Electromagnetic Waves and Electromagnetic Spectrum
EM Waves are Transverse Waves without a medium. They travel in electrical and magnetic fields
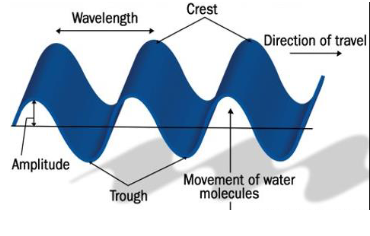
When an electric field changes, so does the magnetic field.
The changing magnetic field causes the electric field to change.
“Electromagnetic Waves results when one field vibrates, so does the other”
Speed of Light (300,000 km/s)–The speed on how fast EM Waves can travel
Electromagnetic Spectrum – name for the range of electromagnetic waves when placed in order of frequency and wavelength.
^^The Electromagnetic Spectrum according to Frequency:^^
- Radio Waves (lowest frequency)
- Microwaves-Infrared
- Visible Light
- UV Rays
- X-Rays
- Gamma Rays (highest frequency)
^^The Electromagnetic Spectrum according to their wavelengths:^^
- Radio Wave (longest wavelength)
- Microwave-Infrared
- Visible Light
- UV Rays
- X-Rays
- Gamma Rays (shortest wavelength)
==Radio Waves== are waves that has the lowest frequency and longest wavelength, while Gamma Rays are waves that has the highest frequency and the shortest wavelength.
RADAR is an acronym of ==Radio Detection And Ranging==
Visible Lights are the only EM Waves that we can see:
- ==Red Light== is the color that has the longest wavelength
- ==Violet Ligh==t is the color that has the shortest wavelength
Cosmic Rays–another high-energy radiation from energetic cosmic events in space. These rays are produced by stars such as the sun. One of the examples of Cosmic Rays are aurora borealis or the northern lights.
Gamma Rays–waves used for eliminating cancer cells and it is harmful to our body once it is used wrong. Exploding nuclear weapons also emits gamma rays.
UV Rays or Ultraviolet Rays has 3 classifications (take in mind that the longer the wavelength, the lower the energy they emit):
- %%UVA%%–its wavelength is 315 nm to 400 nm (low energy)
- %%UVB%% –its wavelength is 210 nm to 315 nm (medium energy, they stimulate melanin, use sunscreen or SPF protection)
- %%UVC%%–its wavelength is 100nm to 210 nm (high energy, the most harmful UV rays that can cause skin cancer)
X-Rays–are wavelengths with 10 nm to 0.01m, these rays have enough energy to penetrate deep into tissues and can cause damage to cells
^^Scientist Contributions:^^
- André-Marie Ampère – the one who demonstrated the magnetic effect based on the direction of the current
- Michael Faraday–the one who formulated the principle behind electromagnetic induction
- Heinrich Hertz–the one who showed experimental evidence of EM Waves and their link to light
- James Clerk Maxwell–the one who contributed in developing equations that showed relationship of electricity and magnetism
- Hans Christian Oersted–the one who showed how a current carrying wire behaves like a magnet
Nature of Light
^^Seven Properties of Light^^^^:^^
- Light travels very fast
- Light has a dual nature
- Light travels in straight lines
- Light can vary in intensity
- Light interacts with matter
- Light is comprised of many colors
- Light carries energy and information
Rays – light waves that travels in straight lines
Reflection – is the change in direction of a wave front at an interface between two different media so that the wave front returns into the medium from which it originated
Refraction - is the change in direction of wave propagation due to a change in its transmission medium
Dispersion–a phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency
Diffraction - is the spreading of light after it passes around the edge of an object
Absorption–the light wave could be absorbed by the object, in which case its energy is converted to heat (THERMAL ENERGY).
^^Historical Background in the study of Dual Nature of Light^^
- Christian Huygens–a Dutch mathematician that believed that light was made up of waves vibrating up and down perpendicular to the direction of light travels (WAVE THEORY OF LIGHT)
- Sir Isaac Newton–the one who thought that Light is made up of very fast and tiny particles that travel in straight lines (PARTICULAR THEORY OF LIGHT)
- James Clark Maxwell–the one who formulates that electromagnetical radiation, bringing together electricity, magnetism, and light.
- Max Planck –who formulates the Quantum Theory and studied emission of light from hot objects
- Albert Einstein–the one who stated that a photon supplies necessary energy to free electrons from the surface of a material
Planck’s Equations:
- E = energy
- f = frequency of radiation
- λ= wavelength
Constant Terms:
c = speed of light (3 x 10^8m/s)
h = planck’s constant (6.63 x 10-^34)
For Finding the Energy:
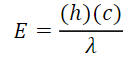
For Finding the Frequency:
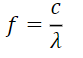
For Finding the Wavelength

Mirrors and Lenses
Terms:
- Center of Curvature (C)–the center of the sphere
- Vertex (V)–the center of the mirror
- Radius of Curvature (R)–the distance between the vertex and the center of curvature
- Focal Point (F)–the point which reflected rays meet
- Focal Length (f)–the distance of the vertex to the focal point
- Principal Axis–a line passing through the center of a lens or a mirror
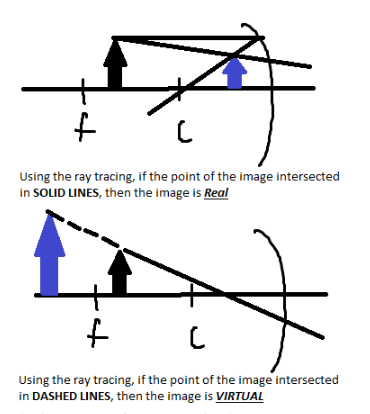
Ray Tracing:
- Ray 1–parallel to the axis and reflects through F
- Ray 2–passes through F before reflecting to the axis
- Ray 3–passes through C and reflects back on its self
- Ray 4–goes to the V and reflects under the same angle below the optical axis
Tips on how to determine the L.O.S.T of an image formed in mirrors and lenses:
THE L (Location):

THE O (Orientation):

THE S (Size):
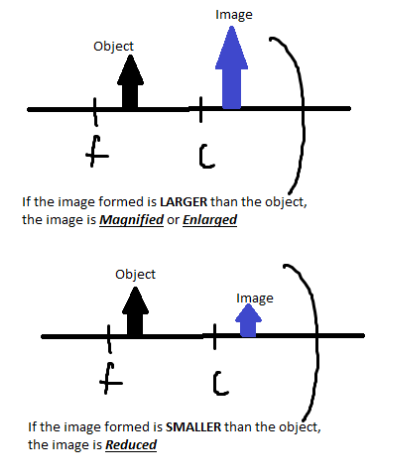
THE T (Type):
EXAMPLE:
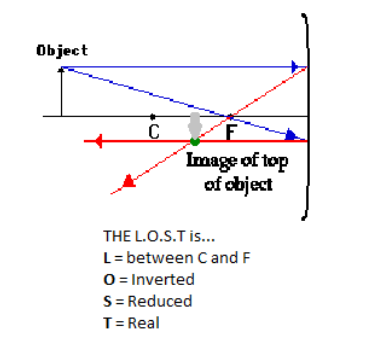
There are special cases when the object is located at “F”, there will be no image formed
^^Thin Lens Equation and Magnification^^

- f–Focal Length
- do–Object distance(always positive)
- di–Image distance(Positive for Real Image and Negative for Virtual Image)
- m–Magnification(Positive for an Upright image and Negative for an Inverted image)
The Human Eye produces a real, inverted image in the retina.
The Camera forms a real and inverted image on a photographic film.
The Compound Microscope forms a real, inverted, and enlarged image near the focus of the eyepiece.
The eyepiece of A Telescope works as magnifier, therefore Telescopes produces enlarged images