Final Exam Review (New Stuff/Old Stuff)
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
What are the functions of the respiratory system?
provide surface area for gas exchange, moving air across surfaces of the lungs along respiratory passageways, protect respiratory surfaces, produce sounds, facilitate detection of odors.
What are the three lobes on the lateral surfaces of the right lung?
Superior lobe, middle lobe, and inferior lobe
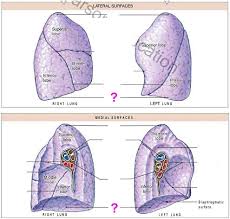
What separates the inferior lobe from the superior and middle lobe on the lateral surface of the right lung?
oblique fissure
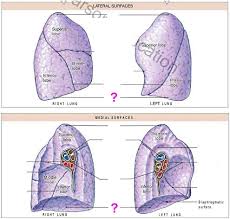
What separates the middle lobe from the superior lobe on the lateral surface of the right lung?
horizontal fissure
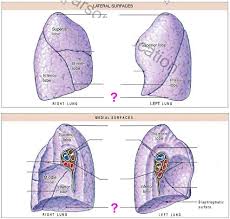
The left lung on the lateral surface only has _____ and _____ and ____ that separate the two?
Superior lobe, inferior lobe, and the oblique fissure
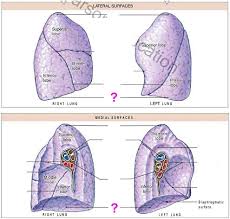
The divot on the medial part of the left lung is called the?
Cardiac notch
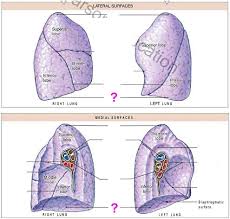
What does the medial surface of the lungs have that the lateral surface doesn’t have?
hilium
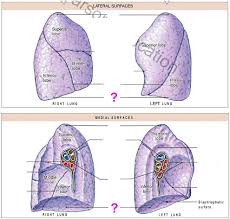
What does the hilium consist of or do for the right and left medial surface of the lungs?
Allows passage of primary bronchi, pulmonary vessels, pulmonary arteries and veins, nerves and lymphatic
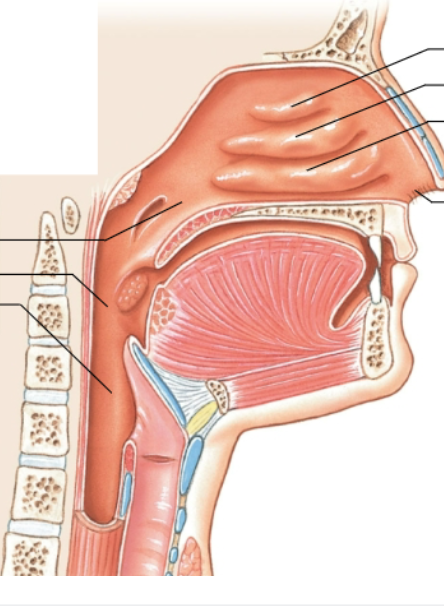
What are the bony structures on the lateral walls of the nasal cavity?
nasal conchae (top arrows)
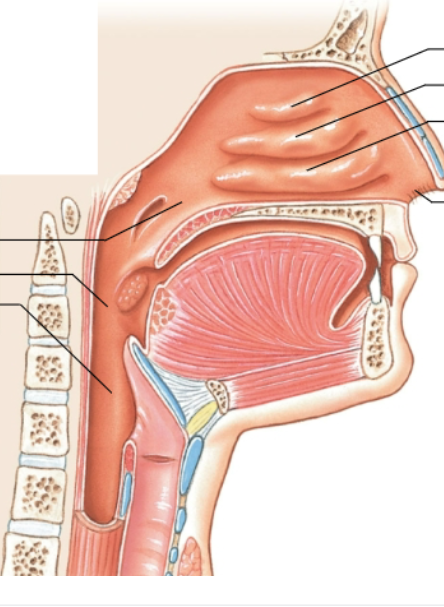
What is the top left arrow pointing at?
Nasopharynx
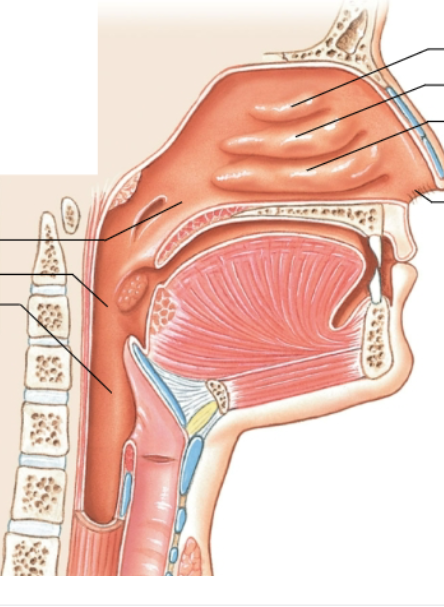
What is the middle left arrow pointing at?
Oropharynx
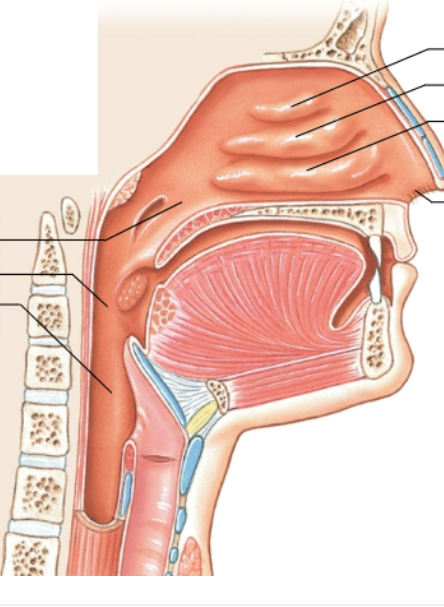
What is the bottom left arrow pointing at?
Laryngopharynx
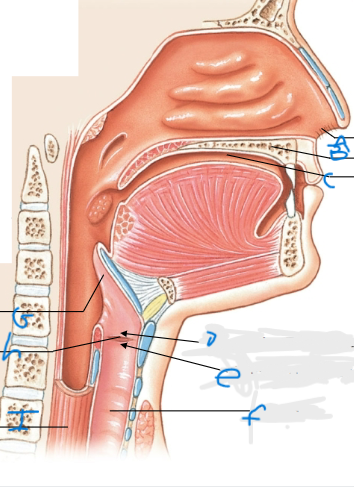
What is A pointing at?
External nares
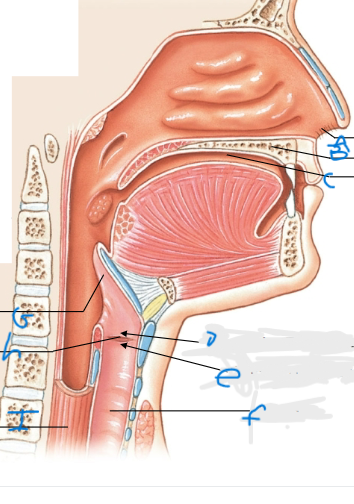
What is B and C pointing at?
Oral cavity
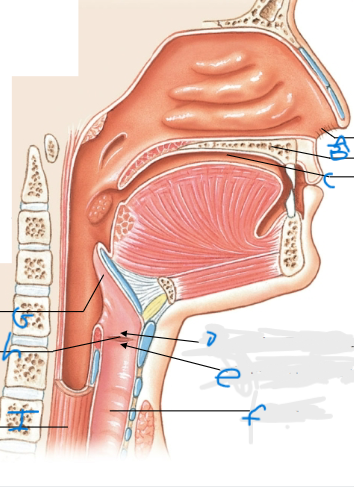
What is D pointing at?
Vestibular fold (false vocal cords)
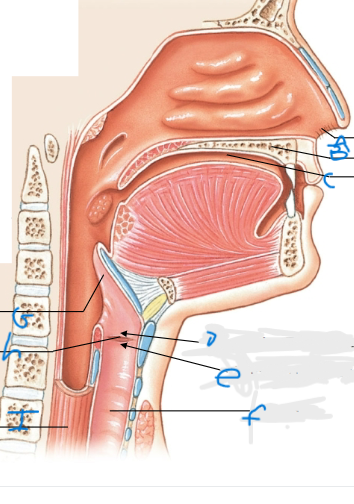
What is E pointing at?
Vocal fold (true vocal cords)
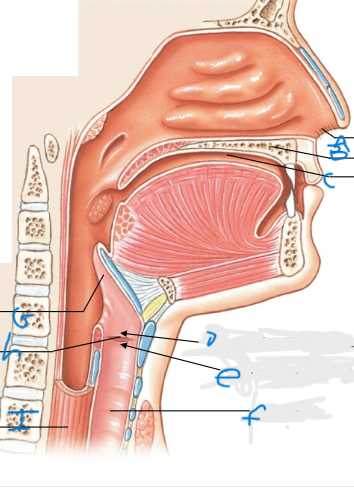
What is F pointing at?
Trachea
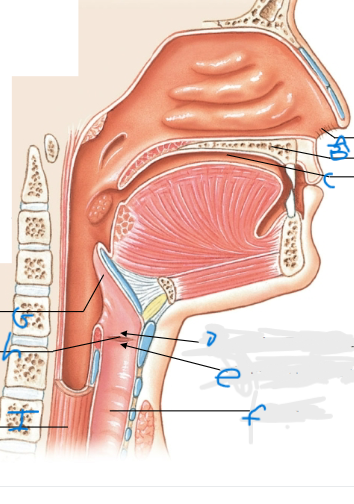
What is G pointing at?
Epiglottis
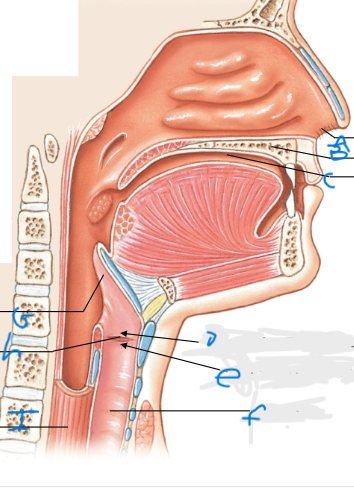
What is H pointing at?
Glottis
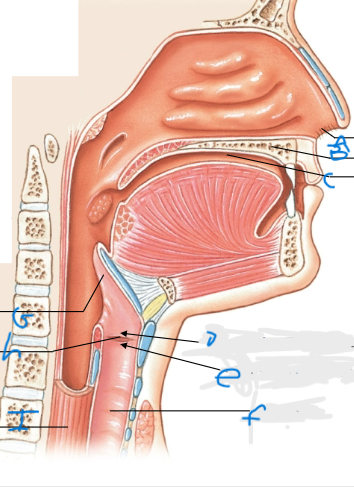
What is I pointing at?
Esophagus
What is the laryngeal prominence?
the Adam apple. Its thyroid cartilage surrounding the larynx. (A)
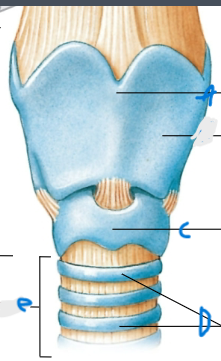
What is the thing between the Larynx and the Trachea?
Cricoid cartilage (C)
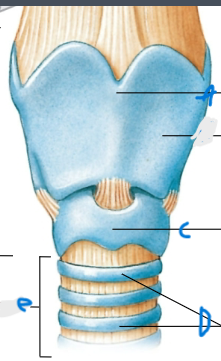
What does the cricoid cartilage do?
connects the trachea to the larynx and maintains airway patency (open)
What are the rings that surround the trachea?
tracheal cartilage (D)
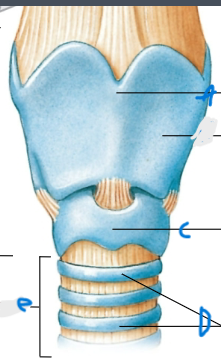
What is the thing connected inferiorly to the Larynx?
Trachea (e)
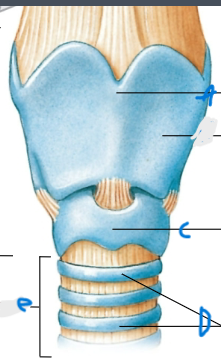
What is the top part of the Larynx?
Epiglottis
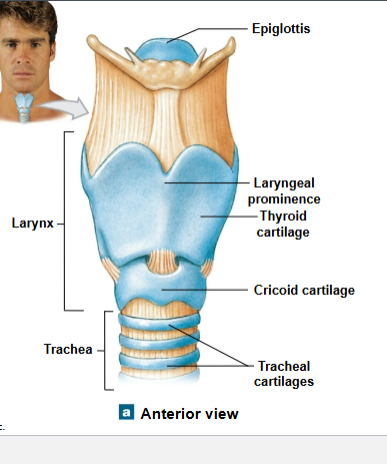
What is the ring above the glottis?
Epiglottis
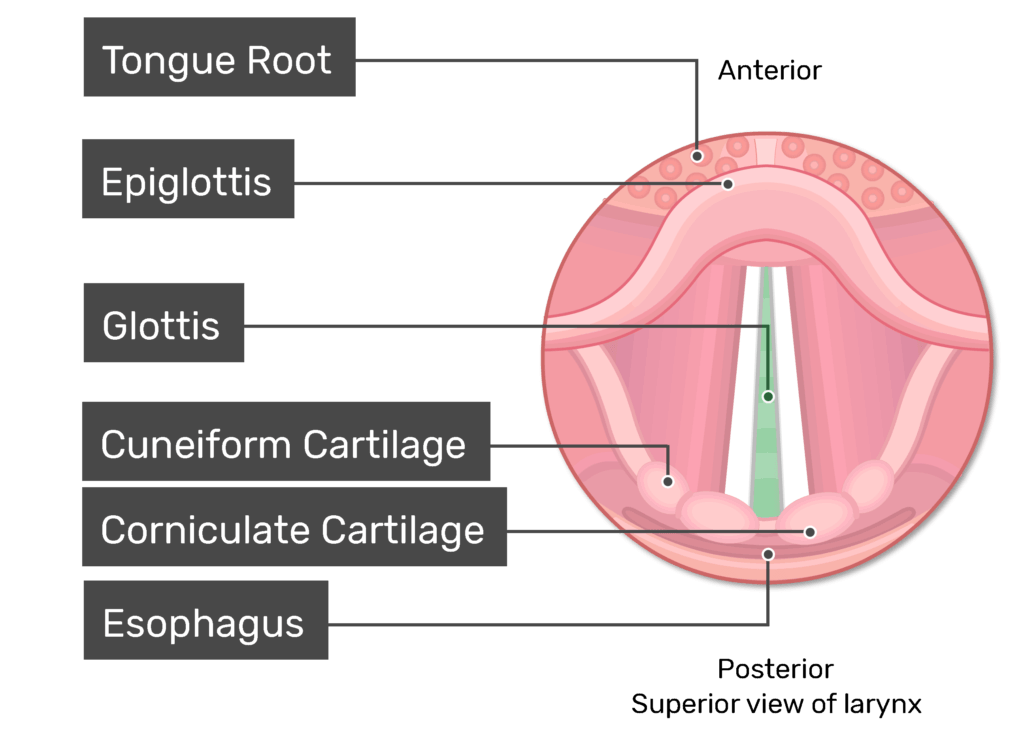
What is the top part of the Larynx?
Tongue root
What is the opening of the larynx?
Glottis
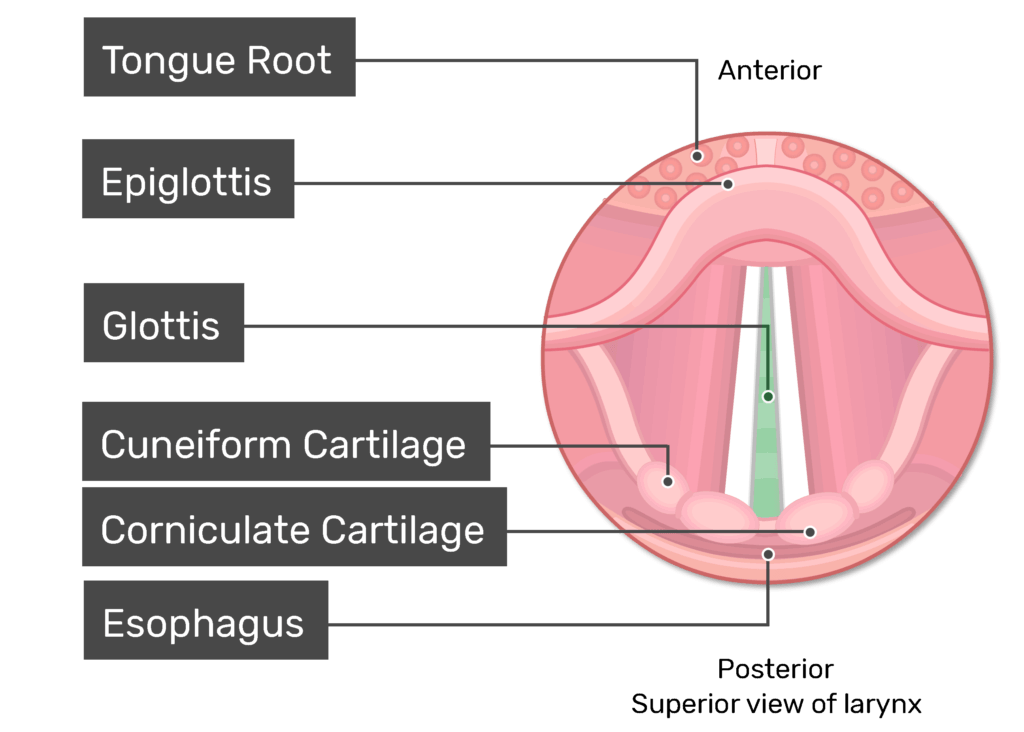
What is lateral to the Glottis?
Vocal folds (true vocal folds)
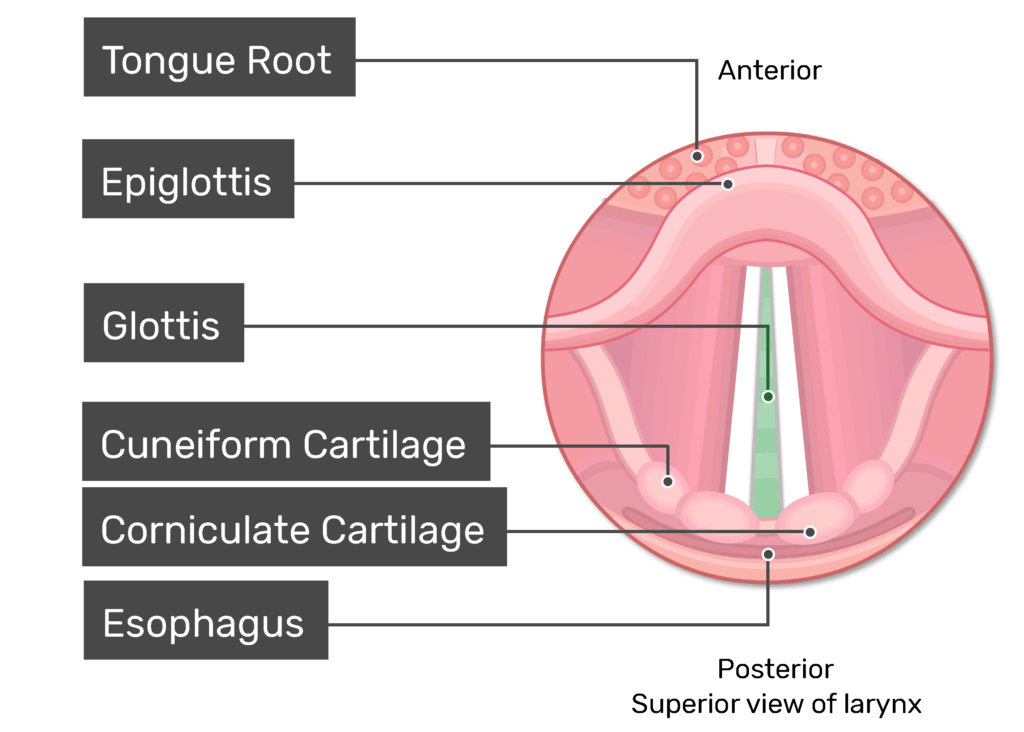
What is lateral to the Vocal folds?
Vestibular folds (false vocal folds)
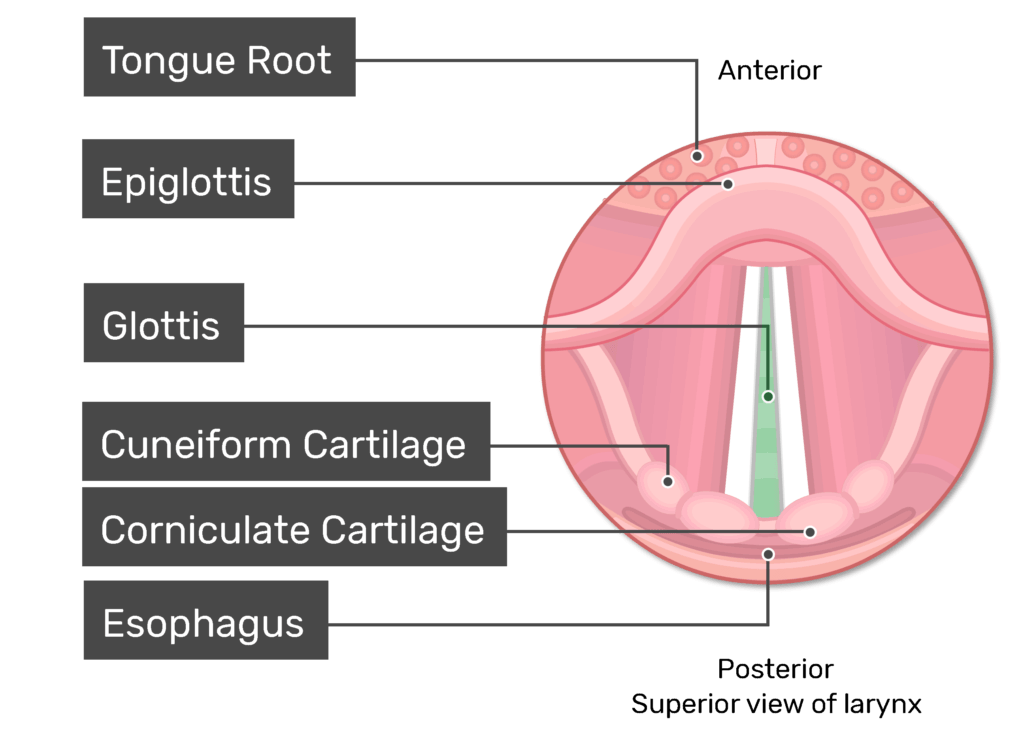
Where is the Corniculate cartilage of the larynx?
Inferior to the vocal folds
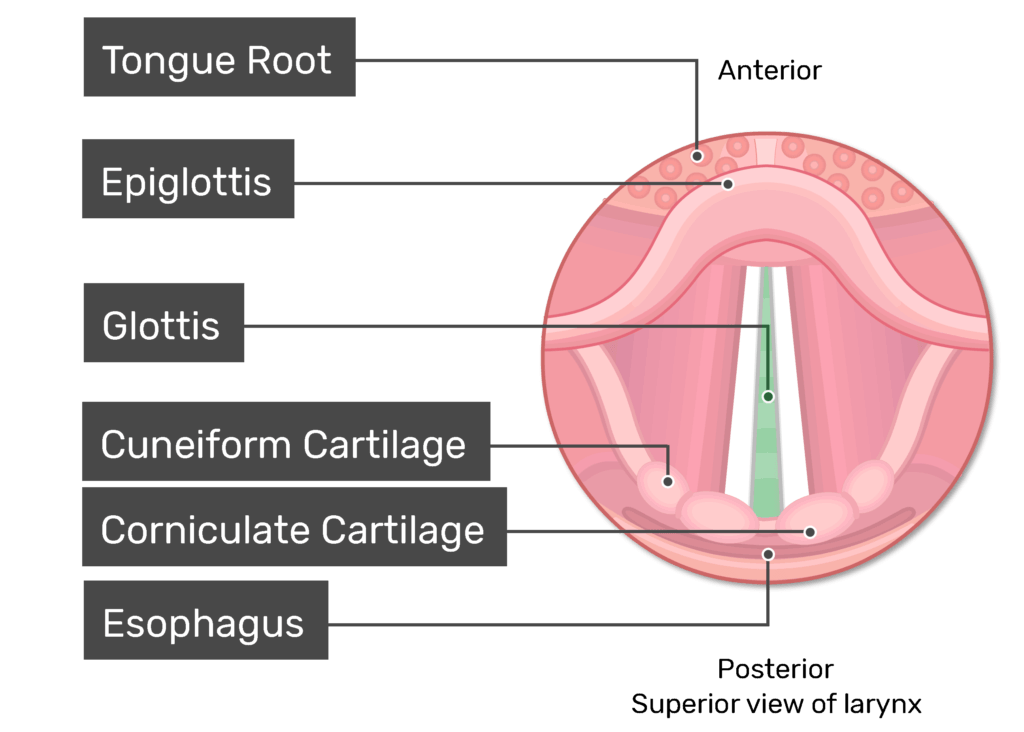
Where is the Cuneiform cartilage of the larynx?
Inferior to the vestibular folds (false vocal folds)
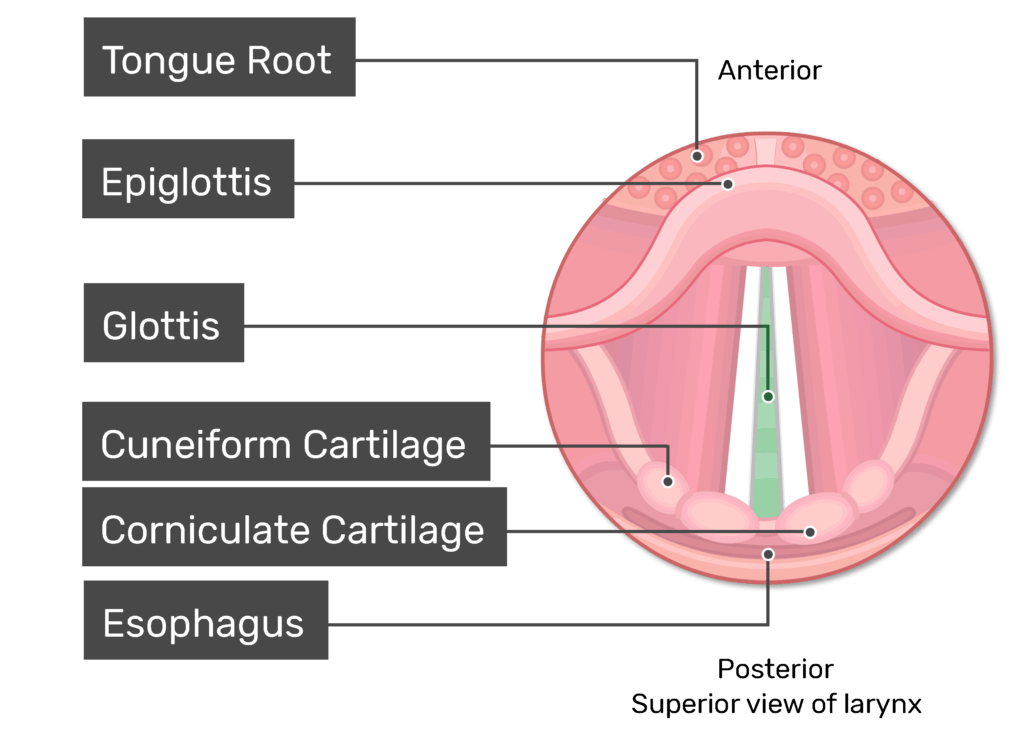
Where is the Trachea of the Larynx?
Inferior and posterior to the Glottis (Glottis is the opening to it)
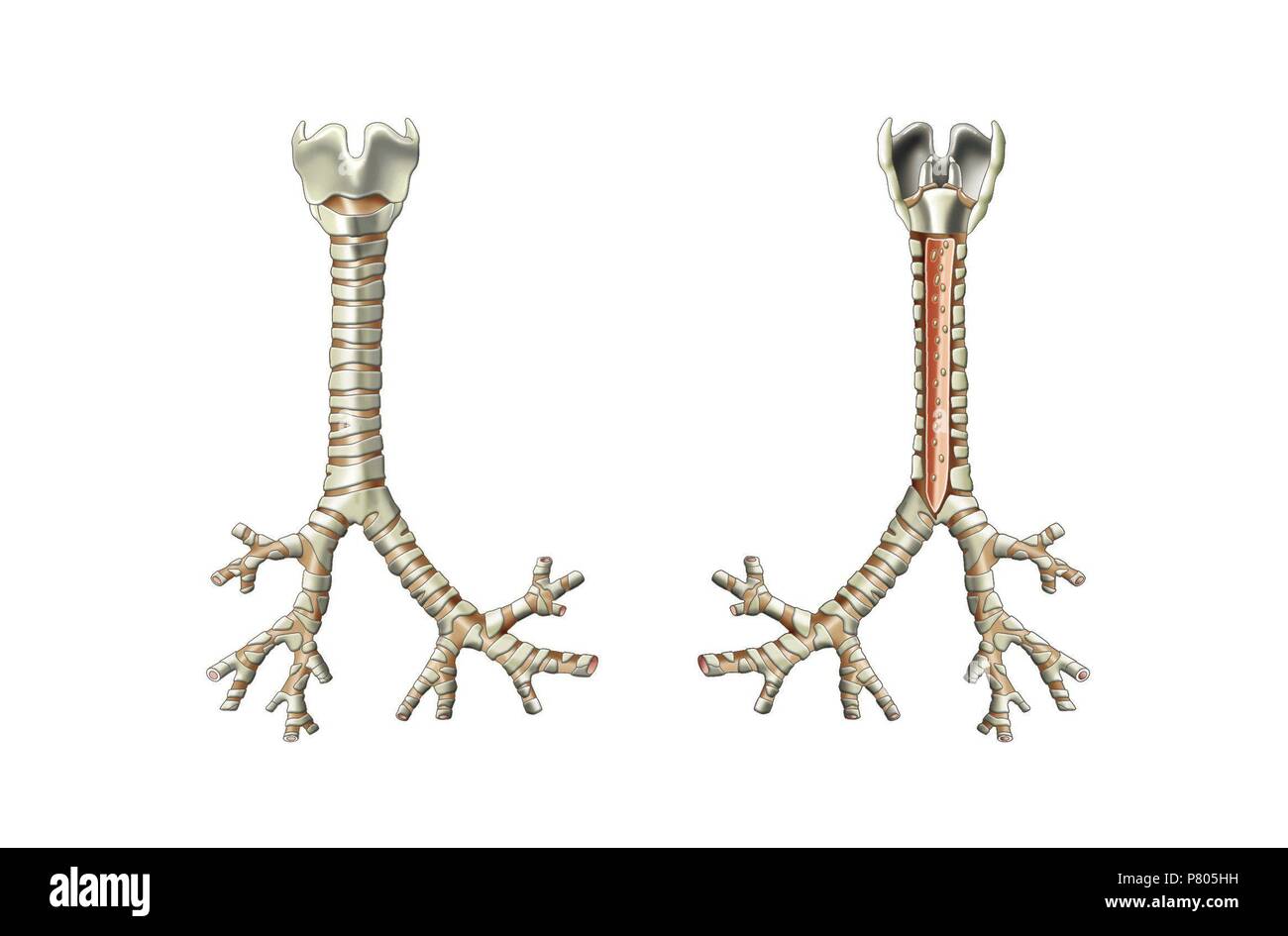
What is below the larynx?
Trachea (A)
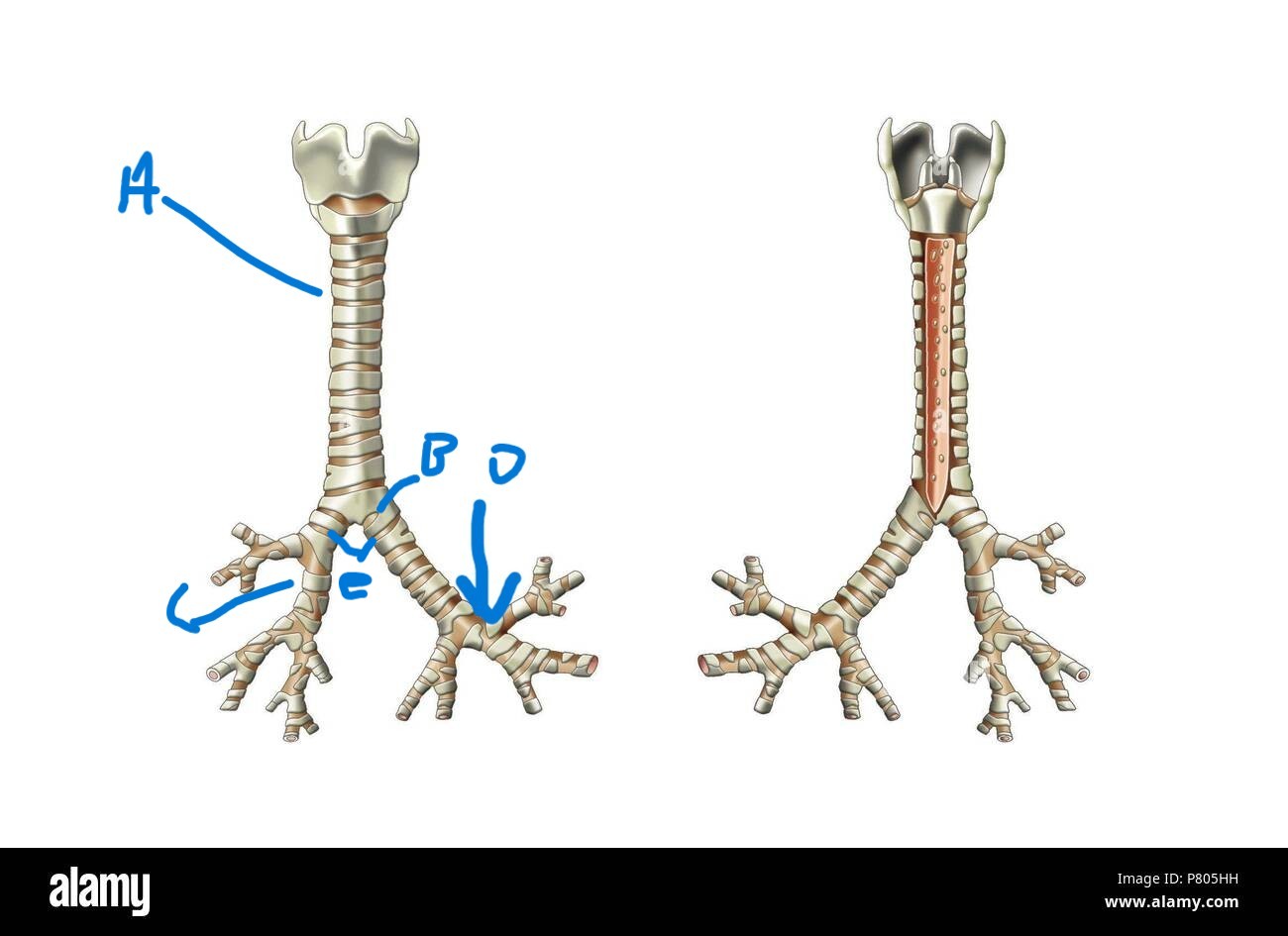
What is the term for the split at the bottom of the trachea?
Carina (B)
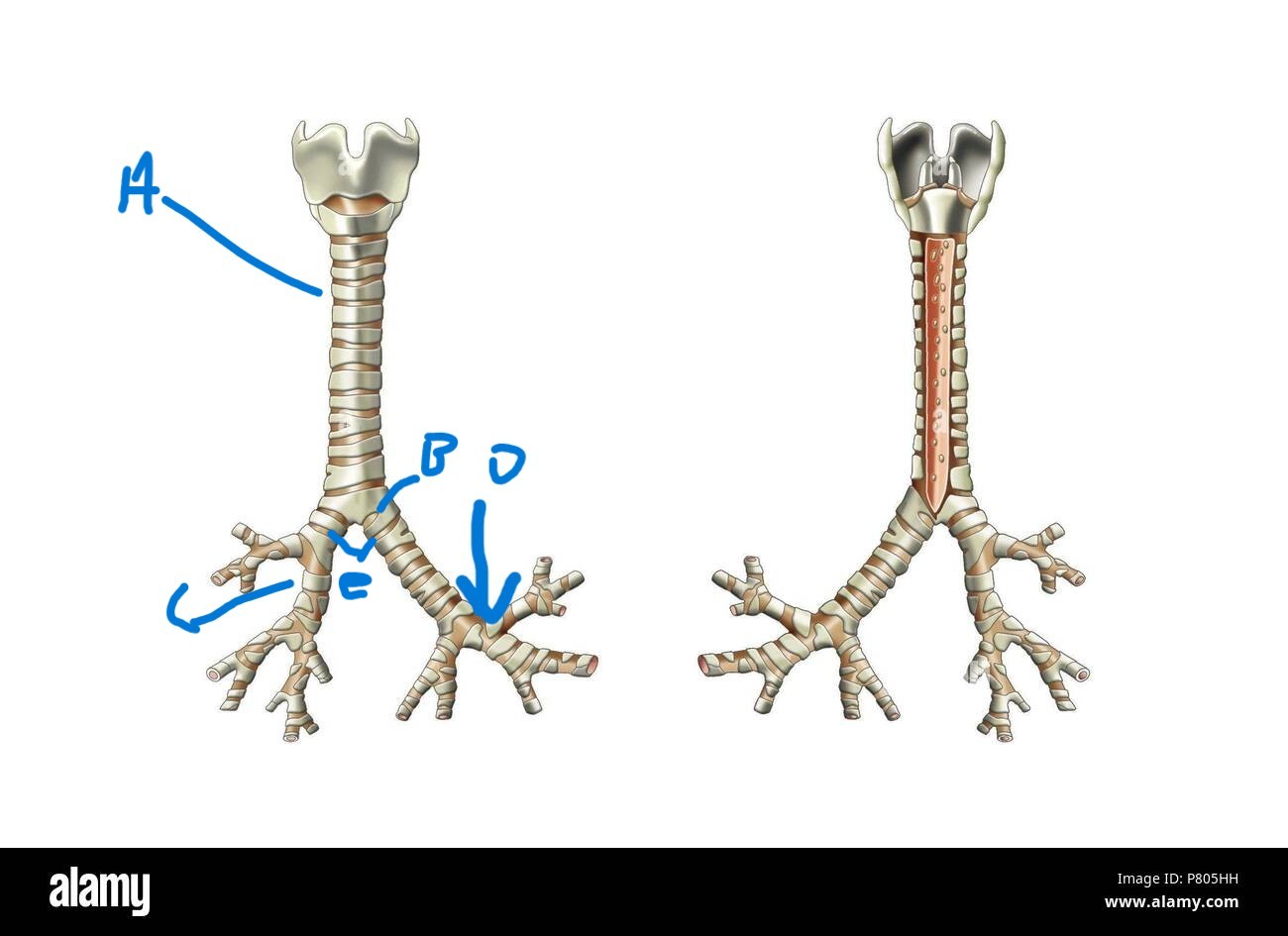
What is the area lateral and inferior from the Carina on the Trachea?
Primary bronchi (E)
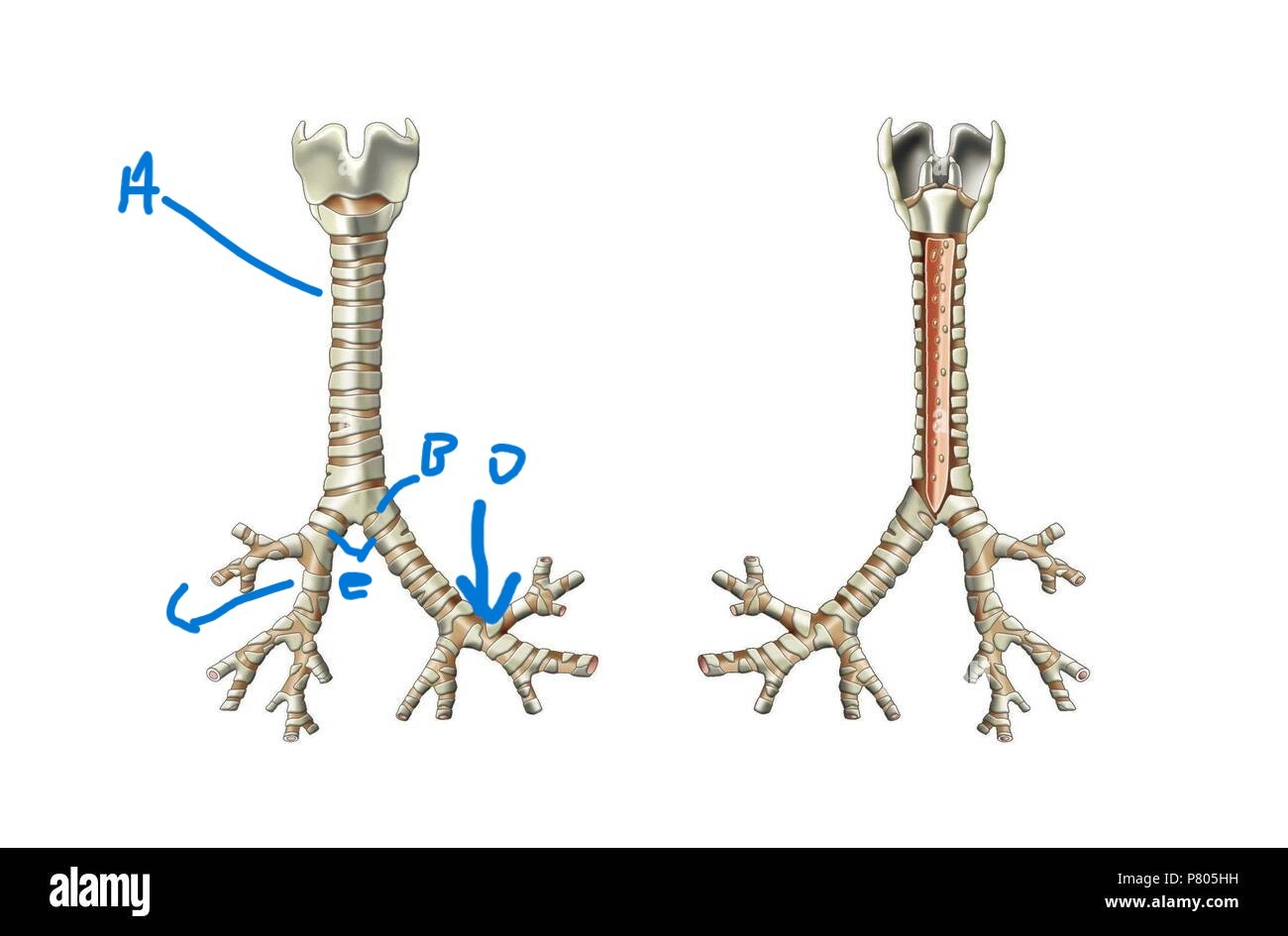
What is after the primary bronchi?
Root of left and right lung (C)
What is after the roots of left/right lungs?
Secondary bronchi (D)
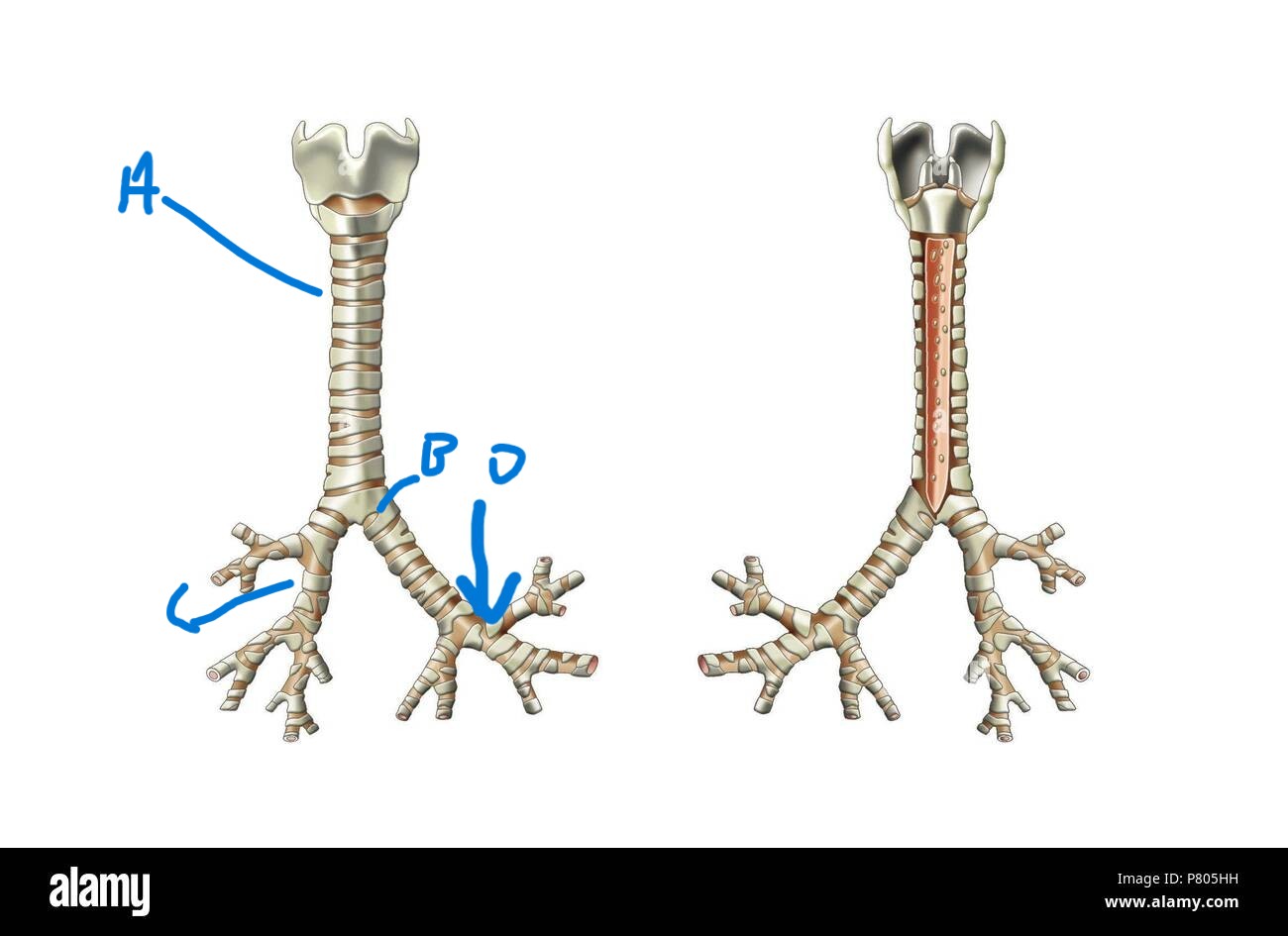
What does the secondary bronchus lead into?
Tertiary bronchi
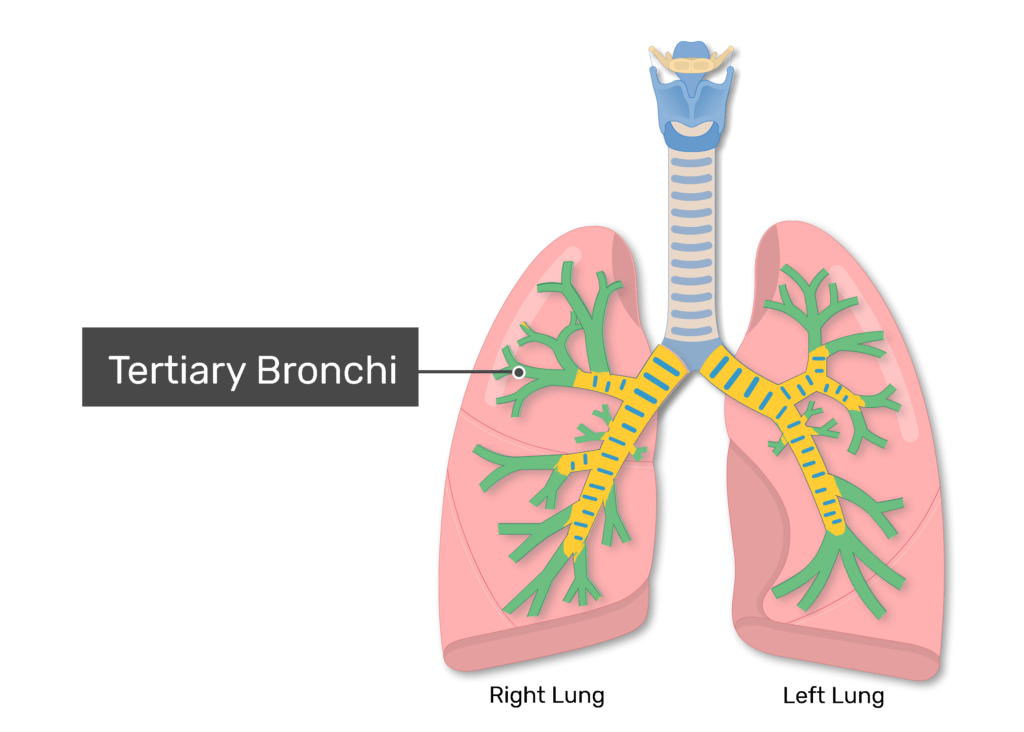
What do Tertiary bronchi lead into?
Bronchioles
What do Bronchioles lead into?
Alveoli in pulmonary lobule
What are the three major types of cells found in the Alveoli?
Type I alveolar cells- simple squamous epithelium, Type II alveolar cells- cuboidal epithelial cells, Alveolar macrophages.
What do type II alveolar cells (cuboidal epithelial cells) do?
secrete surfactant
What does Alveolar macrophages do?
Consume bacteria, dust, and other debris
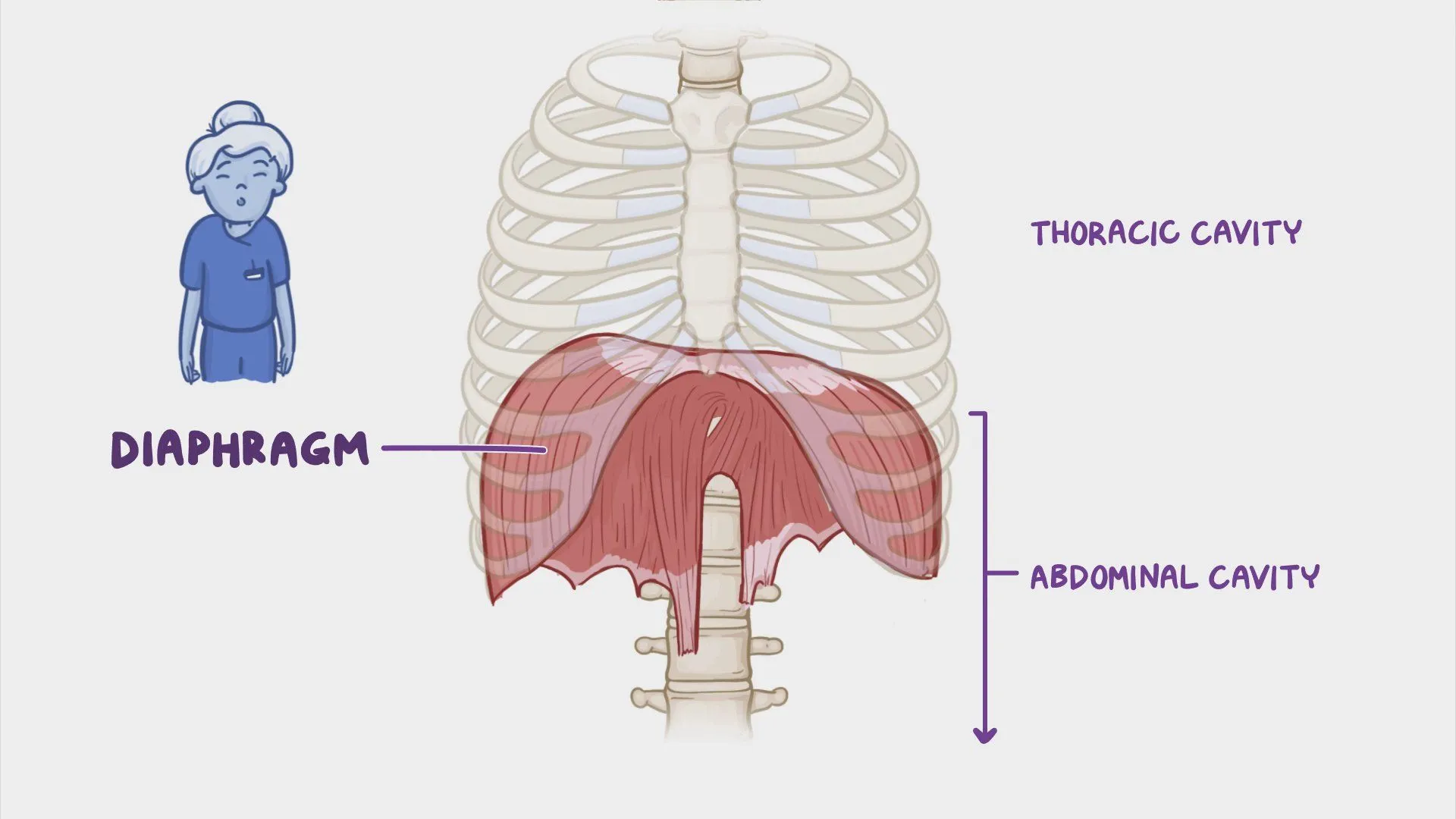
What is the Diaphragm muscle?
dome-shaped muscle separating the thorax from the abdomen
What does the Diaphragm attach to?
sternum, bottom of rib cage and spine
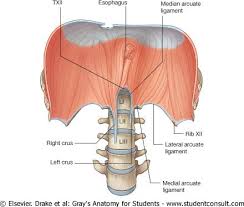
What do the right crus muscle and left crus muscle do?
Extend bellow the diaphragm and connect it to the vertebral column
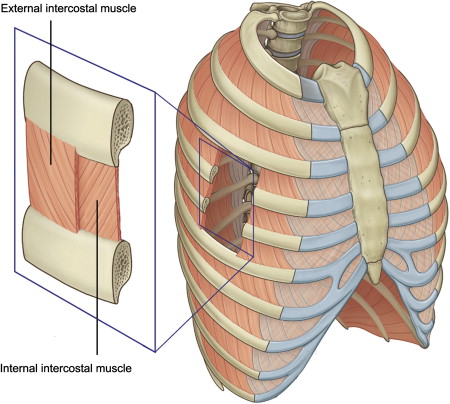
What is the External Intercostal muscles?
The external layer of muscles in between the ribs and chest wall
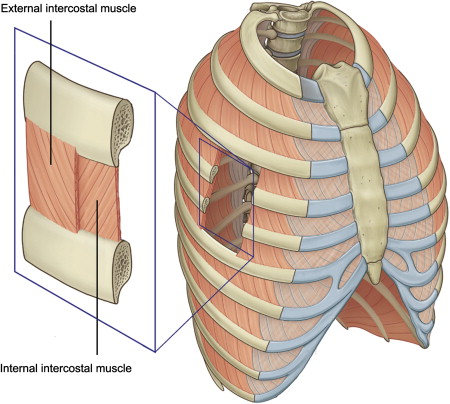
What is the internal intercostal muscles?
The internal layer of muscles in between the ribs and chest wall
What happens when the diaphragm and external intercostal muscle contract?
passive inhalation
What does Relaxion of the diaphragm and external intercostal muscle cause?
passive exhalation
What causes active exhalation?
Internal Intercostal muscles
What are the other muscles involved in active exhalation?
Rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, external obliques and internal obliques
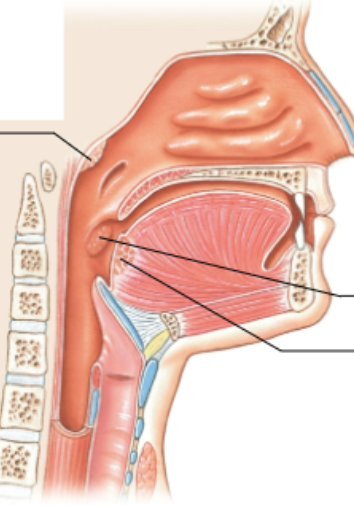
What is the top arrow pointing at?
pharyngeal tonsil
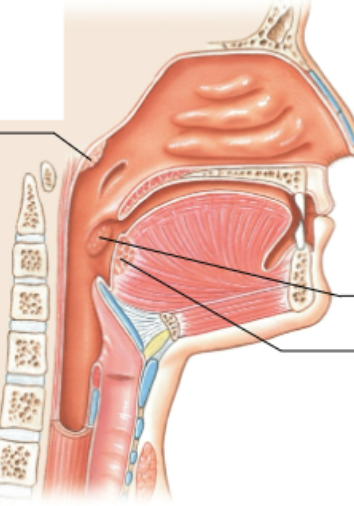
What is the middle arrow pointing at?
palatine tonsil
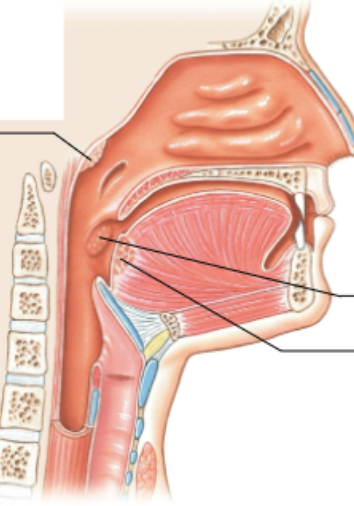
What is the bottom arrow pointing at?
Lingual tonsil
What is the purpose of the Pharynx?
Muscular propulsion of materials into the esophagus
What is the purpose of the stomach?
Chemical breakdown of materials by acid and enzymes; mechanical processing through muscular contractions
Purpose of the small intestine?
Enzymatic digestion and absorption of water, organic substrates, vitamins, and ions.
What does the large intestine do?
Enzymatic digestion and absorption of water, organic substrates, vitamins, and ions
What does the Gallbladder do?
Stores and concentrates bile
What does the alimentary canal include?
Mouth → pharynx → esophagus → stomach → small intestine → large intestine → rectum → anus
What do enzymes travel through?
Ducts
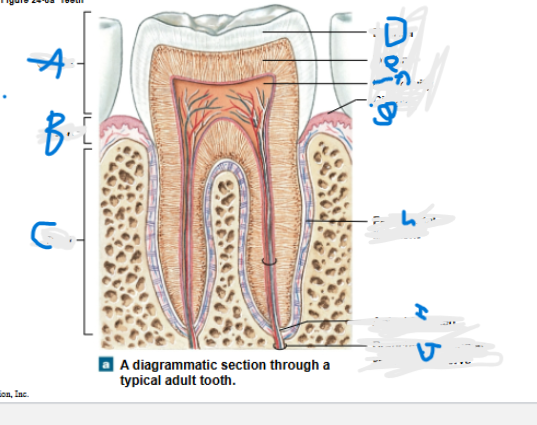
What is A?
Crown
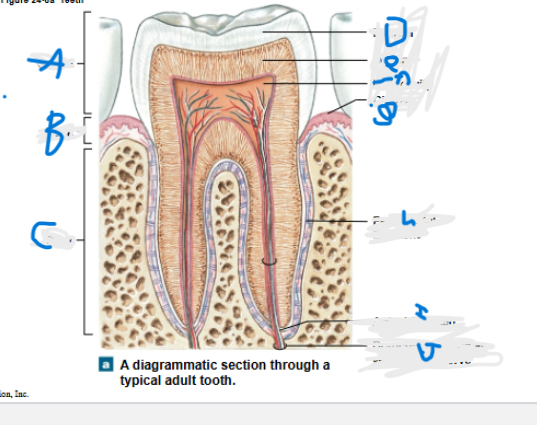
What is B?
neck
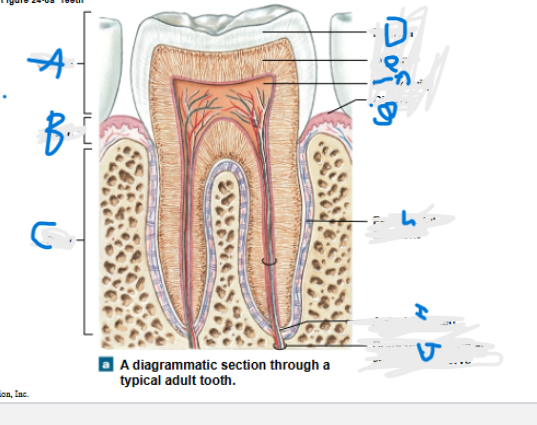
What is C?
Root
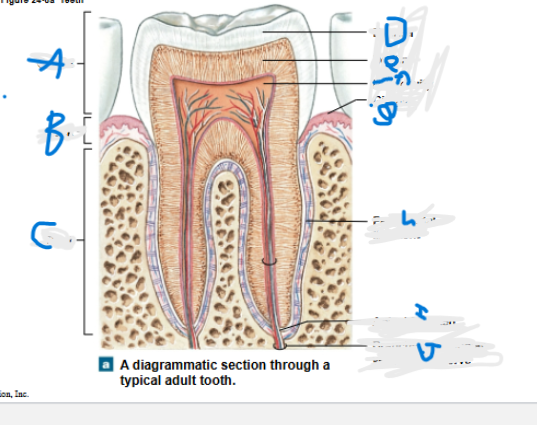
What is D?
Enamel
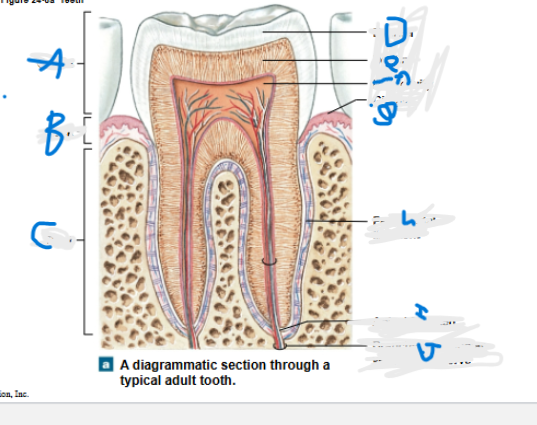
What is E?
Dentin
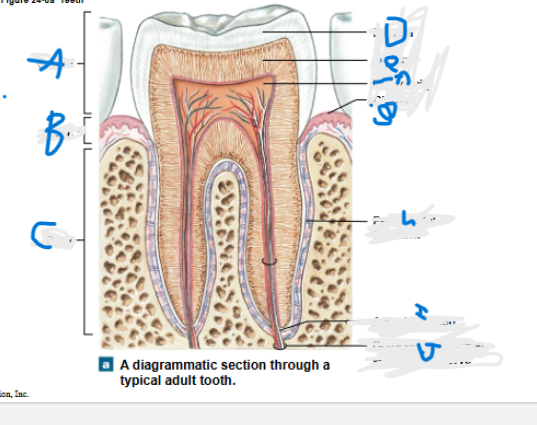
What is F?
Pulp cavity
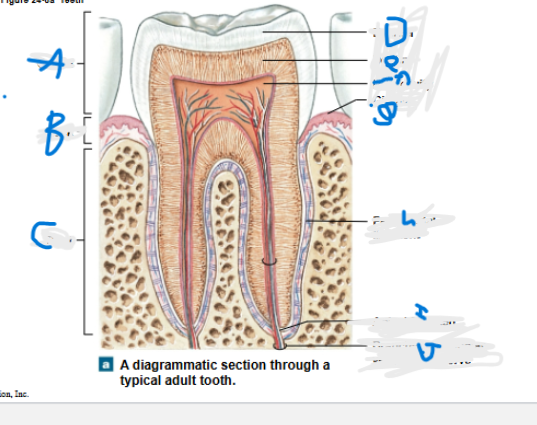
What is G?
Gingiva
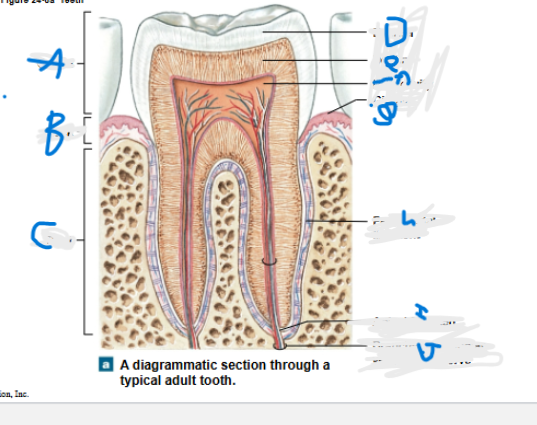
What is H?
Periodontal ligament
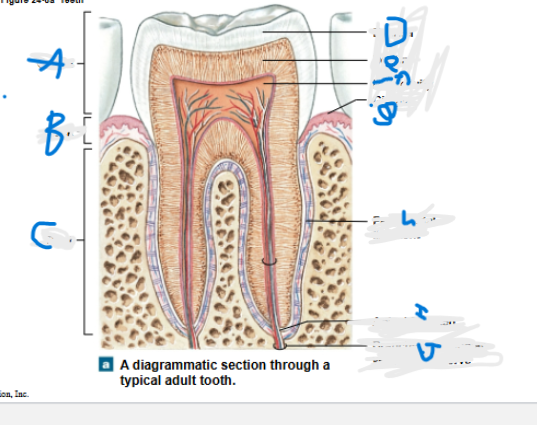
What is I?
Apical foramen
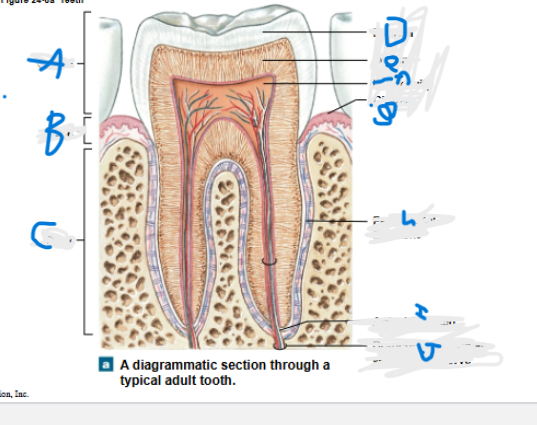
What is J?
Branches of alveolar vessels and nerve
What connects the tongue to the bottom part of our mouth?
Lingual frenulum
What is the hanging part in the back of our mouth?
uvula
What is the area above the uvula?
Palatoglossal arch
What is the two spots on the bottom of the tongue lateral to the lingual frenulum?
Openings of submandibular ducts
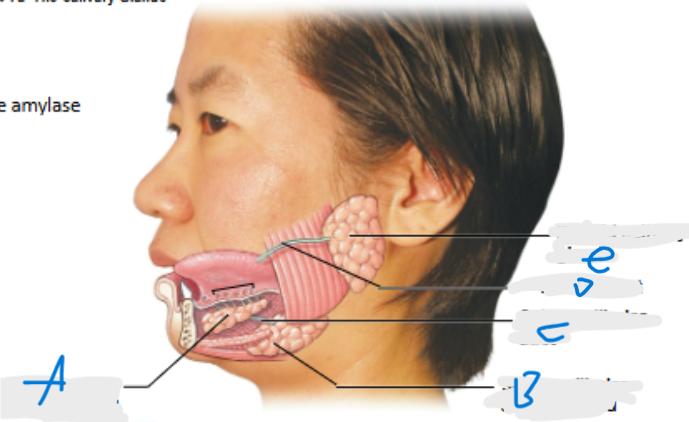
What is A pointing at?
Sublingual salivary gland
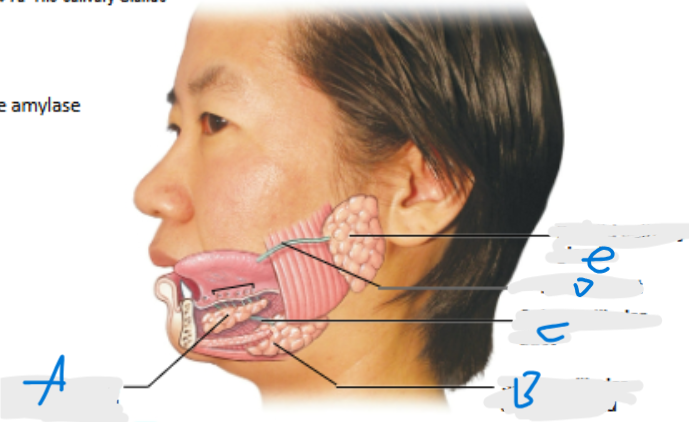
What is B pointing at?
Submandibular salivary gland (inferior to submandibular duct)
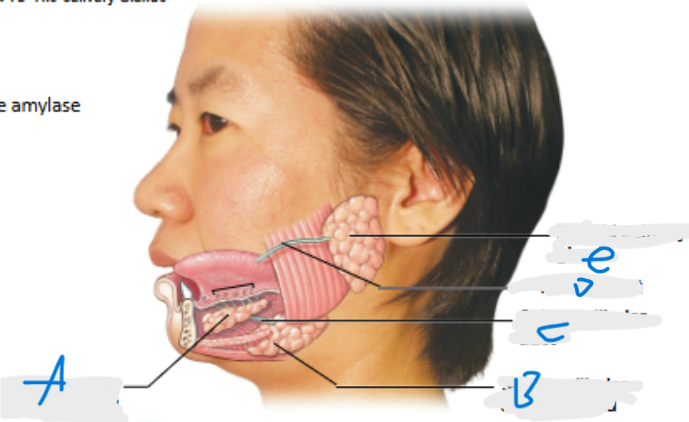
What is C pointing at?
Submandibular duct
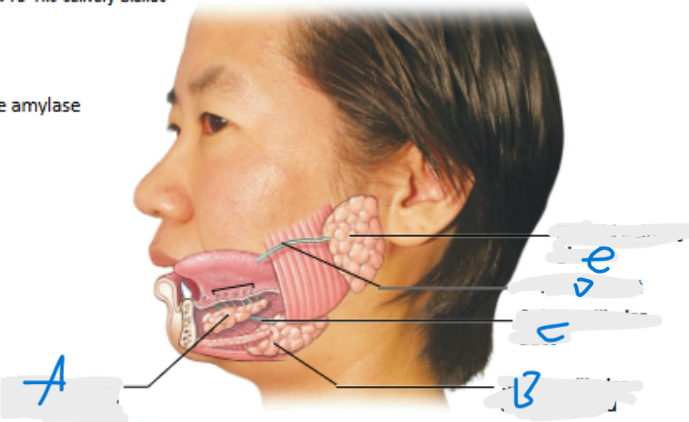
What is D pointing at?
Parotid duct
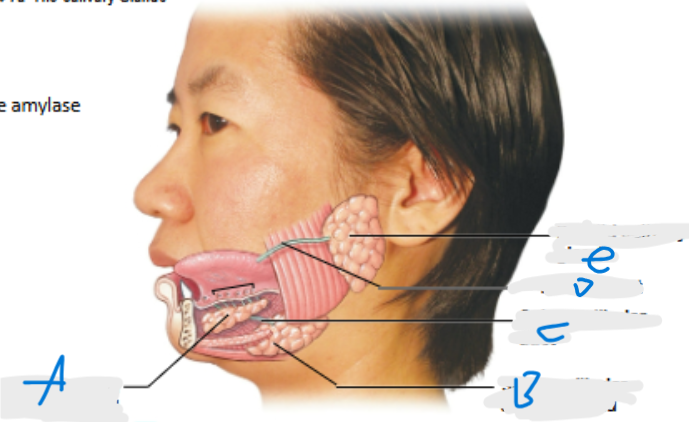
What is E pointing at?
Parotid salivary gland (located posterior to duct)
What is the peristalsis?
wave like muscular contraction that moves food and fluids down the esophagus
Where is the trachea located?
anterior to the esophagus
What does the trachea do?
sends air in and out of lungs
What happens when the bolus gets near the lower esophageal sphincter?
It opens for it
What does the Lower esophageal sphincter do?
Acts as a valve at the end of the esophagus and the beginning of the stomach. It stays close unless to let food into the stomach.
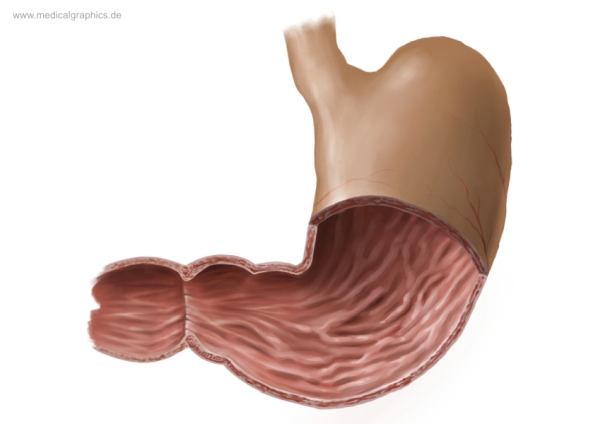
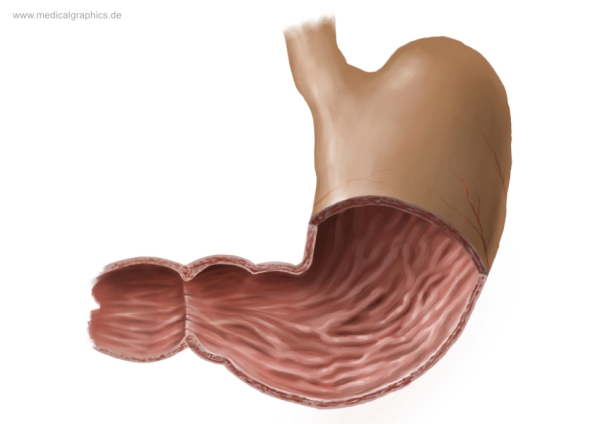
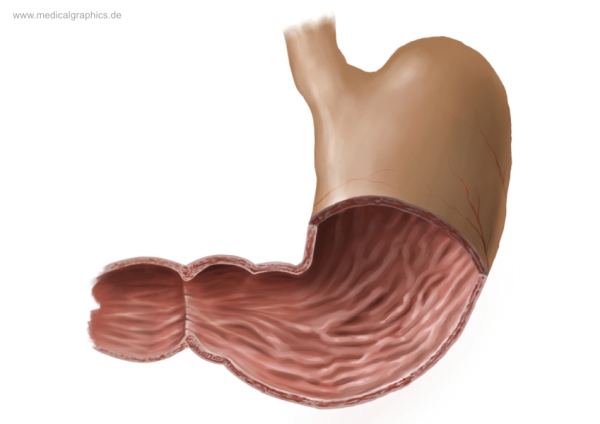
What is the top region of the stomach?
Cardia region
What are the muscles on the interior of the stomach?
Rugae
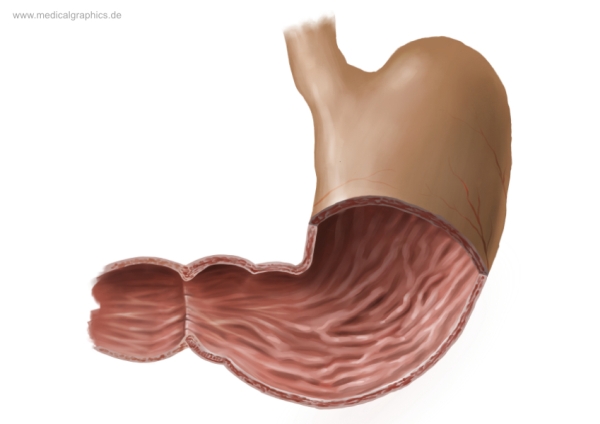
What is the bottom left area of the stomach called?
Pylorus region
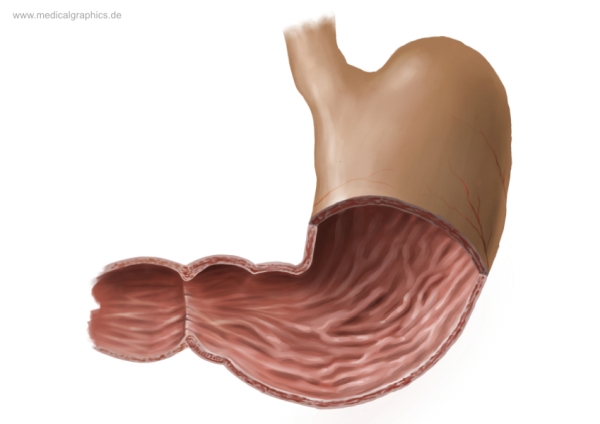
What connects the Duodenum and the stomach together?
Pyloric sphincter
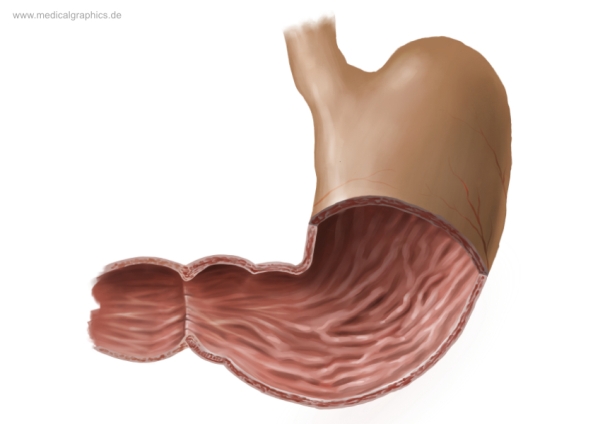
What is the smaller inner curve of the stomach called?
Lesser curvature
What is the larger curve of the stomach called?
Greater curvature (lateral surface)
Where does food go after the stomach?
The Duodenum