Lecture # 12 | Cooperation and Conflict
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Conflict
When the fitness interests of two individuals are different
Cooperative
When one individuals’s behaviors benefits another
Selfish
+ effect on actor
- effect on recipient
Spiteful
- effect on recipient
- effect on actor
Mutalistic
+effect on actor
+effect on recipient
Altruistic
-effect on actor
+effect on recipient
Cheaters
Individuals that benefit from the action of others without providing benefits to them in return
What occurs if a cheater has high fitness in a population of cooperators?
A mutation that causes individuals to cheat will spread and cooperation can collapse
ex: slime mold evolution under lab conditions
Why do individuals exhibit traits that increase the fitness of other individuals (rather than focusing all of their energy on improving their own fitness) ?
1. Group selection
2. Direct benefits (byproducts)
3. Reciprocity
4. Kin selection
Group selection
Variation in reproduction success among groups
group selected traits are beneficial to the groups that bear them
relatively rare
Direct Benefits (byproduct)
Individuals help others because they ultimately gain direct benefit from their cooperative behavior
Initial action is a selfish one, but cooperation is a byproduct
ex: cooperation in herds to protect from individual predation
Reciprocity
Individuals take on a cost to benefit Y, and Y in turn reciprocates that benefit to X
ex: vampire bats rely on giving to one another in hope they will be helped in need
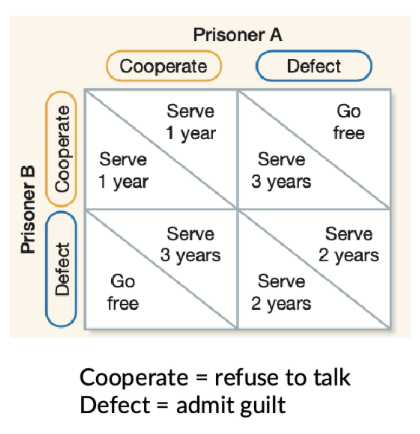
Prisoner’s dilemma
A model to predict the conditions under which reciprocity is favored
each of two individuals will do best by acting selfishly but if they both act selfishly, they will do worse than if they both cooperate
Repeated interactions can favor cooperative behavior
Altruism
Cooperation with no direct benefit for the cooperator
ex: sterile worker bees help others in the hive and do not breed themselves
Kin selection
Selection on alleles that promote cooperative behavior with other individuals that share the same alleles (identical by descent)
unlike other forms of cooperation, kin selection can only evolve among members of the same species
inclusive fitness
logic is formalized in Hamilton’s rule
Direct fitness
The fitness of an allele that included its positive effect on the bear of that allele
Indirect fitness
The positive effect on related individuals that also share the same alleles
Inclusive fitness
The combination of both direct fitness and indirect fitness
Hamilton’s rule
An allele that causes an altruistic behavior will spread if the following condition is met
rB>C
r= relatedness
B= fitness benefit to the recipient
C= the fitness cost to the actor
Inclusive fitness of an allele
rB-C
How to calculate relatedness
Find the common ancestor
Count the generations
Apply the formula r= (1/2)^n, where n is the number of generations between the two individuals
Account for shared family members and multiple by 0.5
How related are first cousins?
Common ancestors are grandparents
2 generations between first cousins through common grandparents
1/2²= ¼
Account for shared grandparents by multiplying by 0.5
Related by 1/8
Conditions needed for spiteful alleles to spread
The actor be less closely related to the recipient than to an average member of the population
harming the recipient enhances the fitness of other individuals in the population that are more closely related to the actor
Eusociality
When some individuals do not reproduce and instead rear the offspring of others
In systems with haplodiploidy, what is r between a sister and a brother
0.25, as the brother shares 100% of his genes with his mother and none of the father
share 50% of their mothers genes and 0% of their fathers
In a system with haploiddiploidy, what is the relatedness between two sisters
0.75, as their share 100% of their fathers and 50% of their mothers
Sexually antagonistic selection
When a trait that is favored to increase in one sex is favored to decrease in the other
Traits like:
Mating frequency
Parental car
How is mating frequency a sexually antagonistic trait?
Males often benefit from mating when females dont
How is parental care a sexually antagonistic trait?
Selection favors offspring abandonment in the parent that pays the greater cost
Infanticide
Killing the young of its own species
sometimes an individuals fitness is enhance by killing the young of its own species
Male infanticide is common in mammals
Examples of infanticide
Male lions that take over a pride will kill all the infants in the pride to speed up the time to sexual receptivity in the females of the pride
Female mice will kill some of their young when resources are scare to save energy for reproduction
Parent-offspring conflict
When what is best for a parent conflicts with what is best for an offspring
selection favors offspring that take more resources from their parents, even if that decreases the number of other offspring they have
as direct fitness is gained → indirect fitness is lost
Human embryos have evolved to extract more resources from mothers than mothers are favored to give
Is natural selection always at the individual level and above?
No, there can be conflict at the genetic level → genic selection
selfish DNA can spread in populations even if it decreases survival or reproduction
Segregation distorters
Mutations that cause an allele to have a greater that 50% chance of inheritance
an example of selfish DNA that can spread in populations
Transposable elements
Short sequences of DNA that are able to insert additional copies of themselves in the genome
an example of selfish DNA that can spread in populations
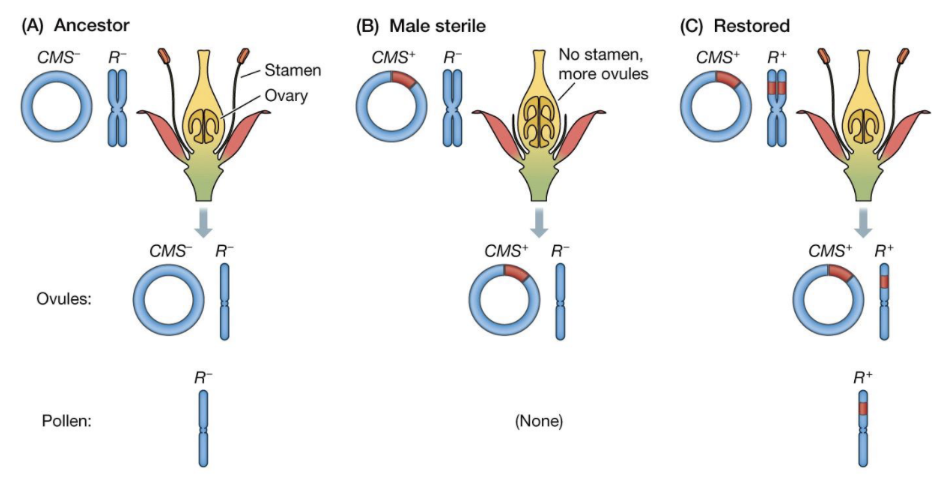
Cytoplasmic male sterility
When a mutation inherited through the cytoplasm causes sterility
an example of selfish DNA that can spread in populations