ALEVEL BIOLOGY- Biodiversity
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Biodiversity
The variety of living organisms in an ecosystem
Importance of Biodiversity
Essential to maintain a balanced ecosystem
Species are interconnected
We rely on ecosystem for survival (yet human activity can lead to reduction in biodiversity)
Ecosystem
The area inhabited by a species. It includes physical/non-living (abiotic) factors as well as living (biotic) factors.
Niche
The role of the organism in its environment, both the physical and environmental conditions it requires (like temperature or terrain) and the interactions it has with other species (like predation or competition)
Community
A group or association of populations of two or more different species occupying the same geographical area at the same time.
Habitat
An environment where an organism lives. It contains all an animal needs to survive such as food and shelter
Habitat Biodiversity
The number of different habitats found within an area e.g. coastal area might contain sand dunes, mudflats, beaches and salt marshes
Species Biodiversity
Not just the number of different species. Includes number of individual and how many places they are found in.
Takes into account species richness and species evenness.
E.g. -Wild Meadow – lots of plants per metre2
-Lawn – may have lots but dominated by one main spp.
Genetic Biodiversity
Variety of genes that make up a species.
e.g. dog breeds
Species richness
The number of different species living in a particular area.
Species Eveness
The degree to which the species are represented.
Estimating Species Evenness- Plants
•Appropriate sampling method
•Count number of plants per unit area
•Percentage cover
•Direct count possible if larger plants
Estimating Species Evenness- Animals
•Direct count for larger animals
•Mark-release-recapture for smaller animals
•Sample-sift-count soil organisms
•Netting for aquatic organisms
Sample
A limited number of things, such as a group of 100 people or 50 pebbles on a beach.
Population
The total number of organisms within a certain habitat at a certain time.
Representative
How closely the relevant characteristics of the sample match the characteristics of the population.
Bias
An inclination or prejudice towards or against a specific finding or outcome.
Individuals
Individuals samples may not be representative of the population.
Sampling
Select a sample which is representative of the population or to estimate the number of organisms in an area.
Types of Sampling
Random
Non-random
Opportunistic
Stratified
Systematic
Random Sampling
Sampling where each individual in the population has an equal likelihood of selection
How?
Mark out a grid across your area.
Use a random number generator to determine your x and y coordinates,
Take a sample at each coordinate.
Non-random sampling
An alternative sampling method to random sampling, where the sample is not chosen at random. It can be opportunistic, stratified or systematic.
Opportunistic Sampling
Sampling using the organisms that are conveniently available.
The weakest form of sampling as it may not be representative of the population.
Stratified Sampling
Sampling where populations are divided into sub-groups (strata) based on a particular characteristic.
A random sample is then taken from each of these strata proportional to their size.
Systematic Sampling
Different areas of a habitat are identified and sampled separately.
Often carried out using a line or belt transect.
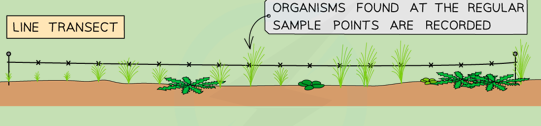
Line Transect
A tape or string is laid along the ground in a straight line between two poles. Sampling is rigorously confined to organisms that are touching the line.
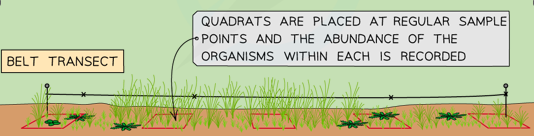
Belt Transect
Similar to the line transect method but a quadrat is laid down along the string and species populations are monitored. This gives information on abundance as well as presence, or absence of species.
How to avoid sampling bias?
Random Sampling
How to avoid selecting organism by chance?
Increasing sample size
Animal Sampling Technique
Pitfall Trap
Pooters
Kick Sampling
Sweep Nets
Tullgren Funnel
Sweep Nets
Large, strong nets with a fine material are used to catch flying insects and insects that live in the long grass.
How? Sweep the net back and forth through the grass
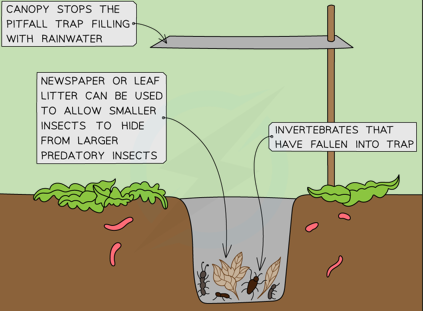
Pitfall Trap
Container buried into the ground used to catch ground-dwelling insects and other invertebrates as they fall into the trap
Pooters
Small containers with two tubes sticking out that are used to suck up small insects and other small invertebrates,

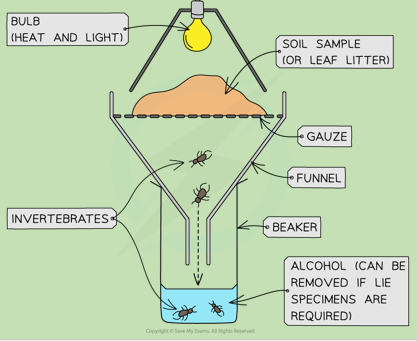
Tullgren Funnel
Funnel with a lightbulb above and a container below that collects invertebrates that live in leaf litter or soil.
How? Leaf litter/soil is placed in the funnel and the light and heat forces the invertebrates to move down until they drop into the container.
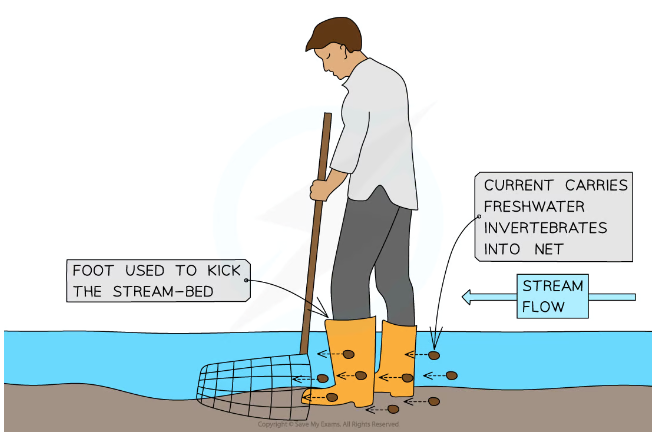
Kick Sampling
Used to catch freshwater invertebrates living in streams or rivers. The net is placed in the stream-bed and water flows into it. Invertebrates are carried by the stream into the net.
Mark-Release Recapture
For a single species in the area:
1) The first large sample is taken. As many individuals as possible are caught, counted and marked in a way that won’t affect their survival e.g. if studying a species of beetle, a small amount of brightly coloured non-toxic paint can be applied to their carapace (shell)
2) The marked individuals are returned to their habitat and allowed to randomly mix with the rest of the population
3) When a sufficient amount of time has passed another large sample is captured
4) The number of marked and unmarked individuals within the sample are counted
5) The proportion of marked to unmarked individuals is used to calculate an estimate of the population size
Formula for Mark-Release-Recapture
N = (n1 × n2) ÷ m2
Where:
N = population estimate
n1 = number of marked individuals released
n2 = number of individuals in the second sample (marked and unmarked)
m2 = number of marked individuals in the second sample
Quadrats
Suitable for plants or slow-moving animals. They can be different sizes and can be laid onto the ground where you can measure the abundance or percentage cover of species present.
3 ways of describing the amount of each species within a frame quadrat:
Density
Percentage cover
Frequency
Density
Count the number of individual plants. This is an absolute measure, not an estimate.
Percentage Cover
Use the small square within the grid, count the number of squares the particular species is in.
Frequency
It is an estimate by eye of the areas a particular species covers.
Simpsons index
àUsed to quantify the biodiversity of an area.
n = number of individuals of a particular species (or % cover)
N = the total number of all individuals of all species
Σ means ‘sum of’
A value between 0 and 1 is calculated
– a value nearer 1 demonstrates greatest diversity.
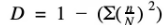
Why is Simpson’s Index a better indicator of biodiversity than richness or evenness alone?
Takes into account both (number of difference species (richness) / how many of each: evenness), instead of one but not the other.
Genetic Biodiversity
Variety of genes that make up a species
Gene pool
Different versions of genes- alleles
more alleles= more genetically biodiversity
e.g. different dog breeds
Importance of genetic biodiversity
Greater biodiversity → more likely to adapt to changes in environment → less likely to become extinct
More likely some organisms will carry advantageous alleles enabling them to survive and reproduce.
Gene pool
A gene pool is made up of all the genes and their different alleles present in an interbreeding population.
Different factors affect changes in allele frequency leading to evolution of a population.
Genetic Diversity
Found where there is more than one allele for a particular locus.
This leads to greater variation and greater genetic differences between gametes
Allele/ Genetic Variant
A version of a gene.
Locus
the position of that gene on a chromosome
Polymorphic Gene Locus
a locus that has more than 2 alleles
Factors that increase Genetic Biodiversity
Mutations
New allele
More alleles = increase biodiversity
Interbreeding
Mixing populations which then breed with each other
Transfer of alleles
Known as ‘gene flow’
Factors that decrease Genetic Biodiversity
Selective breeding
‘artificial selection’
Select individuals based on characteristics and breed them together.
E.g. pedigree
Captive breeding programmes
Small number of captive individuals of a spp. Available for breeding.
Rare breeds
A particular breed of animal or plant with characteristic becomes less popular, only a small number of individuals remain/ are available for breeding.
As a result of selective breeding
Artificial cloning
Asexual reproduction
Natural selection
Alleles with less advantageous characteristics will decrease over time
Genetic bottlenecks
An event (e.g. drought, disease) reduces gene pool
Only alleles of surviving individuals are available to reproduce to produce offspring
Founder effect
Small number of individuals create a new colony which is geographically separate from og. population
New population will have a small gene pool
Genetic drift
Random passing off alleles to offspring → frequency of allele occurrence will vary, could lead to complete eradication
Measuring genetic biodiversity
Proportion of polymorphic gene loci = num, of polymorphic gene loci/ total number of loci
Human activities affecting biodiversity
Habitat destruction
Pollution
Climate change
Over harvesting
Killing for protection
Killing to remove competitors
Introducing non-indigenous species
Human Population Growth
Increasing at a dramatic rate
To support increasing populations, these main problems occur:
Deforestation
Agriculture
Climate Change
Deforestation
Directly reduces the no. of tress in an area, if only one tree is felled, species diversity decreases
reduces animal species in an area, animals are forced to migrate to other areas, increasing biodiversity in that area
Agriculture
Selective breeding → removing additional alleles → reducing biodiversity
Monoculture → farms specialising in the production of of only one crop → decreases biodiversity
Few animals will be supported by just one species of plant
Achieved through intensive farming
Use of pesticides and herbicides → directly and indirectly reduces biodiversity (indirectly, removing food source)
Climate Change
Less genetic biodiverse pops. able to cope with change
So, populations move to follow climate that suit them, here they may have limited food and it may not be ideal conditions
Migrations of populations, communities and ecosystems can be obstructed by major human development and geographically challenges e.g. mountains, great bodies of water
Reasons to maintain Biodiversity
Aesthetic
protecting a beautiful environment for people to live in
Ecological
Protecting keystone species
Interdependence- species depend on each other for survival
Maintaining genetic resource
Economic
less ££ on conservation
natural resources have a range of uses (e.g. medicine)
promotion of tourism
Conservation and e.g.
Active human management of an ecosystem to maintain biodiversity
E.g. replanting trees, culling deer, burning heathland
Preservation and e.g.
Protecting an area by restricting/ banning human interference to maintain ecosystem in its original state
E.g. fenced off areas, marine conservation zones, banning access to newly found caves
Extinct defintion
No organisms exist anywhere in the world
Extinct in wild
Organisms only exist in captivity
Endangered
Organism in danger of extinction
Vulnerable
A species that is considered likely to become endangered in the near future
In Situ Conservation and e.g
Conserving species in their natural habitat. Also maintains evolutionary adaptions and interactions with other species e.g.
Legislation
National parks
Sites of Special Scientific Interest- some of the best wildlife and geological sites In UK
Marine conservation zones
Ex Situ Conservation
Conserving species outside their natural habitat
E.g
Storing genetic material
Sperm freezing
Artificial insemination
IVF + embryo transfer
Botanic gardens
Seed banks
Storage allows repopulation, can be used in natural disasters