Chapter 13 Forensic Toxicology
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
What is the primary objective of forensic toxicology?
To detect and isolate drugs in the body to determine their influence on human behavior.
How is alcohol absorbed into the bloodstream?
Alcohol appears in the blood within minutes after consumption, increasing in concentration as it is absorbed from the stomach and small intestine.
What are the three basic steps of alcohol metabolism?
Absorption, Distribution, and Elimination.
What happens during the absorption phase of alcohol consumption?
Alcohol slowly enters the bloodstream and is carried to all parts of the body.
How is alcohol distributed in the body after absorption?
Alcohol is distributed uniformly throughout the water portions of the body, which is about 2/3 of the body volume.
What factors determine the rate at which alcohol is absorbed?
Total time taken to consume the drink, alcohol content of the beverage, amount consumed, and quantity and type of food present in the stomach.
How does food in the stomach affect alcohol absorption?
Alcohol consumed on an empty stomach is absorbed faster than when food is present.
What is the effect of beer on alcohol absorption compared to water?
Beer is absorbed more slowly than an equivalent concentration of alcohol in water due to its carbohydrate content.
What occurs after the absorption period of alcohol is completed?
A maximum alcohol level is reached in the blood, followed by a decrease in alcohol concentration until it reaches zero.
How long can it take to reach maximum blood-alcohol concentration after consumption?
Depending on various factors, it may take 2 to 3 hours to reach maximum concentration, but typically 30 to 90 minutes under normal social drinking conditions.
What is the role of a forensic toxicologist?
To detect and identify drugs and poisons in body fluids, tissues, and organs, particularly in relation to criminal law.

What is the significance of the 'implied consent' law in relation to blood-alcohol laws?
It addresses constitutional issues raised against blood-alcohol laws as recommended by the NHTSA.
What techniques do forensic toxicologists use to identify substances?
They use various analytical methods to detect and identify drugs and poisons in biological samples.
What is the role of the drug recognition expert program in forensic toxicology?
To coordinate with forensic toxicology results for accurate assessment of drug influence.
What is the significance of toxicology in crime laboratories and medical examiner's offices?
Toxicologists play a crucial role in determining the presence of substances that may relate to criminal investigations.
What is the relationship between alcohol absorption time and peak blood-alcohol concentration?
The longer the absorption time, the lower the peak blood-alcohol concentration.
What is the process of elimination in alcohol metabolism?
Alcohol is broken down by enzymes in the body, transforming it into other chemicals that are easier to eliminate.
How does the presence of food affect the peak alcohol concentration?
Food can slow down absorption, potentially leading to a lower peak alcohol concentration.
What is the role of forensic toxicologists in hospital laboratories?
They detect and identify drugs and poisons in patients, which can aid in medical treatment and legal investigations.
What is the importance of understanding the metabolism of alcohol in forensic toxicology?
It helps in determining the effects of alcohol on behavior and the timing of consumption relative to intoxication.
What are the implications of alcohol's distribution in low water content areas of the body?
Fat, bones, and hair contain little alcohol due to their low water content, affecting overall alcohol distribution.
How does the type of beverage consumed affect alcohol absorption rates?
Different beverages, like beer versus spirits, can have varying absorption rates due to their composition.
What is the significance of detecting alcohol in blood for forensic investigations?
It provides evidence of intoxication levels which can be critical in legal cases involving driving under the influence.
What are the two main mechanisms by which alcohol is eliminated from the body?
Oxidation and excretion.
What percentage of consumed alcohol is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water?
95-98%.
Where does the oxidation of alcohol primarily take place?
In the liver.
What enzyme is involved in the conversion of alcohol to acetaldehyde?
Alcohol dehydrogenase.
What is the average elimination rate of alcohol in the body after absorption?
0.015 percent w/v (weight per volume) per hour.
How long does it take for a blood alcohol level of 0.10% to reach zero?
About 6.5 hours.
What is Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) used for?
It relates alcohol intake to its effects on the body.
What is the most widespread method for rapidly determining alcohol intoxication?
Breath testing.

What does a breath test measure?
The alcohol concentration in the pulmonary artery by measuring its concentration in alveolar breath.
What was the first widely used instrument for measuring alcohol content in breath?
The Breathalyzer.
What assumption is made regarding the ratio of alcohol in blood to alcohol in alveolar breath?
2,100 to 1 at a mouth temperature of 34°.
What modern technologies have replaced the Breathalyzer?
Infrared light-absorption devices and fuel cell detectors.
What is a key feature of breath testing instruments?
They can be connected to an external alcohol standard or simulator.
What does the liquid simulator used in breath testing contain?
A known concentration of alcohol in water.
How does the breath test result during the absorption phase compare to venous blood analysis?
Breath test results may be higher and more reflective of the alcohol concentration reaching the brain.
What happens to any remaining alcohol after oxidation?
It is excreted unchanged in breath, urine, and perspiration.
What is the significance of breath analysis in alcohol testing?
It provides an easily obtainable specimen along with rapid and accurate results.
What does the term 'burn-off' refer to in the context of alcohol metabolism?
The rate at which alcohol is eliminated from the body.
Why might breath test results be more accurate for assessing intoxication than blood tests?
They reflect the concentration of alcohol reaching the brain.
What is the role of alcohol dehydrogenase in alcohol metabolism?
It converts alcohol into acetaldehyde, which is then further metabolized.
What is the relationship between blood alcohol levels and their effects on the body?
Blood alcohol levels serve as a standard for relating alcohol intake to physiological effects.
What is the importance of the breath test's connection to an external alcohol standard?
It ensures the instrument registers the test sample within a small percentage of error compared to the known concentration.
What is the key to the accuracy of a breath-testing device?
The device must capture the alcohol in the alveolar (deep-lung) breath of the subject.
What is the minimum breath volume required by the Intoxilyzer 9000?
The unit requires no less than 1.1 to 1.5 liters of breath from the subject.
How long must a subject blow into the Intoxilyzer 9000?
The subject must blow for a minimum of 6 seconds.
What is the minimum breath flow rate required for the Intoxilyzer 9000?
The minimum breath flow rate is 3 liters per minute.
What feature do breath-test instruments have to ensure sample quality?
Breath-test instruments feature a slope detector to ensure the sample is alveolar breath.
What must be avoided to ensure accurate breath test results?
Avoid measuring 'mouth alcohol' from regurgitation, belching, or recent alcohol intake.
How long should a subject avoid foreign material in their mouth before a breath test?
At least 15 minutes.
What is an important check of the integrity of a breath test?
Measurements of independent breath samples taken within a few minutes of each other.
What does significant agreement between two breath tests reduce?
It reduces the possibility of errors caused by operator mistakes, mouth alcohol, instrument failures, and spurious signals.
What preliminary tests are conducted by officers suspecting alcohol influence?
Field sobriety tests to ascertain the degree of physical impairment.
What do field sobriety tests typically include?
A series of psychophysical tests and a preliminary breath test.
What is the purpose of the horizontal-gaze nystagmus test?
To observe involuntary jerking of the eye as it moves to the side, indicating intoxication.

What happens to the eye movement of an intoxicated person during the horizontal-gaze nystagmus test?
The eye jerks before it can move fully to the side.
What are the walk-and-turn and one-leg stand tests designed to assess?
They test the subject's ability to comprehend and carry out multiple instructions simultaneously.
What is the most widely used method for determining alcohol levels in blood?
Gas chromatography (GC).
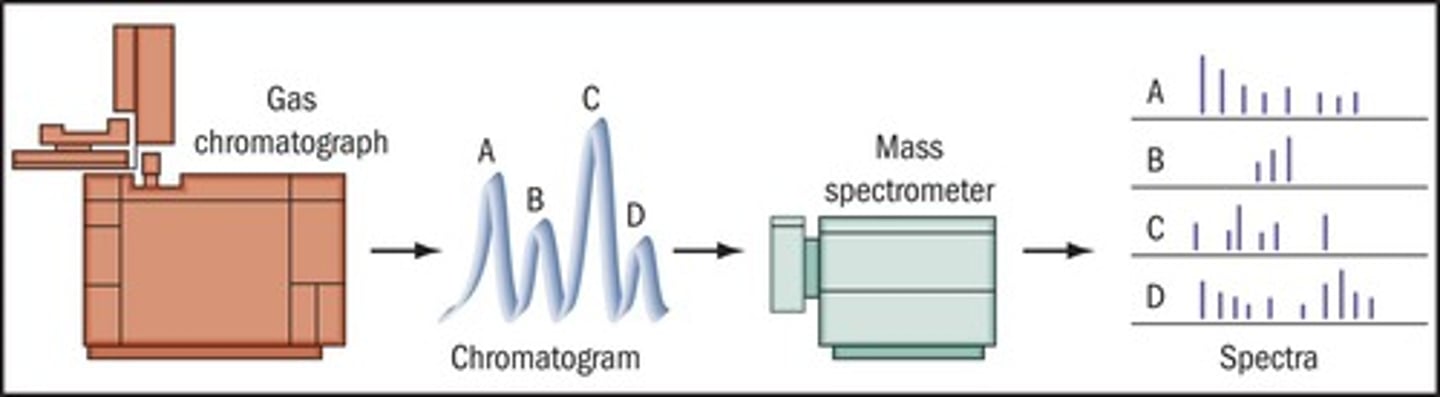
How does gas chromatography separate ethanol from other substances?
Ethanol is separated from other volatile substances in the blood under proper GC conditions.
How can investigators calculate the ethanol level in blood using gas chromatography?
By comparing the resultant ethanol peak area to known blood-alcohol standards.
What conditions must be met for blood collection for alcohol analysis?
Blood must be drawn under medically accepted conditions by a qualified individual.
What type of disinfectant should be used before drawing blood?
A nonalcoholic disinfectant.
What is the role of the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration regarding breath testers?
They have approved the use of certain devices as evidential breath testers.
What is the significance of the slope detector in breath-testing devices?
It ensures that the breath sample is from deep-lung breath, improving accuracy.
What can recent gargling with mouthwash lead to in breath tests?
The presence of mouth alcohol, which can affect test results.
What is the purpose of field sobriety tests?
To determine if an evidential breath or blood test is justified based on physical impairment.
What is the best way to preserve blood after it is removed from an individual?
Seal it in an airtight container with an anticoagulant and a preservative, then store it in a refrigerator.
What role does potassium oxalate play in blood preservation?
Potassium oxalate acts as an anticoagulant, preventing clotting.
What is the function of sodium fluoride in blood preservation?
Sodium fluoride serves as a preservative that inhibits the growth of microorganisms that could destroy alcohol.
What can happen if blood is not properly preserved after removal from living individuals?
There may be a decline in the blood alcohol level.
What phenomenon can occur in decedents regarding blood alcohol levels?
Alcohol may be produced during decomposition, leading to an elevated blood alcohol level.
What do per se laws regarding blood alcohol concentration state?
Any individual with a defined blood alcohol concentration (typically 0.08%) is deemed intoxicated.
How much more likely is a driver to be involved in an accident at a blood alcohol level of 0.08%?
Four times more likely.
What does the implied consent law require from individuals operating a motor vehicle?
They must consent to a test for alcohol intoxication or lose their license for a designated period.
What was the ruling in Schmerber v. California (1966) regarding blood samples?
The Supreme Court ruled that taking blood samples was not protected by the Fifth Amendment.
What did the Supreme Court decide in Missouri v. McNeely (2013) regarding blood tests?
Police must obtain a search warrant prior to drawing a person's blood for alcohol testing.
What is the primary responsibility of a toxicologist?
To detect and identify the presence of drugs and poisons in body fluids, tissues, and organs.
What challenges do toxicologists face when analyzing body fluids?
They must deal with a variety of drugs and poisons, often without supportive evidence.
Why is the analysis of drugs in the body more complex than in powders and pills?
Drugs consumed are dissipated and distributed throughout the body, complicating detection.
What happens to many substances in the body that complicates toxicology analysis?
Many substances are chemically changed or metabolized into different chemical substances.
What percentage of drugs encountered in toxicology laboratories are typically accounted for by alcohol, marijuana, and cocaine?
90% or more.
What defines an acid in terms of hydrogen ions?
An acid is capable of donating a hydrogen ion.
What defines a base in terms of hydrogen ions?
A base is capable of accepting a hydrogen ion.
How is acidity and basicity measured?
By the pH scale.
How can a toxicologist control the type of drug that is recovered from a solution?
By controlling the pH of the water solution into which blood, urine, or tissues are dissolved.
What is the significance of controlling pH in toxicology?
It provides a general technique for extracting and categorizing drugs.
What is the two-step approach used in toxicology for identifying drugs?
Screening and Confirmation.
What is the purpose of screening tests in toxicology?
To provide quick insight into the likelihood that a specimen contains a drug substance.
What are the most widely used screening tests in toxicology?
Gas chromatography (GC) and immunoassay.
What is the confirmation test of choice in toxicology?
Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS).
How does gas chromatography/mass spectrometry work in toxicology?
GC separates the sample into its components, while MS provides a unique fingerprint pattern for identification.
What specimen is typically tested for drug content in living individuals?
Blood.
What alternative specimen is becoming common for drug testing in workplaces?
Urine.
How do drugs become trapped in hair?
Drugs in blood diffuse through capillary walls into the hair base and become trapped in the hair's protein structure.
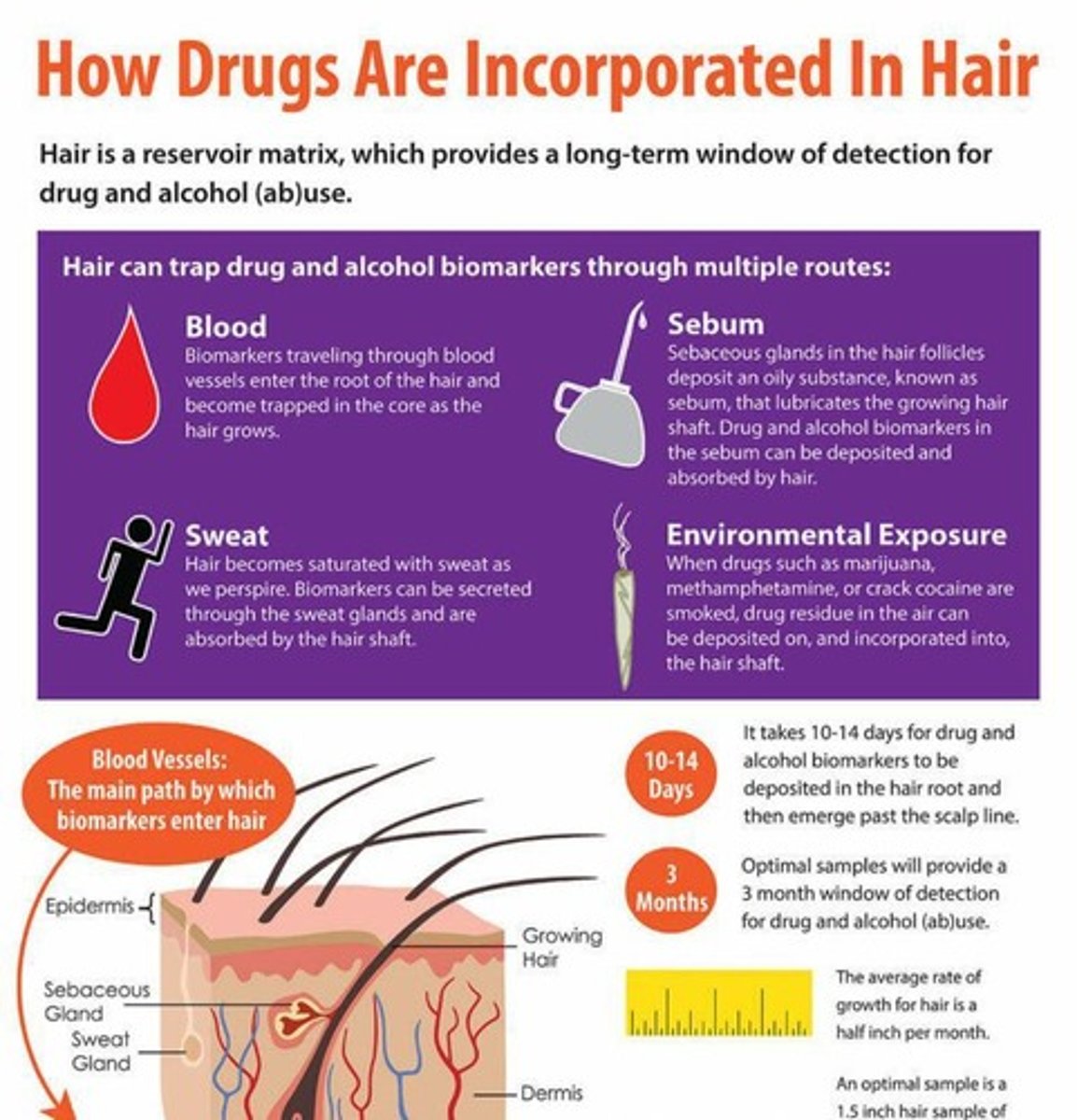
What is the average growth rate of human hair?
Approximately 1 cm per month.
What types of nondrug poisons may be encountered in toxicology?
Heavy metals like arsenic, bismuth, antimony, mercury, thallium, and carbon monoxide.
What is the fatal blood saturation level of carbon monoxide in a healthy individual?
Greater than 50-60%.

What factors must be considered when evaluating drug-induced behavior?
Age, health, and tolerance.