Macroeconomic Fluctuations and Fiscal Policy: Key Concepts and Effects
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
What is the average annual growth rate of Real GDP in the United States over the past 65 years?
About 3.1% per year.
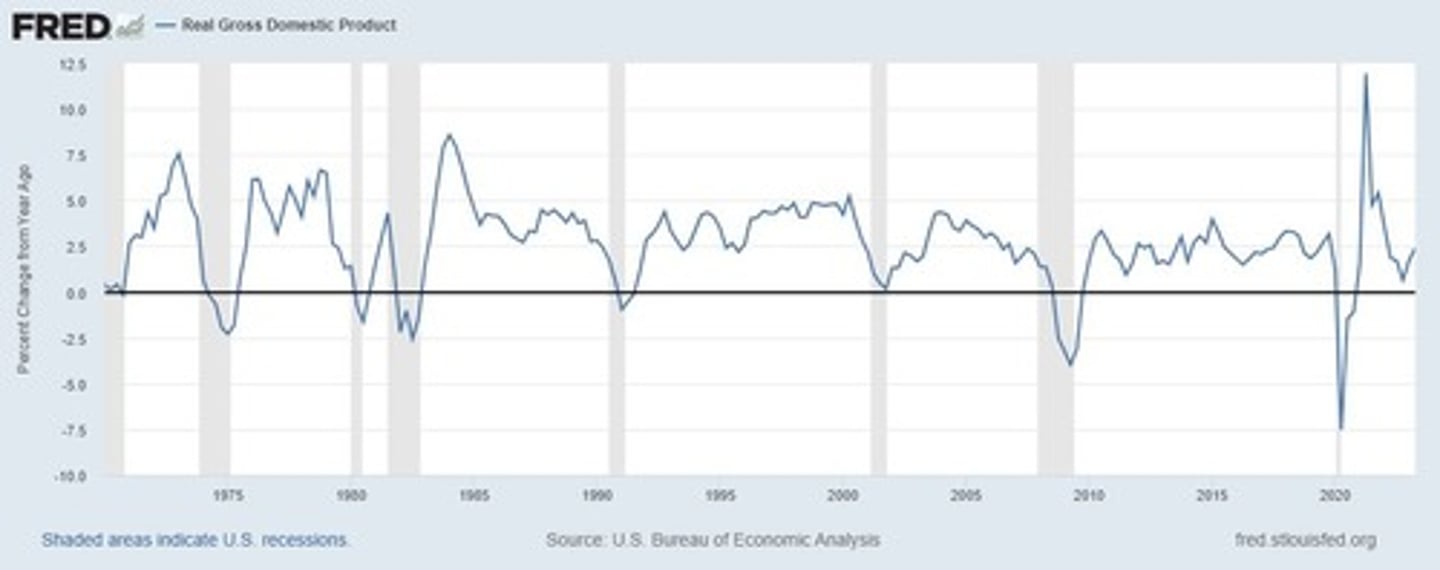
What do we call the fluctuations of real GDP around its long-term trend?
Business fluctuations or business cycles.
What defines a recession according to the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER)?
A significant decline in economic activity lasting more than a few months, affecting GDP, employment, industrial production, and consumer spending.

When does a recession officially begin and end?
It begins at the peak of economic activity and ends at the trough.
How long do recessions typically last?
About one to two years.
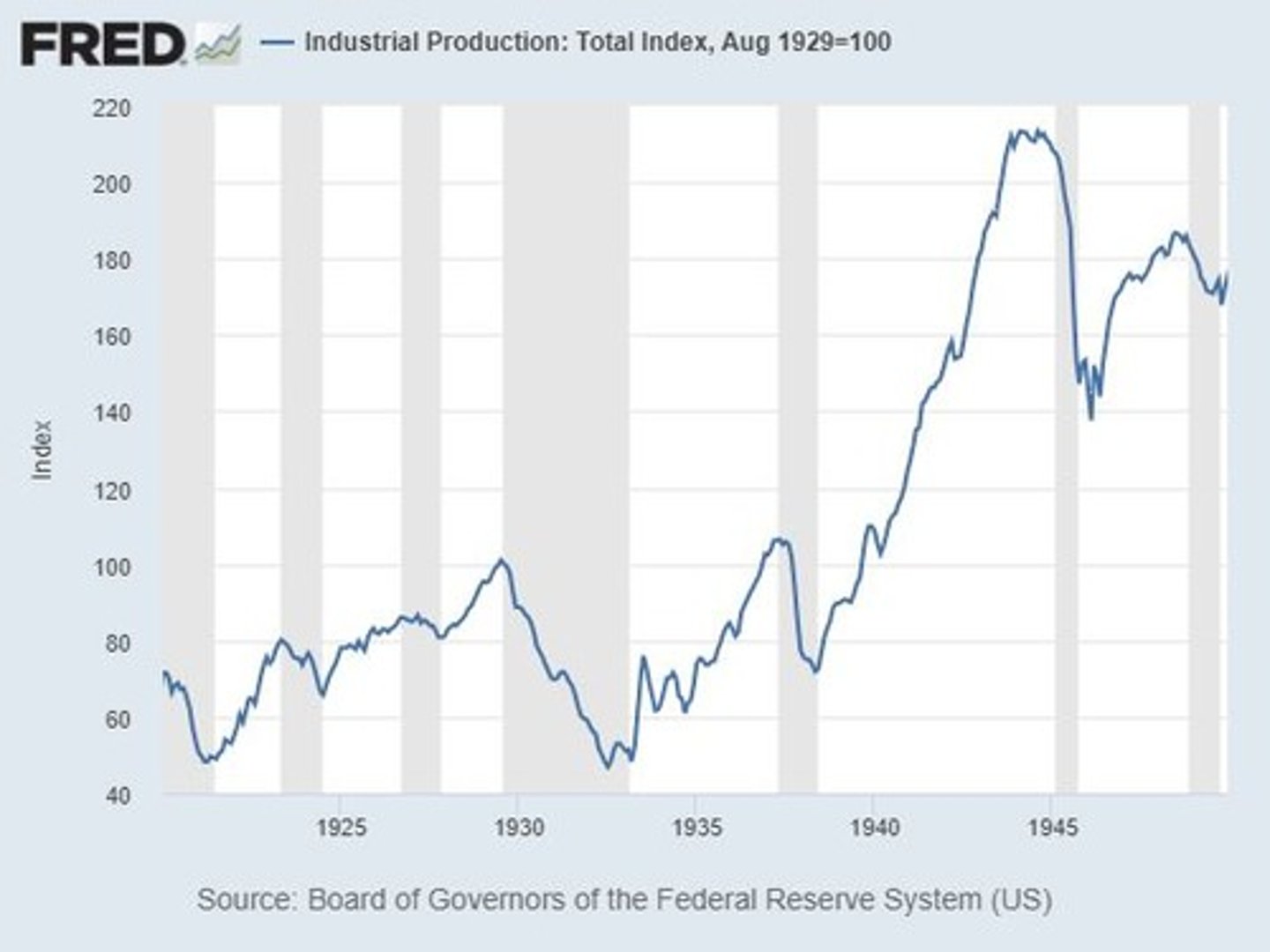
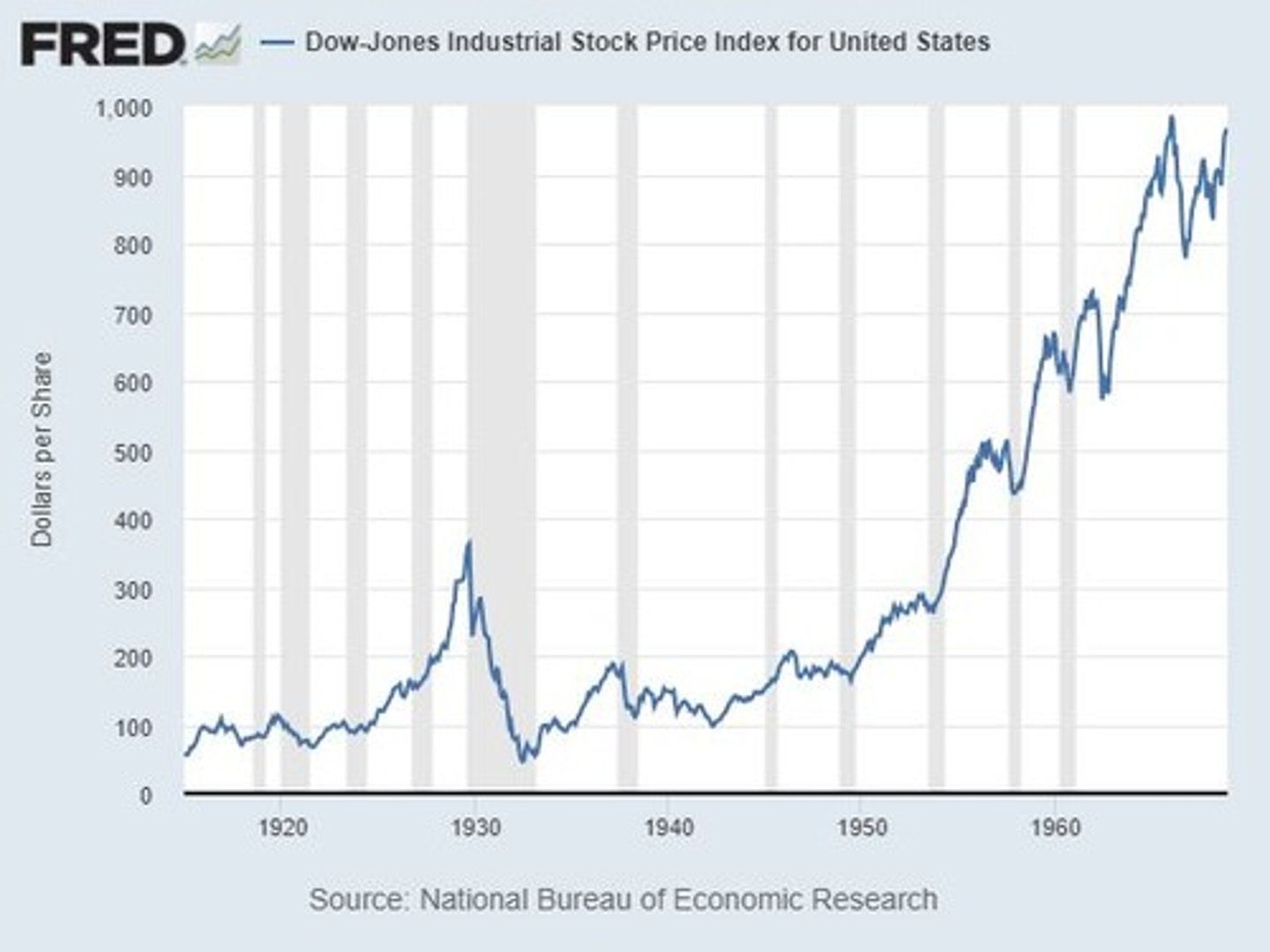
What was the percentage drop in U.S. real GDP from 1929 to 1933 during the Great Depression?
31%.
What was the unemployment rate in the U.S. by 1933 during the Great Depression?
25%.
What significant economic event occurred in October 1929?
The stock market crash.
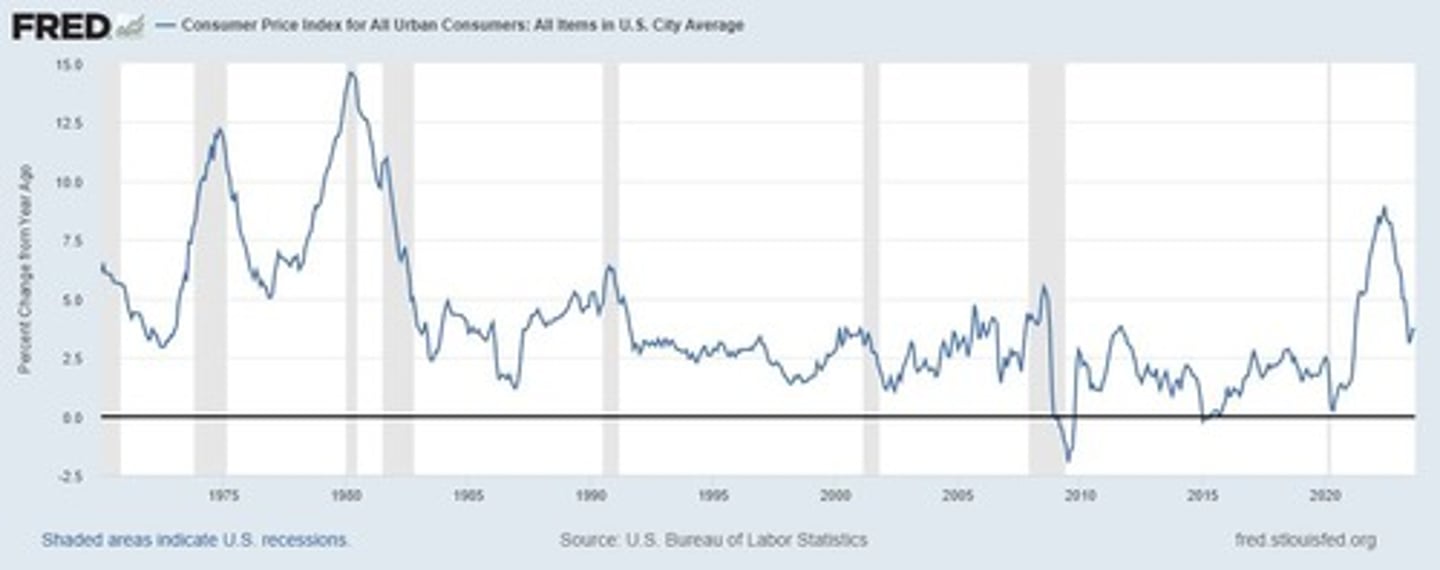
What was the inflation rate between 1929 and 1933?
-10% every year.
What happened to approximately 40% of U.S. banks between 1929 and 1933?
They went bankrupt.
What major government program did FDR implement in 1936 to stimulate aggregate demand?
The New Deal.
What role did World War II play in the U.S. economy?
It created a vast economic stimulus through expanded government spending.
What is the relationship between aggregate demand and recessions?
Aggregate demand shocks can lead to recessions.
What is one of the goals of economic thinking regarding booms and recessions?
To understand their causes and how policy might help smooth out fluctuations.
What was one of the worst direct consequences of the Great Depression?
Widespread unemployment and human suffering.
What economic phenomenon characterized the 1920s in the U.S.?
A boom in mass consumer goods and relaxed lending standards.
What is the critical role of financial intermediation in the economy?
Banks intermediate saving and investment and solve information asymmetry problems between borrowers and lenders.
What is the Quantity Theory of Money?
A theory that relates the money supply to price levels and inflation.
What does countercyclical government spending aim to do?
Manage aggregate demand during economic downturns.
What is the Taylor Rule?
A monetary policy rule that suggests how central banks should change interest rates in response to changes in economic conditions.
What is the significance of the Great Depression in economic history?
It was the most significant economic downturn in recent history, affecting global economies.

What is a key theme to be studied in the next blocks regarding macroeconomic cycles?
The interaction between money in the economy and inflation.
What was the impact of speculation and cheap credit on the stock market in the 1920s?
It led to a stock market bubble.
What are the aftereffects of recessions?
They can last for years even after the recession has ended.
Why is understanding the causes of recessions important for policymakers?
To limit the frequency and severity of recessions.
What economic conditions are typically present during a recession?
Increased unemployment and underutilization of resources.
What was the global GDP drop during the Great Depression?
Around 15% between 1929 and 1932.
What is fiscal policy?
Federal government policy on taxes, spending, and borrowing designed to influence business fluctuations.
Why can fiscal policy work during unemployment?
It can employ unemployed resources, potentially paying for itself.
What happens to GDP when the economy is at full employment and government spending increases?
The net effect on GDP will be approximately zero due to crowding out.
What is the multiplier effect?
The additional increase in spending caused by an increase in government spending.
How can government spending during a recession affect GDP?
It can add to GDP if it employs unemployed resources, potentially increasing GDP by more than the amount spent.
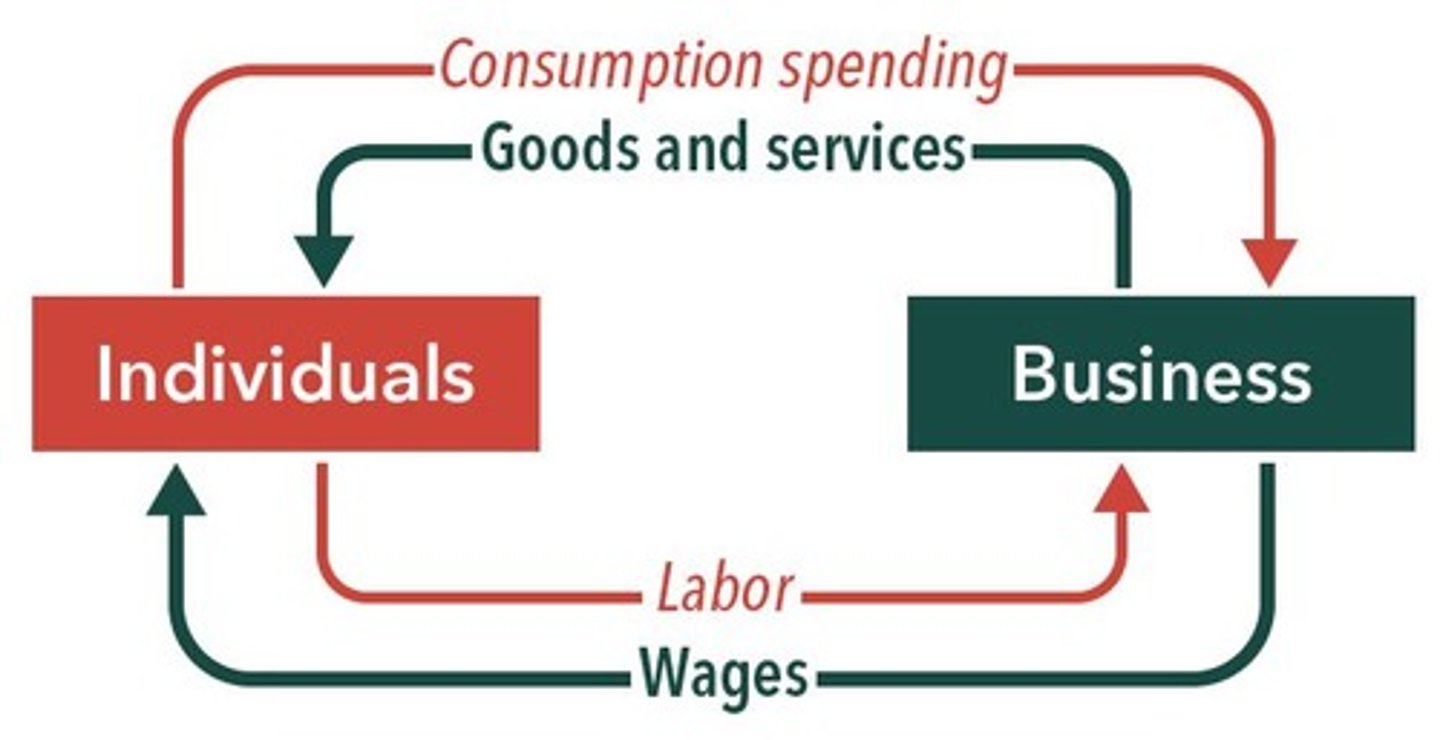
What is the relationship between consumption spending and business revenues?
Consumption spending by individuals is in exchange for goods and services provided by businesses, which in turn pay wages.
What occurs in the AS-AD model when consumers cut back on consumption?
The aggregate demand shifts leftward, leading to a recession.
What is the long-run effect in the AS-AD model after a recession?
Prices and wages become 'unstuck,' and the economy returns to its previous growth rate.
How can government stimulus help during a recession?
By increasing government spending to shift aggregate demand back to the right.
What factors influence the size of the spending multiplier?
The multiplier increases when spending uses unemployed resources effectively.
What are the advantages of welfare spending as a government stimulus?
It expands during recessions, targets the impoverished, and encourages immediate spending.
What is a potential downside of tax cuts during a recession?
People may choose to save their tax cuts rather than spend them, reducing immediate economic stimulus.
What is Ricardian Equivalence?
The theory that individuals may save tax cuts in anticipation of future tax increases.
What is the impact of crowding out during good economic times?
Increased government spending pulls resources from the private sector, limiting overall GDP growth.
What is the effect of government spending on GDP when many resources are unemployed?
Every dollar spent can add one dollar or more to GDP due to the multiplier effect.
How does the government stimulate the economy through lower taxes?
By encouraging private spending without needing to target specific economic sectors.
What is the role of consumption in the circular flow of the economy?
Consumption spending generates income for businesses, which then pay wages and invest in production.
What happens to the economy when fear affects consumer spending?
Real growth decreases due to sticky wages and prices, leading to a recession.
How does government spending during a recession affect consumer spending?
It can increase consumer spending by employing unemployed workers, leading to a positive multiplier effect.
What is the significance of the spending multiplier in fiscal policy debates?
It summarizes the balance between crowding out and the multiplier effect in determining fiscal policy effectiveness.
What is the impact of government spending on sectors other than construction?
If spending is less well-targeted, the multiplier effect may be smaller.
What is the relationship between government spending and the employment of resources?
Effective government spending employs unemployed resources, enhancing the multiplier effect.
What are the implications of a demand-driven recession in the AS-AD model?
It leads to decreased real growth and inflation as consumer spending declines.
What are the two means by which the government can finance its stimulus?
Increase taxes or borrow.
How do higher taxes affect private spending?
Higher taxes reduce the amount of money private individuals have to spend.
When is the multiplier for tax-financed spending likely to be bigger?
When the government can tax unproductive savings rather than consumption.
What effect does government borrowing have on interest rates?
It tends to increase interest rates, encouraging people to save more and spend less.
What are the conditions under which stimulus is most effective?
When there are unemployed resources, targeted spending on the unemployed, tax cuts for immediate spenders, taxing savings, and minimal crowding out of private investment.
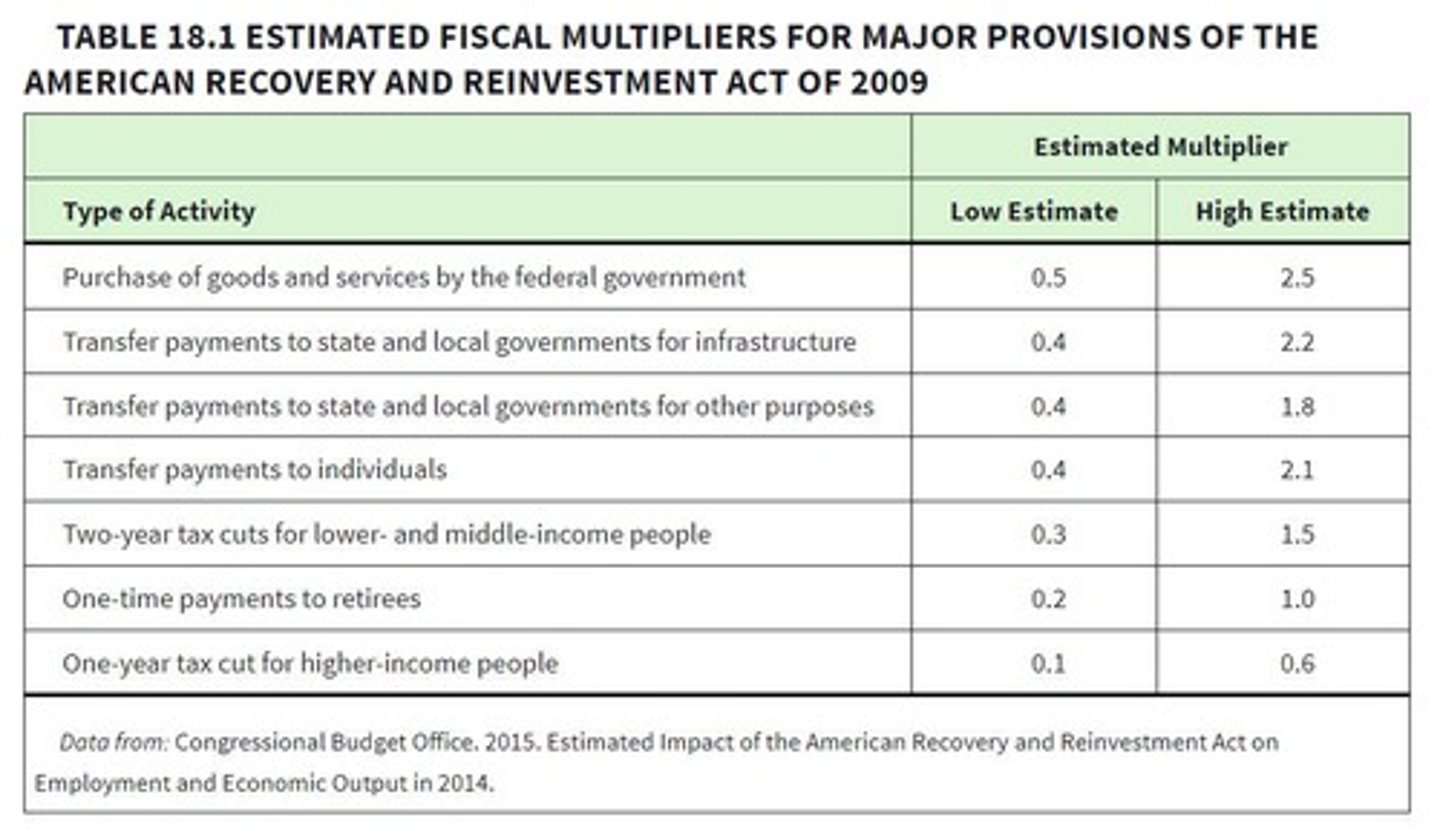
What was the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA)?
A stimulus provided by the government during the 2008-2009 recession.
What is a recognition lag in fiscal policy?
The time it takes to recognize that a problem exists.
What is a legislative lag?
The time it takes for Congress to propose and pass a fiscal policy plan.
What is an implementation lag?
The time it takes for bureaucracies to implement a fiscal policy plan.
What is an effectiveness lag?
The time it takes for a fiscal policy plan to have an impact on the economy.
What are automatic stabilizers in fiscal policy?
Changes in fiscal policy that stimulate aggregate demand during a recession without explicit action by policymakers.
How does unemployment insurance act as an automatic stabilizer?
Claims increase during recessions, helping maintain aggregate demand.
What happens to income and corporate taxes during a recession?
Wage incomes and profits decrease, leading to lower taxes.
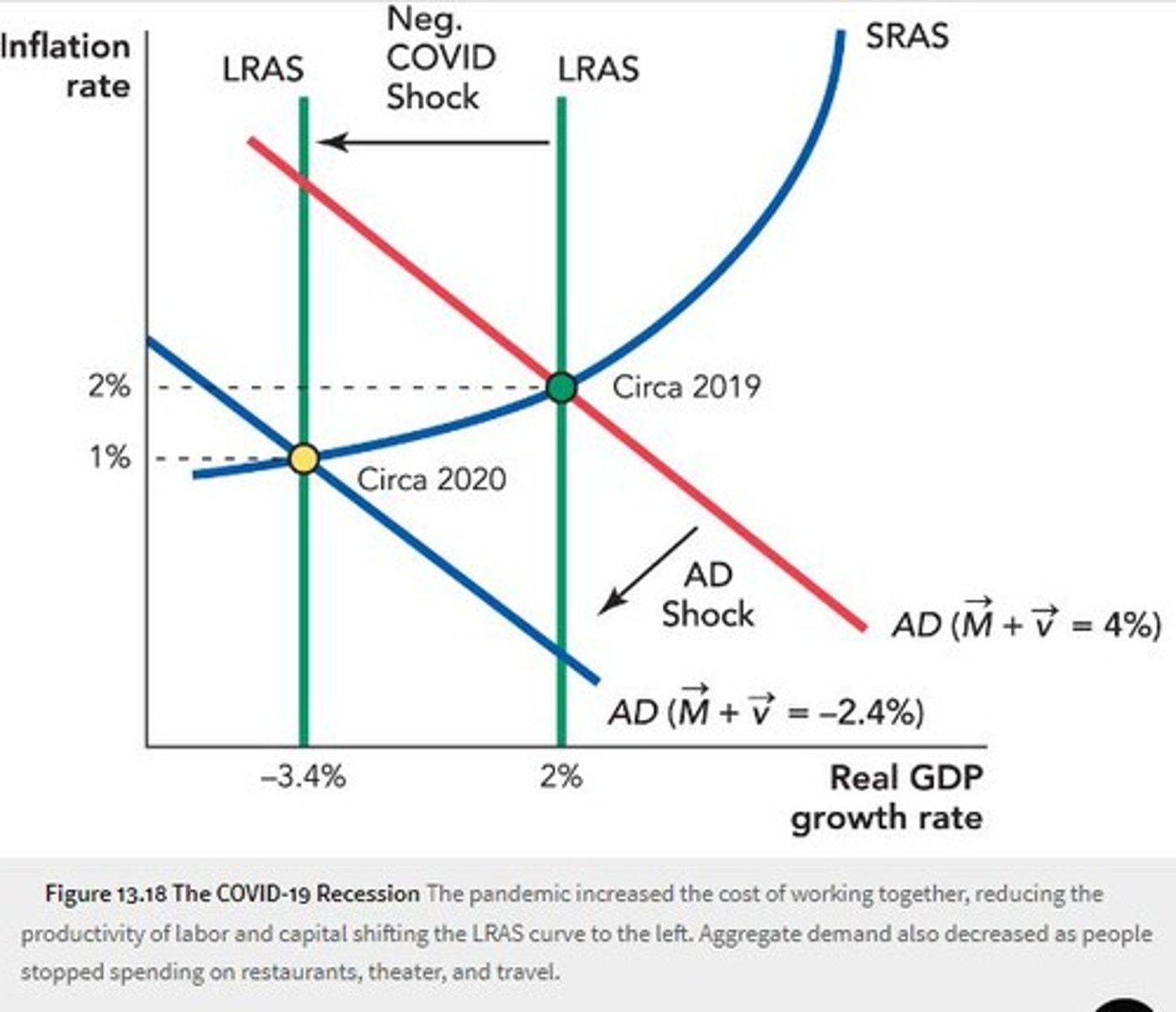
What are the two shocks that caused the COVID-19 recession?
A negative supply shock (decline in work productivity) and a negative demand shock (decrease in leisure activities).
What was the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on unemployment and GDP growth?
Unemployment shot up, output growth tanked, and inflation dropped.
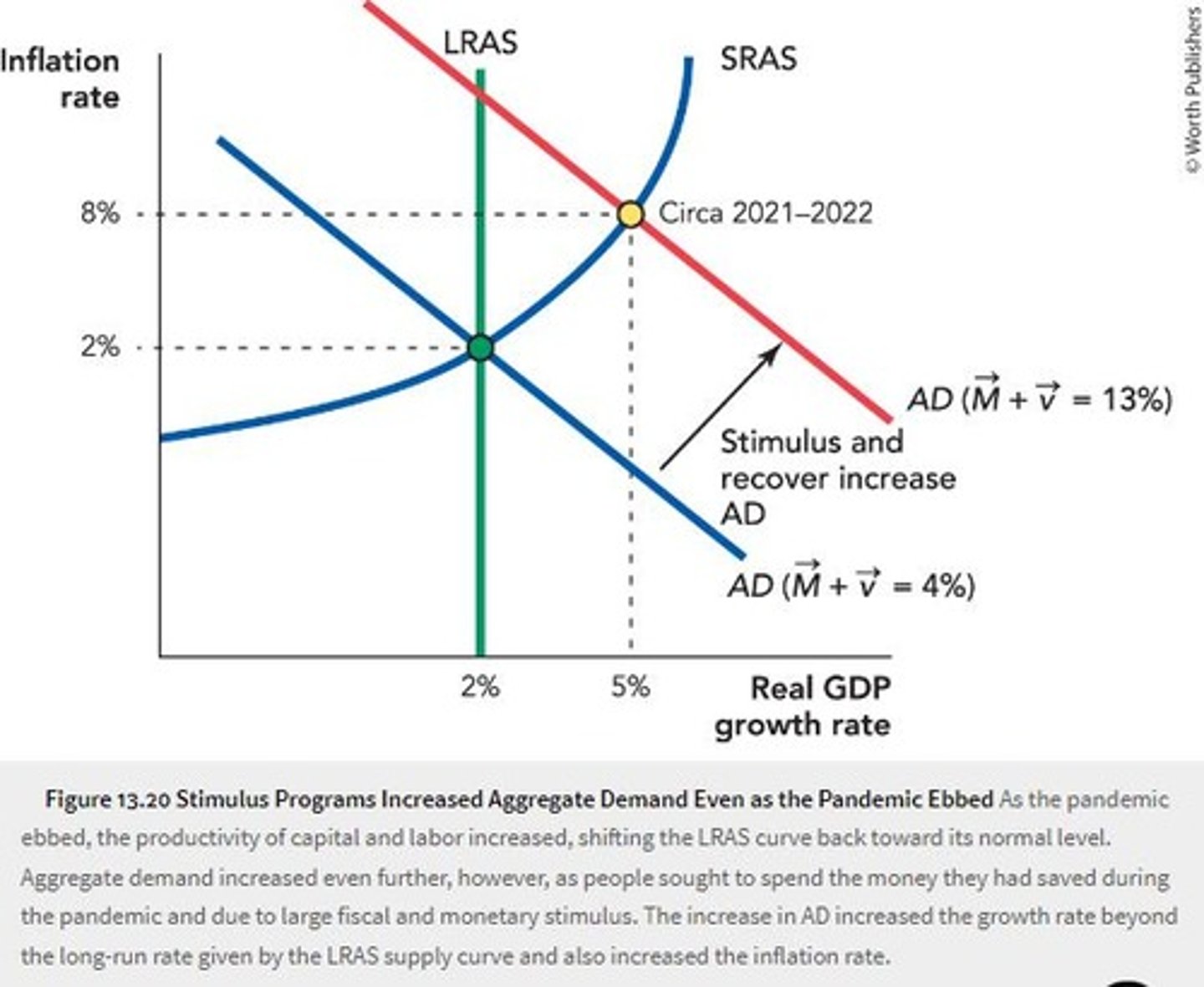
What characterized the recovery phase after the COVID-19 recession?
Most negative supply shocks were eliminated, leading to a return to usual productivity levels.
What led to the rightward shift of aggregate demand (AD) during the recovery?
Large relief programs and cash payments to individuals.
What was the impact of the combination of shifts in LRAS and AD during the recovery?
Increased real GDP growth and inflation.
What challenges did the economy face post-COVID recovery?
Negative inflationary shocks such as supply chain disruptions and rising oil prices.
What is the significance of a fiscal policy multiplier of 2?
For every dollar spent, GDP increases by two dollars.
When is fiscal policy considered ineffective?
When facing a real shock, as it cannot solve underlying inefficiencies.
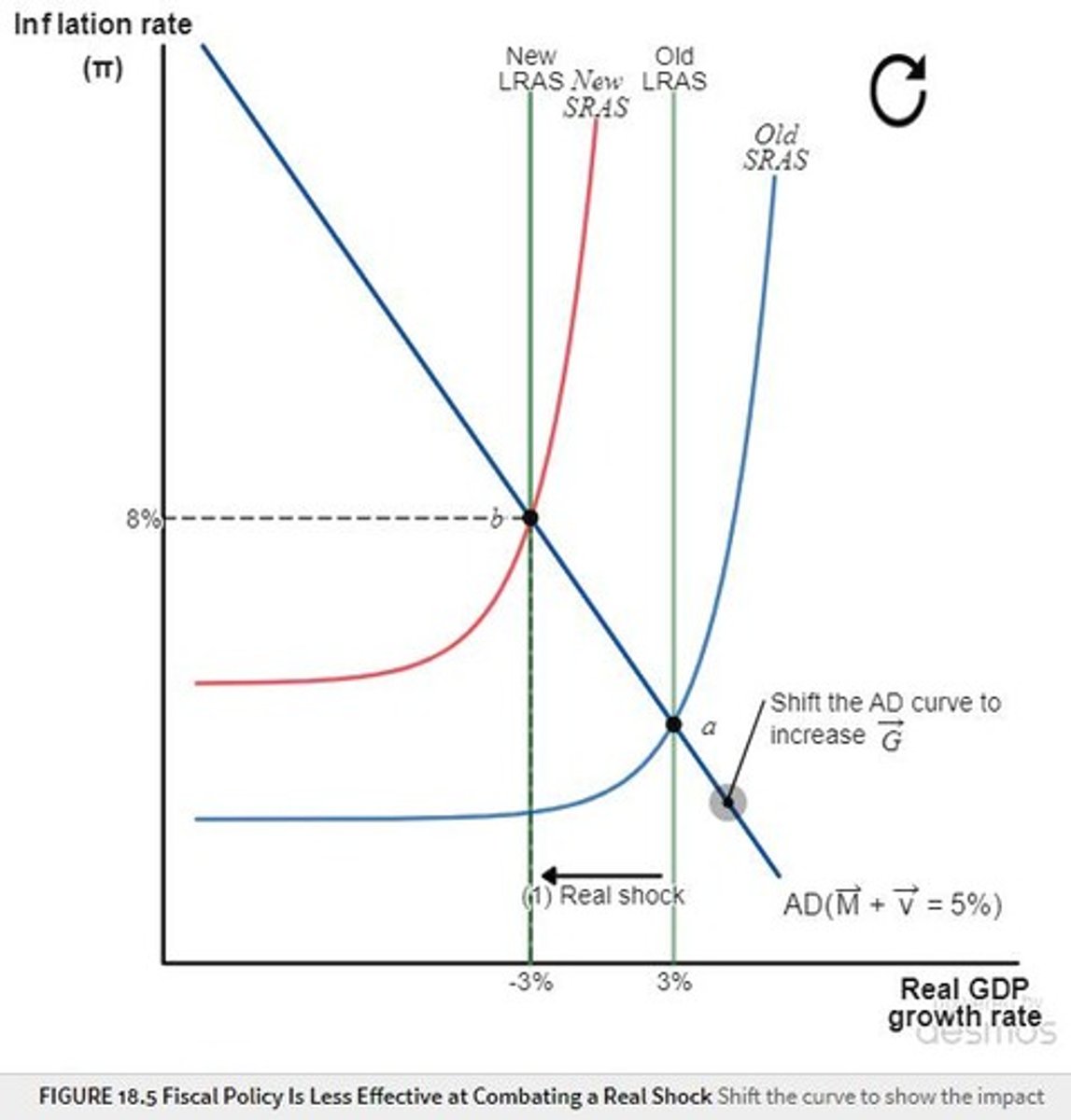
What role does government spending play in the context of social insurance?
It is justified as a form of social insurance and redistribution.
What is the effect of fiscal policy on private investment during government borrowing?
It can lead to reduced private investment due to higher interest rates.
What is the relationship between unemployment insurance and aggregate demand?
Payments to the unemployed increase aggregate demand as they tend to spend benefits quickly.
What was the economic condition before the COVID-19 pandemic?
Stable growth rate of real GDP (2%), inflation (2%), and unemployment (5%).
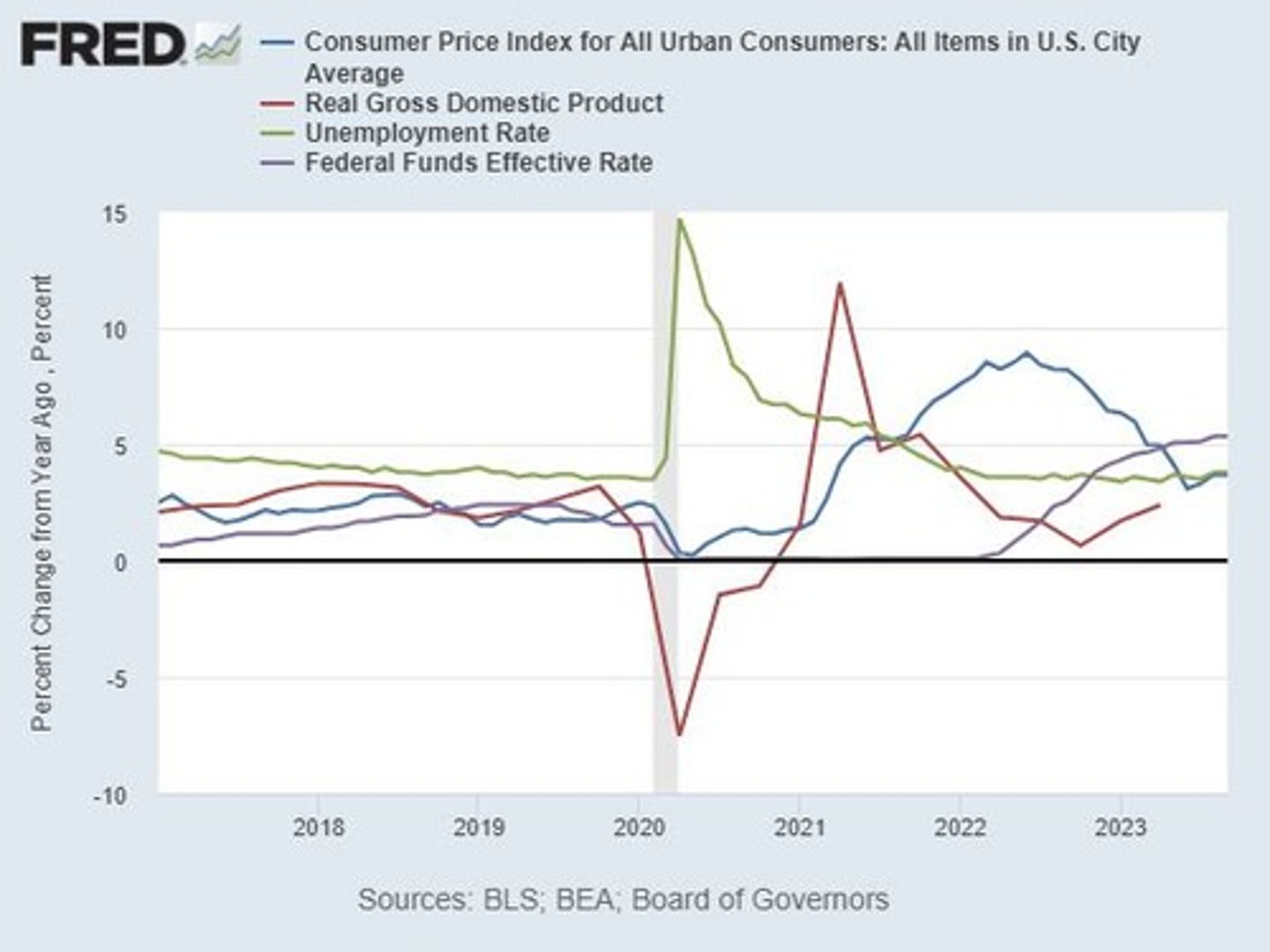
What was the outcome of the fiscal stimulus during the COVID-19 pandemic?
It helped mitigate the severity of the recession and facilitated a quicker recovery.