11. Carotid Duplex
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What transducers does Carotid Duplex uses?
High frequency linear array 7-9 MHz.
What is the sample volume for Carotid Duplex?
1 - 1.5mm.
What is the doppler angle for Carotid Duplex?
45 - 60 degrees. Never above 60.
Dopper angle must be what to the flow and positioned how to get a accurate velocity calculation?
Dopple angle must be parallel to the flow and midstream/center.
Carotid Duplex in B-mode: Sag and Trans must demonstrate what?
Demonstrate presence/absence/severity of plaque.
Carotid Duplex in Color: Looking for?
Turbulent patterns/Aliasing.
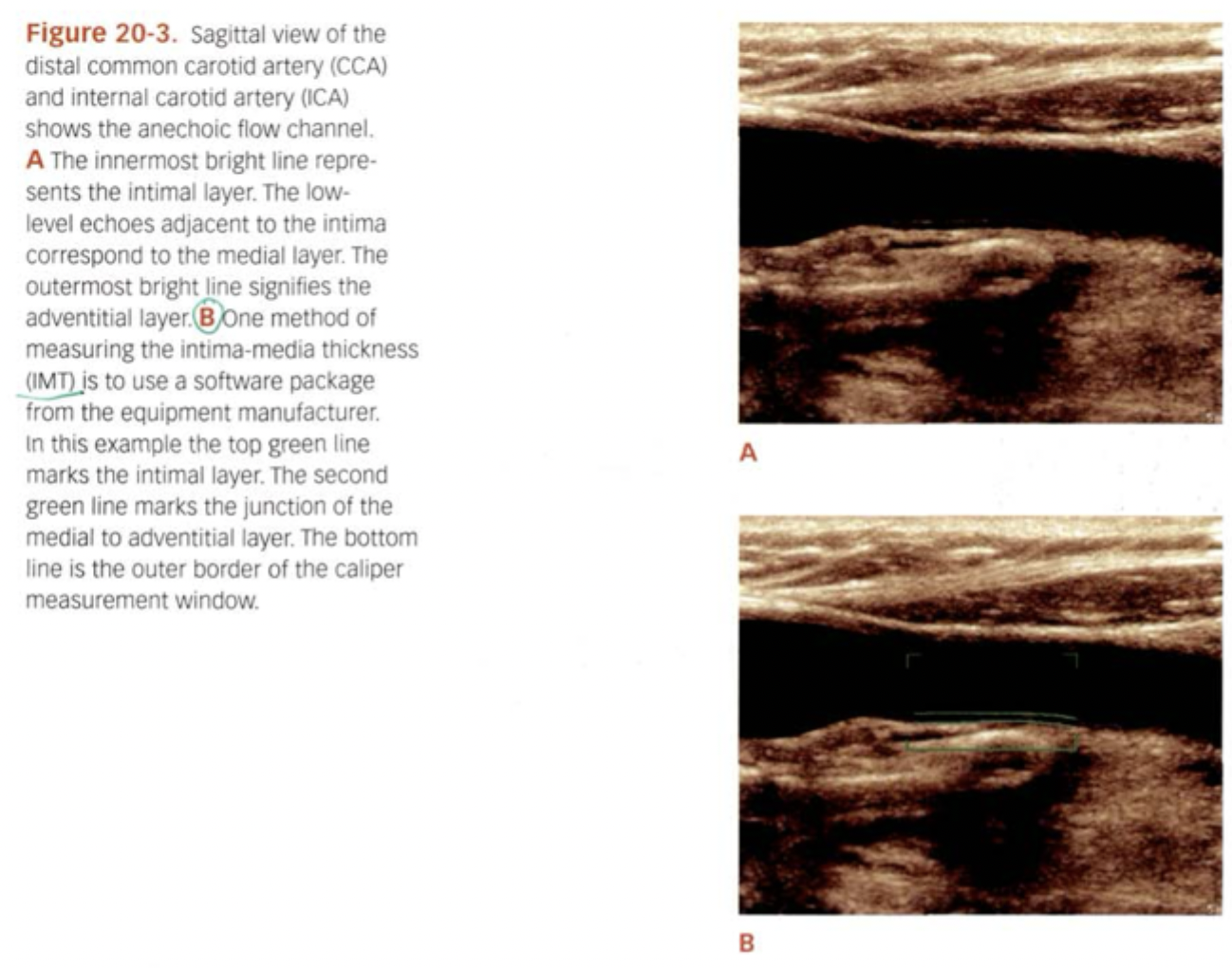
What does IMT stand for? What is it? Greater than what = Intimal thickening?
Intima media thickness. Predictor for cardiovascular disease. Greater than 0.9mm = Intimal thickening.
What are the 6 types of plaque classification?
Fatty
Fibrous/Homogeneous
Complex/Heterogenous
Calcified
Ulcerative
Intraplaque Hemorrhage
Thrombosis - Acute will be sonographically hypoehoic or hyperechoic? Small or Large caliber?
Hypoechoic. Large caliber.
Chronic occlusion - Increase or decrease vessel size? Hypoechoic or Hyperechoic? What type of pattern?
Decrease vessel size. Hypoechoic. Thumping pattern.
Guidelines for determining or estimating % diameter stenosis. PSV Greater than 125 cm/s indicates?
Hemodynamic significant stenosis.
Guidelines for determining or estimating % diameter stenosis. EDV Less than 140 cm/s indicates?
50 - 79% Diameter Reduction.
Guidelines for determining or estimating % diameter stenosis. EDV Greater than 140 cm/s indicates?
80 - 99% Diameter Reduction.
Guidelines for determining or estimating % diameter stenosis. Absent PSV, EDV?
Occluded.
What does NASCET stand for?
North America Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trials.
How to get the NASCET?
Highest ICA PSV divided by Distal CCA. If ICA/CCA ratio is 4.0 or greater = 70% or Greater Diameter Reduction in ICA.
What does Fatty plaque look like?
Hypoechoic along wall.
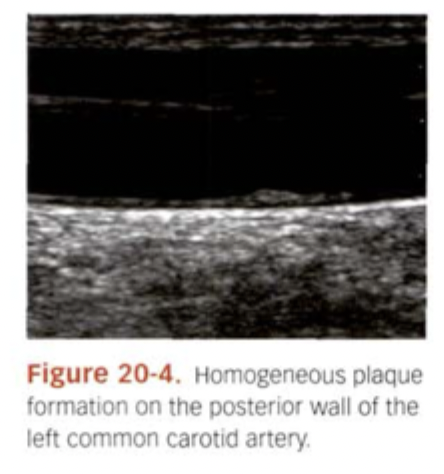
What does Fibrous/Homogeneous plaque look like?
Low to Med level echoes. Overall smooth, even.
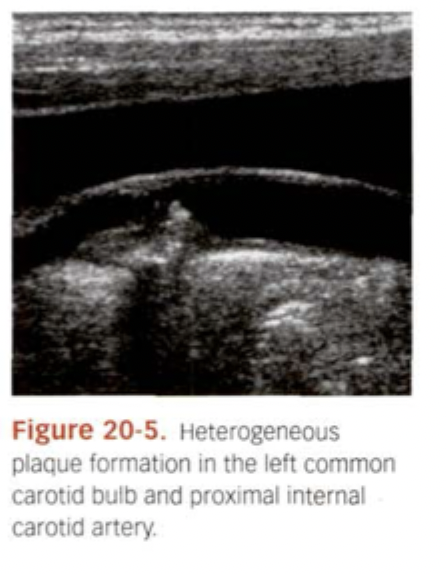
What does Complex/Heterogeneous plaque look like?
Mixed. Low/Medium/High level echoes all within.
What does Calcified plaque look like?
All Hyperechoic with posterior shadowing.
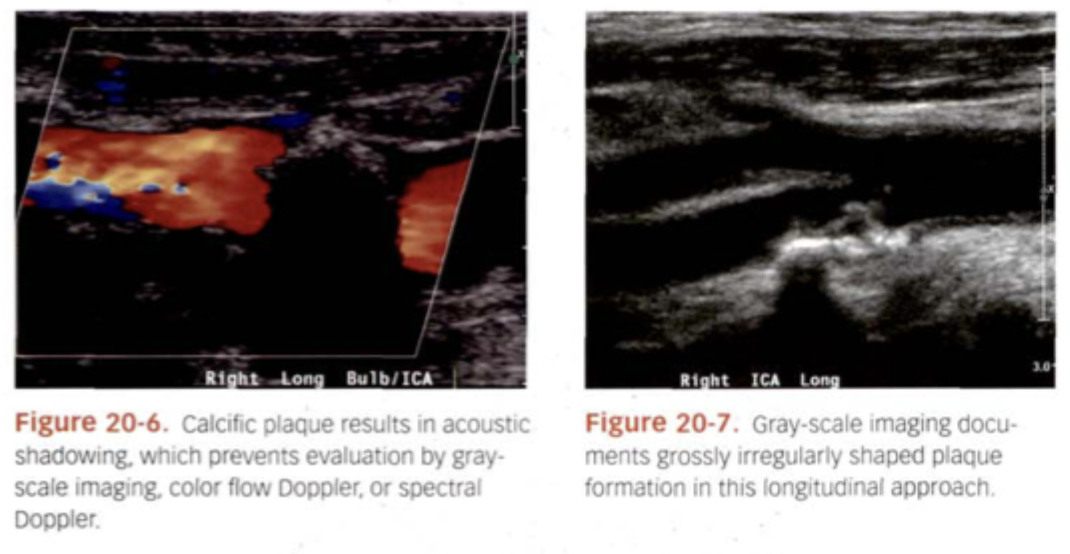
What does Ulcerative plaque look like?
Crater Like.
What does Intraplaque Hemorrhage plaque look like?
Oval Anechoic area within the plaque.
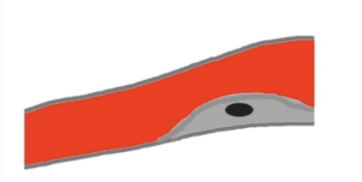
What are reasons for accelerated flow not related to disease?
High cardiac output => Bilateral and throughout.
Decrease blood viscosity => Bilateral and throughout.
Tortuous vessels.
Compensatory flow changes (collaterals).
What are ways you can underestimate stenosis?
Prox Stenosis.
Poor Cardiac Output => Bilateral and throughout.
Congestive Heart Failure.
What are indirect indications of the presence of disease?
Abnormally high resistance.
Absent Diastolic, Distal Occlusion.
If possible occlusion found, use power doppler to evaluate for string sign = near total occlusion.
Dampened Tardus Parvus like pattern.
Prox Disease if unilateral.
Poor cardiac output if bilateral.
Oscillating or helical pattern (low velocity and to-fro) means?
Brain death.
What is Subclavian Steal? Patient VBI symptoms?
Proximal Subclavian/Brachiocephalic obstruction or occlusion causing “steal” of blood from vertebral. Patient may have VBI symptoms with UE Ischemia symptoms and brachial pressures with Greater than 20mmHg difference. Lower pressure on same side as disease.
Which side is Subclavian steal most commonly found?
Left side.
If retrograde caudal flow in vertebral artery indicates?
Occlusion of ipsilateral Prox Subclavian or Brachiocephalic.
If there is bidirectional vertebral flow = ? This is also known as?
Stenosis of Ipsilateral Prox Subclavian or Brachiocephalic. Pre-Steal.
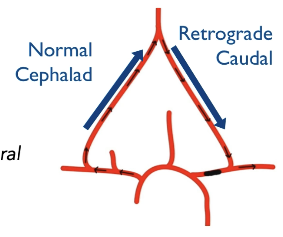
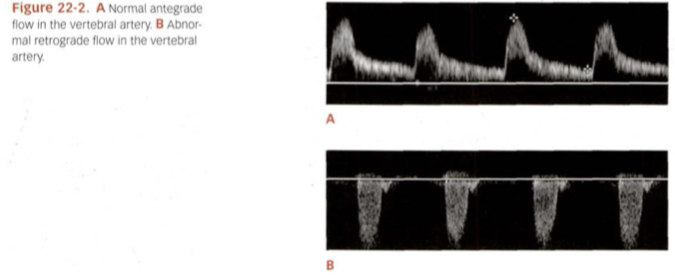
What type of flow, resistance going which direction for A?
Normal antegrade flow, low resistance going cephalad.
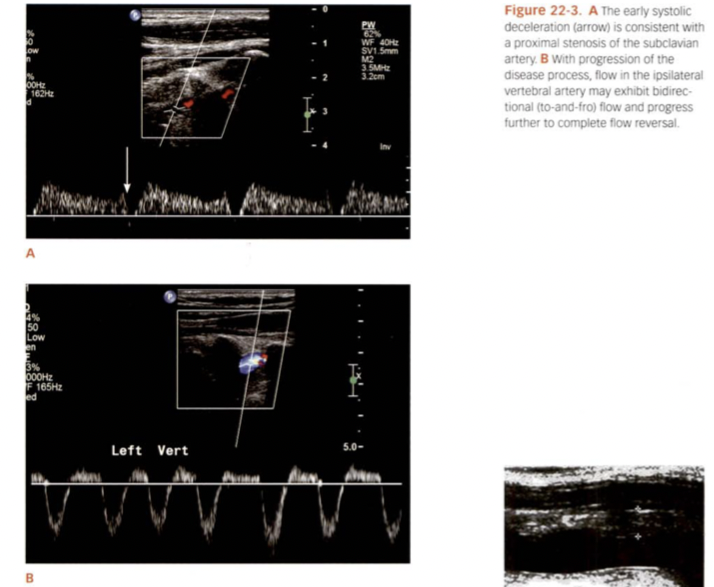
Both of these indicate what of the subclavian artery? Is it a complete steal or not?
Stenosis of subclavian artery but not a complete steal. Eventually will become a complete flow reversal.
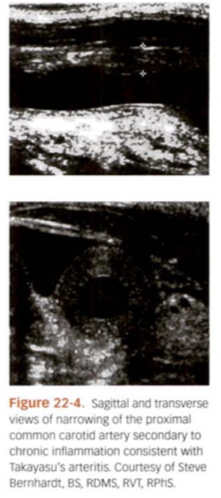
What is Takayasu Arteritis? Who does it affect? AKA? What is sono findings?
Inflammatory disease that affects larger vessels such as Aorta, Subclavian, maybe CCA. Affects usually younger women. AKA “Pulseless disease”. Sono appear like “Donut” vessel. Vessel wall diffusely inflamed.
What is Temporal Arteritis? What does patient usually complain of?
Inflammation of superficial temporal artery. Patient typically complain of headaches. Sono findings appear like “halo” inside vessels.

Intraoperative uses what type of probe? Why are these studies conducted? How is the study conducted, process?
Very high frequency 12-15 MHz “hockey stick” probe. When they are going to perform a endarterectomy. Hockey stick is inserted into surgical opening and goes right on top of vessel.
During carotid endarterectomy what are some acute defects?
Stricture of suture line - Stitches might pull the vessel wall too tight. Can make the artery narrower than it should be, then it’s like a kink in a hose and reduces blood flow.
Intimal flaps - can get a small flap of tissue peeling up inside the vessel after surgery. Flap can stick into blood flow path and cause turbulence, blockage, or clot formation.
Platelet aggregation - can clump together on surgical site, clot can block the artery or break off and cause stroke.
Residual plaque - Leftover plaque can narrow the artery and continue to cause problems with blood flow.
What are some post procedure surveillance?
Immedialtey post op - Thrombosis / Dissections.
6 - 24 months - Neointimal Hyperplasia.
Post stenting - Stented vessels have normally higher velocities. Can’t use same criteria as regular vessels. Up to 225 cm/s is considered WNL.
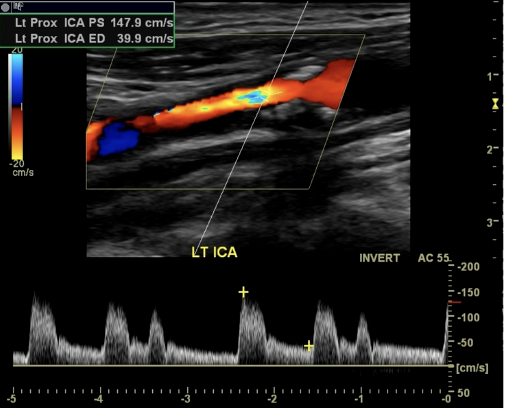
What 4 things does this image show?
Surface Irregularity
Post Stenotic Jet
Spectral Broadening
50 - 79% Diameter Reduction
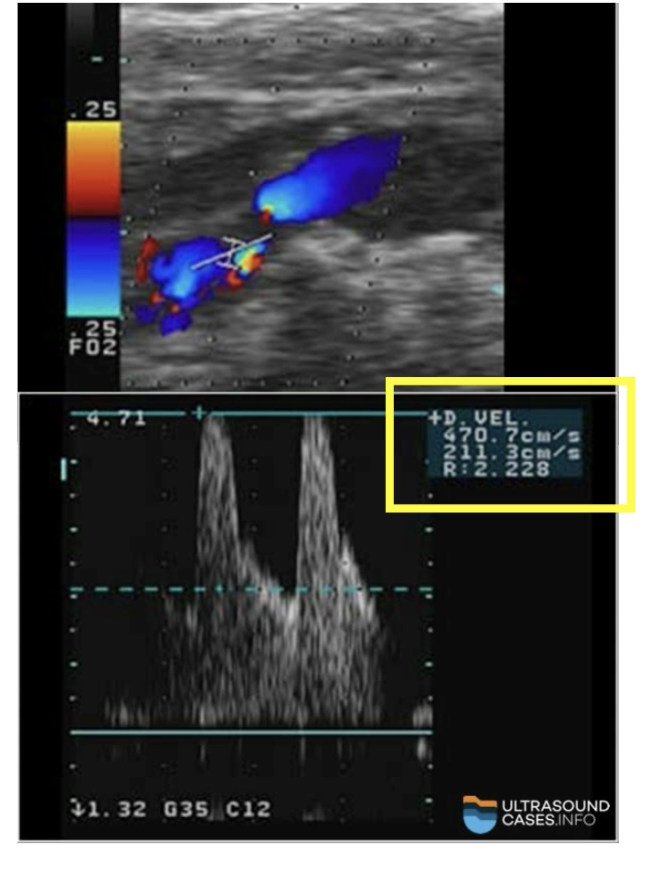
How much diameter reduction?
EDV Greater than 140 cm/s
80 - 99% Diameter Reduction
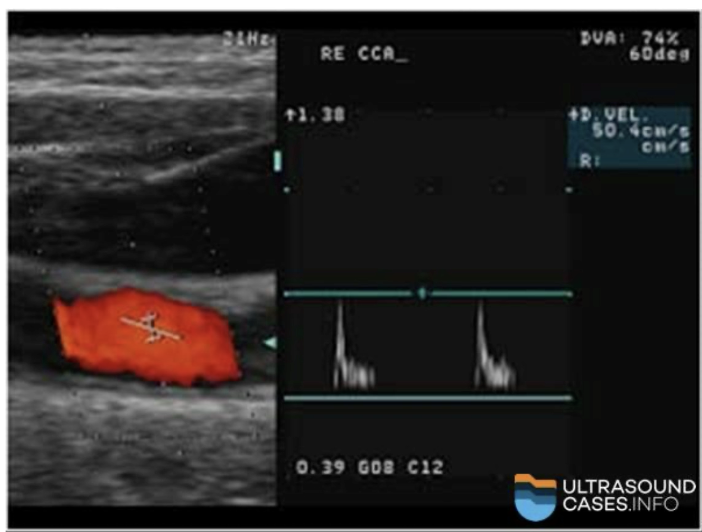
What 4 things does this image show?
Absent EDV
Distal Obstruction = ICA occlusion
Abnormally High resistance waveform = Disease is distal
No diastolic flow = Distal occlusion