Geography GCSE Edexel B - Topic 7: People and the Biosphere
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
what are biomes
large scale global ecosystems
what determines what type of biome forms?
climate
describe climate of taiga
cold, dry

3 features of taiga climate
short summers long winters, low precipitation less than 500mm, lots of daylight in summer little in winter

how does the taiga climate affect soil
cold dry climate means tree needles decompose slowly, so soil is thin, nutrient poor and acidic, some areas have frozen ground
how does the taiga climate affect animals?
few animal species compared to tropical forests as less food and cold climate, black bears, wolves, elk, eagles

how does the taiga climate affect plants?
most trees evergreen, coniferous trees like pine and fir are common also mosses and lichen

describe tundra climate
cold dry

3 features of tundra climate
low temperatures, low precipitation less than 250mm mostly snow, continuous daylight in summer little in winter

what does the soil in the tundra have?
a layer of permafrost
vegetation in tundra
mosses, grasses, low shrubs

animals in tundra
arctic hares, foxes, mosquitoes, birds

describe the climate of temperate forests
mild, wet

3 features of the climate in temperate forests
four distinct seasons, high rainfall (up to 1500mm anually) all year round, short days in winter long days in summer
how does the temperate forests climate affect soil?
plants lose leaves in autumn quick decomposition, soils thick and nutrient rich
how does the temperate forests climate affect plants?
mild, wet climate supports fewer plant species than tropical forests more than boreal forests, broad-leaved trees, shrubs, undergrowth
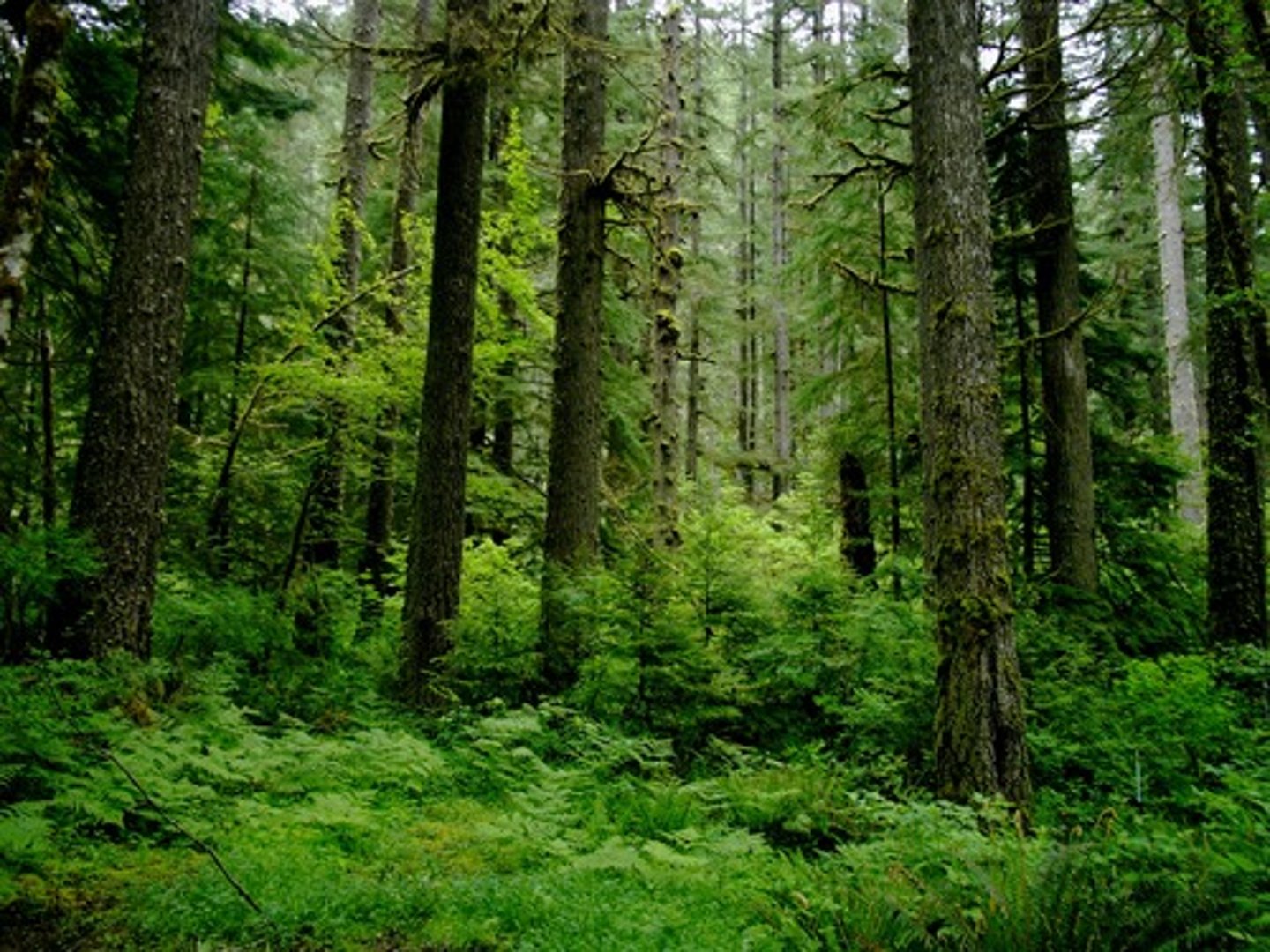

how does the temperate forests climate affect animals?
mild climate and range of plants provide food and habitats for mammals, birds and insects

describe climate of temperate grassland, 3pts
hot summers and cold winters, 250-500mm annually mainly in late spring and early summer, amount of light varies through year
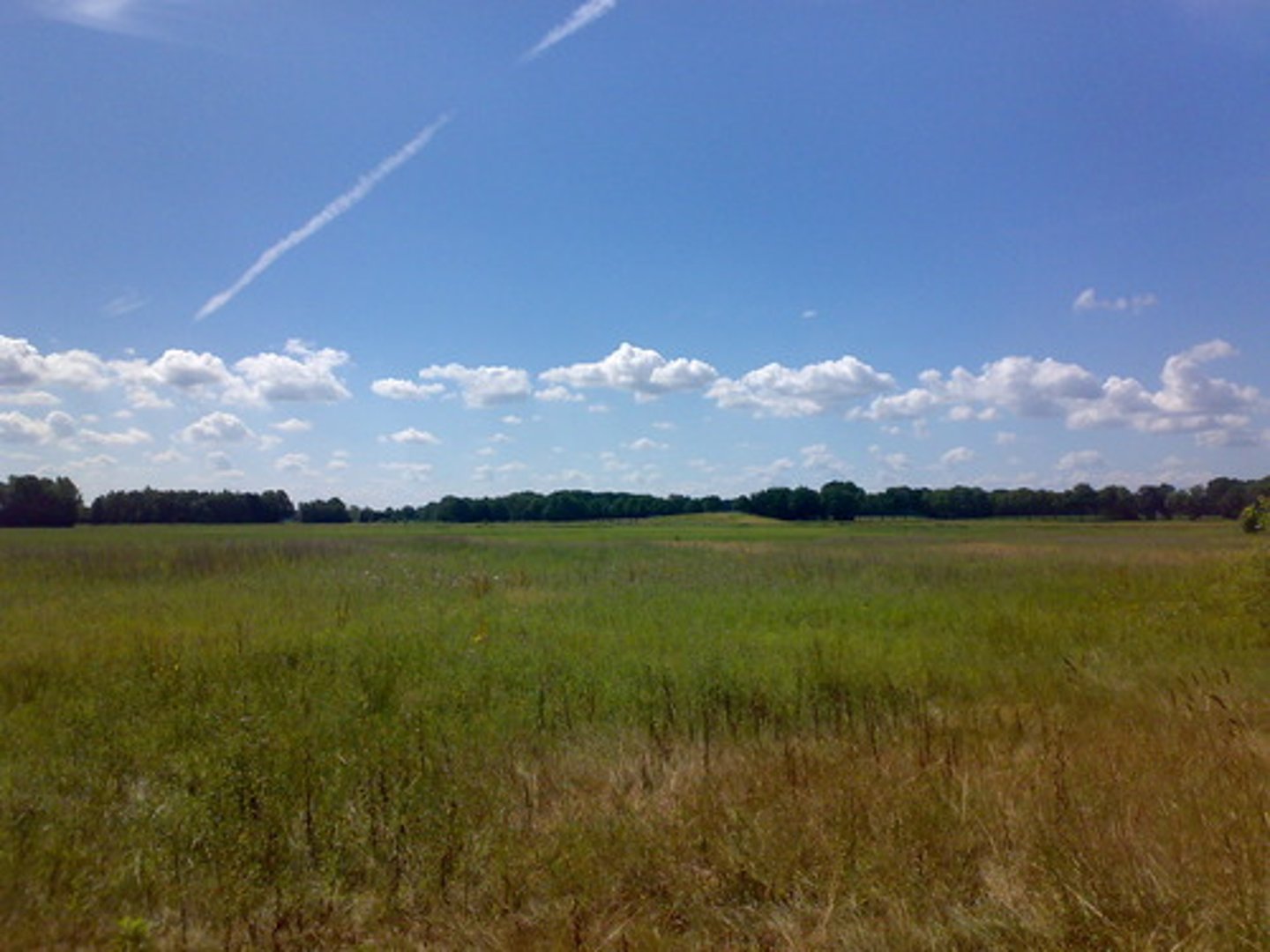

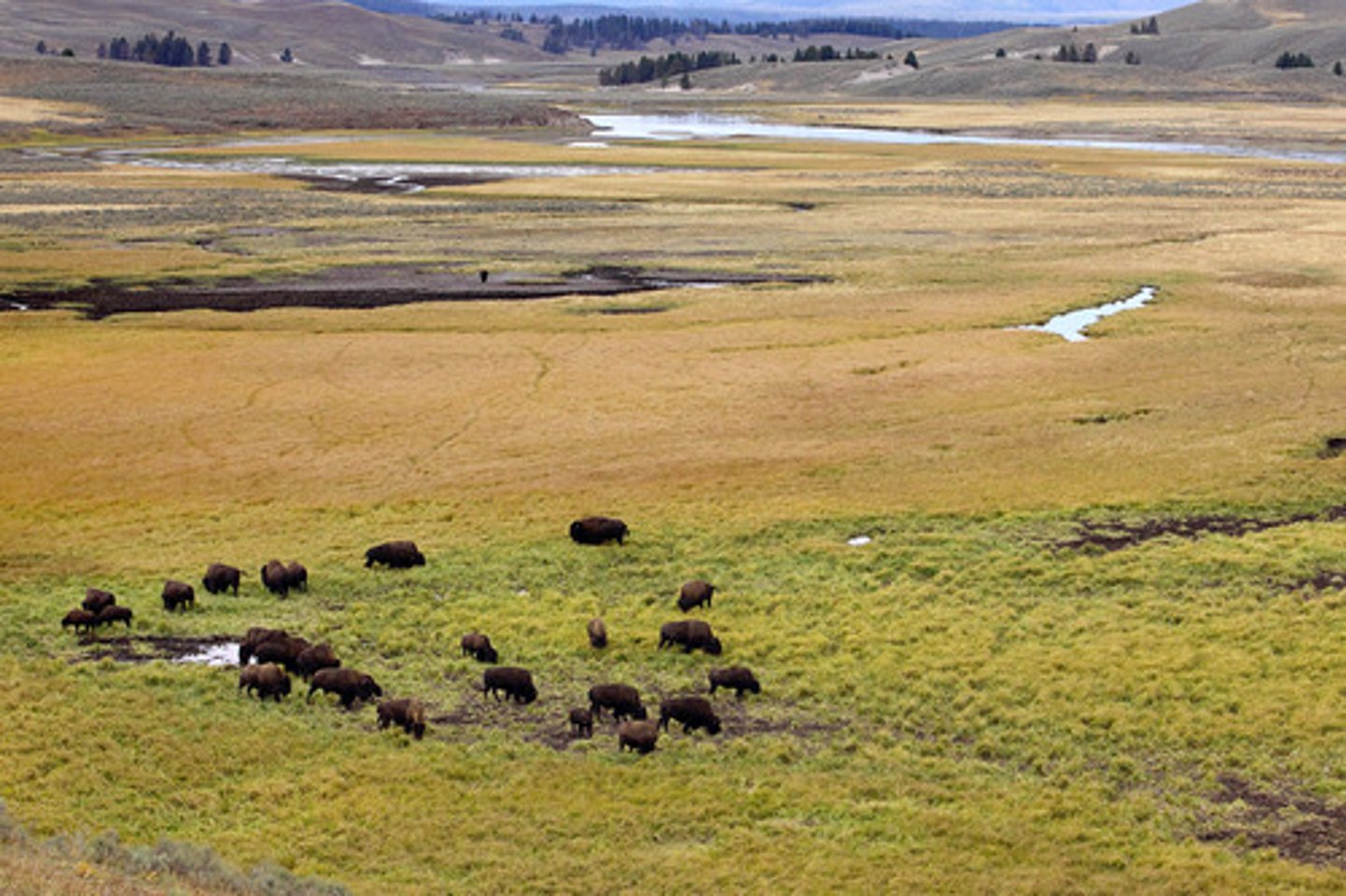
what do temperate grasslands mainly consist of? 3pts
dominated by grasses and small plants and have few trees, fewer animal species than tropical grasslands, bison, wild horses, mole rats

3 features of the climate of deserts
low rainfall less than 250mm, hot temperatures range from hot during day cold at night, more daylight during summer than winter

how does the desert climate affect soil
sparse vegetation so little leaf litter, dry climate so organic matter slow to decompose, thin and nutrient poor

describe climate of tropical grassland
low rainfall, distinct wet and dry season, highest temperature before wet season, lowest temperature after
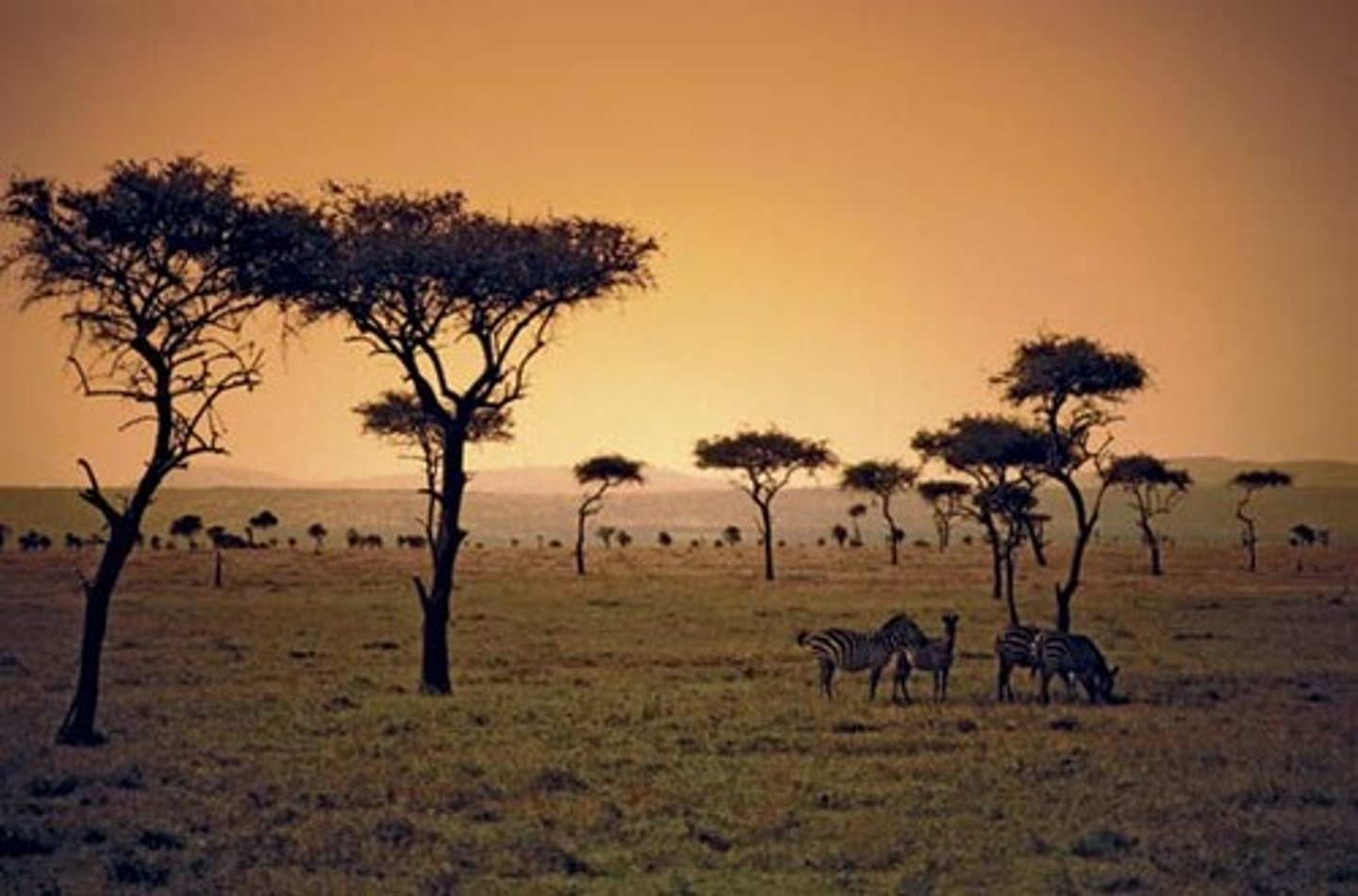

what do tropical grasslands mainly consist of
grass, shrub and small plants, scattered trees
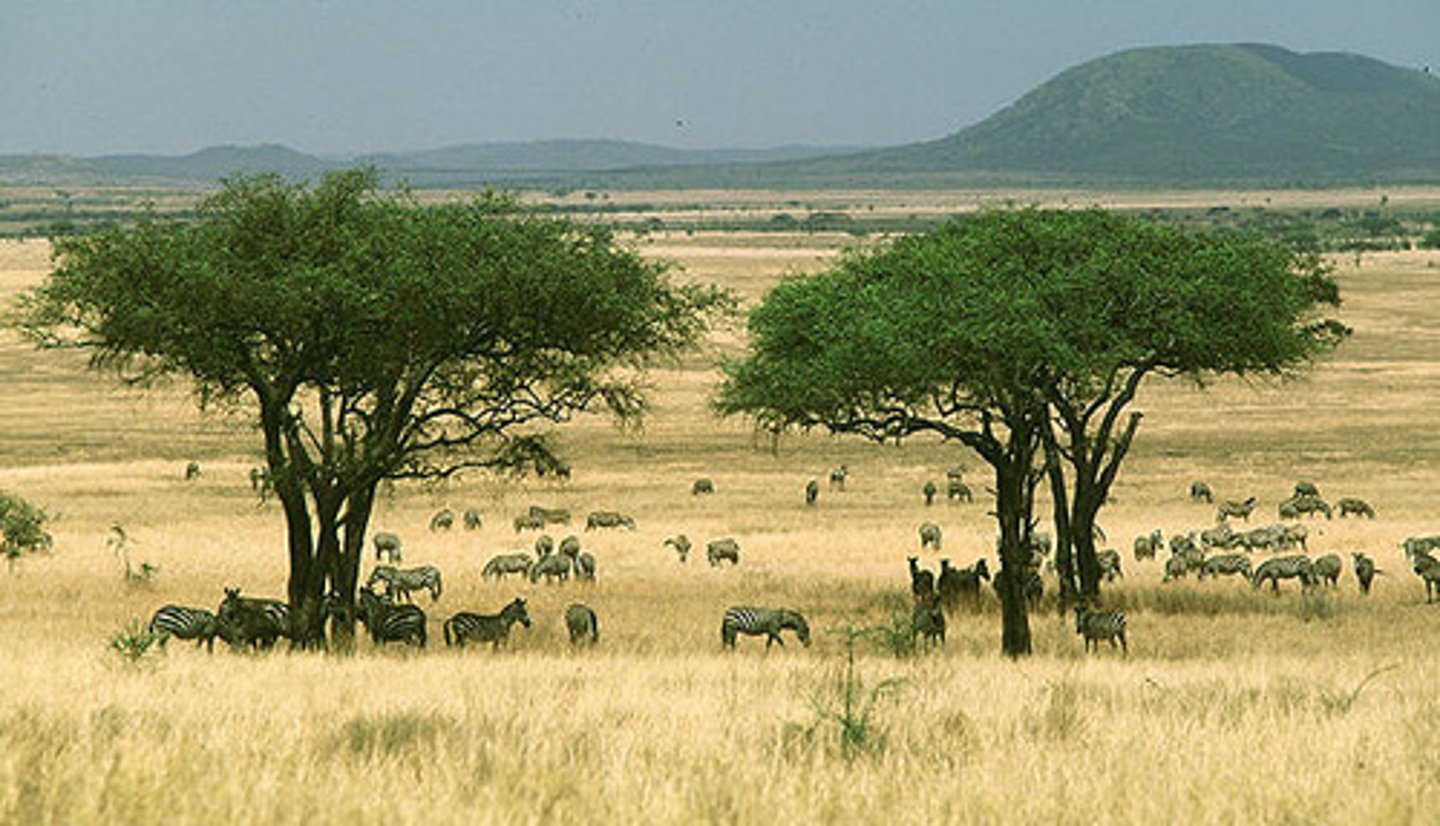

climate of tropical forests (3)
hot, wet, same all year
how much rainfall in tropical forests
2000mm per year
how does the tropical rainforest climate affect plants?
most trees evergreen, plants grow quickly and are adapted to take in maximum light
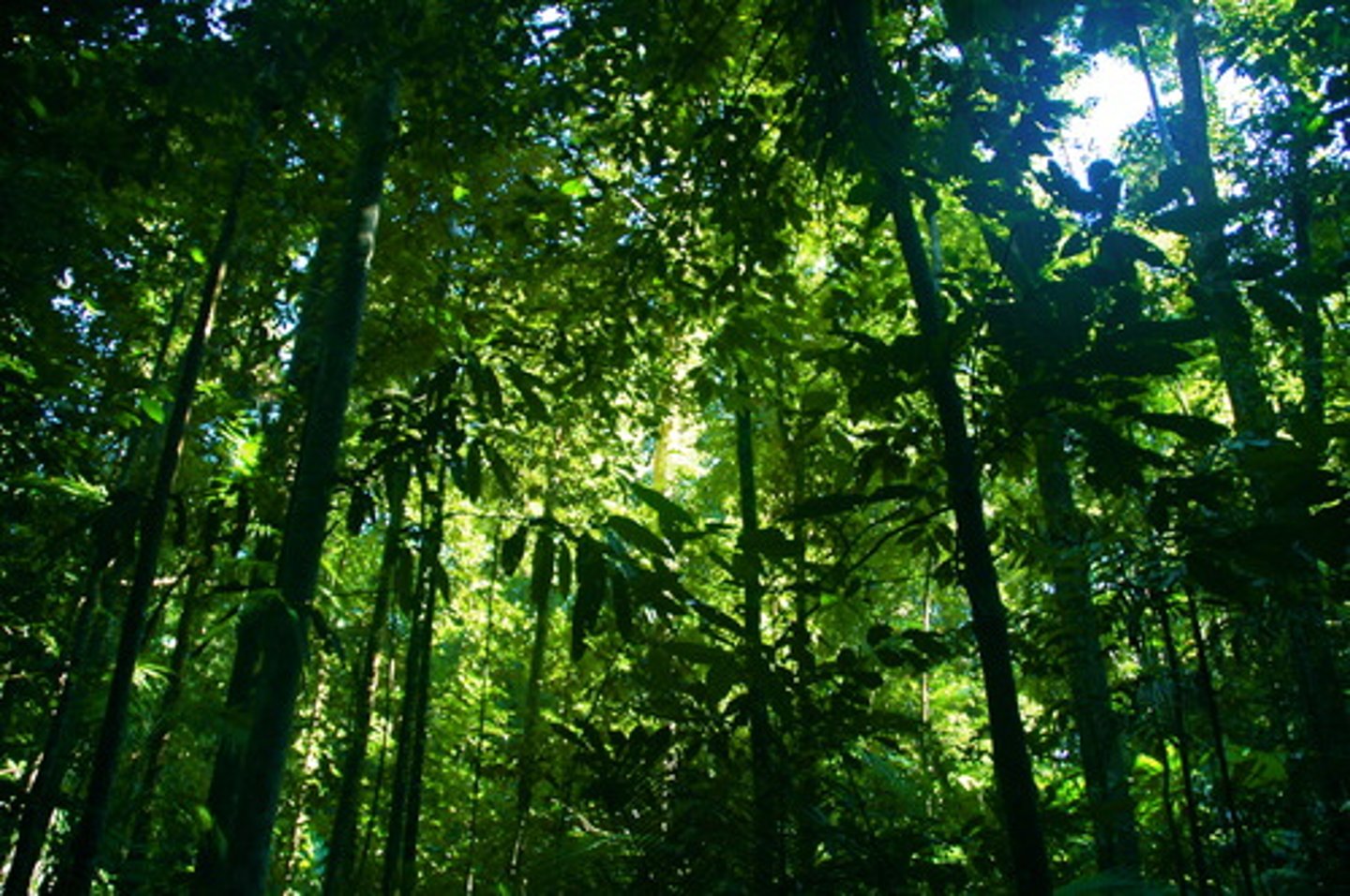

how does the tropical rainforest climate affect animals?
dense vegetation provides lots of food and different habitats so high biodiversity (gorillas, sloths, jaguars, anacondas)

how does the tropical rainforest climate affect soil?
due to heat plants grow quickly and decompose quickly so constant supply of nutrients
what is permafrost and what does it do?
permanently frozen ground, stops water from draining away
4 things other than climate that affect biome distribution
altitude, rock type, soil type, drainage
what two groups are part of biotic components
flora, fauna
4 examples of abiotic components
soil, water, rock, atmosphere
3 examples where biotic and abiotic components interact
water availability affects plants, amount of vegetation affects soil, organisms cause biological weathering
What are the four local factors that affect biomes?
altitude, rock type, soil type, drainage
How does soil type affect biomes?
• Sandy soil is pale and dry as it drains well so plants must be drought tolerant, which are known as xerophytes.
• Clay soil is orange, water does not drain well and holds nutrients well so lots of plants can grow.
How does drainage affect biomes?
If rocks are impermeable, surface water and rain cannot drain away. Waterlogged soils prevent growth of trees so peat bogs may form.
How does altitude affect biomes?
• Temperature goes up about 6 degrees Celsius every 1000m
• Grasses replace forest biomes because the slopes are steeper and there is higher precipitation. Soils are thin so cannot support wide biodiversity, this is known as altitudinal zonation.
How does rock type affect biomes?
When rocks weather, they release nutrients so the softer they are, the faster they erode so the more nutrients are released into the soil impacting what grows there. Also some are permeable some are impermeable and some create acidic soils when they break down, some create more acidic soils
what is the biosphere
all parts of the earth that are occupied by living organisms
4 types of goods indigenous people get from living organisms
food, medicine, building materials, fuel
3 sectors in which humans are exploiting the biosphere
energy, water, minerals
How do humans exploit energy resources?
large areas of forests cuts down to clear land for growing crops (used for biofuel) / or to build coal mines/power stations
some areas flooded due to HEP dams
drilling for oil and gas in tundra. (pipelines melting permafrost) damaging a carbon sink
How do humans exploit water resources?
increasing population= increased water demand
rivers, aquifers are over exploited, eg Sahara desert.
this damages the biosphere as plants and animals no longer have enough water.
how do humans exploit mineral resources?
minerals are required for building, scientific instruments, electrical appliances etc
often extracted by mining = deforestation and toxic chemicals washed into streams and rivers
killing wildlife + biodiversity
open cast mining removes large areas of lands and opens carbon sinks
2 ways the biosphere helps to control the gases in the atmosphere
plants take in CO2 and give off oxygen, animals take in oxygen and give off CO2
4 reasons why it is important to maintain a balance of gases in the atmosphere
most organisms need oxygen, increased CO2 leads to global warming, increased CO2 makes oceans acidic, some CO2 is needed to keep the earth warm
3 ways the biosphere is important for maintaining soil nutrients and structure
roots and animals (worms) spread nutrients through soil, roots hold soil together and prevent erosion, vegetation intercepts rain to prevent leaching
what is another name for the water cycle
hydrological cycle
what is the water cycle
movement of water between land, bodies of water and the atmosphere
outline the water cycle
it rains - water runs to rivers and sea - evaporates - clouds form
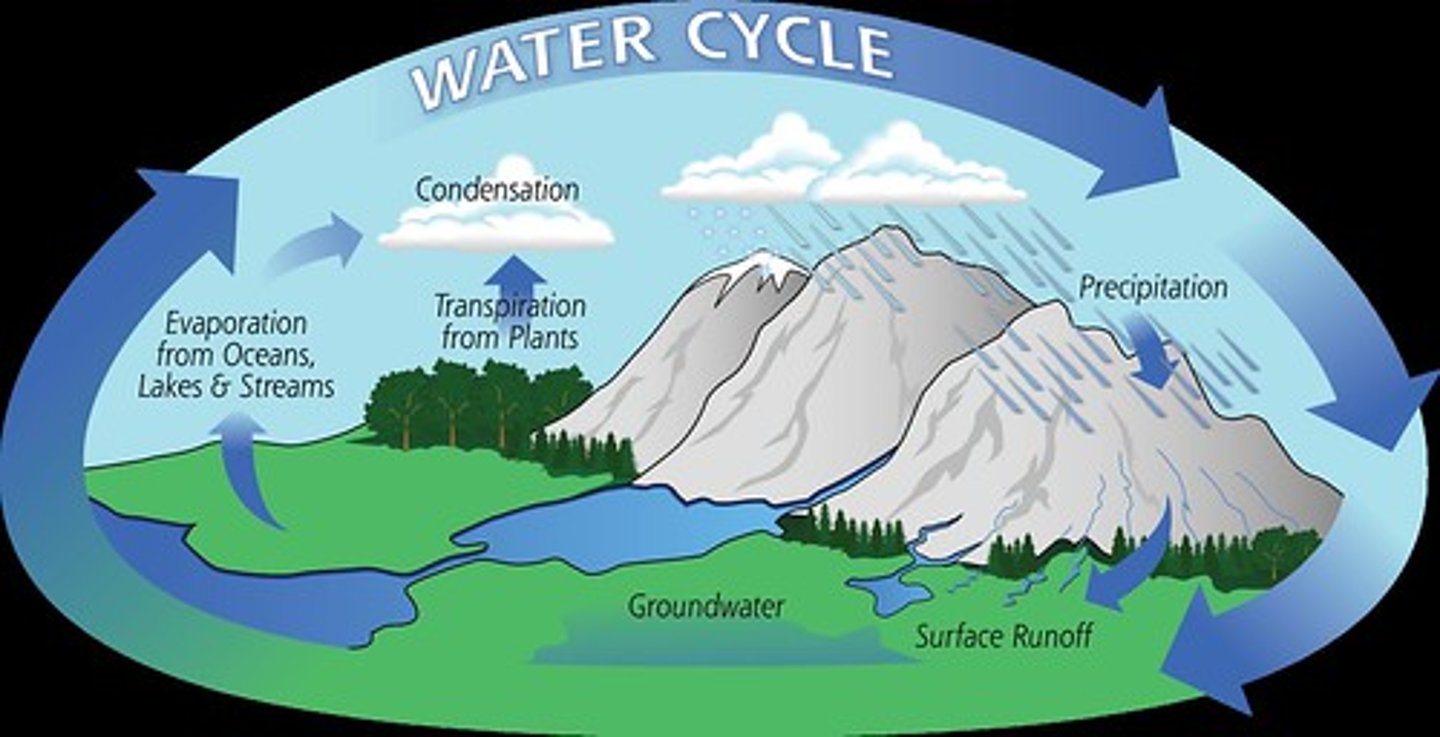
how does the biosphere control the water cycle
water taken up by plants so prevents rivers flooding, plants help to regulate global water cycle by storing water and releasing it into the atmosphere slowly
What are the natural resources?
Water, food and energy
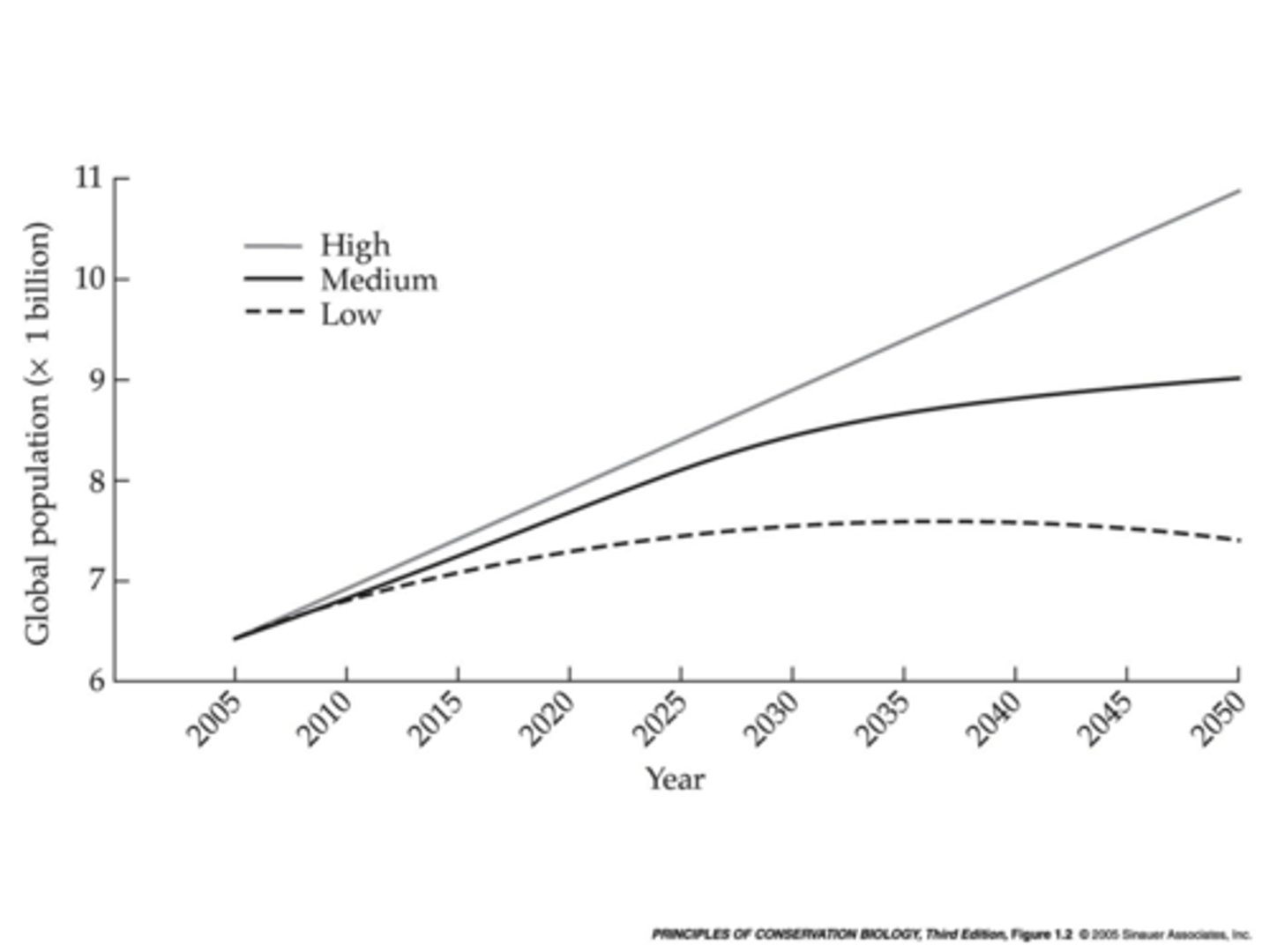
what are population projections
predictions of how many people there will be in the world in the future
If the population reached this how would this affect the demand for natural resources?
It would increase the demand
The UN has made 3 predictions about population growth. What does the highest one predict?
shows the world's total population reaching 14 billion people
What are the three things which will increase the demand for natural resources?
Rising global population, Rising affluence (wealth) and increasing urbanisation.
Why would rising affluence increase demand for natural resources?
Because more wealth means more luxury items which need more energy and water.
Why would increasing urbanisation increase demand for natural resources?
If there are more towns, there are fewer biomes so there are fewer resources available.
Also, the people coming into urban areas are from rural areas which are usually farms and if there are less farms, less food is being produced so there is increased demand.
What is the Malthusian theory?
As the population grows, it will overtake the food supply where there will be a crisis when the population will drop.
What is Boserup's theory?
humans will always find a way to increase food production using technology to feed growing populations