Urine and diagnosis
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
What do pregnancy tests detect?
Hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hcG) - only found in pregnant woman
Monoclonal antibodies
Antibodies from a single clone of cells that are produced to target particular cells or chemicals in the body
Making monoclonal antibodies
Mouse injected w. hcG, so it makes its antibody
B-cells that make required antibody are removed from spleen of mouse and fused w. myeloma
Type of cancer cell that divides v. rapidly
Fused cell = hybridoma
Reproduced rapidly, so many B-cells making desired antibody
Antibodies collected, purified and used
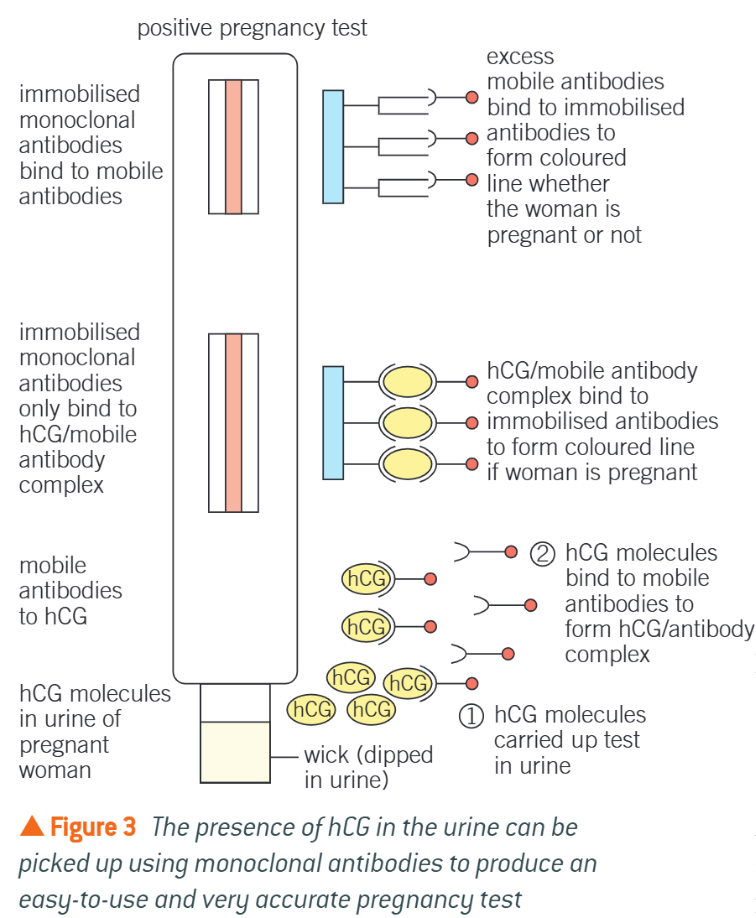
Stages in pregnancy test
Wick soaked in 1st urine passed in morning (highest hcG)
When urine applied to application area, hcG will bind to mobile monoclonal antibodies on beads
Forms hcG-antibody complex
Form coloured line if woman is pregnant
Urine moves up strip, carrying beads w. it
Reaches a window w. immobilised monoclonal antibodies
Binds to any mobile antibodies (control)
Pregnant = 2 lines
Anabolic steroids
Drugs that mimic the action of testosterone and stimulate the growth of muscles
Testing for anabolic steroids
As they are excreted in urine:
Tested for in urine using gas chromatography & mass spec
Urine vaporised w. known solvent & passed along tube
Lining of tube absorbs gases & analysed to give chromatogram that is read to show drugs present
Testing for drugs
1st sample may be tested by immunoassay, using monoclonal antibodies to bind to drug/breakdown prod.
If positive, run thru gas chroma / mass spec to confirm its presence