5.5. - Influenza & AIDS/HIV
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What’s the portal of entry of Influenza?
mouth/nose
What’s the portal of exit of Influenza?
mouth/nose
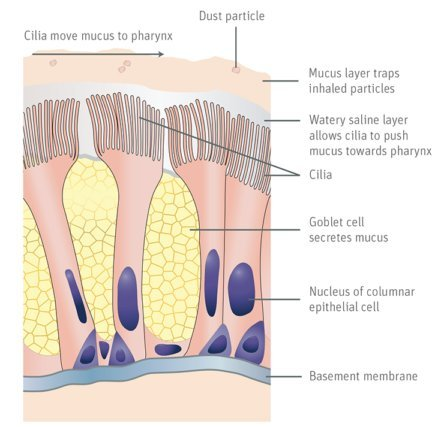
What does Influenza target? (what cells)
mucocilliary escelator
Since Influenza damages the mucocilliary escelator, it sets a person up for risk of secondary infection of ______ _______.
bacterial pneumonia
Typically, the age mortality of influenza is within the ____ _____ and ____ _____.
very young, very old
Why do infants/children under 1 years old have a higher influenza mortality rate?
anatomy of their mucocilliary escelator is shorter
Why do older people have higher influenza mortality rate?
immunocompromised
H1N1 is ___ type Influenza; It caused a pandemic in ____
A; 2009
H2N3 is ___ type
A
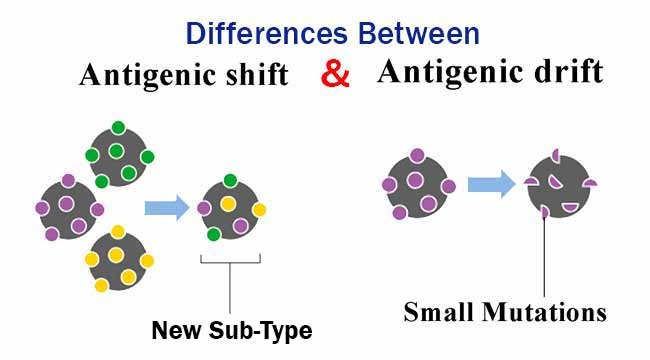
Antigenic shift = ______
pandemic (big deal!)
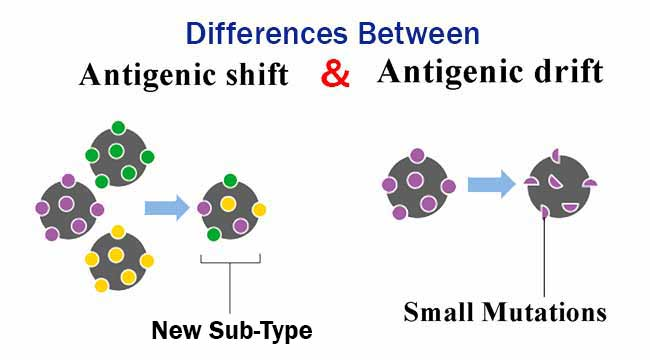
Antigenic drift =
common (happens every year)
Spanish Flu occurred in _____; It’s considered one of the most devestating pandemics
1918
What type and strain of influenza was the Spanish Flu?
H1N1 type A
What was the death rate of the Spanish Flu?
100 million
Mortality rates of the Spanish Flue ____ around the world.
varied
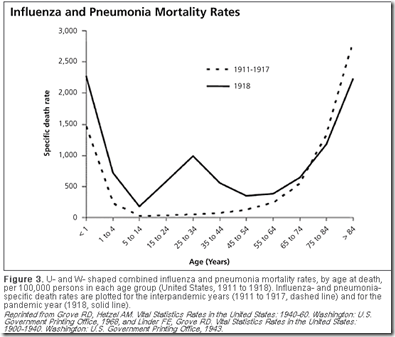
The spanish flu not only affected infants and elderly people, but also ____ ______.
young adults (20 year olds)
What war was going on at the time the Spanish Flu was around?
WW1
So since (young adult) soldiers had high stress → weaker immune systems → so more of them _____ due to Influenza
died
Older adults had lower mortality rates than the 20 y/o because?
they had prior immunity from H1N1 in 1870s (younger gen unfamiliar so no antibodies)
Also the influenza virus depnding on a persons ______ ______ went from the upper respiratory → lower respiratory (destructive pneumonia, cytokine storm)
genetic predisoposition
What’s the typically strain of Bird Flu or Avion Flu?
H5N1
The goal as of now is to prevent ______ _____ with bird flu (prevent risk of making supervirus)
human contact
Most humans are currently ____ susceptible to bird flu, but a few are due to ______ ________
not; genetic predisposition
The fear of Bird Flu is that a suceptible human will become host to bird flu & _____ ____ causing Antigenic _____
human flu; shift
This combination of a person having bird & human flue can create a _____ _______ that is human transmissible
novel supervirus
Worst case scenario, this supervirus of bird flu & human flu would have a mortality rate of ___%
50%
AIDS →
aquired immunodeficiency syndrome
The Risk Groups for AIDS was (4H)
homosexual men, heroin addicts, hemophiliac (blood transfusion), Haiti
Back then though, the only sympathy of the 4H’s mostly went to the _______.
Hemophiliacs
By _____, a retrovirus (HIV) was suspected to be the cause of AIDS
1984
HIV →
human immunodeficiency virus
What was the first drug used to treat HIV? (1987)
AZT
Was AZT successful in the long run?
no
HIV is what type of virus? (3) (nucleic acid strategy, type of virus)
enveloped, retrovirus, (+) ss RNA
HIV in particular had an enzyme called →
reverse transcriptase
Reverse Transcriptase allows ____ to convert back into ____
RNA; DNA
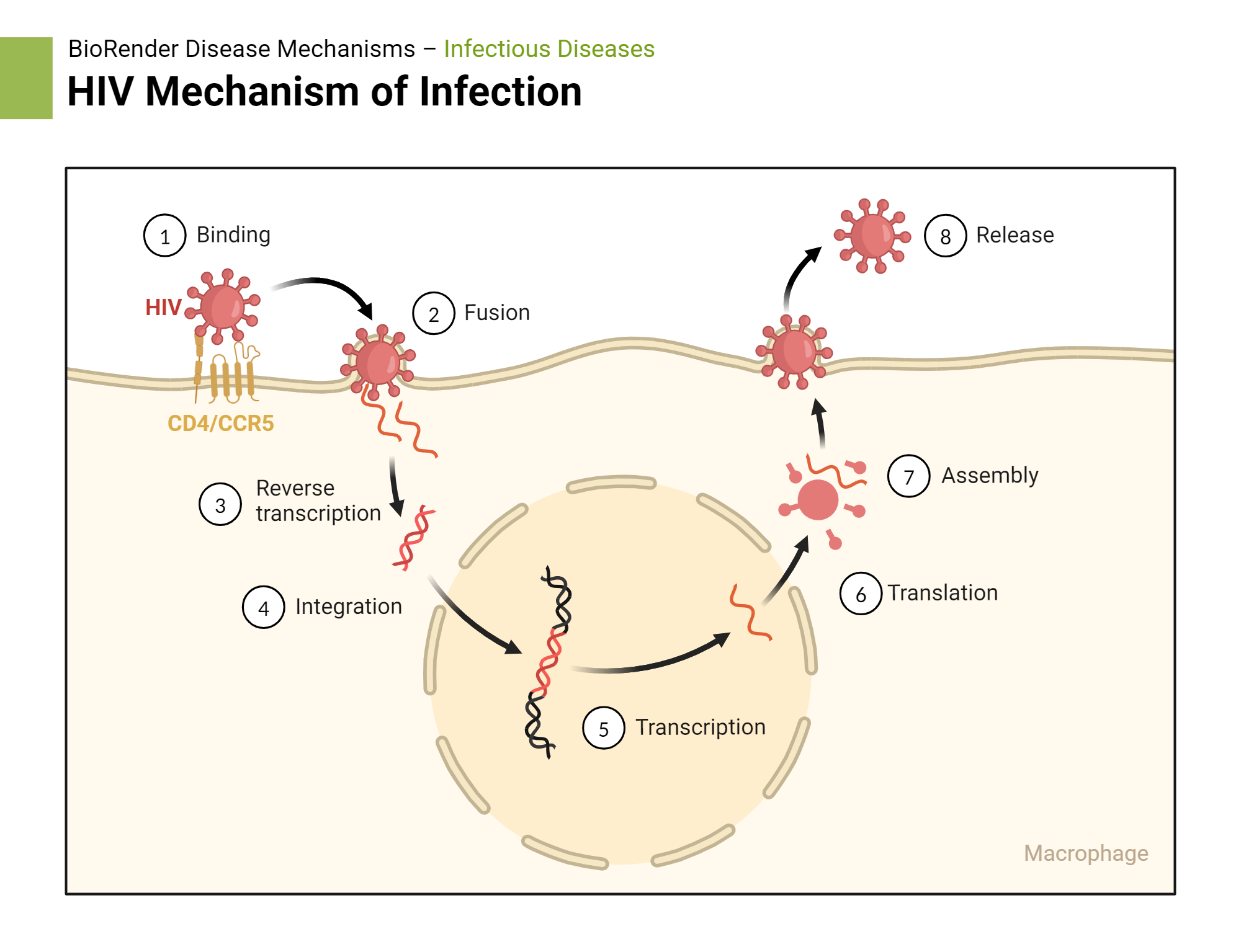
So HIV’s (+) ss RNA → reverse transcriptase → created ?
ds DNA
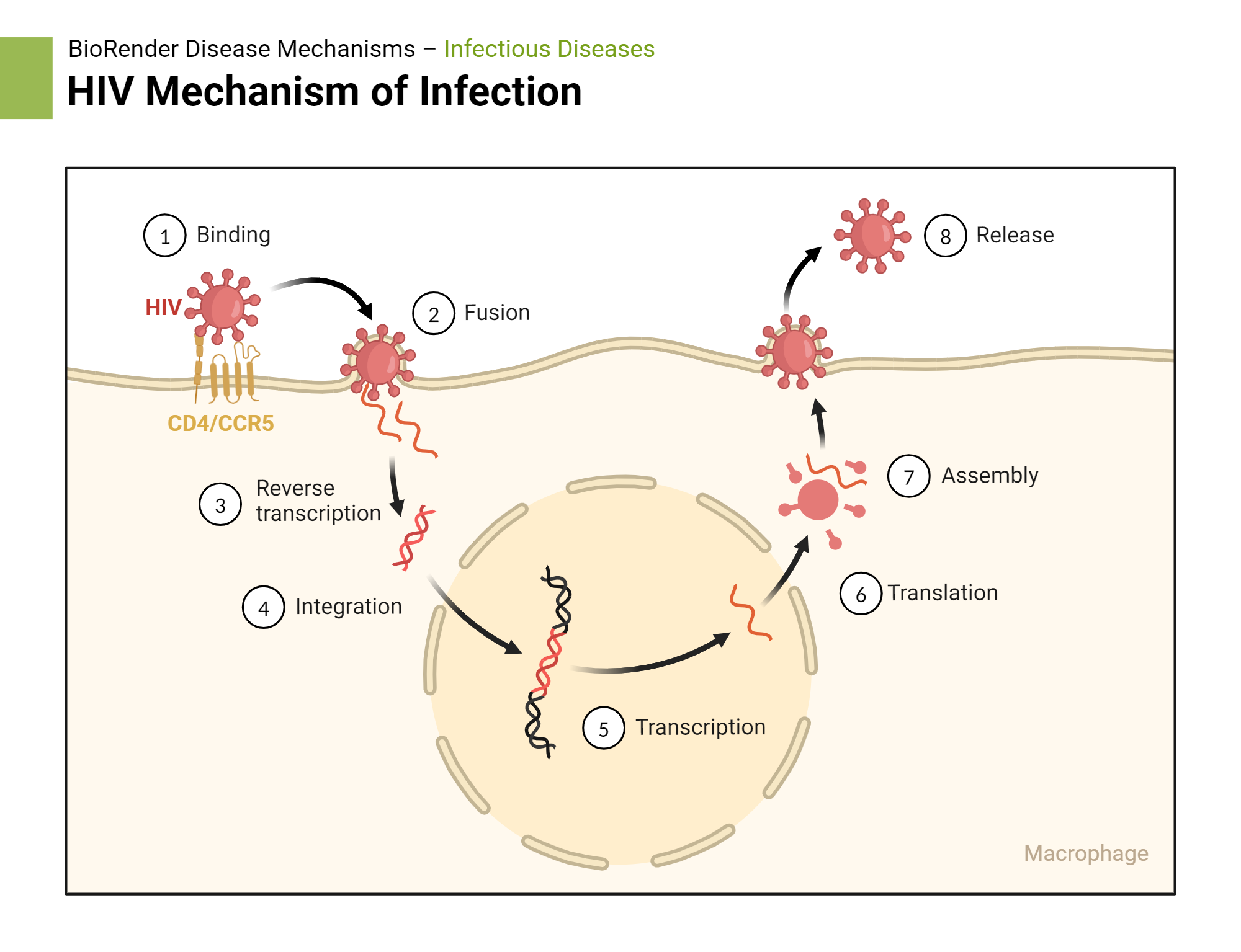
So from there, the HIV’s newly created ds DNA will do either 2 things:
latency
create active virus
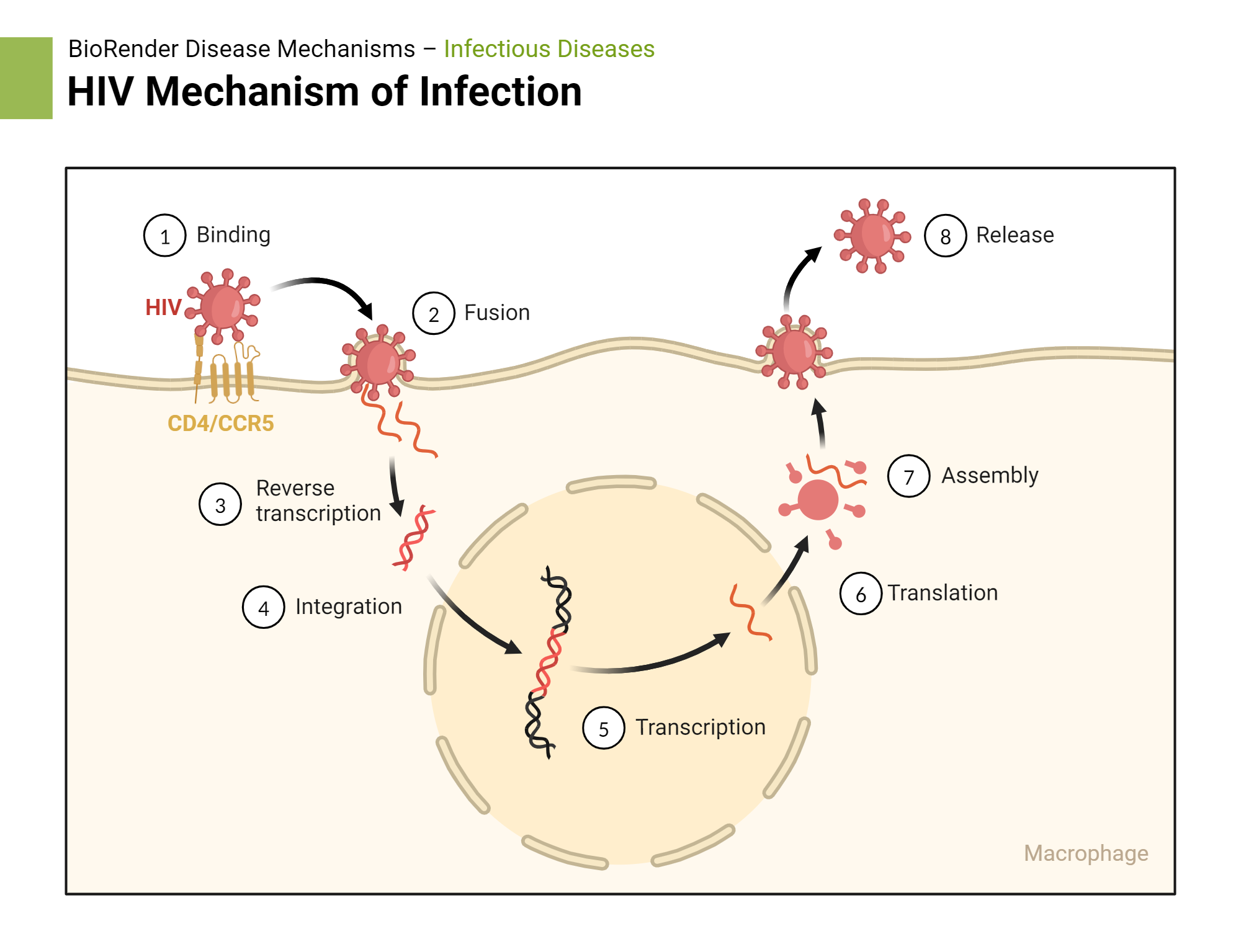
To make an active HIV virus, the ds DNA uses ____ ________ to make many (+) ss RNA strands
RNA polymerase
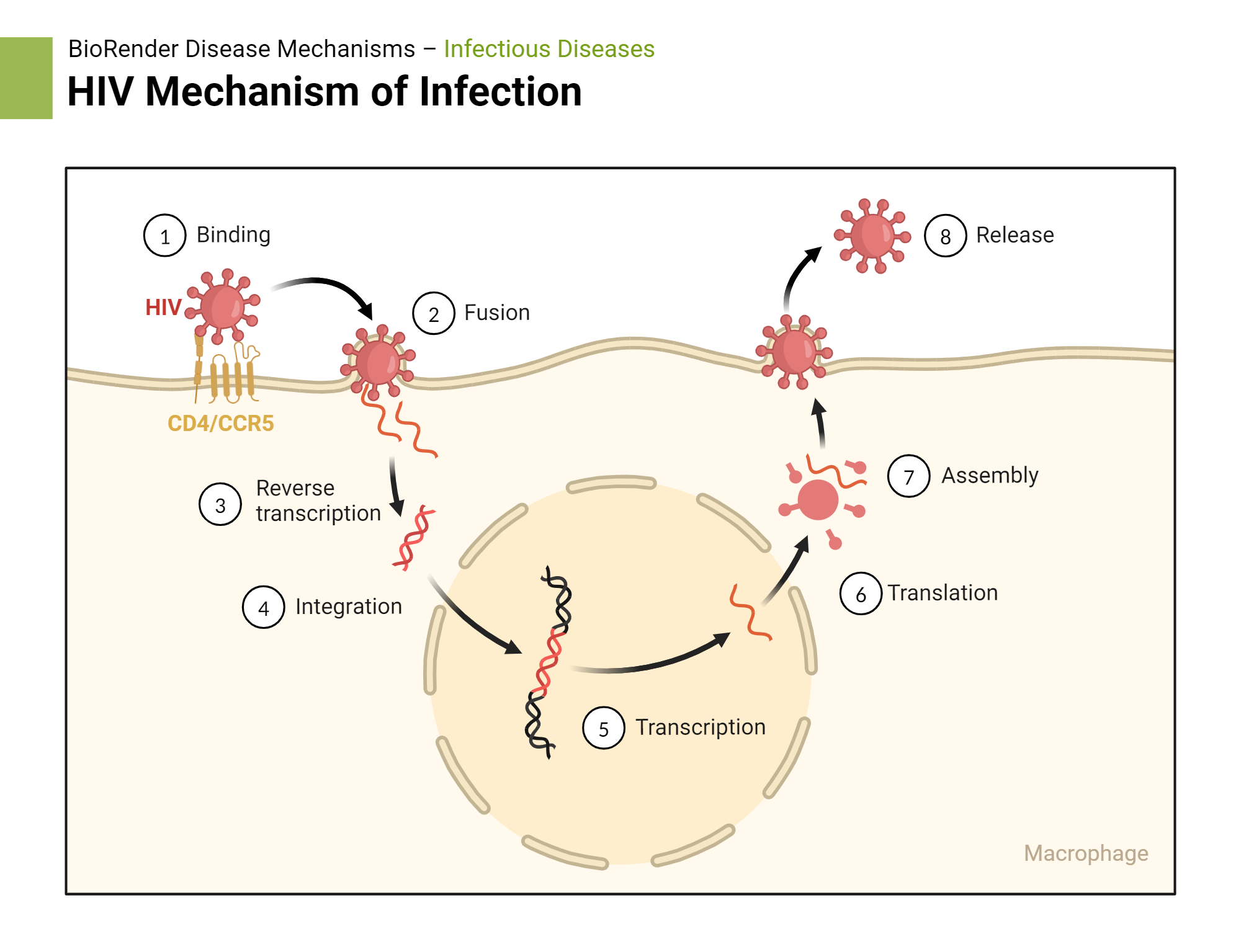
Then it will send the newly made (+) ss RNA strands to a ______ to make ____ _____, ______, and ______ _______.
ribosome: protien capsid, spikes, reverse transcriptase
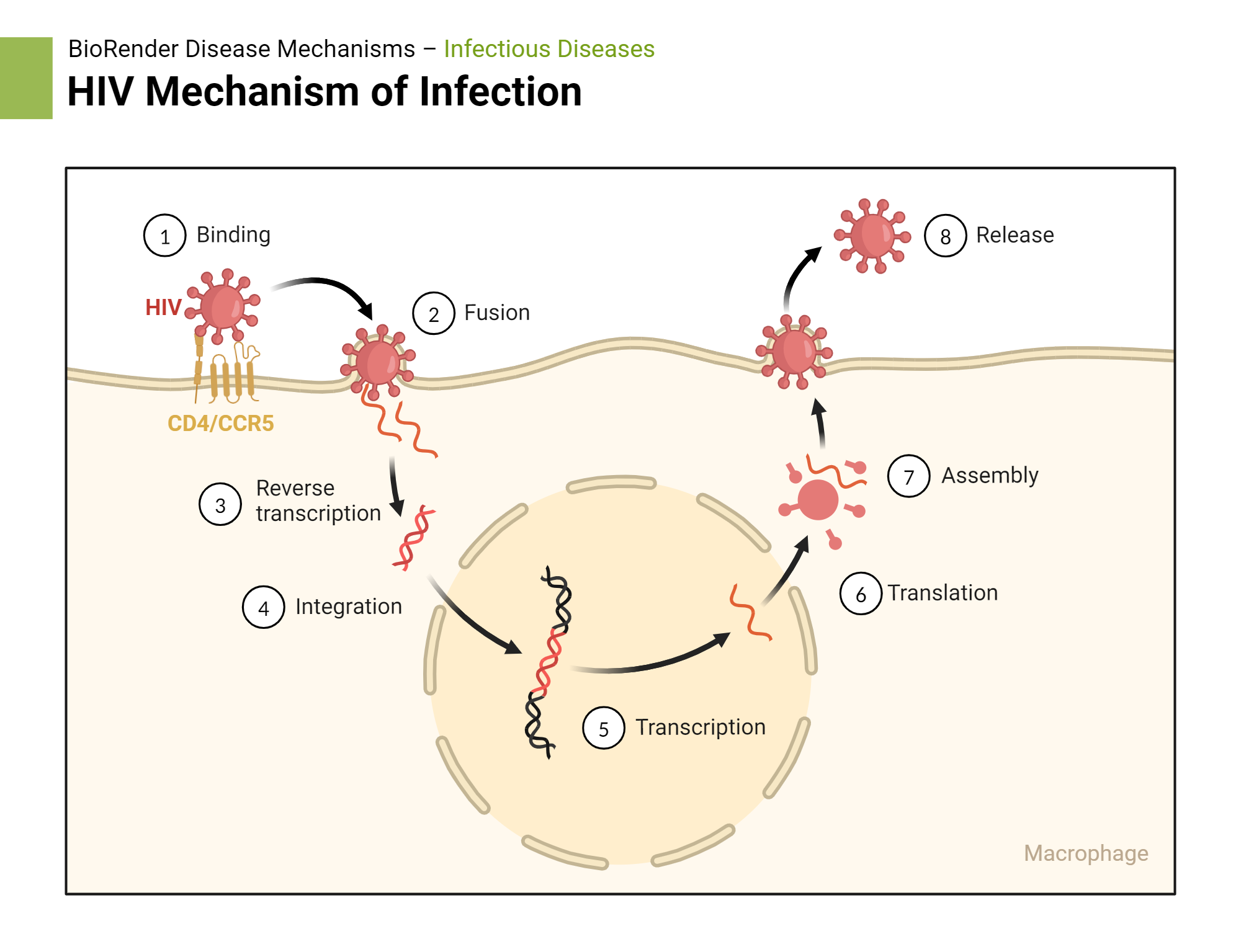
Then the (+) ss RNA and ____ ____ will get packaged into the newly made HIV viruses.
reverse transcriptase
HIV adsorbs to what type of cells?
CD4+ cells
What is a known CD4+ cell that HIV targets?
helper T cells (TH)
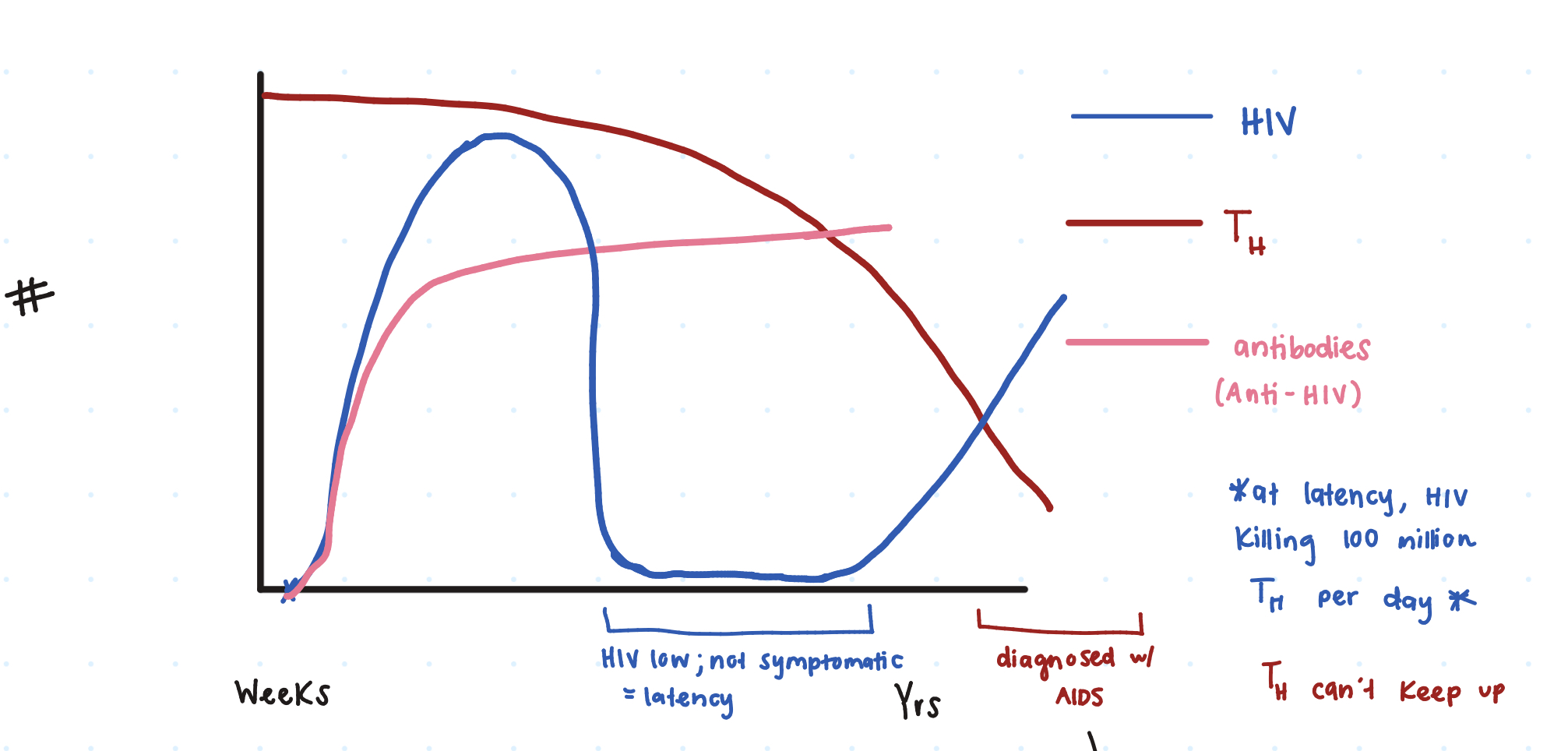
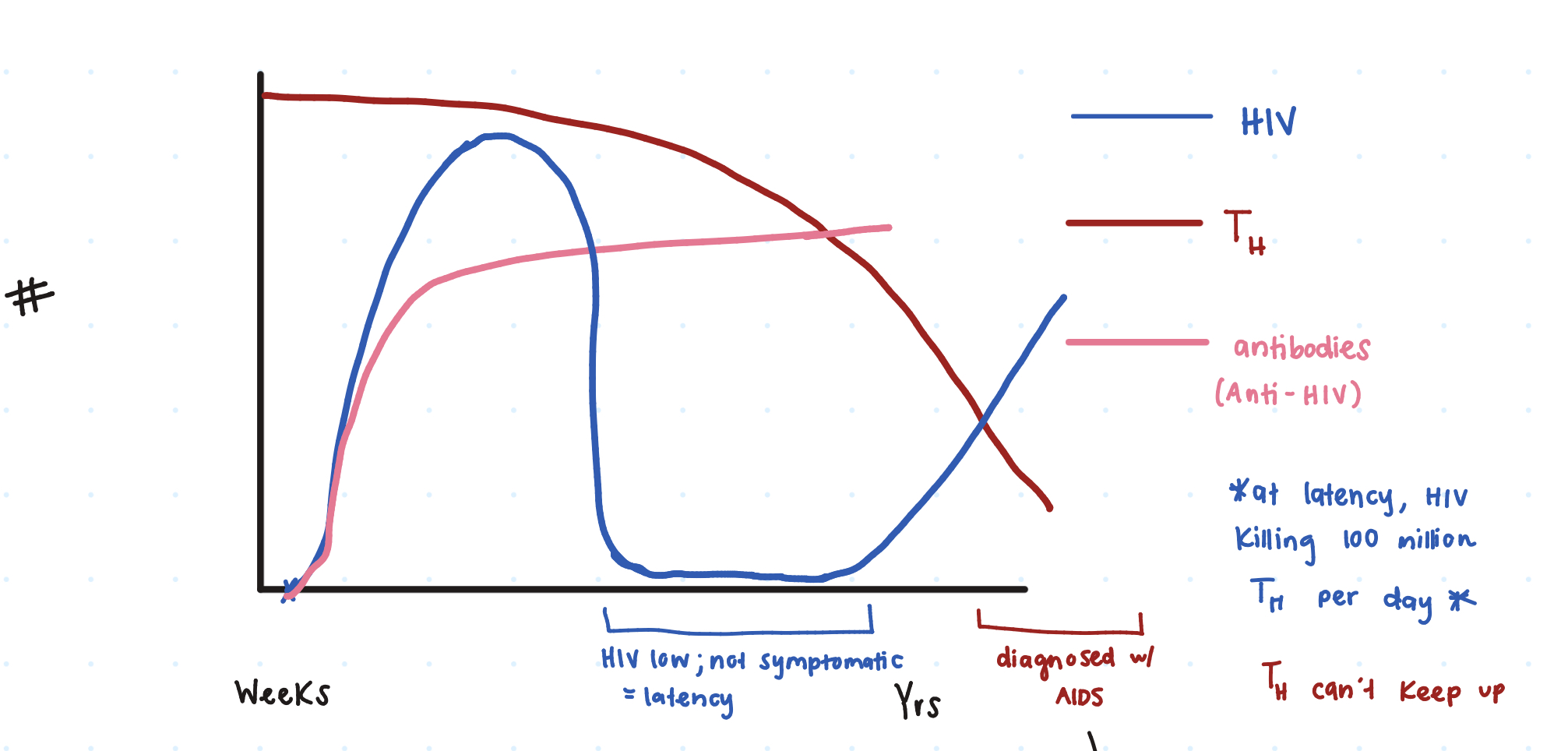
So at first innoculation of HIV, there’s a ____ _____ seen on the graph.
huge spike
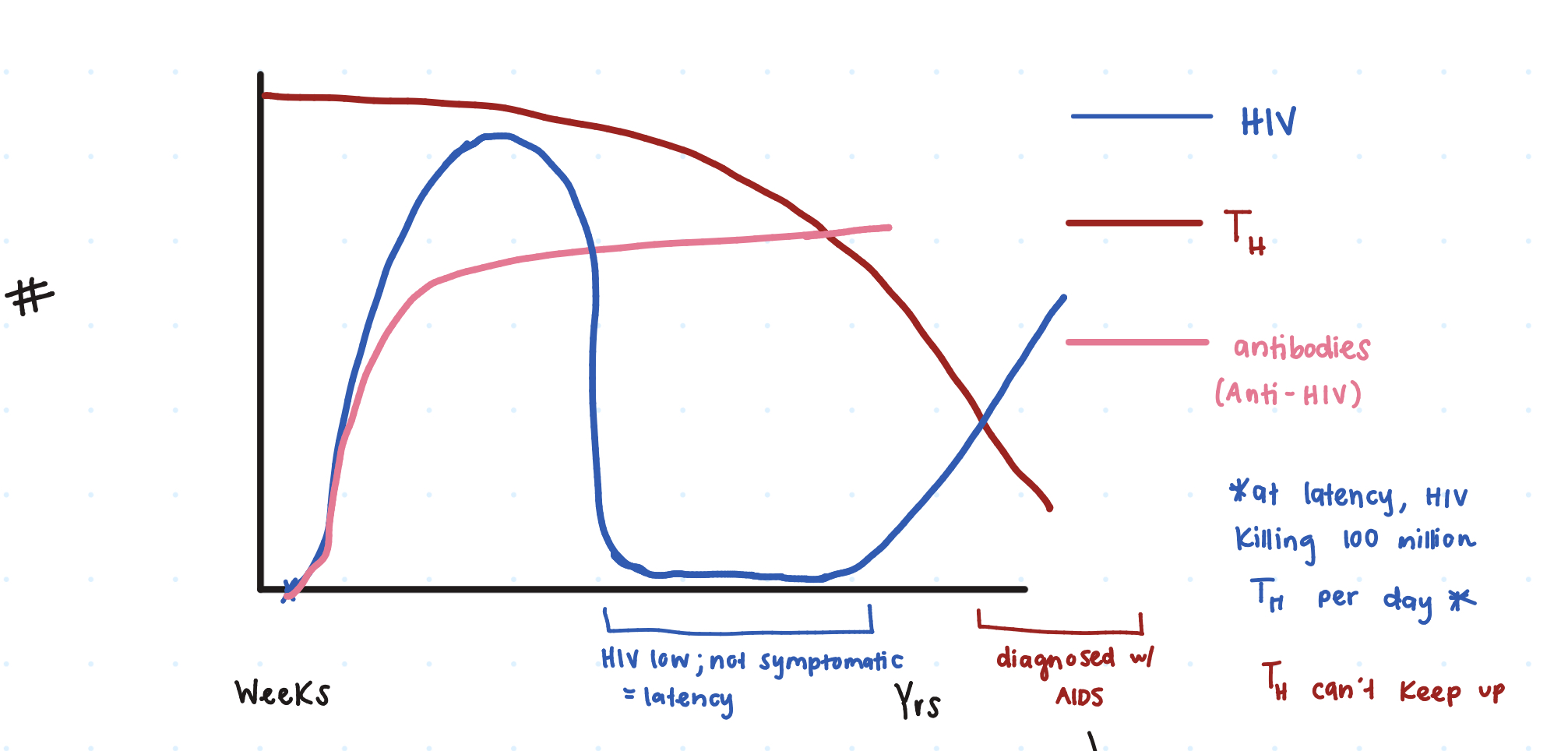
Then the HIV dies down due to our _______ producing Anti-HIV
antibodies
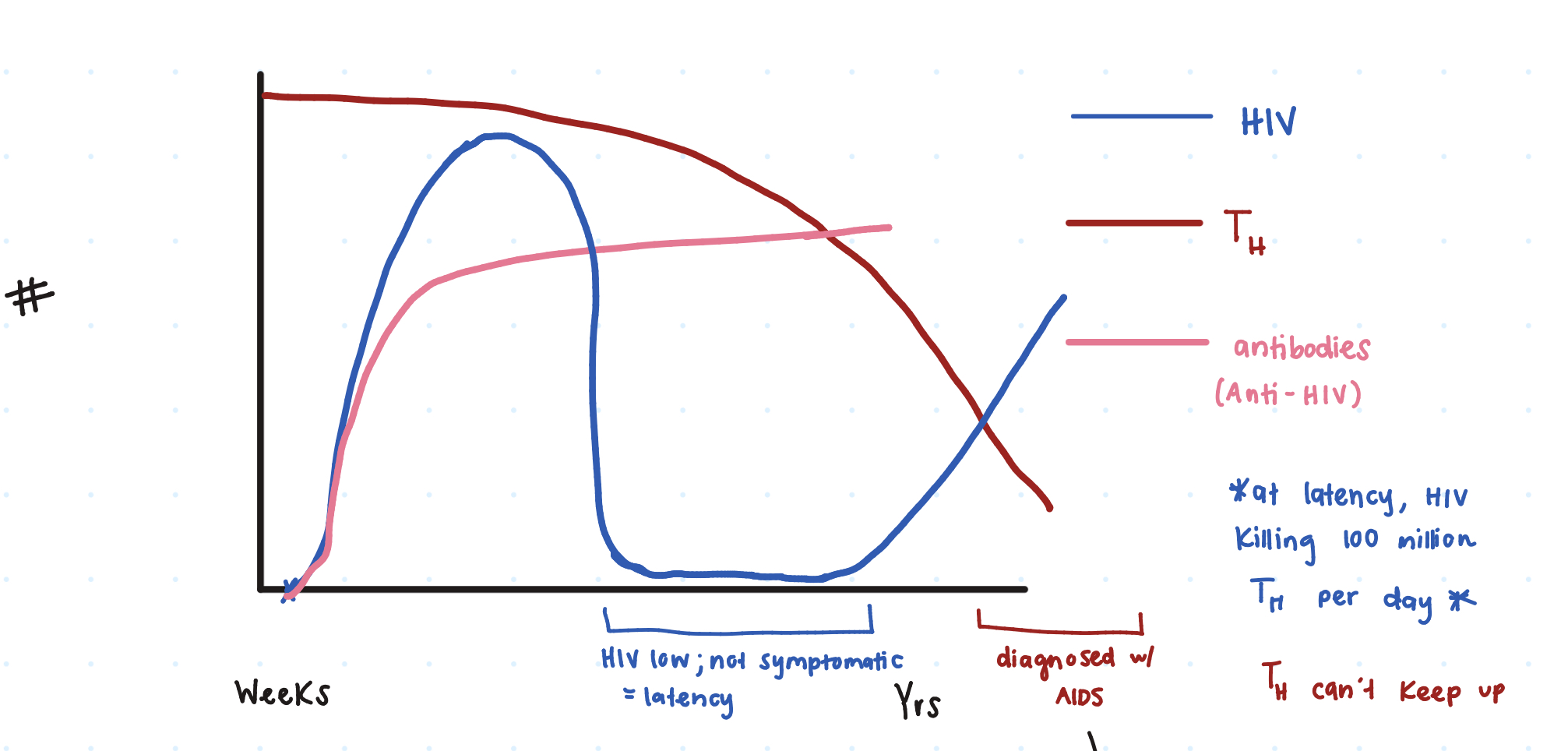
However, does the HIV ever get reduced to 0?
no (latency period)
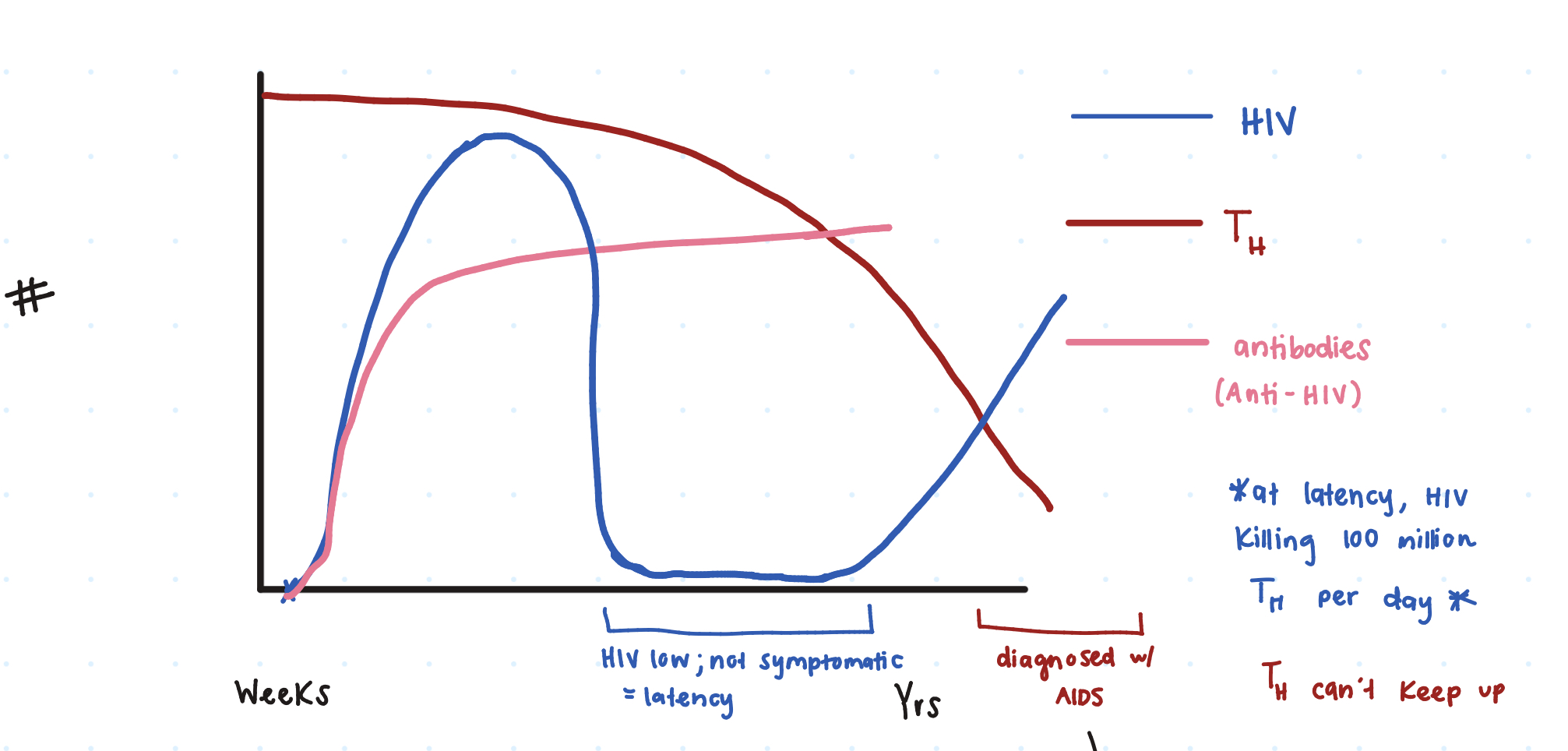
So when a person has HIV latency, are they symptomatic or not symptomatic?
not
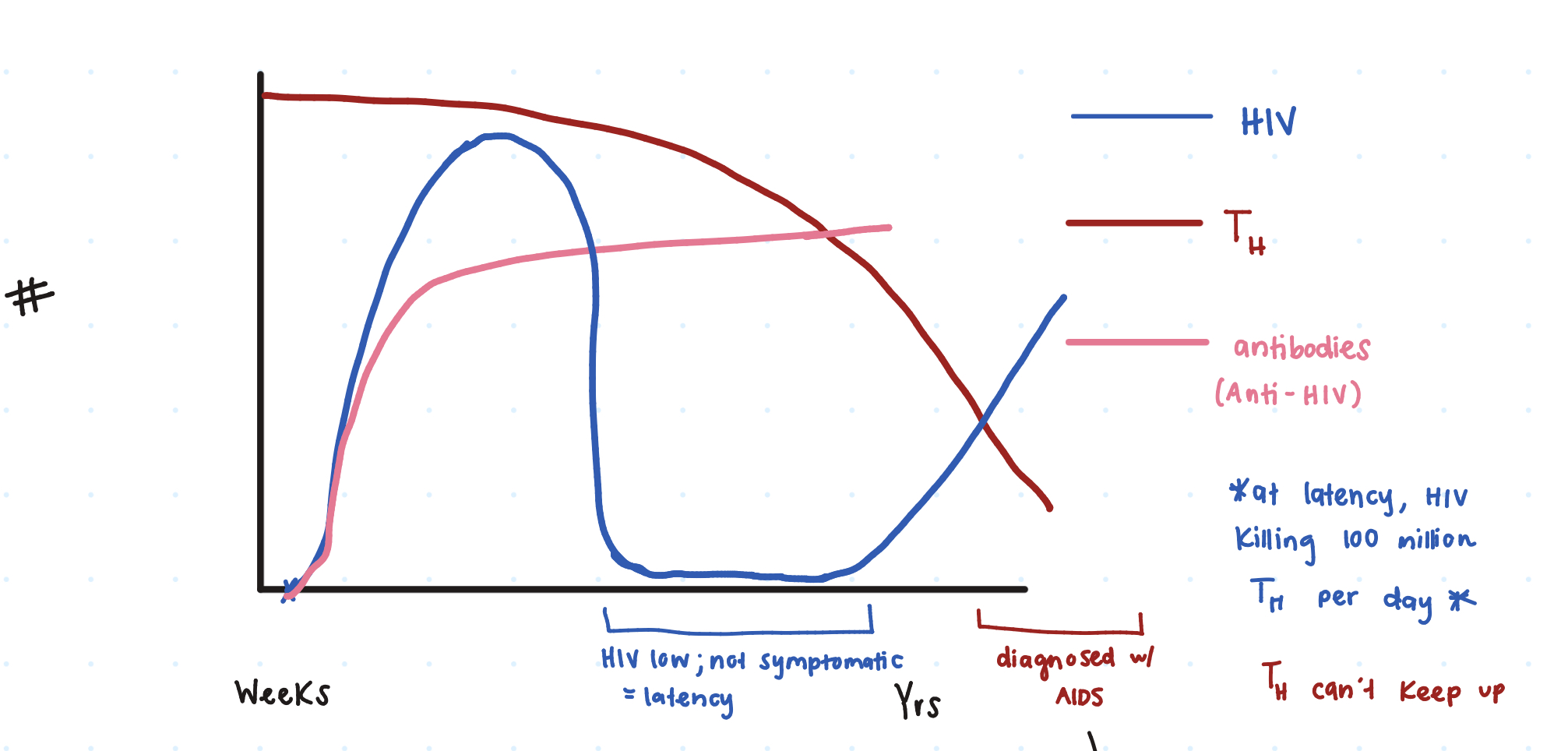
Additionally, gradually our TH cells decrease, causing a rise in ____. (comes out of latency)
HIV
When HIV+ individuals have a TH ≤ _____ microliters, a clinical diagnosis fo AIDS is given
200
Most people die from AIDS from 2 things:
opportunistic pathogens
cancer

HIV transmisibility is based on 2 things:
Viral Load
Likelihood virus finds CD4+ cell
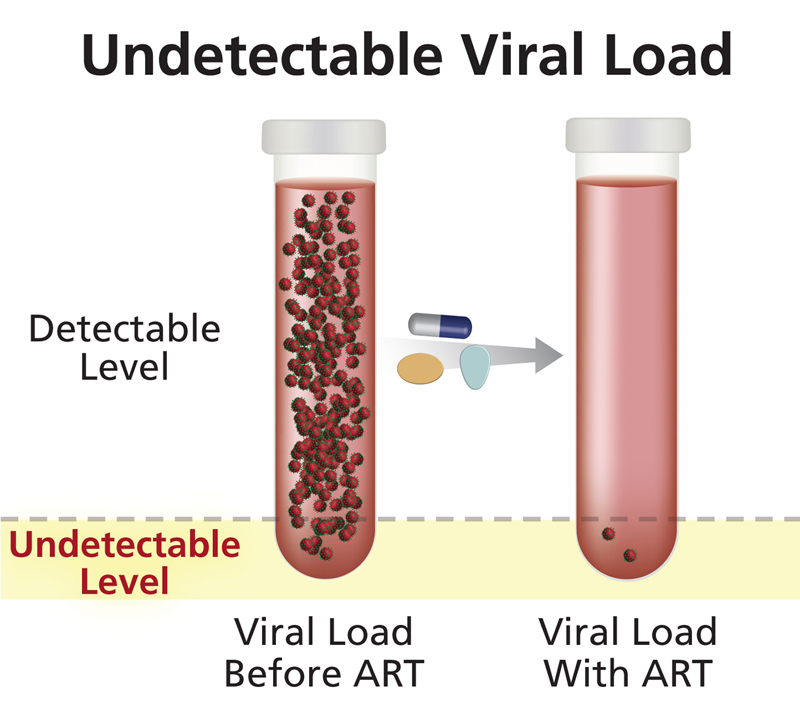
Viral Load is →
how many viruses are within a drop of body fluid
Viral Load really depends on what ____ of HIV the person’s in
stage (latency has less viral load than other)
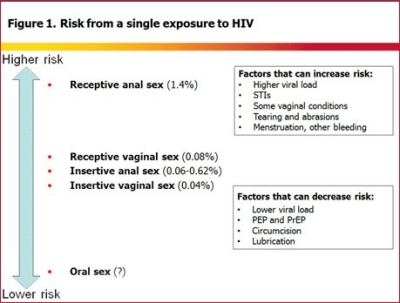
Likelihood virus finds CD4+ cell is based on likelihood virus finds its way into ____.
blood (sharing dirty needles, sexual transmitance)
Semen contains a lot of ____; and anal sex causes tearing = blood access
HIV
The treatment of HIV and AIDS is a _____ ______ called _____
drug cocktail; HAART
Is HAART expensive or cheap?
exspensive
HAART is composed of 3+ drugs to ensure ?
virus mutations don’t cause treatment resistance
Does HAART cure AIDS/HIV? Why?
no; there’s always going to be some virsuses in latency
HAART is very ______; most people will live an _____ lifespan if taken accordingly.
effective; average