Midterm I terms - biochem
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
metabolic pathway
one set molecule is converted step-by-step to other molecules
metabolite
any one of a single molecule involved in metabolism
metabolome
the total number of metabolites in a given cell, tissue, or organism
metabolomics
the study of all the metabolites as they interact in a given tissue, cell, or sample
functional groups
a group of atoms responsible for characteristic reactions of a particular compound
catabolism
exergonic breakdown of complex molecules in living organisms to form simpler ones together with the release of energy
anabolism
build up endergonic, the synthesis of complex molecules in living organisms from simpler molecules together with the storage of energy
L-amino acid
every single biological amino acid is this, it is one of two possible mirror images of the molecule with the amino group always being on the left side in a fischer projection
peptide bond
amide linkage between a carboxyl group and an amino group
C-terminus
carboxyl-terminal end of a polypeptide chain
N-terminus
amino-terminal end of a polypeptide chain
residue
a single unit that makes up a polymer such as an amino acid, polypeptide or protein
alpha helix
a common, tightly coiled, right-handed secondary structure in proteins, stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the carbonyl oxygen of one amino acid and the amide hydrogen of an amino acid four residues away
beta sheet
consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet
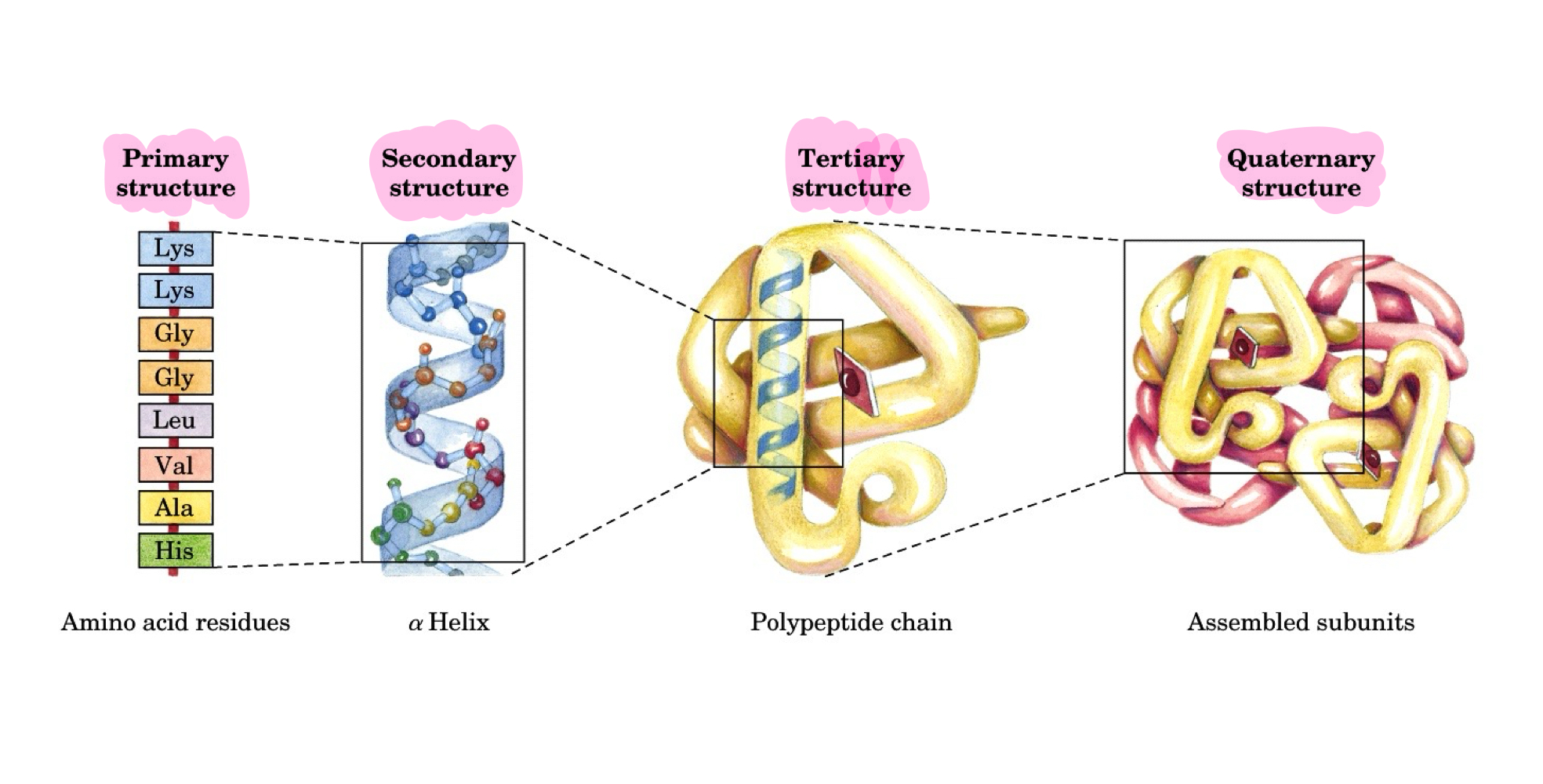
1,2,3,4 degree structures
1 is amino acid residues, 2 is alpha helix, 3 is polypeptide chain, 4 is assembled subunits
cofactor
a molecule other than an amino acid whose presence is essential for the activity of an enzyme
enzyme
a protein that acts as a biological catalyst, accelerating the rate of specific chemical reactions in living organisms
steady state
condition where concentrations of molecules or ions within a cell or organ remain relatively constant over time despite a continuous flow of materials and energy through biochemical pathways
substrate
a molecule or substance that an enzyme acts upon to catalzye a chemical reaction
product
molecules formed as a result of a chemical reaction
reaction
reaction coordinate diagram
activation energy (delta G+)
entropy reduction
ensures two molecules are sufficiently restricted so that they have a higher chance of finding each other
acid-base catalysis
acid or base accelerates a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process.
metal ion catalysis
act as catalysts by binding to reactants, orienting them, and/or stabilizing transition states
covalent intermediate
a transition state formed during an enzyme-catalyzed reaction where a covalent bond forms between the enzyme and the substrate
non-covalent bonds
interaction between atoms dues to electrostatic forces
ionic
complete transfer of electrons between atoms, typically a metal and non-metal
van der waals
weak electrostatic forces that attract neutral molecules to each other
hydrogen bond
electrostatic attraction between a proton in one atom and an electronegative atom in the other
hydrophobic
relation between water and nonpolar molecules that have a long chain of carbons that do not interact with water molecules typically
ligand
small molecule that binds to large molecule binding site (like a protein)
Kd
the dissociation constant for concentration of ligand bound to binding site
saturation
occurs when all available enzyme active sites are occupied by substrate molecules, preventing any further increase in reaction rate
fraction saturation (L/(L+Kd))
the concentration of ligand that is bound to the binding site
active site
the region of eznyme that binds to a protein or other substance during a reaction
competitive inhibitor
competes with the substrate for binding to an active site
chymotrypsin
a selective protease (this enzyme only cleaves proteins that have correctly oriented aromatic R groups)
catalytic triad
3 different amino acids/R groups that are at the right place at the right time, an example of the three members of a catalytic triad is serine, proton acceptor, and a third member of the triad that helps the acceptor be a little more charged (ser, his, asp are the three this is talking about)
hydrophobic pocket
helps selectively bind and cleave peptide bonds with aromatic amino acids
oxyanion hole
stabilizes the transition site (tetrahedral intermediate) giving lower activation energy
Michaelis-menton equation
this equation tells us how the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction changes as the substrate concentration changes
Vmax
the maximum rate of an enzymatic reaction when the enzyme is fully saturated with substrate
Kcat
the turnover number, the maximum number of substrate molecules an enzyme can convert to product per active site per unit of time when the enzyme is saturated with substrate
Km
the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is half of the maximum reaction rate (Vmax)
myoglobin
constant K, one subunit/monomeric, hyperbola, found in skeletal and cardiac muscles, oxygen storage
hemoglobin
sigmoidal curve, K is not constant/cooperative binding, tetrameric subunit, binds and releases oxygen
sigmoidal/cooperative binding
the binding of one substrate/subunit has an impact on the binding affinity for other subunits of the same ligand
allosteric enzyme
proteins that regulate their activity by binding effector molecules at sites separate from the active site, causing conformational changes that alter enzyme function
sigmoidal isotherm
a type of isotherm that exhibits an S-shaped curve
hill coefficient
describes the degree of sigmoidal behavior, never observed something of over 4
allosteric inhibitor
a molecule that binds to an enzyme at a site other than the active site, altering the enzymes shape and preventing it from binding to its substrate effectively
allosteric activator
binds to the enzyme at a site other than the active site, increasing the enzymes activity
chorismate mutase
substrate of chorismate and product of prehenate. Chorismate mutase is an example of a simple allosteric enzyme
Lineweaver-Burke plot
a graphical representation of enzyme kinetics derived from the michaelis-menten equation that helps analyze the constant Km and maximum reaction velocity Vmax
Gibbs free energy
the energy available to do work at a constant temperature and pressure
enthalpy (deltaH)
heat
entropy (deltaS)
order, number of states something can occupy
deltaG knot
deltaG
the change in free energy
Keq
spontaneous
phosphoanhydride bond
ATP, ADP, AMP, P-P
Pi
hydrolysis
dehydration condensation