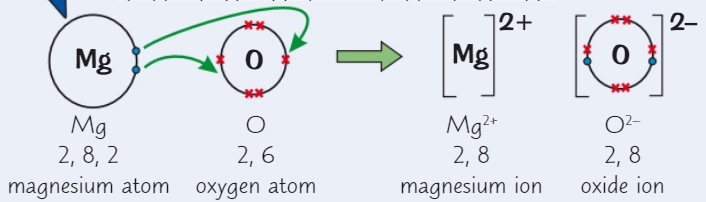
Draw a dot and cross diagram for magnesium oxide (MgO)
( Mg→ group 2 ) ( O→ group 6 )
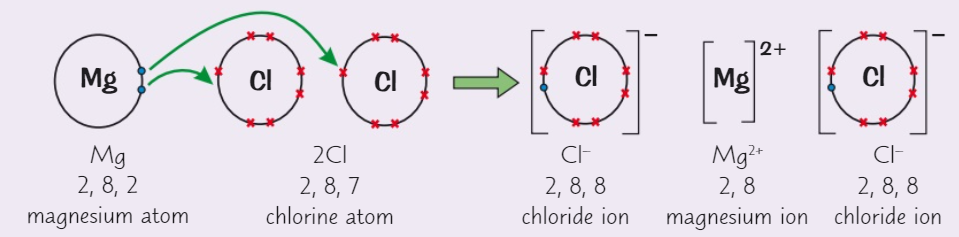
Draw a dot and cross diagram for magnesium chloride (MgCl2)
( Mg→ group 2 ) ( Cl→ group 7 )
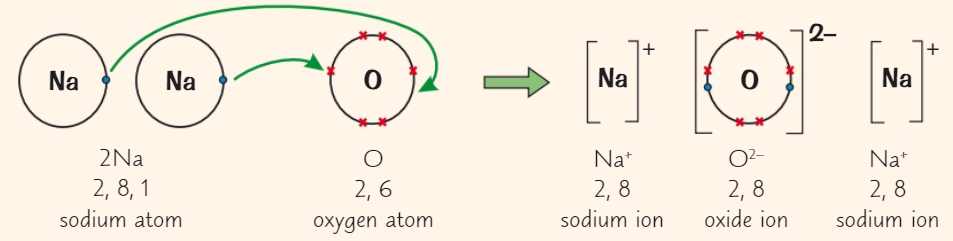
Draw a dot and cross diagram for (Na2O)
( Na→ group 1 ) ( O→ group 6 )
What is an ionic compound?
A giant structure of ions
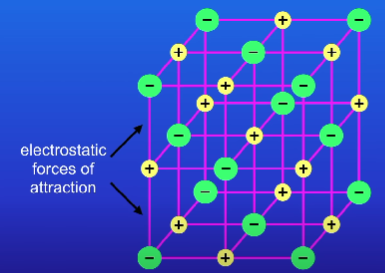
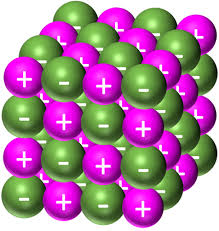
What are ionic compounds held together by?
Strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions
What direction do the electrostatic forces in a ionic compound act in + what is this called?
The forces act in all directions between oppositely charged ions and this is called ionic bonding
What is the ionic compound structure called?
A giant ionic lattice
What are the 2 ways to a draw giant ionic lattice?
Space filling
Ball and stick diagrams
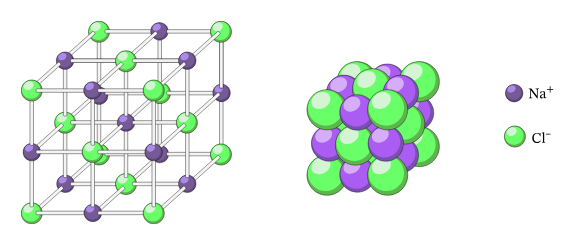
Draw a ball and stick diagram + label the diagram
Draw a space filling diagram and label the diagram
What are the properties of ionic compounds + why? (3)
High melting + boiling points → strong electrostatic forces which need a lot of energy to overcome
When solid, can’t conduct electricity → ions aren’t free to move
When molten (melted) or dissolved in water, can conduct electricity → ions are free to move and will carry charge
What does covalent bonding occur between?
Non metal and a non metal
What happens to the electrons in covalent bonding?
The electrons on the outer shell are shared
What 3 diagrams are used to draw covalent bond?
Dot and cross diagrams
Displayed formula
3D model
For covalent bond what happens to the electrons in a dot and cross diagram?
They overlap
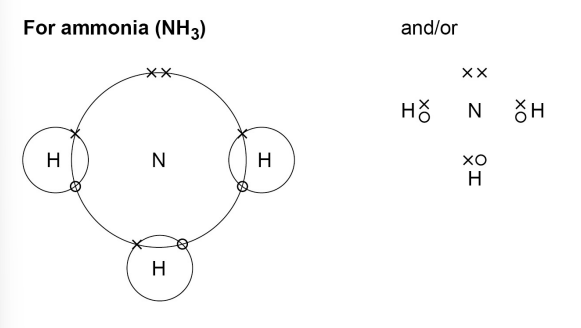
Draw a dot and cross diagram for ammonia NH3
(Nitrogen → group 5) (Hydrogen → group 1)
(both are fine)
Draw the displayed formula for ammonia NH3
(Nitrogen → group 5) (Hydrogen → group 1)
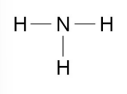
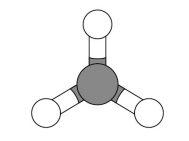
Draw a 3D model for ammonia NH3
(Nitrogen → group 5) (Hydrogen → group 1)


Name the 8 simple molecular substances
Hydrogen
Chlorine
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Methane
Water
Hydrogen chloride
Ammonia

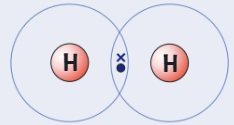
Draw a dot and cross diagram for
(Hydrogen → group 1)

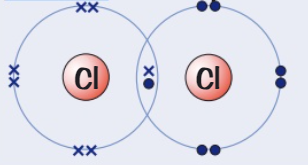
Draw a dot and cross diagram for
(Chlorine → group 7)

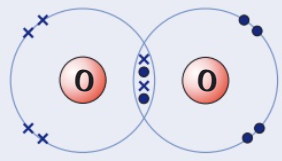
Draw a dot and cross diagram for
(Oxygen → group 6)

Draw a dot and cross diagram for
(Nitrogen → group 5)
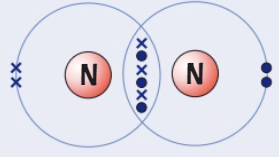

Draw a dot and cross diagram for
(Carbon → group 4) (Hydrogen → group 1)
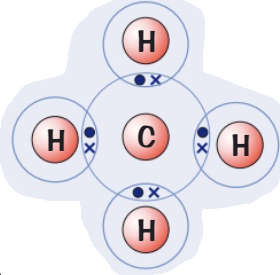

Draw a dot and cross diagram for
(Hydrogen → group 1) (Oxygen → group 6)
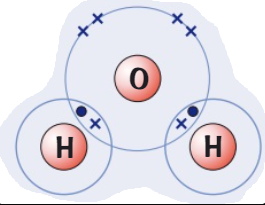

Draw a dot and cross diagram for
(Hydrogen → group 1)(Chlorine → group 7)
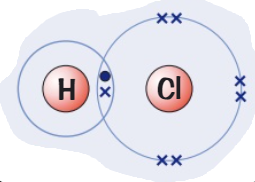
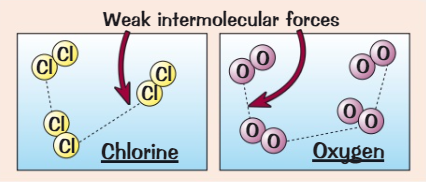
What are the properties of simple molecular compounds? (4)
Low melting and boiling points
Gases or liquids at room temperature
They do not conduct electricity because there are no free ions to carry charge
The bigger they get, the stronger the intermolecular forces get so their melting + boiling points increase
Why do simple molecular substances have low melting and boiling points?
Because they have weak intermolecular forces between them which do not require a lot of energy to break
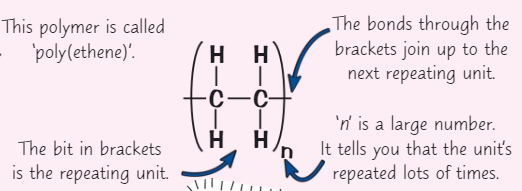
What is a polymer?
A long molecule made up of many monomers
What bond are polymers joined by?
Covalent bonds
How are polymers represented?
With a repeating unit
Draw poly(ethene) + label it
What are the properties of polymers?
Solid at room temperature as intermolecular forces are relatively strong
In giant covalent structures what are the atoms bonded by?
Strong covalent bonds
What are the properties of giant covalent structures? (3)
Solids
Vey high melting and boiling points
Don’t conduct electricity
Give 3 examples of giant covalent structures
Diamond
Graphite
Silicon dioxide (silica)
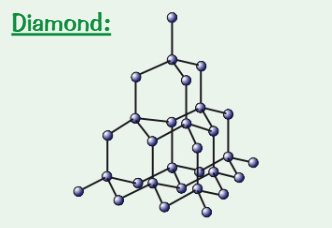
Draw + describe the structure of diamond
Each carbon atom forms four covalent bonds in a very rigid giant covalent structure
Draw + describe the structure of graphite
Each carbon forms 3 covalent bonds to create layers of hexagons + each carbon atom has a delocalised electron
Made up of layers of graphene which are held together weakly
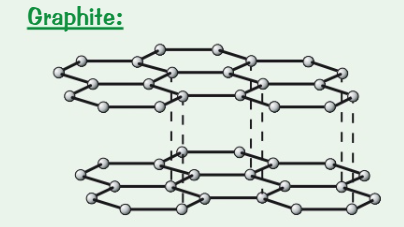
What is graphene + how big is it?
A sheet of carbon atoms joined together in hexagons + is one atom thick
What are the properties of graphite? (6)
High melting + boiling points → covalent bonds need a lot of energy to break them
Conduct electricity → have a delocalised electron
Conduct thermal electricity → particles free to move
Light
Slippery
Soft
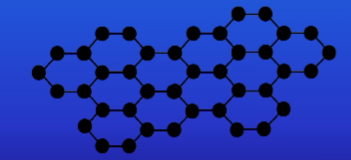
Draw + describe the structure of silicon dioxide (silica) + what is it also known as?
Silicon and oxygen bonded together with covalent bonding
Also know as sand
What is are allotropes?
Different structural forms of the same elements in the same physical state
Give the 3 allotropes of carbon
Diamond
Graphite + Graphene
Fullerenes
What are the properties of diamond? (3)
Hard → made up of carbon atoms each having 4 covalent bonds making diamond
High melting point → strong covalent bonds
Doesn’t conduct electricity
What are fullerenes?
Molecules of carbon shaped like closed tubes or hallow balls
What shapes can fullerenes be made up of? (3)
Hexagons
Pentagons
Heptagons
What was the first fullerene discovered calls + what is it molecular formular and what shape is it?
Buckminsterfullerene (C60) which has a spherical shape
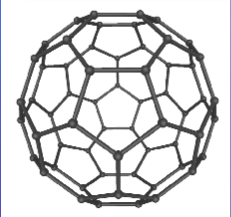
What are the uses of fullerenes? (3)
Pharmaceutical delivery → ‘cage’ other molecules such as a drug which would be delivered into the body
Lubricants
Catalysts
What are carbon nanotubes?
Fullerenes shaped into long cylinders
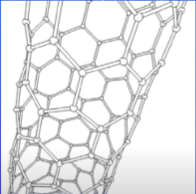
What are the properties of carbon nanotubes? (2)
Have very high tensile stretch (can be stretched without breaking)
Conductors of heat and electricity
What is nanotechnology + when can it be used? (2)
Technology that uses nanotubes
used in electronics
or to strengthen materials without add much weight such as in tennis rackets
What does metallic bonding happen between?
Metal and metals
What happens to the electrons in metallic bonding?
They are free to move
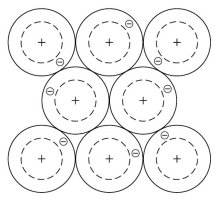
What is the structure of metals?
A giant structure of atoms arranged in regular layers
What are the properties of metals? (5)
Solid at room temperature
High melting + boiling points
Conduct electricity + heat → sea of delocalised electrons are free to move
Malleable → can be bend and shaped
Layers are able to slide over each other
What is an alloy?
A mixture of metals
What is the disadvantage of pure metals + how can this problem be fixed?
Pure metals are too soft so they can be mixed with other metals to become harder → different sized atoms when joined together distort layer making it more difficult to slide over each other
What are the 3 states of matter?
Solid
Liquid
Gas
What 3 factors do forces of attraction depend on?
Material (structure of substance + type of bonds)
Temperature
Pressure
How do the particles behave in a solid? (3)
Strong forces of attraction between particles → close together which form a regular giant arrangements
Particles don’t move from their positions → keep definite shape + volume
Vibrate in fixed positions

How do the particles behave in a liquids? (3)
Weak forces of attraction between particles → move past each other
Have a definite volume but don’t keep a definite shape
Particles move in different directions
How do the particles behave in a gases? (3)
Weak forces of attraction between particles → move past each other + far apart
Don’t have a definite volume or a definite shape
Particles move in different directions
What are the 4 state symbols?
Solid → (s)
Liquid → (l)
Gas → (g)
Aqueous (in solution) → (aq)
How would you predict the state of a substance? (3)
Temperature below melting → Solid
Temperature above boiling → Gas
Temperature in between → Liquid
What is the diameter of coarse particles, fine particles + nanoparticles? (in nm)
Coarse particles (PM10, or dust) → between 2500 to 10,000 nm
Fine particles (PM2.5) → between 100 to 2,500 nm
Nanoparticles → between 1 to 100 nm
What happens to a particles surface area : volume ratio if the particle size decreases by 10?
The surface area : volume ration increases by 10
What are the uses of nanoparticles? (6)
Medicine
Sun creams
Cosmetics
Deodorants
Electronics
Catalysts
What are the risks of using nanoparticles?
When used in cosmetic products or sun creams nanoparticles could be absorbed into the body and the dangers of them are unknown

a) Solid
b) Liquid
c) Liquid
d) Gas

What are the pros + cons of dot and cross diagrams? (2)
Can see where electrons have moved from and to
Don’t tell us the shape of the molecule
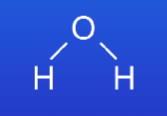
What are the cons of 2D stick diagrams diagrams? (2)
The covalent bond is represented as a stick so we can’t tell which electrons in the bond came from which atom
Don’t tell us the shape of the molecule
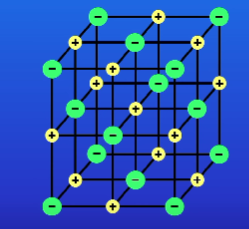
What are the pros + cons of ball and stick diagrams? (3)
Allow is to see the ions in 3 dimensions
The ions are widely spaced which is inaccurate
Gives a mistaken impression about the size of the structures
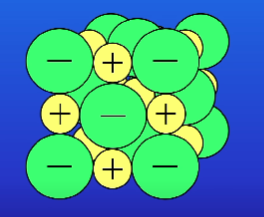
What are the pros + cons of space filling diagrams? (3)
Show how closely packed ions are
Difficult to see all the atoms clearly
Gives a mistaken impression about the size of the structures
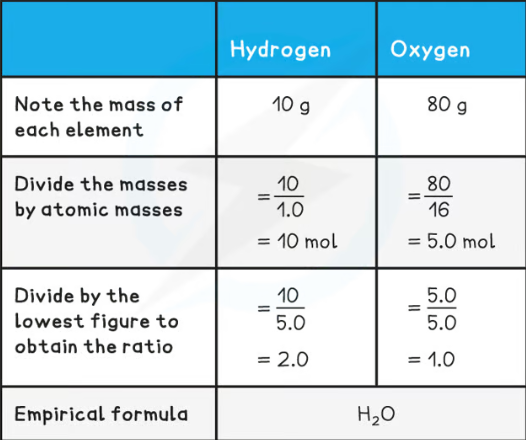
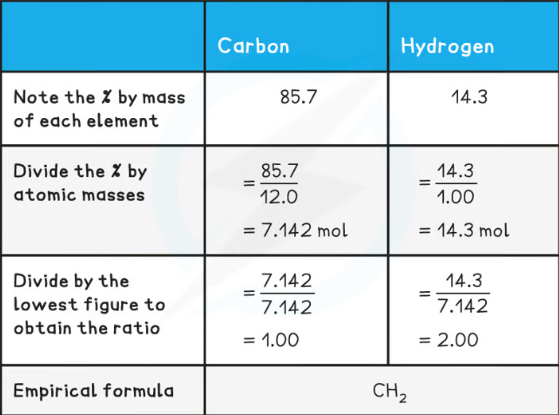
What is the empirical formula?
The simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound
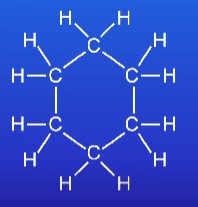
Work our the empirical formula of
CH2

(Atomic mass for Hydrogen = 1) (Atomic mass for Oxygen = 16)