AP Environmental Science UNIT 3
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area
environment complex level
individuals populations communities ecosystems and biospheres
Community
All the different populations that live together in an area
population size
the total number of individuals within a defined area at a given time
population density
the number of individuals per unit area at a given time
population distribution
a description of how individuals are distributed with respect to one another
Population sex ratio (PSR)
the ratio of males to females in a population
population age structure
a description of how many individuals fit into particular age categories
density dependent factors
limiting factor that depends on population size
limiting resource
a resource that a population cannot live without and that occurs in quantities lower than the population would require to increase in size (water, food supply, nest sites...)
carrying capacity (K)
the limit of how many individuals in a population the environment can sustain
density-independent factor
limiting factor that affects all populations in similar ways, regardless of population size
population growth rate
the number of offspring an individual can produce in a given time period, minus the deaths of the individual or its offspring during the same period
intrinsic growth rate
the maximum potential for growth of a population under ideal conditions with unlimited resources
exponential growth model (Nt=N0e^rt)
a growth model that estimates a population's future size (Nt) after a period of time (t), based on the intrinsic growth rate (r) and the number of reproducing individuals currently in the population (N0)
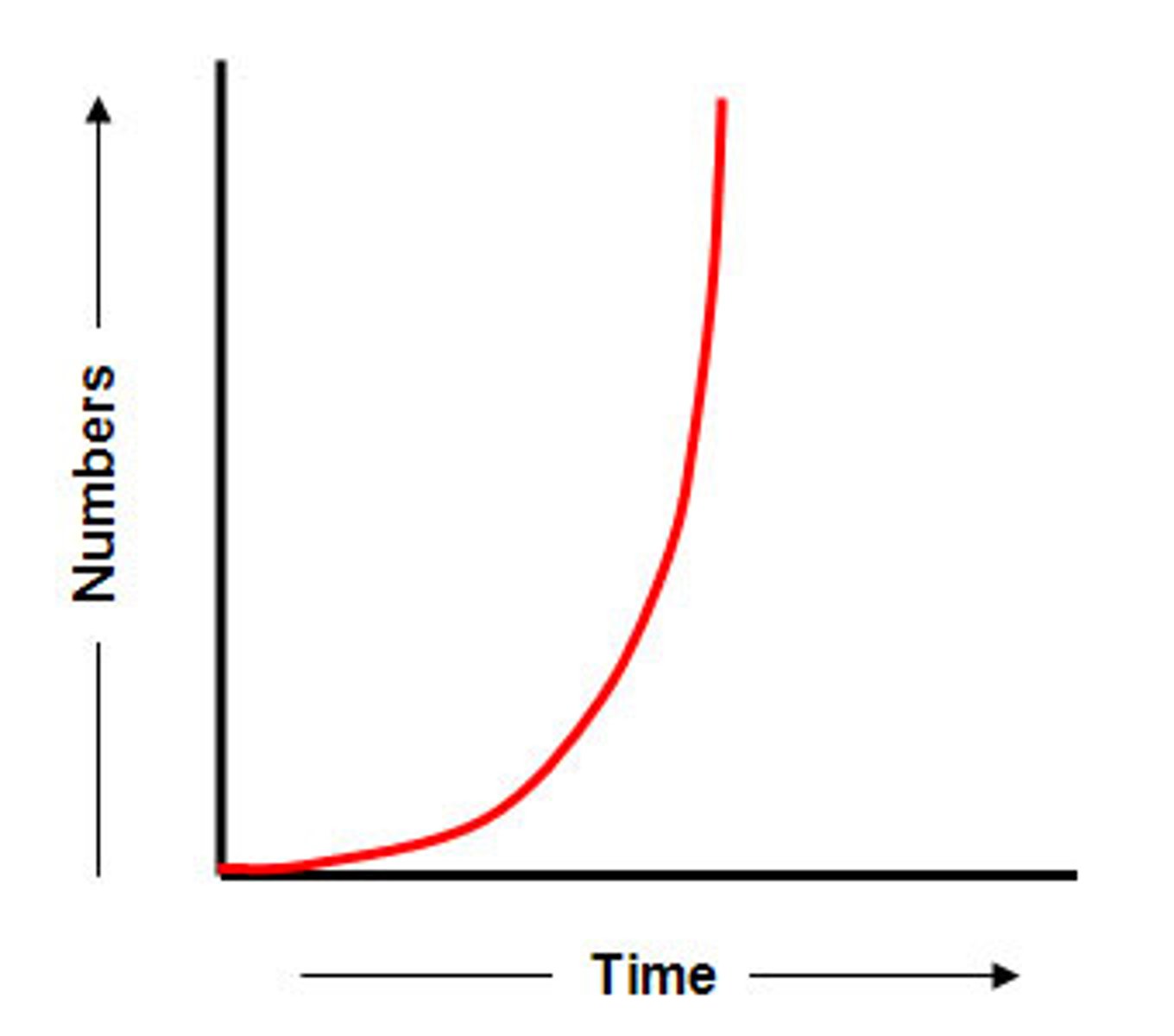
J-shaped curve
the curve of the exponential growth model when graphed
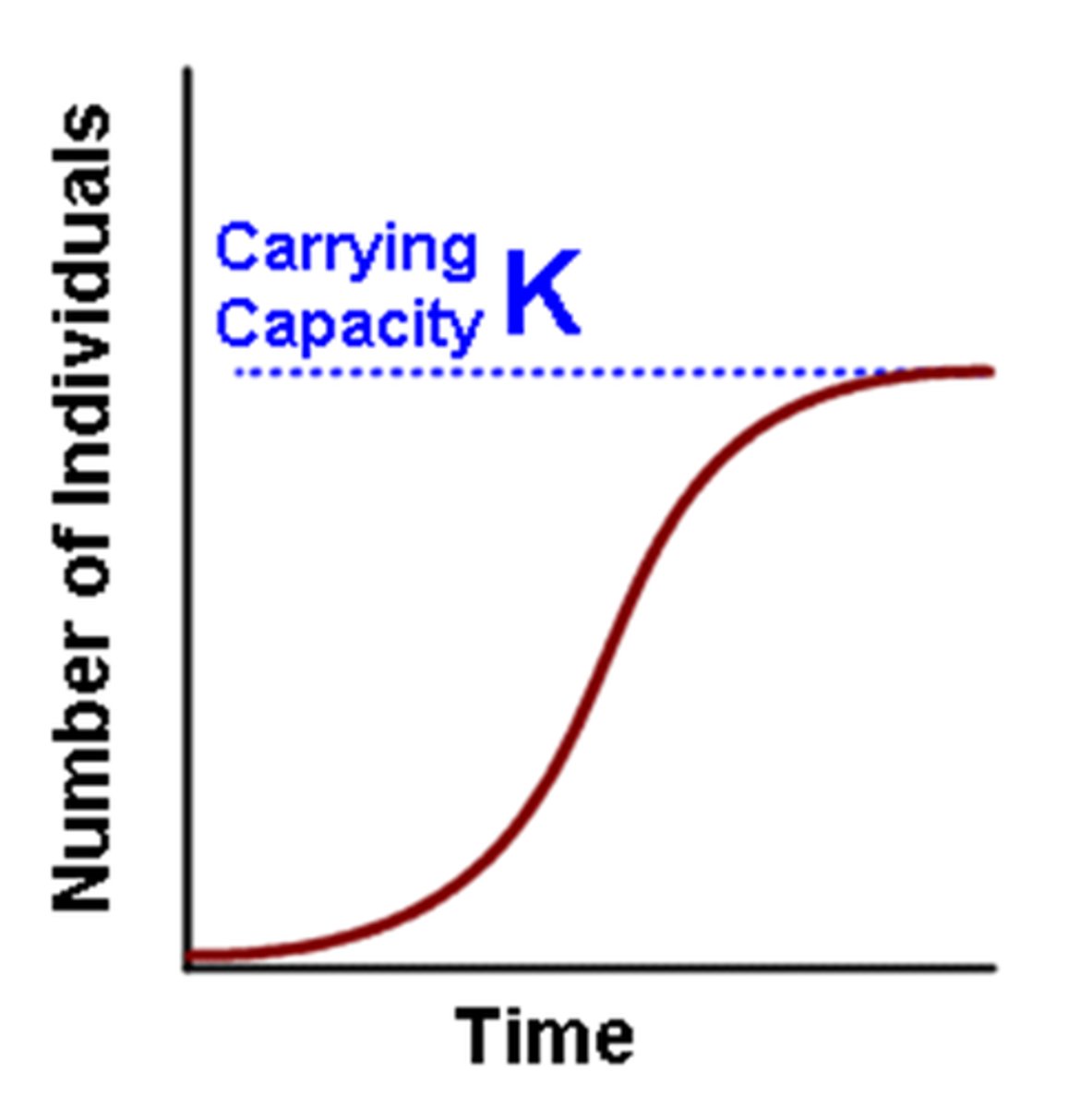
logistic growth model
a growth model that describes a population whose growth is initially exponential, but slows as the population approaches the carrying capacity of the environment
S-shaped curve
the shape of the logistic growth model when graphed
Overshoot
when a population becomes larger than the environment's carrying capacity
die-off
a rapid decline in a population due to death
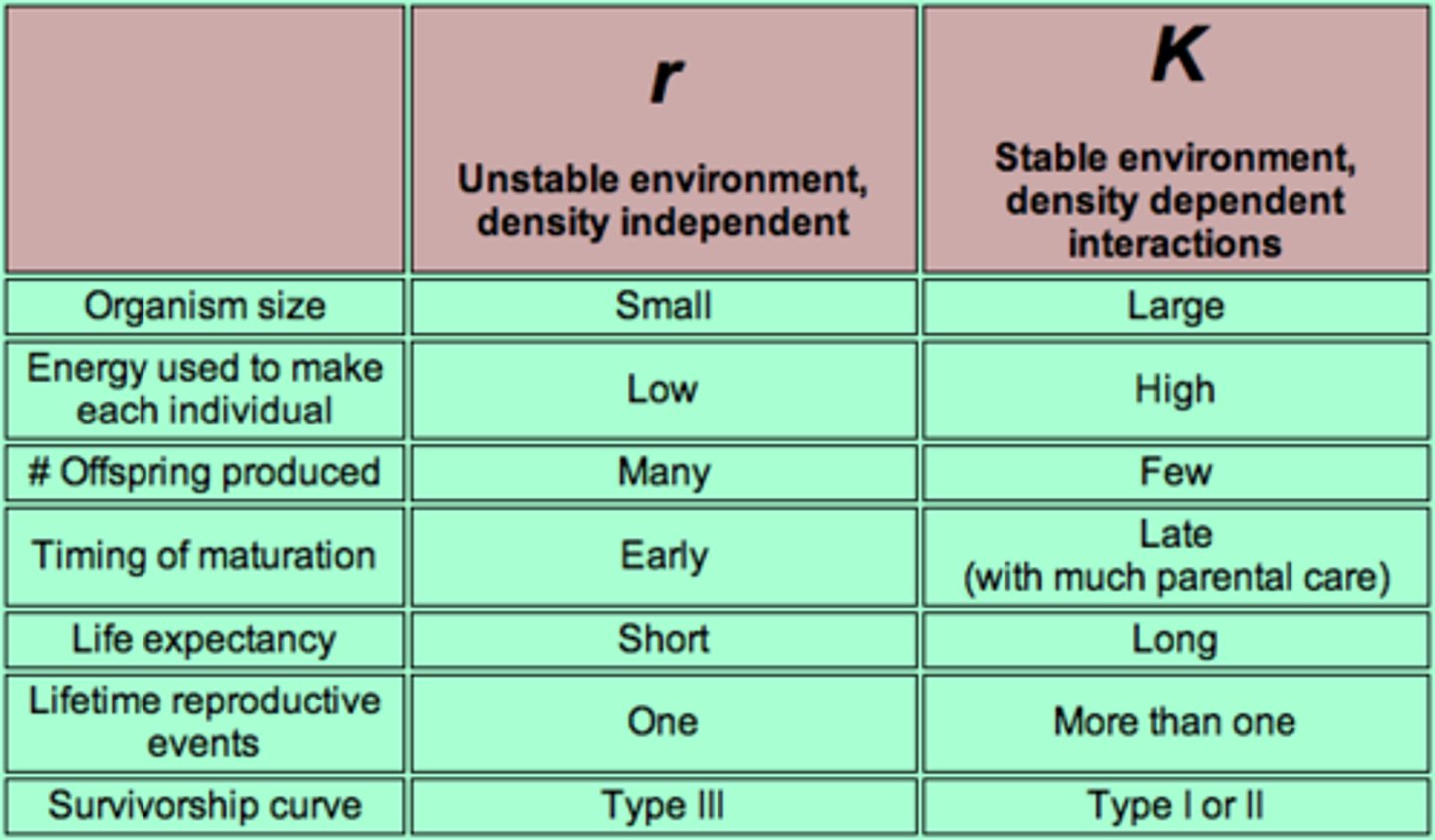
K-selected species
a species with a low intrinsic growth rate that causes the population to increase slowly until it reaches carrying capacity
r-selected species
a species that has a high intrinsic growth rate, which often leads to population overshoots and die-offs
Traits of K-selected and R-selected species
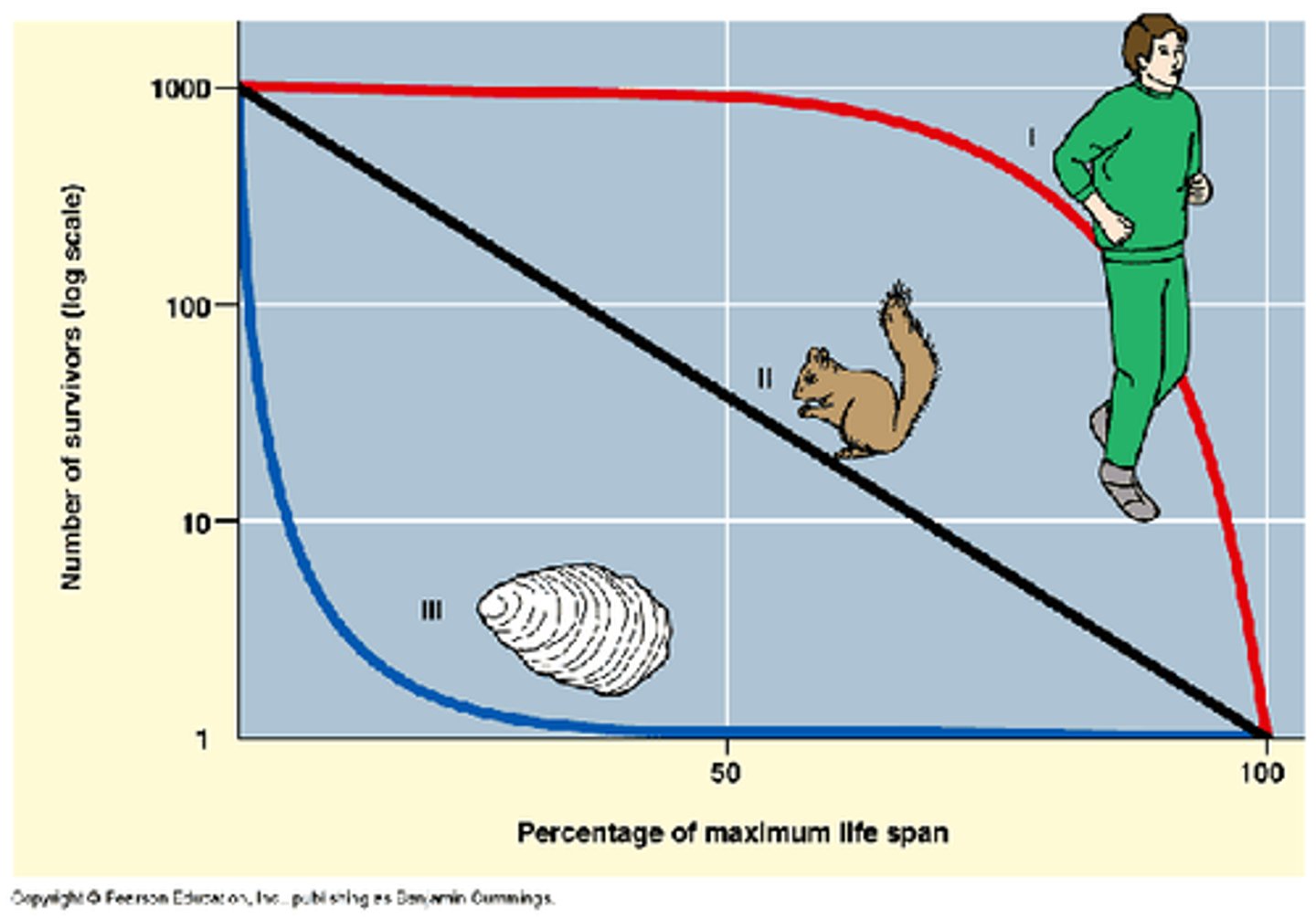
survivorship curve
a graph that represents the distinct patterns of species survival as a function of age
corridor
strips of natural habitat that connect populations
inbreeding depression
when individuals with similar genotypes - typically relatives - breed with each other and produce offspring that have an impaired ability to survive and reproduce
community ecology
The study of how interactions between species affect community structure and organization
symbiotic relationship
The relationship between two species that live in close association with each other
competition
the struggle between organisms to survive in a habitat with limited resources
competitive exclusion principle
no two species can occupy the same niche in the same habitat at the same time
resource partitioning
when two species divide a resource based on differences in their behavior or morphology (temporal resource partitioning; spatial resource partitioning; morphological resource paritioning )
Predation
An interaction in which one organism kills another for food.
parasitism
A relationship in which one organism lives on or in a host and harms it.
Pathogen
an organismthat causes disease in its host
Demography
The scientific study of population characteristics.
Immigration
the movement of people into one country from another for the purpose of settlement
Emigration
movement of individuals out of an area
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
The total number of deaths in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
doubling time
the time required for a population to double in size
the rule of 70
to find doubling time of pop, divide 70 by the percent of growth
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
The average number of children a woman will have throughout her childbearing years.
Replacement level fertility
the total fertility rate required to offset the average number of deaths in a population in order to maintain the current population size
developed country
a country with relatively high levels of industrialization and income
developing country
a country with relatively low levels of industrialization and income
life expectancy
The average number of years an individual can be expected to live, given current social, economic, and medical conditions.
infant mortality
the number of deaths of children under 1 year of age per 1000 live birth
child mortality
the number of deaths of children under age 5 per 1,000 live births
Age-structure diagram
a visual representation of the number of individuals within specific age groups for a country, typically expressed for males and females
Population Pyramid
an age structure diagram that is widest at the bottom and smallest at the top, typical of developing countries
population momentum
continued population growth that does not slow in response to growth reduction measures
theory of demographic transition
the theory that as a country moves from a subsistence economy to industrialization and increased affluence it undergoes a predictable shift in population growth
family planning
the practice of regulating the number or spacing of offspring through the use of birth control
Affluence
wealth
IPAT equation
Impact = Population x Affluence x Technology
urban area
an area that contains more than 385 people per square kilometer (1,000 people per square mile)