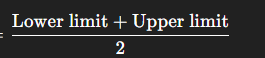Measures of Spread
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Mean
Sum of values
Divide by # of values
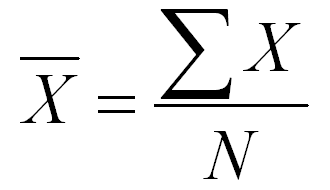
Median
Of ranked data:
If odd, position # of values +1 / 2
If even, average middle numbers
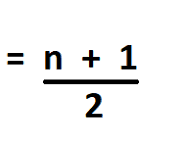
Mode
Most frequent
Grouped mean
The sum of all frequencies multiplied by the midpoints
Divide by the number of values
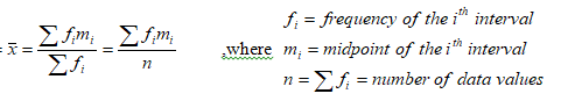
Weighted mean
The sum of the frequencies multiplied by the weights
Divided by the sum of the weights
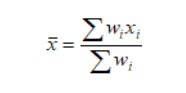
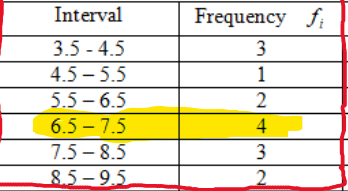
Grouped mode
The most frequent interval
Grouped median
The lower bound added onto the distance into the interval (use cumulative frequency to find this) divided by the frequency that is multiplied by the upper bound minus the lower bound

Deviation
The value minus the mean

Standard Deviation
The sum of the x values minus the mean, squared
Divided by the number of values (minus one if sample)
Square rooted

Variance
The sum of the x values minus the mean, squared
Divided by the number of values (-1 if sample)

First quartile, Q1, position
One quarter multiplied by the number of values plus one
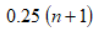
Quartile or quartile position when not a whole number
Use lower number added onto the decimal multiplied by the higher number minus the lower number
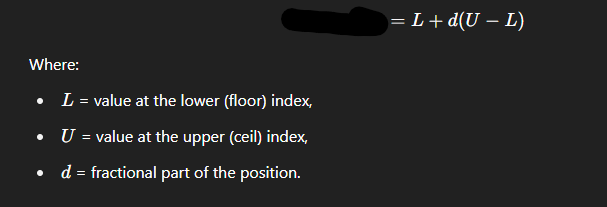
Second quartile, Q2 or median, position
One half multiplied by the number of values plus one
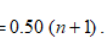
Third quartile, Q3, position
Three quarters multiplied by the number of values plus one
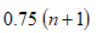
Percentile
K percent times the number of values plus one
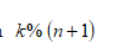
Z-scores
The value minus the mean
Divided by the standard deviation

Values from z-scores
Mean plus the z-score multiplied by the standard deviation

Interquartile range
Q3 - Q1
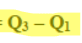
Outlier tests
Q1 - 1.5(IQR)
Q3 + 1.5(IQR)
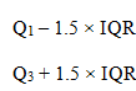
Within standard deviation
Mean minus standard deviation and mean plus standard deviation

Grouped standard deviation
The sum of the frequencies then times the midpoints subtract the mean
Squared
Divided by number of values (minus one if sample)
Square rooted

Stratified samples
Take the size of the group divided by the total number of people
Multiply by the desired sample size

Bell marks
Find z-score
Take the desired mean and add the desired standard deviation multiplied by the z-score
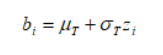
Midpoint
Lower limit plus upper limit
Divided by two