Regulatory interventions with externalities
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
What is the purpose of gov interventions with externalities?
To internalise externalities, so the price of the transaction will cover the cost of the externality.
Examples of govt. interventions
Smoking bans in public places
Age restrictions on gambling/ tanning beds/ alcohol/ drugs
Limit on CO2 emissions for new vehicles
Recycling directives for household appliances
Banning west wood for use in indoor burners
Fishing quotas to protect stocks from overfishing
Advantages of regulating activities with -ve externalities
- Act as a spur for business innovation to cut the level of carbon emissions
- More effective if demand is unresponsive to price changes
- They can be gradually toughened year by year, helping stimulate investment.
Costs of extra regulations on businesses
- High cost of enforcement/ administration of strict laws
- They can lead to unintended consequences (market failure)
- The cost of meeting regulations can discourage small businesses.
What are 3 negative externalities caused by chemicals and sewage leaked into rivers?
Health: risk of drinking polluted water leading to sickness, increased health costs
Nature: loss of biodiversity
Economic impact: wider cost to tourist businesses and impact on house prices
What are some interventions to curb river pollution?
Investment in new sewage infrastructure
Unlimited fines/ risk of prosecution
Pollution tax - internalises the externality
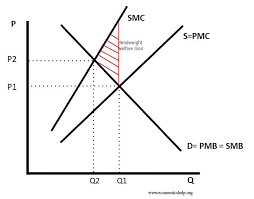
Diagram of this river pollution externality
Negative production externality
A carbon tax would shift the MPC leftward toward the MSC, internalising the externality and reducing the welfare loss.