P2 : Electricity
1/130
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
How many circuit symbols are there?
14
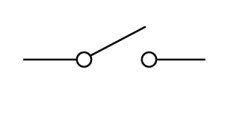
Name this symbol
Open switch
What does an open switch look like?
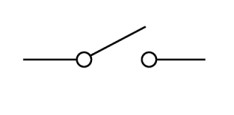
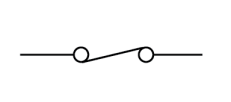
Name this symbol
Closed switch
What does a close switch look like?
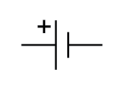
Name this symbol
Cell
What does a cell look like?
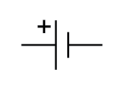
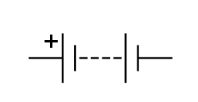
Name this symbol
Battery
What does a battery look like?
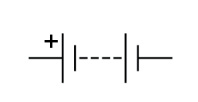
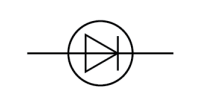
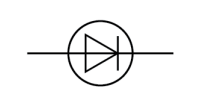
Name this symbol
Diode
What does a diode look like?
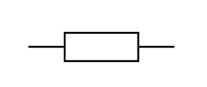
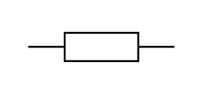
Name this symbol
Resistor
What does a resistor look like?
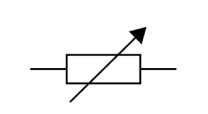
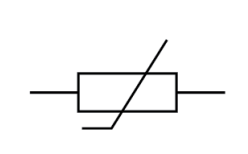
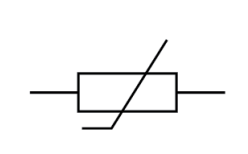
Name this symbol
Variable resistor
What does a variable resistor look like?
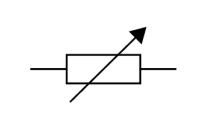
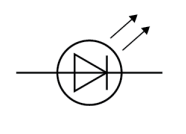
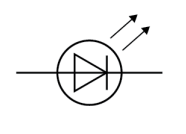
Name this symbol
LED
What does an LED look like?
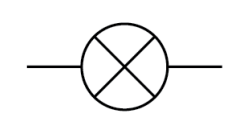
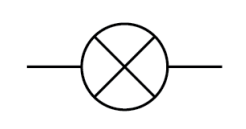
Name this symbol
Filament lamp
What does a filament lamp look like?
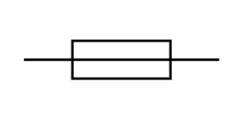
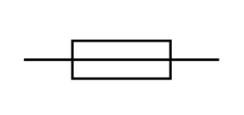
Name this symbol
Fuse
What does a fuse look like?
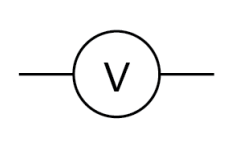
Name this symbol
Voltmeter
What does a voltmeter look like?
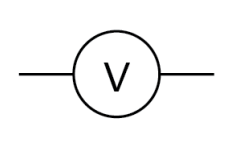
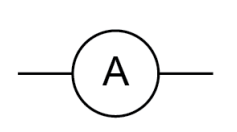
Name this symbol
Ammeter
What does an ammeter look like?
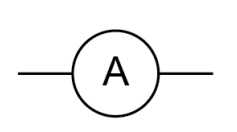
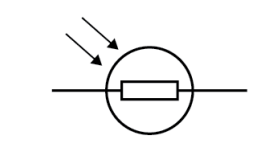
Name this symbol
Thermistor
What does a thermistor look like?
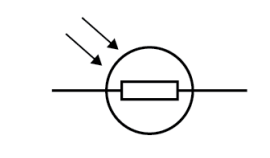
Name this symbol
LDR
What does an LDR look like?
What is current?
The rate of flow of charge
What is current measured in + with?
Measured in amps (A)
Measured with an ammeter
In a circuit what flows out of any power source?
Electrons
What is the flow of electrons called?
An electric current
What end does the conventional current flow from and to?
The positive end to the negative end
What is current represented as in a circuit diagram?
An arrow
What is the only way a current will flow in a closed circuit?
A source of potential difference
How does current behave in a series circuit?
Current is never used up, it is the same all the way around
Explain the energy transfer in a circuit
The power source contains chemical energy which is transferred to electrical energy and is carried by the current
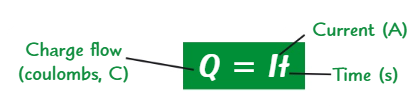
What is charge?
The total current that flows in a certain period of time
What is the equation for charge?
Q = It
What is potential difference also known as?
Voltage
What is potential difference?
The driving force that pushes the charge around
What is potential difference measured in + with?
Measured in volts
Measured with a voltmeter
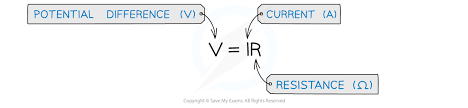
What is resistance?
Anything that slows the flow down
What is resistance measured in?
Ohms (Ω)
What is the equation for potential difference?
V = IR
Where should the ammeter be placed in regards with what you’re investigating?
Connected in series
Where should the voltmeter be placed in regards with what you’re investigating?
Added in parallel
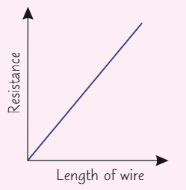
Explain how to investigate the factors effecting resistance (8)
Attach a crocodile clip to a thin wire level with 0cm on the ruler
Attach another crocodile clip the wire e.g. 10cm away from the first clip, record the length between the clips
Close the switch, the record the current through the wire and the pd across it
Open the switch, move the clip another 10cm along the wire, close the switch, then record the new length, current and pd
Repeat this for a number of different lengths of the test wire
Use R = V/I to calculate the resistance
Plot a graph and draw the line best of fit
If graph doesn’t have a positive correlation its a systematic error
What should the graph for investigating the length of the wire affecting resistance look like?
Give an example of an ohmic conductor
Wire
Describe the relationship between resistance and current in ohmic conductors
The resistance stays constant as the current changes
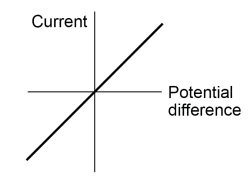
Describe the relationship between current and potential difference in an ohmic conductor (at a constant temperature) ?
They are directly proportional
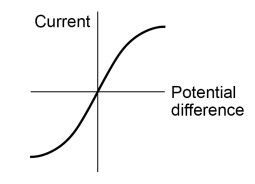
Describe the relationship between resistance and current in components such as filament lamps, diodes, thermistors and LDR’s
As current increases so does resistance
Explain why resistance is not constant in components such as filament lamps (2)
This is because when electric charge flows through the lamp some of the energy is transferred to the thermal energy store of the lamp which increases the temperature
An increase in temperature results in the increase of current (as particles gain more energy) which results in an increase in resistance
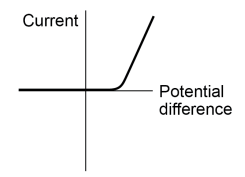
What does the resistance depend on for diodes? (2)
The direction of current
If the direction is reversed the resistance is very high
What does the current and potential difference graph in an ohmic conductor (at a constant temperature) look like
What does the current and potential difference graph in a filament lamp look like
What does the current and potential difference graph in a diode look like
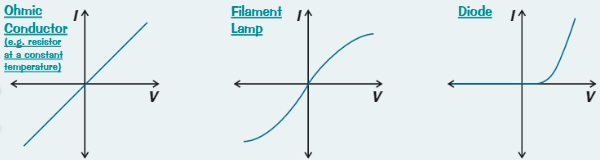
What are these graphs called?
I-V characteristics
Explain how to find out a components I-V characteristics (5)
Set up a test circuit with a battery, variable resistor, the desired component and the ammeter in series with a voltmeter in parallel with the desired component
Begin to vary the variable resistor which alters the current and pd
Take several readings from the ammeter and voltmeter to see how the pd across the component varies as current changes
Repeat this 2 more times and remove anomalies and calculate a mean to find the average
Plot a graph of current against pd
What does LDR stand for?
Light dependant resistor
What happens to resistance when its bright and dark in an LDR (2)
Bright → resistance decreases
Dark → resistance increases
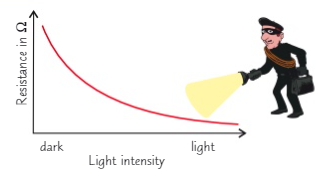
What are the 3 uses for an LDR?
Automatic night lights
Outdoor lighting
Burglar detection
What is a thermsitor?
A temperature dependant resistor
What happens to resistance when its hot + cold in a thermistor (2)
Hot → resistance decreases
Cold → resistance increases
What are the 3 uses of a thermistor?
Temperature detectors
Car engine temperature detectors
Electronic thermostats
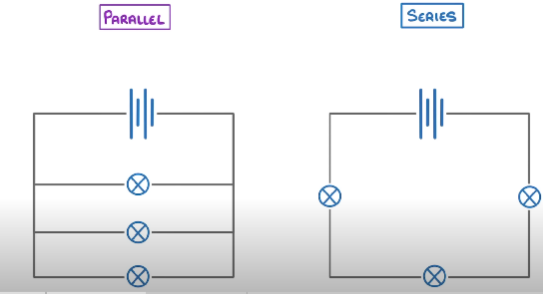
What are the 2 types of circuits?
Series
Parallel
In a series circuit if one component is removed or disconnected what happens?
The circuit is broken and all the components stop working
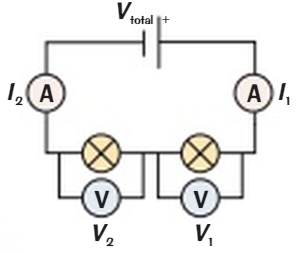
In a series circuit what is the behaviour of pd?
It is shared between components
What is the formula for pd in a series circuit?
Total V = V1 + V2 + …

In a series circuit what is the behaviour of current?
Current is the same through each component
What is the formula for current in a series circuit?
I1 = I2 = …

In a series circuit what is the behaviour of resistance?
The total resistance of 2 resistors is their resistances added up
What is the formula for resistance in a series circuit?
R = R1 + R2

In a parallel circuit if one component is removed or disconnected what happens?
Basically nothing
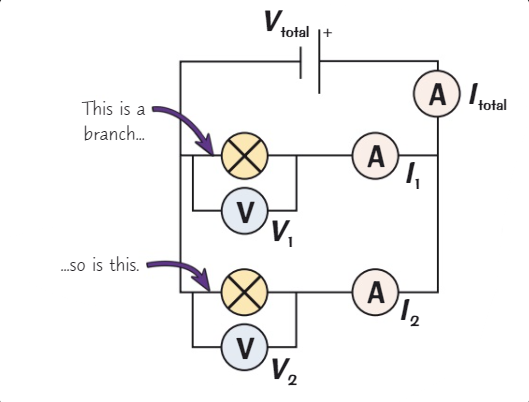
In a parallel circuit what is the behaviour of pd?
Pd is the same across all components
What is the formula for pd in a parallel circuit?
V1 = V2 = …

In a parallel circuit what is the behaviour of current?
Current is shared between branches
What is the formula for current in a parallel circuit?
I = I1 + I2 + …
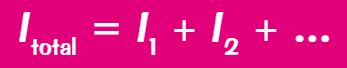
In a parallel circuit what is the behaviour of resistance?
With 2 resistors in parallel, their total resistance is less than the resistance of the smallest of the 2 resistors
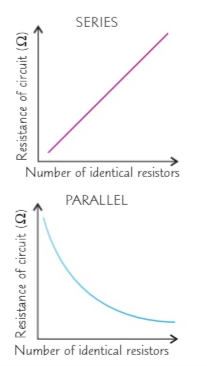
Why does adding resistors in series increases the total resistance whilst adding resistors in parallel decreases the total resistance?
In series when a resistor is added the current decreases (I1=I2=… ) which means the resistance increases
In parallel when a resistor is added the current increases because current has more pathways to go in when another loop has been added (I= I1+12+…) which means the resistance decreases
What are the 2 types of electricity supplies?
DC → Direct Current
AC → Alternating Current
What does current do in terms of DC + why?
Flow in one direction because they are produced by alternating voltages
What 2 things supplies DC?
Batteries
Cells
What does current do in terms of AC + why?
Constantly change directions because they are produced by direct voltages
What is supplied by AC?
The mains electricity
What is the pd of the mains electricity supply?
230V
What is the mains electric supply frequency?
50Hz
How many wires does the cable have which connects the mains supply into our homes?
3 wires
What are the 3 wires in our cables made out of?
A core of copper and an insulating coloured plastic coating
What are the 3 wires called and what colour are they?
Neutral wire → Blue
Live wire → Brown
Earth wire → Green + Yellow
What is the pd of the neutral wire?
0V
What is the job of the neutral wire?
It completes the circuit, where current normally flows through
What is the pd of the live wire?
230V
What is the job of the live wire?
Provides the alternating pd from the mains supply, where current normally flows through
What is the pd of the earth wire?
0V
When does the earth wire carry current?
If there is a fault
What is the job of the earth wire
For safety, stops the appliance from becoming live
Explain how if touched the live wire can give you an electric shock (3)
Your body and the earth are at 0V
If you touch the live wire (230V) a large potential difference is produced across your body and a current flows through you and into the earth
This causes an electric shock which could harm or even kill