9.1 - Homeostasis
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is homeostasis?
Internal environment is maintained in dynamic equilibrium within set limits around an optimum
What are the components of a typical control system?
Stimulus (input)
A change from the ‘set point’
Receptor:
Detects the deviation from the ‘set point’ → information is sent to the…
Coordinator:
Co-ordinates information from several receptors & sends instructions to an appropriate…
Effector:
This brings about the corrective mechanisms needed to return the system to the ‘set point’ → this is then fed back to the receptor
Why is it important the information is fed back to the receptor after the effector has corrected any deviation?
The receptor would continue to stimulate the effector, leading to an over-correction, causing a deviation in the opposite direction
Why does body temperature need to be controlled?
To ensure enzymes work at their optimum temperature:
too low → enzyme & substrate molecules have insufficient kinetic energy
too high → enzymes denature
Why does blood pH need to be controlled?
To keep enzymes working near their optimum pH → increases or decreases in pH can denature enzymes by breaking hydrogen & ionic bonds in the tertiary structure
Why does blood glucose need to be controlled?
To ensure there is enough of this carbohydrate substrate for cellular respiration, but not enough to lower blood water potential & dehydrate cells
Why does blood water potential need to be controlled?
To prevent loss or gain of water from cells by osmosis
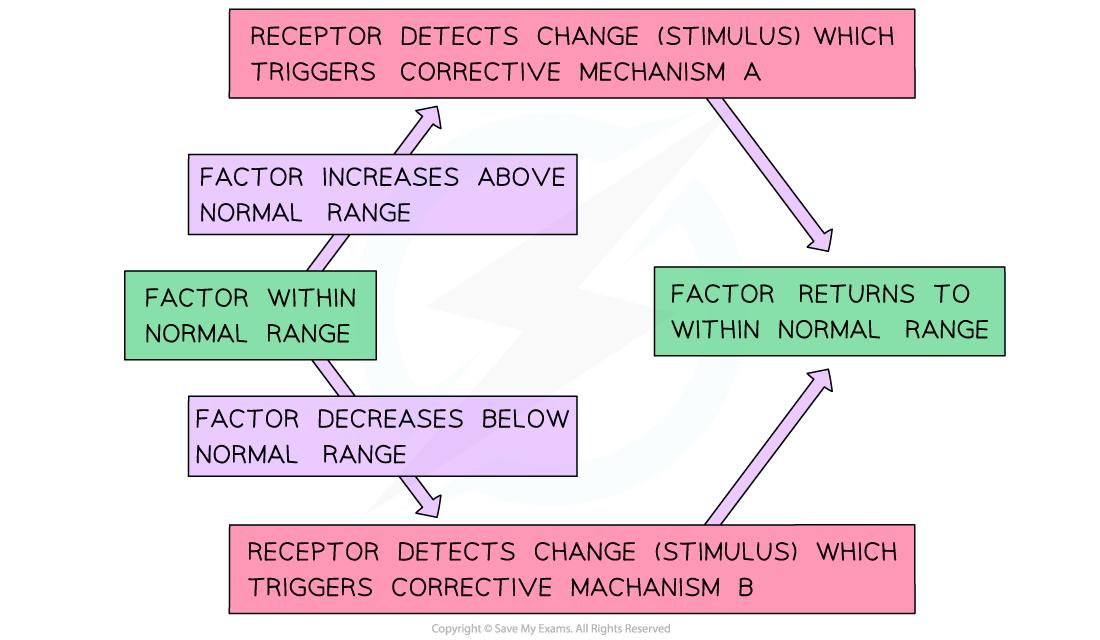
What is negative feedback?
Self-regulatory mechanisms return the internal environment back to the set point when there is a fluctuation
What is positive feedback?
A fluctuation triggers changes that result in an even greater deviation away from the set point
What is an example of positive feedback?
Typhoid fever:
a disease that leads to the breakdown of thermoregulation
this results in a rise in body temperature & ultimately, death
Why is the onset of contractions during childbirth a positive biological feedback loop?
When contractions occurs, the hormone oxytocin is released
Oxytocin stimulates further contractions & thus causes them to increase in amplitude & frequency
Why are neurons a positive biological feedback loop?
A stimulus causes the influx of sodium ions that increases the permeability of the neurons to sodium ions
This allows more sodium ions to enter, further increasing the permeability of these ions
This result is a rapid build up of an action potential, enabling a rapid response to a stimulus