Option Unit D - Medicinal Chemistry
1/115
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
Drug vs Medicine
Drug: A chemical that affects the body in a good or bad way
Medicine: a substance that improves health, known as a therapeutic effect
Effect of Pharmaceutical Products on the target molecule
Can stop the target molecule from functioning or stimulate it.
Stages of Drug Development
Discovery Research, development research, regulatory review, post marketing monotoring
Stage 1: Discovery Research
Identification of lead compounds (usually from plants)
Optimization (analogues tested through combinatory chemistry or high-throughput screening)
analogues: chemically related compounds
Initial Testing of the potential medicine (determines human dosage)
Stage 2: Development research
3 clinical trials on humans. Each phase increases the # of patients
Stage 3+4: regulatory review and post-marketing monitoring
application for marketing of the product, collection of any adverse drug reactions
Drug Doses
LD50, TD50, ED50
LD50
Lethal Dose
Dose of drug required to kill 50% of the laboratory animals tests (mass/kg)
TD50
Toxic Dose
Dose required to produce a toxic effect on 50% of the tested human population
ED50
Effective Dose
Minimum dose required to produce a therapeutic effect in 50% of the population
Therapeutic Index
TI = LD50/ED50 or TI = TD50/ED50
The greater the TI, the safer the drug
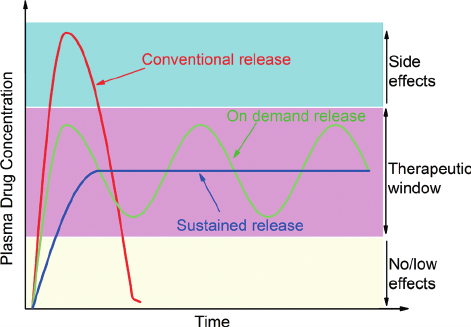
Therapeutic Window
Range of dosage between the minimum required to cause a therapeutic effect and the level that produces toxic effects
Drug Administration
Depends on:
chemical nature of drug, condition of patient, bioavailability
Methods of administrating drugs
oral, inhalation, skin patches, suppositories (rectal), ear/eye drops, paranetal (injection)
Intramuscular (deepest), intravenous, subcutaneous (needles)
Bioavailability
The fraction of the administered dosage that is absorbed into the bloodstream and reaches the target sit
Intravenous injection = 100% bioavailability
Depends on: solubility, polarity, presence of functional groups
Analgesics
Drugs that relieve pain
Mild: aspirin, ibuprofen
Strong: morphine, heroin, codeine
how are pain receptors stimulated
Stimulated by prostaglandins, which are released from cells damaged by thermal, mechanical or chemical energy
Prostaglandins
Mediate the inflammatory response, causing dilation of blood vessels near the site of the injury and may result in fever
Produce thromboxanes, which stimulate the clustering of platelets and blood clots
Mild Analgesics (non-narcotics)
Act by preventing stimulation of the nerve endings at the site of pain
Inhibit the release of prostaglandins at the site of injury by inhibiting an enzyme (cox)
Key enzyme in the synthesis of prostaglandins
COX (cyclooxygenase)
Mild Analgesics: Salicylic Acid
relatively strong acid, unpleasant to take orally and damages the membrane lining of the mouth, esophagus and stomach
sodium salicylate also used, but same side effect
Ester of Salicylic Acid (Acetyl Salicylic Acid → Aspirin)
Pro: reduces fever and pain, reduces risk of colon cancer, prevents the formation of thromboxanes (clusters of platelets), anticoagulant (reduces risk of stroke/heart attack)
Con: causes irritation/bleeding in stomach/duodenum, Reye’s syndrome (kids under 12 → liver/brain damage), allergies, acidosis (decreased pH of blood)
Synergism
when 2+ drugs, given at the same time, have an effect on the body that is greater than the sum of their individual effects
ex: alcohol + aspirin: increased risk of bleeding in the stomach
Purification of Aspirin
Crude sample of aspirin contains impurities and must be purified using recrystallization with hot ethanol
How Aspirin is purified
solubility of a compound in a solvent increases with temperature
as the solution cools, crystal forms
molecules in a crystal have a greater affinity for molecules of the same kind
Determination of purity (aspirin)
By chromatography or by measuring the melting point
pure substances has a well defined melting point
impurities lower the melting point (138-140 ºC) and increases the range
IR spectrum: 2 peaks in the C=O region, very broad O-H stretch
Solubility of Aspirin
Insoluble, meaning limited bioavailability
The carbox. acid group can be made into an ionic salt by reacting it with NaOH
Penicillin
Bicyclic structure, contains a beta-lactam ring
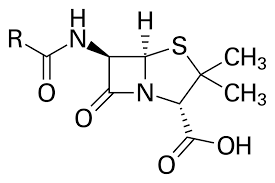
Penicillin G (Benzylpenicillin)
First one to be isolated and purified, but its is easily broken down in the stomach and must be injected
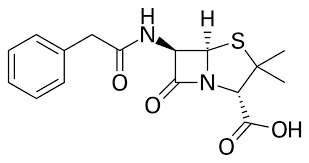
Modern/Semi-synthetic penicillin (ampicillin)
Side chain has been modified to alter its properties
Pro: reduces occurrence of penicillin resistant bacteria, resistant to breakdowns from stomach acid
Action on bacteria cell walls (penicillin)
Deactivates the transpeptidase enzyme, prevents formation of cross links in the cell wall.
Beta-lactam ring opens, covalent bonds form between the enzymes active site and penicillin leading to deactivation.
Bacteria will absorb water and burst
Bacterial Resistance
Resistant bacteria produces penicillinase, an enzyme which breaks open the Beta-lactam ring in the penicillin molecule
resistance arises from mutations in the bacterial DNA
The more bacteria are exposed to antibacterials, the more opportunities for the bacteria to mutate
Strong Analgesics (opiates)
temporarily binds to the opioid receptors in the brain, which then blocks the transmission of the pain signals and alters the perception of pain without depressing the nervous system
Narcotics
act on the brain and can cause drowsiness and changes in behaviour and mood
Opium
extract from poppy seeds
contains naturally occurring nitrogen containing compounds (alkaloids)
Narcotics derived from opiates
codeine < morphine < heroine
Codeine: 0.5% of raw opium
Morphine: 10% of raw opium
Heroine: synthesized from morphine
Blood-Brain barrier
a series of lipophilic cell membranes that coat the blood vessels in the brain and prevent polar molecules from entering the CNS
the psychological activity of opiates depends on their ability to cross the barrier
Opiates and the blood-brain barrier
heroine: 2 ester groups, less polar, H-bonds
Morphine: 2 hydroxyl groups
Codeine readily crosses the barrier but is metabolized slowly (does not bind to the opioid receptor because of the steric effect of the ester group)
pH of the stomach
pH of 1-2, generated by hydrochloric acid from the gastric glands. produced by parietal cells in the lining of the stomach
acid environment needed to:
kill bacteria
provide the optimum pH environment for digestive enzymes to act
Excess acid production in the stomach
can be caused by excess alcohol consumption, smoking stress, and anti-inflammatory drugs
leads to the following issues:
acid indigestion
heartburn (acid reflux)
ulcer
Antacids
neutralize the excess hydrochloric acid
common bases: Mg/Al hydroxide, Ca/Na carbonate, Na bicarbonate
not Na/K hydroxide since they are strong alkalis and corrode body tissue
Alginates
Some antacides contain alginates. They float to the top of the stomach and form a “raft”. Acts as a barrier and prevents reflux into the oesophagus.
Anti-foaming agents
Antacids with carbonates. ex: dimethicone
Reduce bloating
Treatment of peptic ulcers
treated by regulating the acid levels
2 main approaches: stopping the production of acid, preventing the release of the acid into the stomach
Ranitidine (Zantac)
inhibits the production of the acid, short term relief
binds to the receptor protein (histamine H2-receptor) in the membrane of the parietal cells.
stops histamine from binding to turn on the the production of acid
Omeprazole (losec, prilosec) and esomeprazole (nexium)
proton pump inhibitors - prevent the release of acid, long term
non polar (lipid soluble), so they can cross the cell membrane of parietal cells
become protonated inside the cell due to the acidic environment
binds irreversible to the proton pump
effective until the cell produces new proton pumps
Active Metabolites
active form of drugs after they have been processed in the body
ex:
codeine converts to morphine in the body, which binds more strongly
omeprazole/esomeprazole: converted to different forms that bind to proton pumps
aspirin: converted into the active form (salicylic acid)
Why is treatment and prevention for antiviral medications difficult
viruses multiply quickly, they spread throughout the body before symptoms appear
can multiply their DNA/RNA (provides drug resistance)
hard to target only the virus without affecting the host
Antiviral drugs work in a number of ways
alter the genetic material within cells
inhibit the activity of enzymes within the host cell
prevent binding of the virus to the host cell surface by binding to the cell receptor or capsid protein
prevent the virus from leaving host cell (oseltamivir & zanamivir)
inhibits the uncoating/injection of the virus into the cell
Neuraminidase
enzyme that breaks down the membrane of host cells, allowing the virus access to target cells “budding”
Influenza
antiviral drugs are neuraminidase inhibitors
nuclear waste
byproduct of the use of radioisotopes in medicine
low level nuclear waste
low activity, contains isotopes with short half lives
includes items that have been contaminated with radioactive material or have been exposed to radioactivity
Disposal strategies of low level nuclear waste
may be stored on site until it has decayed enough to dispose ordinarily, may be incinerated, can be buried underground
High level nuclear waste
high activity, contains isotopes with longer half lives
includes spent fuel rods and other material from nuclear reactions
remains hazardous to humans and other living things for thousands of years
disposal of high level nuclear waste
can be converted to glass (vitrification), kept in storage pools underwater then moved to dry storage casks inside concrete bunkers, long term storage is problematic
release of antibiotics into the environment
can enter the water supply by several routes:
incorrect disposal of unwanted medicines
agriculture
problematic:
causes damage to aquatic organisms
results in increased resistance of bacteria to antibiotics
Green Chemistry
seeks to minimize the production of hazardous substances and their release in the environmet
Best synthetic routes to a drug
use readily available and safe materials
have the minimum number of steps
convert as much of the starting materials as possible into the required product at each step
use as little solvents and energy possible
Atom economy
measures how efficient a particular reaction is
molar mass of desired product / total molar mass of all reactants
Synthesis of oseltamivir
uses a naturally occurring material - shikimic acid - as a starting material
extracted from star anise, glucose by fermentation using GMO’d bacteria
Waste Solvents
used as a medium for reactions or in the extraction/purification of compounds
many are non-polar, organic, but toxic
chirality in drugs
enantiomers can behave differently in the body as a result of their different shaped
ex: enantiomer of thalidomide caused birth defects
Obtaining a single enantiomer in drug synthesis DELETE
synthesis of a racemic mixture followed by separation using chiral chromatography
stereoselective (asymmetric synthesis) - a synthesis reaction is used selectively to produce one of the enantiomers
Chiral auxilary
one enantiomer of an optically active substance that is temporarily incorporates into a non-chiral molecule to produce a single enantiomer of a product in an organic synthesis reaction
identify/purity found with a polarimeter
Taxol (paclitaxel)
used to treat several forms of cancer
usually given intravenously, acts by preventing cell division
binds to microtubules in the cytoplasm, preventing them from breaking down during cell division
Semi-synthesis of taxol (chiral auxiliary)
originally obtained from pacific yew tree bark
takes bark from more than one tree to provide enough to treat one patient
semi-synthetic process was developed
uses the needles
nuclear reactions
involves changes of the nuclei of atoms
results in particles and sometimes also electromagnetic radiation being emitted from the nucleus (alpha and beta)
After a drug has been synthesized, 2 steps occur:
extraction of the drug from the reaction mixture
purification of the drug
extraction of the drug from the reaction mixture
solvent extraction using a separatory funnel (drugs will seperate into the non-polar organic bilayer)
high density is at the bottom, low density is at the top
several rounds done to increase yield
after drug extraction:
a drying agent is added to remove residual water
drying agent is then filtered off and the organic solvent is removed using a rotary evaporator
purification of the drug
recrystallization, distillation, or chromatography
purification via chromatography
fractional distillation
separates liquids that have similar boiling points
the liquid with the lower boiling point is collected by condensing the vapour
Raoult’s Law
the partial vapour pressure of any volatile component of an ideal solution is equal to the vapour pressure of the pure liquid manipulated by the mole fraction that liquid in the solution
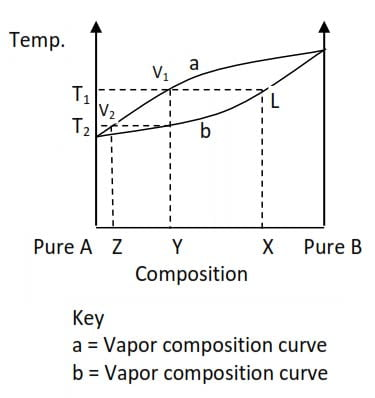
Vapour pressure
Pressure exerted by a vapor when the rate of condensation = the rate of evaporation
for a pure liquid, the vp depends on:
the nature of the liquid
the temperature
for a mixture, the vp depends on how much of each liquid is present
BP of a liquid (raoult’s law)
the more volatile (how fast something evaporates), the higher the vapour pressure, the lower the boiling point
How is the lead compound/new chemical entity found
Drug Discovery: isolated from natural products with known therapeutic effects or synthesized in the laboratory and screened against cell cultures, bacteria or animals. Slow, expensive, and inefficient. Often Fails.
Drug Design: Relies on knowledge about drug receptor interactions. If the chemical composition is known a small molecule with a complementary structure can be designed.
How do drugs interact with receptors and enzymes
the structures of drugs are complementary to the structures of active (or allosteric) sites of enzymes or receptors
Drawbacks of natural medicines
low efficiency, variable composition, instability, side effects caused by the presence of many bioactive substances in the same material
Beta-Lactam Ring
four-membraned, responsible for the antibacterial properties of drugs
Bond angles of the C and N are 90º, creates a significant ring strain and make the amide group very reactive
Analgesic Effect
pain reducing
Antipyretic Effect
Fever reducing
Why is codeine most widely used
10 times less potent than morphine, low activity, wide therapeutic window, limited potential for abuse
Diamorphine (AKA Heroin, AKA semi-synthetic morphine)
Both OH groups are substituted with ester groups → reduces polarity, can easily cross blood-brain barrier, easily metabolizes, 5 times more potent than morphine
Side Effects of antacids
Aluminum Hydroxide: reduces the concentration of phosphates in bodily fluids
Carbonates/Hydrogencarbonates: produce CO2, causes bloating and belching
Calcium/Magnesium/Sodium: affects electrolyte balance → diarrhea, kidney stones, hearth failure
Oseltamivir/Zanamivir
prevent the release of virus copies from the cell by inhibiting viral enzymes (neuraminidase). Keeps the viruses trapped within the cell and slows their spreading.
Oseltamivir: in the liver it is hydrolysed to its active metabolite – carboxylate
Docetaxel
More active than taxol, more soluble, remains in cancer cells longer, reduces the effective dose and leads to fewer side effect, more suitable for intravenous administration
radiopharmaceuticals
unstable isotopes + biologically active compounds
drugs that deliver radionuclides to specific tissues or cellular receptors
brachytherapy/internal radiotherapy
radiation sources are inserted into the patients body in the form of metal wires/pellets that deliver radiation directly to the site of disease
External radiotherapy
cancerous cells are destroyed by precisely directed beams of gamma rays, protons, electrons or neutrons
Cancer cells
ionizing radiation induces errors in the DNA sequence, which passes on through division, eventually limiting their ability to grow and multiply
reduced ability to repair their genetic material

Top - mass number (total protons and neutrons)
Botton - atomic number/nuclear charge (number of protons in the nucleus)
Targeted Alpha Therapy
treats leukaemia/dispersed cancers
alpha emitters are delivered by a carrier drug/protein to the cancer cells, which will be destroyed by radiation without damage to surrounding tissue
collision of alpha and beta particles produce secondary gamma radiation, which can be detected and used for mapping the distribution of cancer cells
Alpha Particles
cause most damage to cellular tissue but have low penetrating power and are absorbed within a short range of their emission (0.05-1mm)
lutetium-177
beta/gamma emitter, used for targeted radiotherapy by being incorporated into molecules that can bind to receptors on certain types of cell. Only destroys a particular type of cells within a very limited area, good for neuroendocrine cancers
emits just enough gamma rays for visualizing tumours and monitoring the treatment
Boron neutron capture therapy
uses the ability of boron-10 to absorb neutrons
tumours can be destroyed if they accumulate sufficient boron-10
can be intravenously injected (through organoboron compounds)
Proton Beam Therapy
protons produced by a particle accelerator are released towards the tumour
minimum radiation damage to healthy tissue
Gamma Radiation
multiple low intensity rays or a single ray fired multiple times from different angles
Gamma Knife
treats brain tumors
200 cobalt-60 sources mounted on a heavily shielded helmet, each source emits a narrow ray of radiation
high local effect but sparing normal brain cells from extensive damage
Computed Tomography (CT)
cross-section images generated by a computer from multiple 2D x-ray scans taken at various angles