Cardiovascular
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/57
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
1
New cards
Fun Facts
1) heart is a hollow muscular organ roughly the size of your fist (+) and weighs less than 1-lb
2) fully developed about 8 weeks after conception (begin beating at 4 weeks)
3) every minute the heart pumps our entire supply of blood through the body. about 5 quarts
4) women have faster heart beats than men
5) normal pulse is 70 heart beats per minute
2) fully developed about 8 weeks after conception (begin beating at 4 weeks)
3) every minute the heart pumps our entire supply of blood through the body. about 5 quarts
4) women have faster heart beats than men
5) normal pulse is 70 heart beats per minute
2
New cards
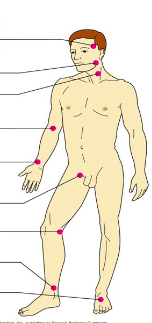
Pulse points
Label:
-Dorsalis pedis artery
-brachial artery
-popliteal artery
-temporal artery
-radial artery
-posterior tibial artery
-carotid artery
-femoral artery
-facial artery
-Dorsalis pedis artery
-brachial artery
-popliteal artery
-temporal artery
-radial artery
-posterior tibial artery
-carotid artery
-femoral artery
-facial artery
3
New cards
Function
To deliver O2 and nutrients and to remove CO2 and other waste products
4
New cards
Heart anatomy- Location
-Medially in the thoracic cavity
-Pointed tip (apex) directed toward left hip
*the apex is 9cm to the left of the midsternal line
-Pointed tip (apex) directed toward left hip
*the apex is 9cm to the left of the midsternal line
5
New cards
Heart anatomy- coverings
1) outer coverings
- pericardium- a double membrane, protective sac around the heart
visceral pericardium- inner layer
parietal pericardium- outside layer
-serous fluid fills the space between pericardium layers
2) inner coverings
-walls of the heart are made of 3 layers of tissue
outer layer--> epitheal tissue... called epicardium
middle layer--> cardiac muscle tissue... called endocardium
inner layer--> epitheal tissue... called endocardium
- pericardium- a double membrane, protective sac around the heart
visceral pericardium- inner layer
parietal pericardium- outside layer
-serous fluid fills the space between pericardium layers
2) inner coverings
-walls of the heart are made of 3 layers of tissue
outer layer--> epitheal tissue... called epicardium
middle layer--> cardiac muscle tissue... called endocardium
inner layer--> epitheal tissue... called endocardium
6
New cards
Heart anatomy- chambers
1. Atria- the top chambers (receiving)
2. Ventricles- bottome chambers (the actual "pumps" in the heart)
2. Ventricles- bottome chambers (the actual "pumps" in the heart)
7
New cards
Valves
1) Bicuspid valve (Mitral valve) - left side
- Atrioventricular - between atria and ventricles
2) Tricuspid vlve - right side
- Atrioventricular - between atria and ventricles
3) Pulmonary Semilunar valve
- Semilunar valves - between ventricle and artery
4) Aortic Semilunar valve
- Semilunar valves - between ventricle and artery
#1 and #2 prevent backflow into atria
#3 and #4 prevent backflow into ventricle
-held in place by chordae tendineae - "heart strings"
- Atrioventricular - between atria and ventricles
2) Tricuspid vlve - right side
- Atrioventricular - between atria and ventricles
3) Pulmonary Semilunar valve
- Semilunar valves - between ventricle and artery
4) Aortic Semilunar valve
- Semilunar valves - between ventricle and artery
#1 and #2 prevent backflow into atria
#3 and #4 prevent backflow into ventricle
-held in place by chordae tendineae - "heart strings"
8
New cards
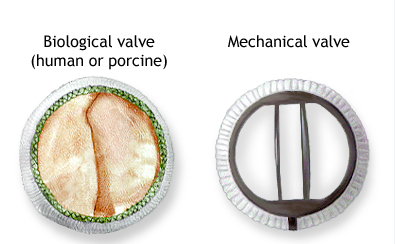
Biological valve (human or porcine) and Mechanical valve
-Porcine - pig -Bovine - cow
-Biological needs future replacement and does NOT require blood thinners (10-15 years)
-Mechanical lasts forever BUT requires use of blood thinners
-Biological needs future replacement and does NOT require blood thinners (10-15 years)
-Mechanical lasts forever BUT requires use of blood thinners
9
New cards
Vessels
1. Vena cavas- superior and inferior
-brings deoxygenated blood from the body tissues back to the heart
2. Pulmonary arteries
-carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart and to the lungs
3. Pulmonary veins
-brings oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart
4. Aorta
-carries oxygenated blood away from the heart and to the body tissues
-size of a garden hose
*arteries carry blood away from the heart
*veins carry blood tot he heart
-brings deoxygenated blood from the body tissues back to the heart
2. Pulmonary arteries
-carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart and to the lungs
3. Pulmonary veins
-brings oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart
4. Aorta
-carries oxygenated blood away from the heart and to the body tissues
-size of a garden hose
*arteries carry blood away from the heart
*veins carry blood tot he heart
10
New cards
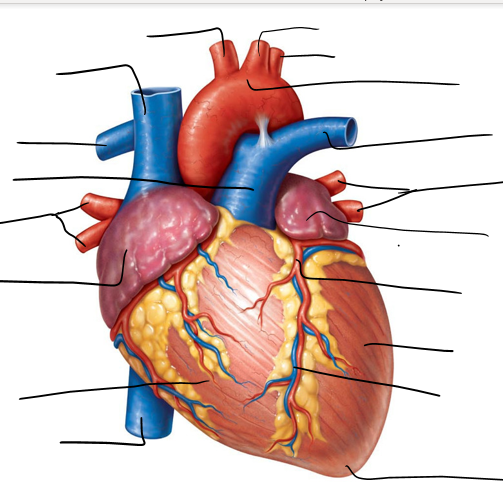
Exterior heart diagram
Label:
-Apex
-Right ventricle
-Left coronary artery
-Left common carotid artery
-Superior vena cava
-inferior vena cava
-Brachiocephalic artery
-right pulmonary artery
-left subclavian artery
-left ventricle
-right atrium
-left atrium
-right pulmonary veins
-ascending aorta
-pulmonary trunk
-aortic arch
-left pulmonary artery
-left pulmonary veins
-great cardiac vein
-Apex
-Right ventricle
-Left coronary artery
-Left common carotid artery
-Superior vena cava
-inferior vena cava
-Brachiocephalic artery
-right pulmonary artery
-left subclavian artery
-left ventricle
-right atrium
-left atrium
-right pulmonary veins
-ascending aorta
-pulmonary trunk
-aortic arch
-left pulmonary artery
-left pulmonary veins
-great cardiac vein
11
New cards
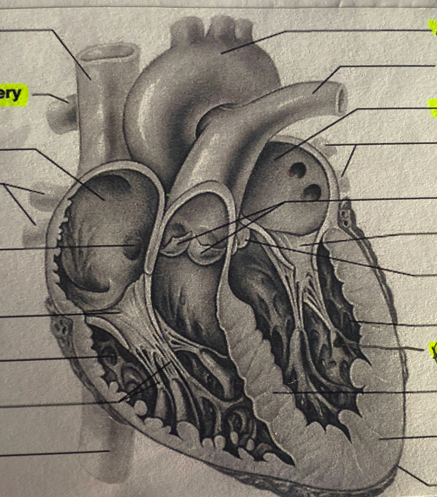
interior heart diagram
Label:
-Aorta
-Mitral valve
-left atrium
-left pulmonary artery
-tricuspid valve
-left pulmonary artery
-aortic semilunar valve
-left ventricle
-papillary muscle
-interventricular septum
-myocardium
-apex
-inferior vena cava
-chordae tendineae
-right ventricle
-right pulmonary artery
-fossa ovalis
-right pulmonary veins
-right atrium
-bicuspid valve
-superior vena cava
-Aorta
-Mitral valve
-left atrium
-left pulmonary artery
-tricuspid valve
-left pulmonary artery
-aortic semilunar valve
-left ventricle
-papillary muscle
-interventricular septum
-myocardium
-apex
-inferior vena cava
-chordae tendineae
-right ventricle
-right pulmonary artery
-fossa ovalis
-right pulmonary veins
-right atrium
-bicuspid valve
-superior vena cava
12
New cards
Circulation-Pulmonary
path
-right side of heart --> lungs --> left side of heart
function
-carry blood to the lungs for gas exchange
*right ventricle = pulmonary pump
-right side of heart --> lungs --> left side of heart
function
-carry blood to the lungs for gas exchange
*right ventricle = pulmonary pump
13
New cards
Circulation- systemic
path
-left side of heart --> body tissues --> right side of heart
function
-supply oxygen and nutrients rich blood to all body systems
*left ventricle = systemic pump
-left side of heart --> body tissues --> right side of heart
function
-supply oxygen and nutrients rich blood to all body systems
*left ventricle = systemic pump
14
New cards
Circulation-cardiac
-blood in heart chambers does not nourish the myocardium
-heart has its own nourishing circulatory system
-coronary arteries
-cardias veins
-heart has its own nourishing circulatory system
-coronary arteries
-cardias veins
15
New cards
the path of the blood through the heart
Vena cavas
right atrium
tricuspid valve
right ventricle
pulmonary semilunar valve
right and left pulmonary arteries
lungs
right and left pulmonary veins
left atrium
mitral valve
left ventricle
aortic semilunar valve
aorta
body tissues
right atrium
tricuspid valve
right ventricle
pulmonary semilunar valve
right and left pulmonary arteries
lungs
right and left pulmonary veins
left atrium
mitral valve
left ventricle
aortic semilunar valve
aorta
body tissues
16
New cards
Heart surgery- heart-lung machine
Cardio-pulmonary bypass
17
New cards
Heart surgery- body cooling
More time for surgery without causing brain damage (56 degrees.... approx. 4-6 hours)
18
New cards
Heart surgery- KCI injections
Paralyzes the heart muscle, temporarily
19
New cards
heart surgery- artificial heart transplant
Dr. robert jarvik began in mid 70s; success in 1982
20
New cards
Heart physiology
Intrinsic conduction system (nodal system)
21
New cards
Nodes
specialized tissue that functions as both muscle and nervous tissue; contracts like muscle tissue and generates impulses like nervous tissue
22
New cards
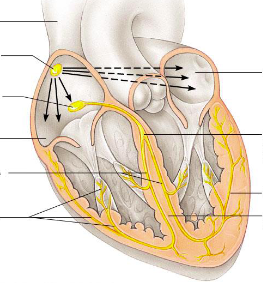
LABEL
nodes on internal heart
nodes on internal heart
1) Sinoatrial Node (pacemaker)
2) Atrioventricular node (Av node)
3) AV bundle (Bundle of His)
4) Bundle branches
5) Purkinje fibers
6) right atrium
7) left atrium
8) interventricular system
9) superior vena cava
2) Atrioventricular node (Av node)
3) AV bundle (Bundle of His)
4) Bundle branches
5) Purkinje fibers
6) right atrium
7) left atrium
8) interventricular system
9) superior vena cava
23
New cards
path for the transmission of an impulse in the intrinsic conduction system of the heart
sinoatrial node--> atrioventriular node--> atrioventricular bundle--> right and left bundle branches--> purkinje fibers
24
New cards
electrocardiogram
= EKG/ECG --> maps the electrical activity of the heart
25
New cards
cardiac cycle
events of one complete heartbeat (.8s)
26
New cards
Polarization
refers to the heart at rest. no impulse, no stimulation, no contraction and no measurable activity
27
New cards
Depolarization
another word for the discharge of electrical energy or the activity of the heart during the impulse that causes contraction but not the contraction itself can by measured by ECG
28
New cards
repolarization
the electrical recovery of the heart as the cells recharge themselves
29
New cards
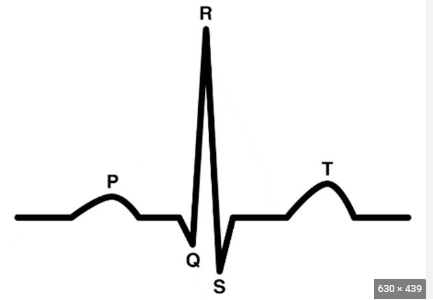
3 main EKG waves
1) P wave: represents depolarization of both atria
2) QRS wave: represents ventricular depolarization
3) T wave: ventricular repolarization
ST segment: important in identifying pathology such as myocardial infarctions (elevations) and ischemia (depressions)
2) QRS wave: represents ventricular depolarization
3) T wave: ventricular repolarization
ST segment: important in identifying pathology such as myocardial infarctions (elevations) and ischemia (depressions)
30
New cards
when does atrial repolarization take place?
QRS segment
31
New cards
LABEL EKG wave
1) p wave
2) t wave
3) QRS complex
4) atrial depolarization
5) atria contract
6) ventricular depolarization
7) atrial repolarization
8) ventricle contract
9) ventricular repolarization
10) polarization
11) Time (s)
12) electrical potential (m)
2) t wave
3) QRS complex
4) atrial depolarization
5) atria contract
6) ventricular depolarization
7) atrial repolarization
8) ventricle contract
9) ventricular repolarization
10) polarization
11) Time (s)
12) electrical potential (m)
32
New cards
Systole
Diastole
Diastole
Systole= contraction
Diastole= relaxation
Diastole= relaxation
33
New cards
Cardiac sounds
LUB
-closing of AV valves
DUB
-closing of SL valves
-closing of AV valves
DUB
-closing of SL valves
34
New cards
irregularity of the hearts
Arrhythmia- irregular heart beat
heart murmur- extra heart beat
fibrillation- rapid, irregular, and unsynchronized
bradycardia- below 60
tachycardia- above 100
arteriosclerosis- build up of fat/plaque on the artery wall
heart murmur- extra heart beat
fibrillation- rapid, irregular, and unsynchronized
bradycardia- below 60
tachycardia- above 100
arteriosclerosis- build up of fat/plaque on the artery wall
35
New cards
Difibulator
Machine used to stop the heart
36
New cards
composition of blood vessels
Heart->arteries->arterioles->capillary beds->venules->veins->heart and repeat
37
New cards
three layers of blood vessels (tunics)
1) tunica interna- endothelium (ET)
2) tunica media- smooth muscle tissue (MT)
3) tunica externa- mostly fibrous connective tissue (CT)
2) tunica media- smooth muscle tissue (MT)
3) tunica externa- mostly fibrous connective tissue (CT)
38
New cards
Arteries
-narrow lumen
-more muscle/elastic tissue
-transports blood under higher pressure
-do not have valves (except the SL valves)
-carry oxygenated blood
-more muscle/elastic tissue
-transports blood under higher pressure
-do not have valves (except the SL valves)
-carry oxygenated blood
39
New cards
Veins
-wide lumens
-less muscle/elastic tissue
-transports blood under lower pressure
-have valves throughout the main veins of the body
-carry deoxygenated blood
-less muscle/elastic tissue
-transports blood under lower pressure
-have valves throughout the main veins of the body
-carry deoxygenated blood
40
New cards
Sphincters
loose= red like juice (red)
tight= really really white (pale)
tight= really really white (pale)
41
New cards
Renal
=kidney
42
New cards
Hep
=Liver
43
New cards
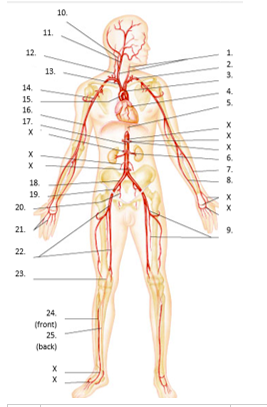
LABEL Artery man
common carotid
subclavian
aortic arch
coronary
thoracic aorta
renal
radial
ulnar
deep femoral
internal carotid
external carotid
vertebral
brachiocephalic
axillary
ascending aorta
brachial
abdominal aorta
common iliac
external iliac
internal iliac
digital
femoral
popliteal
anterior tibial
posterior tibial
subclavian
aortic arch
coronary
thoracic aorta
renal
radial
ulnar
deep femoral
internal carotid
external carotid
vertebral
brachiocephalic
axillary
ascending aorta
brachial
abdominal aorta
common iliac
external iliac
internal iliac
digital
femoral
popliteal
anterior tibial
posterior tibial
44
New cards
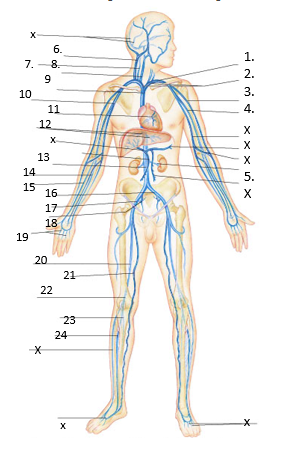
LABEL vein man
subclavian
brachiocephalic
cephalic
brachial
renal
external jugular
vertebral
internal jugular
superior vena cava
axillary
great cardiac
hepatic
inferior vena cava
ulnar
radial
common iliac
external iliac
internal iliac
digital
femoral
great saphenous
popliteal
posterior tibial
anterior tibial
brachiocephalic
cephalic
brachial
renal
external jugular
vertebral
internal jugular
superior vena cava
axillary
great cardiac
hepatic
inferior vena cava
ulnar
radial
common iliac
external iliac
internal iliac
digital
femoral
great saphenous
popliteal
posterior tibial
anterior tibial
45
New cards
pressure points
- pulse- pressure wave of blood
- monitored at "pressure points" where pulse is easily palpated
- monitored at "pressure points" where pulse is easily palpated
46
New cards
recording blood pressure
-measurements by health professionals are made on the pressure in large arteries
47
New cards
systolic
pressure at the peak of ventricular contraction (norm=120)
48
New cards
diastolic
pressure when ventricles relax (norm=80)
49
New cards
Steps for taking blood pressure
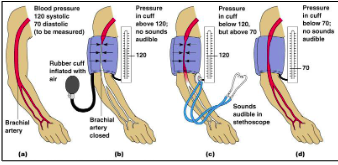
50
New cards
Normal blood pressure
110-140mm Hg systolic
75-80mm Hg diastolic
75-80mm Hg diastolic
51
New cards
Hypotension blood pressure
low systolic (below 110mm Hg)
-often associated with illness (heat=vasodilation)
-often associated with illness (heat=vasodilation)
52
New cards
Hypertension blood pressure
high systolic (above 140mm Hg)
-can be dangerous if it is chronic
-can be dangerous if it is chronic
53
New cards
Blood pressure effects
-temperature
-chemicals
-diet
-chemicals
-diet
54
New cards
LABEL vessel compositions
1) epithelial tissue
2) smooth muscle tissue
3) fibrous connective tissue
2) smooth muscle tissue
3) fibrous connective tissue
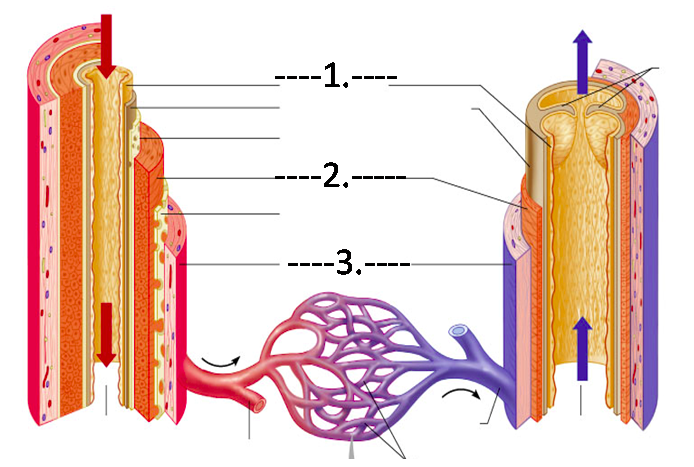
55
New cards
what blood vessel has the highest blood pressure
aorta
56
New cards
during cardio-pulmonary bypass, what vessels are clamped?
-superior vena cava
-aorta
-inferior vena cava
-aorta
-inferior vena cava
57
New cards
what vessels are part of cardiac circulation
-coronary sinus
-cardiac vein
-coronary artery
-cardiac vein
-coronary artery
58
New cards
what vessel receives blood during right ventricular systole:
pulmonary trunk